HN World History Semester 1 Final
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
SPICE-T: Social
The development and transformation of social structures.
Involves gender roles & relations, family & kinship, racial & ethnic constructions, and social & economic classes.
Who had status and why?
What inequalities are present?
SPICE-T: Political
State-Building, Expansion, and Conflict.
Involves political structures, forms of governance, empires, nations & nationalism, revolts & revolutions, and regional/inter-regional/global structures and organization.
Who had power & how did they wield it?
What was their power based on?
SPICE-T: Interaction
Interaction Between Humans & the Environment.
Involves demography & disease, migration, patterns of settlement (rural vs. urban), and technology used to master/exploit the environment.
How did the environment shape society and vice versa?
SPICE-T: Cultural
Development and Interaction of Cultures
Involves belief systems, philosophies, ideologies, religions, architecture, and arts.
How did art, music, literature, and religion affect society & the individual?
SPICE-T: Economic
Creation, Expansion, and Interaction of Economic Systems.
Involves agricultural & pastoral production, trade & commerce, labor systems, industrialization, capitalism & socialism.
How was wealth generated & how did this affect society and the individuals within it?
SPICE-T: Technology
Technology and Innovation.
Involves scientific discoveries, metallurgy, weaponry, new ideas/techniques, and inventions.
Paleolithic Period
From the beginning of human existence to 10,000-15,000 years ago; "Old Stone Age"term-13
Africa (MAP)
Eurasia (MAP)
Australia (MAP)
Oceania (MAP)
Islands scattered through the Pacific Ocean
Americas (MAP)
Savanna
An area of grassland with scattered trees and bushes

Desert
An extremely dry area with little water and few plants

Tundra
A vast treeless plain in the arctic regions between the ice cap and the tree line

Hunter-Gatherers
Nomadic people who mainly lived by hunting/fishing and harvesting wild food & plants (lifestyle)
Foragers
People who widely search for food & provisions (occupation)
Homo Sapiens
Consciously thinking human
Neolithic Period
Started ~10,000-15,000 years ago; "New Stone Age"
Prehistory
History before written language
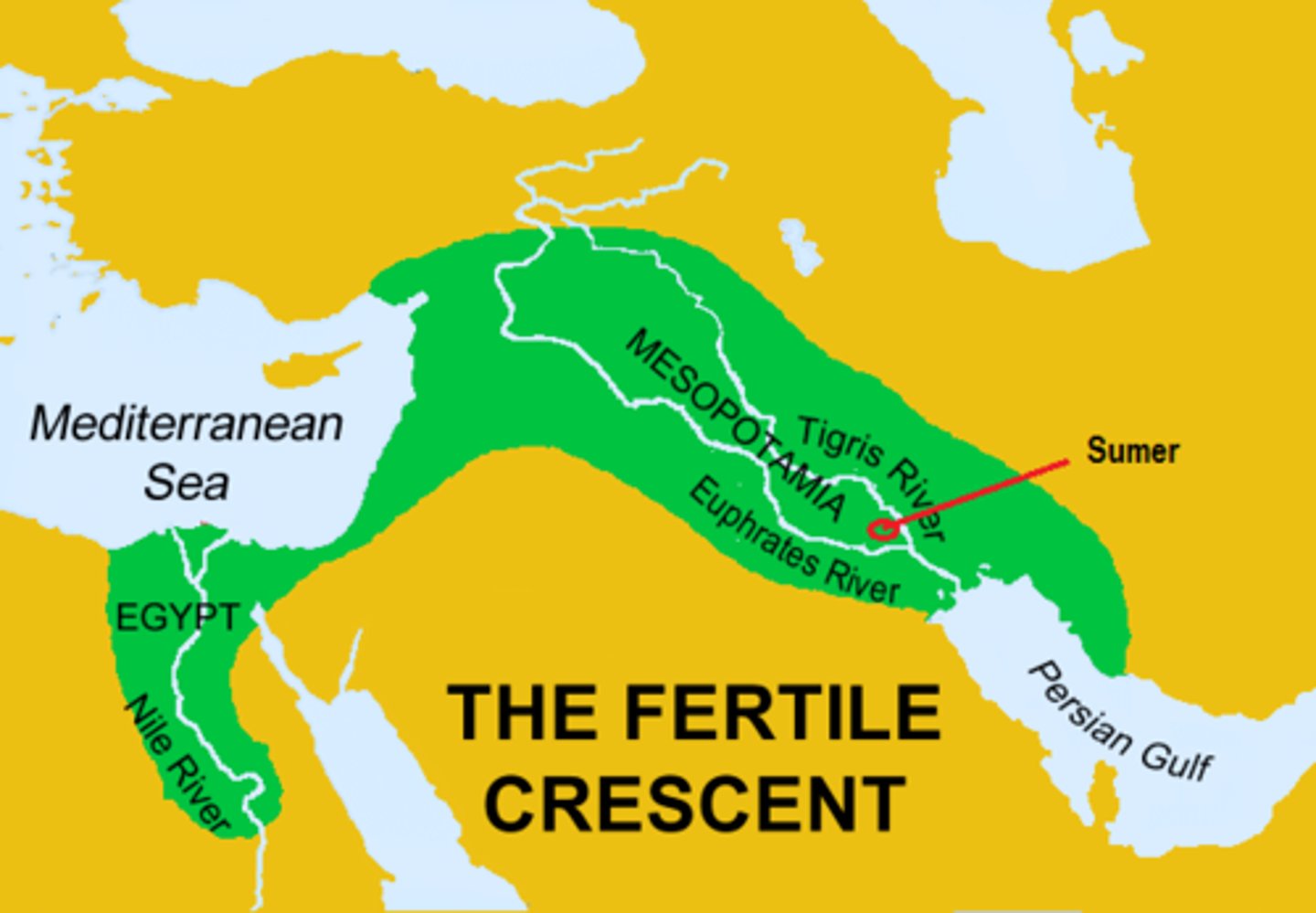
