Chemistry - properties and uses of water
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Properties of water - relatively high MP/BP
-when compared to other group 16 hydrides
-Due to h-bonds that will form
Properties of water - freezing
-Denser when liquid than solid
-Cooling causes hexagonal structure
-This has space inside it therefore it is less dense
Properties of water - surface tension
-Very high surface tension
-H20 does not bond with air/most solids so will exert attractive forces internally
Water as a solvent
-A “universal solvent” in that it is often the basis for what most solutions are comprised of.
-Forms aqueous solutions (compound or molecule that exists within the water molecule)
3 Key terms with solution
1.Solvent: a substance that acts to dissolve
2.Solute: A substance that is being dissolved
3.Solution: Forms when a substance is dissolved and particles are free to move within liquid
characteristics of a solution
1.Solute and solvent are indistinguishable (homogenous solution)
2.Amount of dissolve solute will depend on various conditions (pressure, temp, etc)
Dissolution
the process where a solute dissolves in a solvent to form a solution
Dissolution process
1.Solute particles separate from each other (IMF bonds break)
2.Solvent particles separate from each other (IMF bonds break)
3.Solute and solvent particles form new IMF bonds to form a solution
3a.Often, the solvent particles (especially water) will surround solute particles
Forces involved in dissolution
-solute and solvent molecules are held together by respective IMF
-Attractive forces between solute and solvent molecules will cause a solution to form if certain rules are met
Consider in Dissolution
-Strength of IMF between solute and solvent individually
-How solute/solvent interact (what IMF if bonded)
-Solvent-solute interaction must be stronger than IMF between solute and solvent individually
Methods of water and covalent molecules dissolution
1.Formation of h-bonds with water molecules
2.Ionisation of molecule in the presence of water
Water and covalent molecules - H-bond formation
-Polar molecules that from h-bonds will be able to dissolve in water
-H-bonds between molecule and water will break the IMF holding water molecules together.
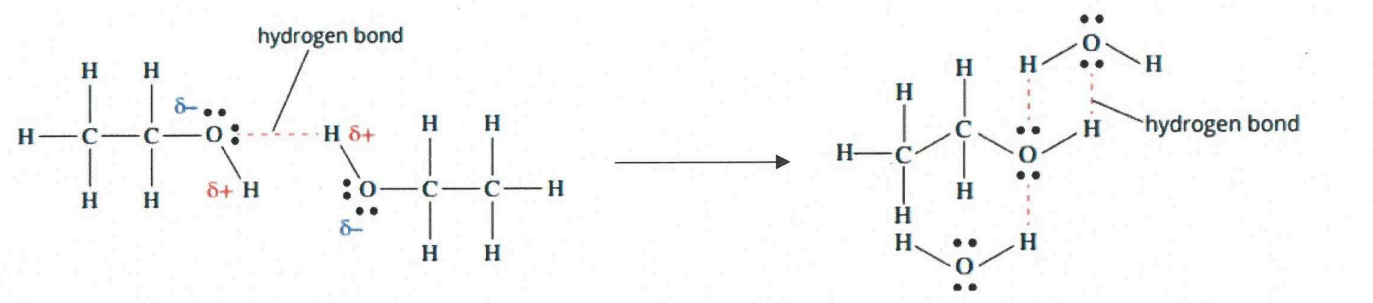
Water and covalent molecules - ionisation of molecules
-Some polar molecules have such high polarity they will separate and ionise when exposed to water
-When placed in water the attractive forces of water breaks the covalent bond to form ions
Water and ionic compounds
-As water molecules move near ionic compound, they will form ion-dipole attractions
-The ions are attracted to +/- dipoles of water and separate from the lattice
-They are surrounded by water molecules and become hydrated
-Process is called dissociation
water and ionic compounds (short)
1.Ionic bonds within lattice break
2.H-bonds between water molecules break
3.Ion-dipole force will from between opposing charges.
Solubility
-refers to the maximum amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent (normally this is using a base of 100g).
-Also used to describe whether a substance will dissolve or not
Saturated solution
-No more solute can be dissolved under current conditions of liquid
Unsaturated solution
-The solution contains less solute than is needed to make a solution saturated (i.e. can dissolve more of the solute)
Supersaturated solution
-An unstable solution ‘forced’ to hold more solute than normal at current conditions
-Can occur is liquid is heated and cooled slowly.
Solubility depends on
-Nature of solute and solvent (polarity)
-Temp
-Gas pressure (or vapour pressure)
Gas and liquid solubility
-Liquids will generally increase in ability to dissolve substances as temp increases
-Gases will behave in an opposite fashion