Fertile Crescent
A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates. The origin of agriculture.
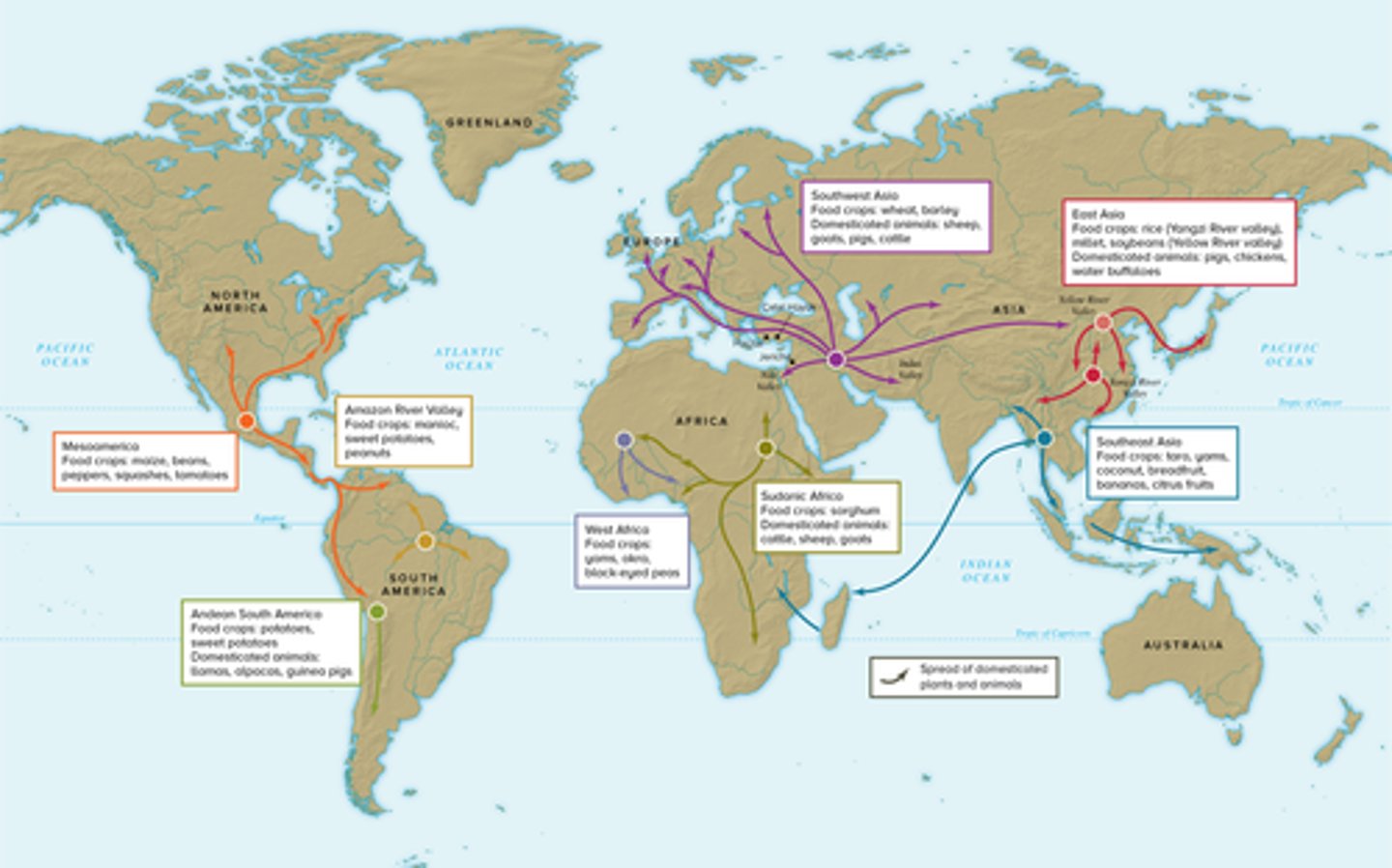
Neolithic Agricultural Revolution (MAP)
Change from hunter-gatherer lifestyle to agricultural lifestyle. Originated in the Fertile Crescent.
Bureaucracy
A large, complex organization composed of appointed officials
Empires
Large political entities made up of several culturally distinct regions held together by force, under the control of a single, dominant region.
Patriarchal
Relating to a society in which men hold the greatest legal and moral authority.
Monotheism
Belief in only one god
Social Hierarchy
Society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors.
Pastoralists/Herders
Shepherds or herdsmen devoted to or based on livestock raising.
Agrarian Societies
Societies whose means of subsistence are based on agricultural production (crop growing).
Urban
City life
Rural
Countryside
Polytheism
Belief in many gods
Politics
The effort to control or influence the conduct and policies of government.
Record Keeping
Entering, transcribing, recording, storing, or maintaining information in writing.
Pictographs
Pictures that stand for words or ideas; picture writing.

Dissemination
The act of spreading knowledge.
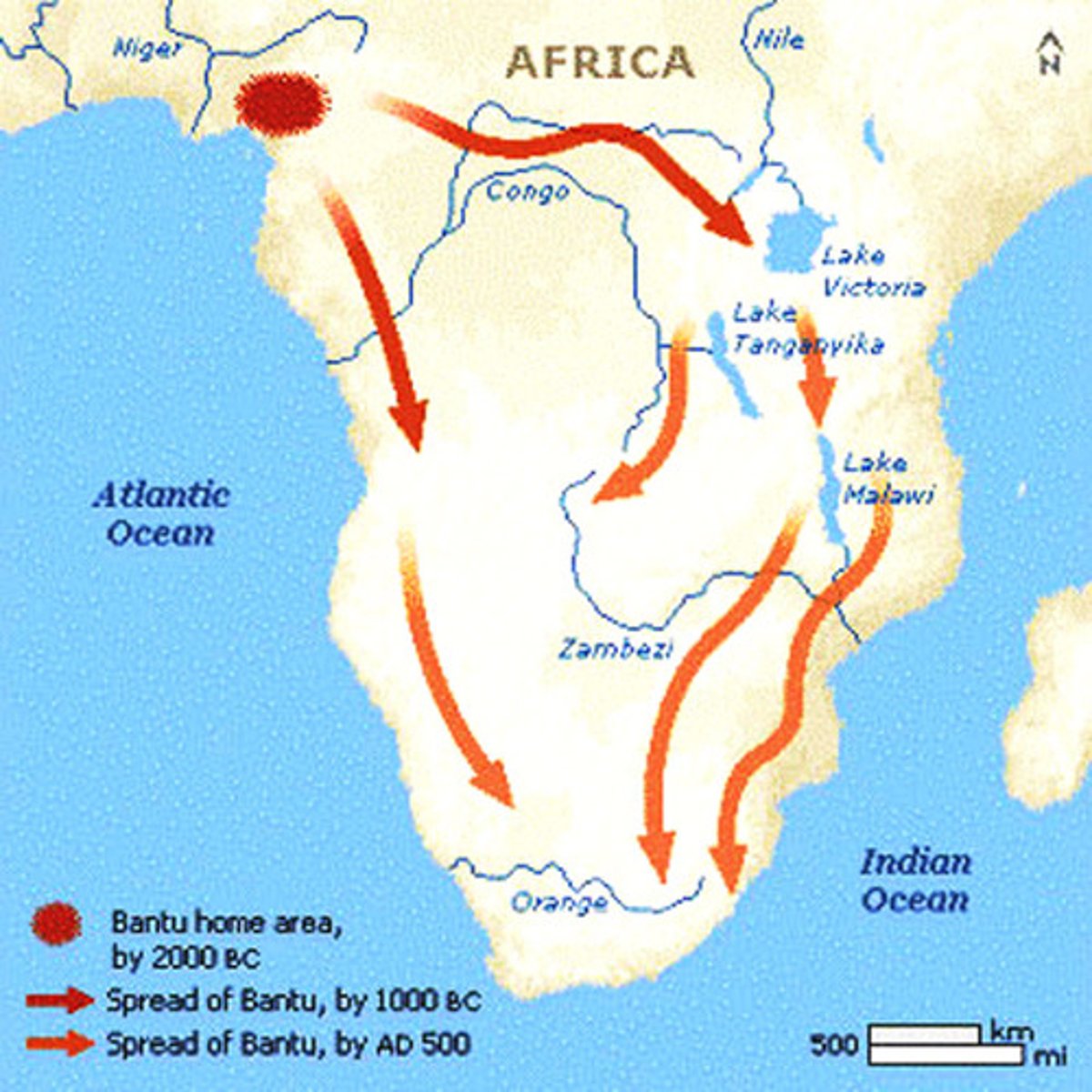
Bantu People
Farmers who migrated throughout Sub-Saharan Africa, spreading their language and culture.
Bantu Migration (MAP)
The movement of the Bantu peoples southward throughout Africa.
Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
The two rivers that surround Mesopotamia.
Code of Hammurabi
The set of laws drawn up by Babylonian king Hammurabi dating to the 18th century BC, the earliest legal code known in its entirety.
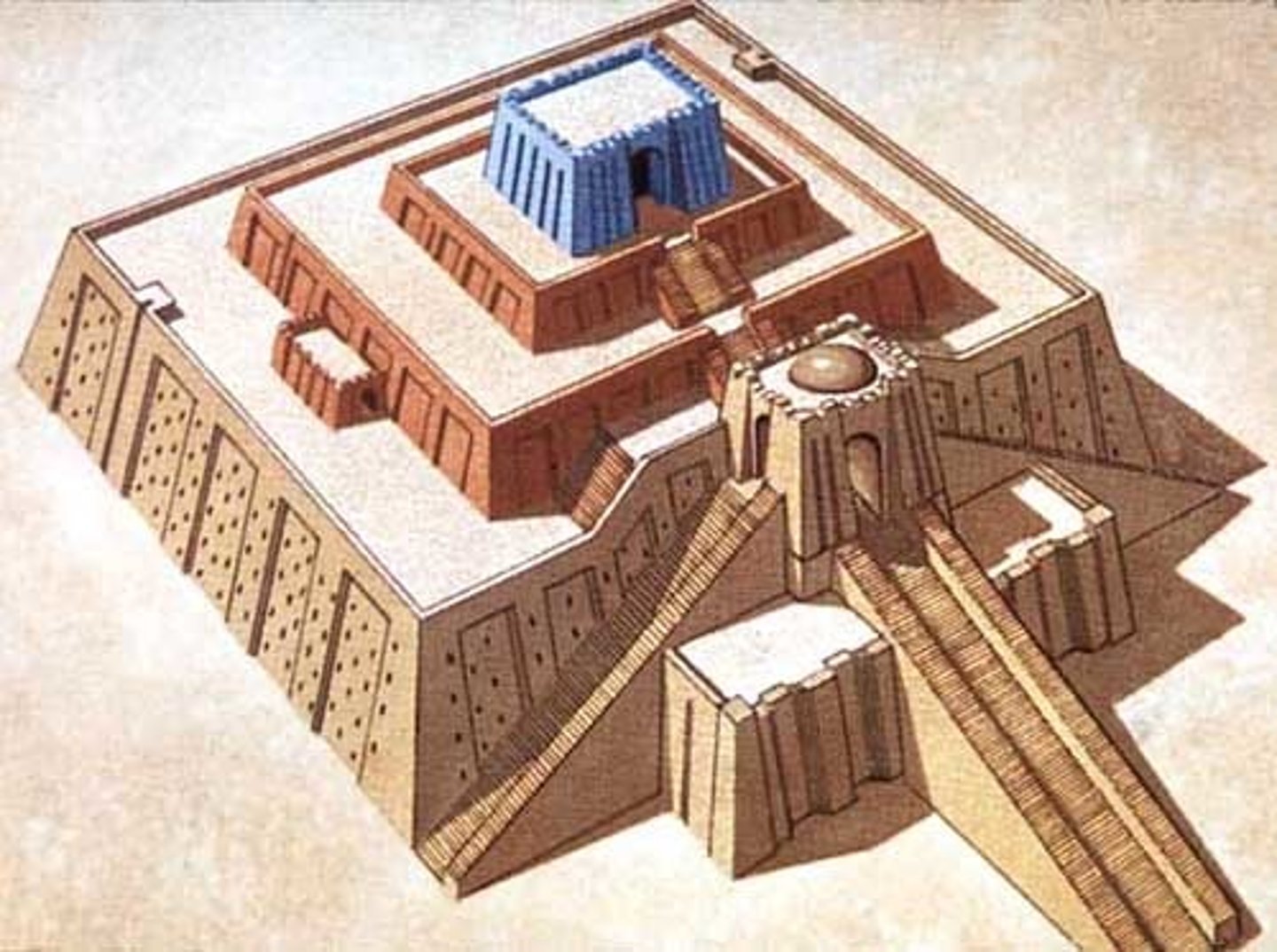
Ziggurat
Mesopotamian temple.
Cuneiform
A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge-shaped stylus and clay tablets.
Epic of Gilgamesh
An epic poem from Mesopotamia that explores themes of friendship, relations between humans and the goods, and the meaning of life & death.
Hittites
Indo-European peoples who were had close relations with the Mesopotamians. They traded with the Babylonians and Assyrians, adapted cuneiform writing to their language, and accepted Mesopotamian deities in their pantheon. They eventually toppled the Babylonian empire and were responsible for two technological innovations--the war chariots and refinement of iron metallurgy.
Judaism
The monotheistic religion of the Jews.
Essential Belief: They believed in Abraham's Covenant (made with Yahweh; belief that Canaan belonged to the Israelites) and that they were to be God's chosen people.
Hebrews/Israelites.
Early Hebrews were influenced by Mesopotamian culture (see influences in Hebrew law and stories) and were polytheistic people.
A group of Hebrews followed Moses and migrated to Israel/Palestine (known as Israelites). They were monotheistic people who worshipped Yahweh (built temple instead of ziggurat to emphasize monotheistic faith).
Phoenicians
People who didn't have resources for agriculture so they relied on trade to support their society. They expanded to maritime trade routes & became very strong sailors. Though this, they adopted different cultural tendencies (like Mesopotamian polytheism and building temples) while spreading their own alphabet to people they interacted with like the Hebrews, Romans, and Greeks.
Nile River
The river in which early kingdoms in Egypt were centered around. Predictably floods twice a year.
Pharaohs
Rulers of ancient Egypt
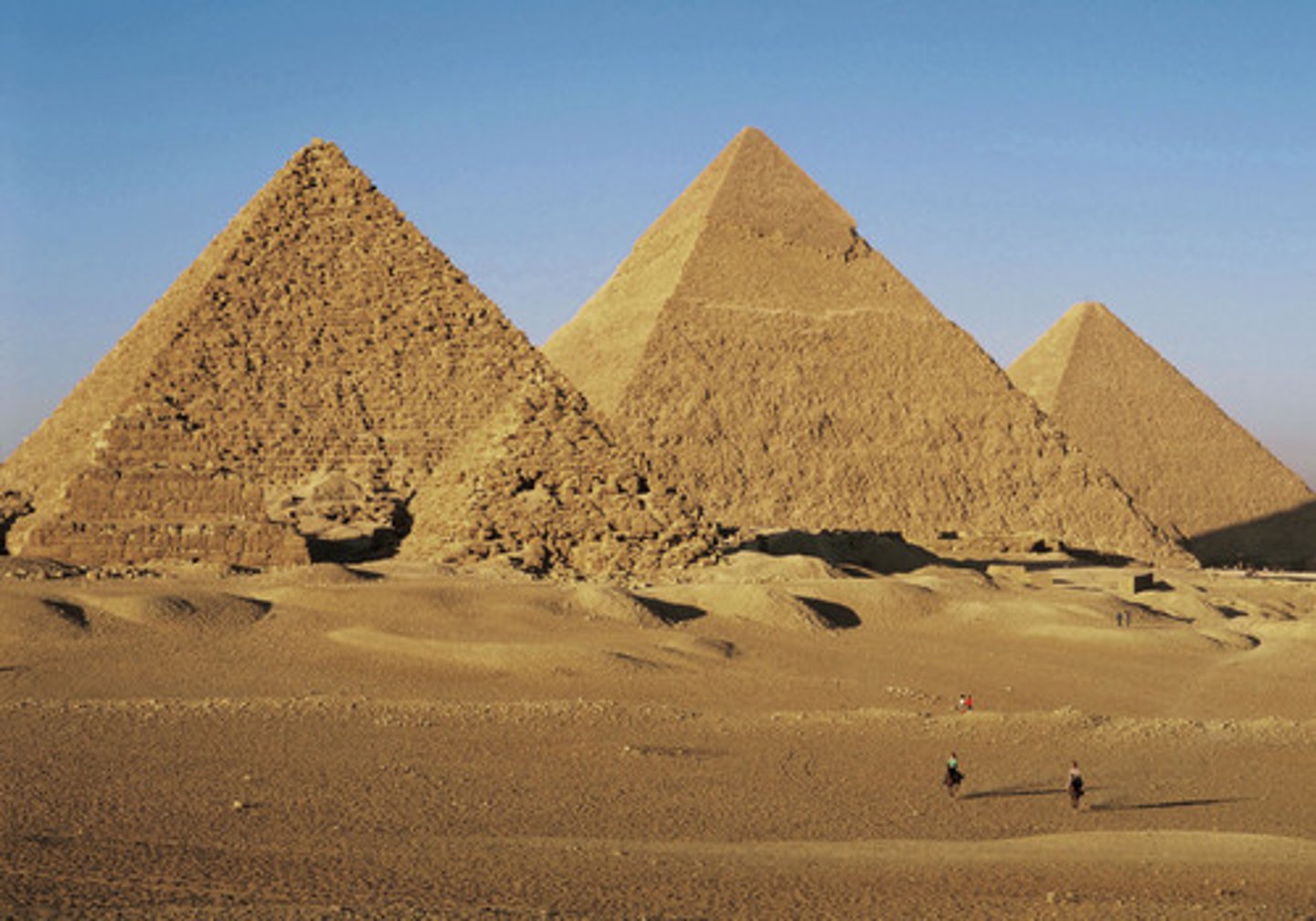
Pyramids
Monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs.

Hieroglyphics
Ancient Egyptian writing system in which pictures were used to represent ideas and sounds

Book of the Dead
Collection of religious spells which were thought to be helpful to the deceased in the afterlife.
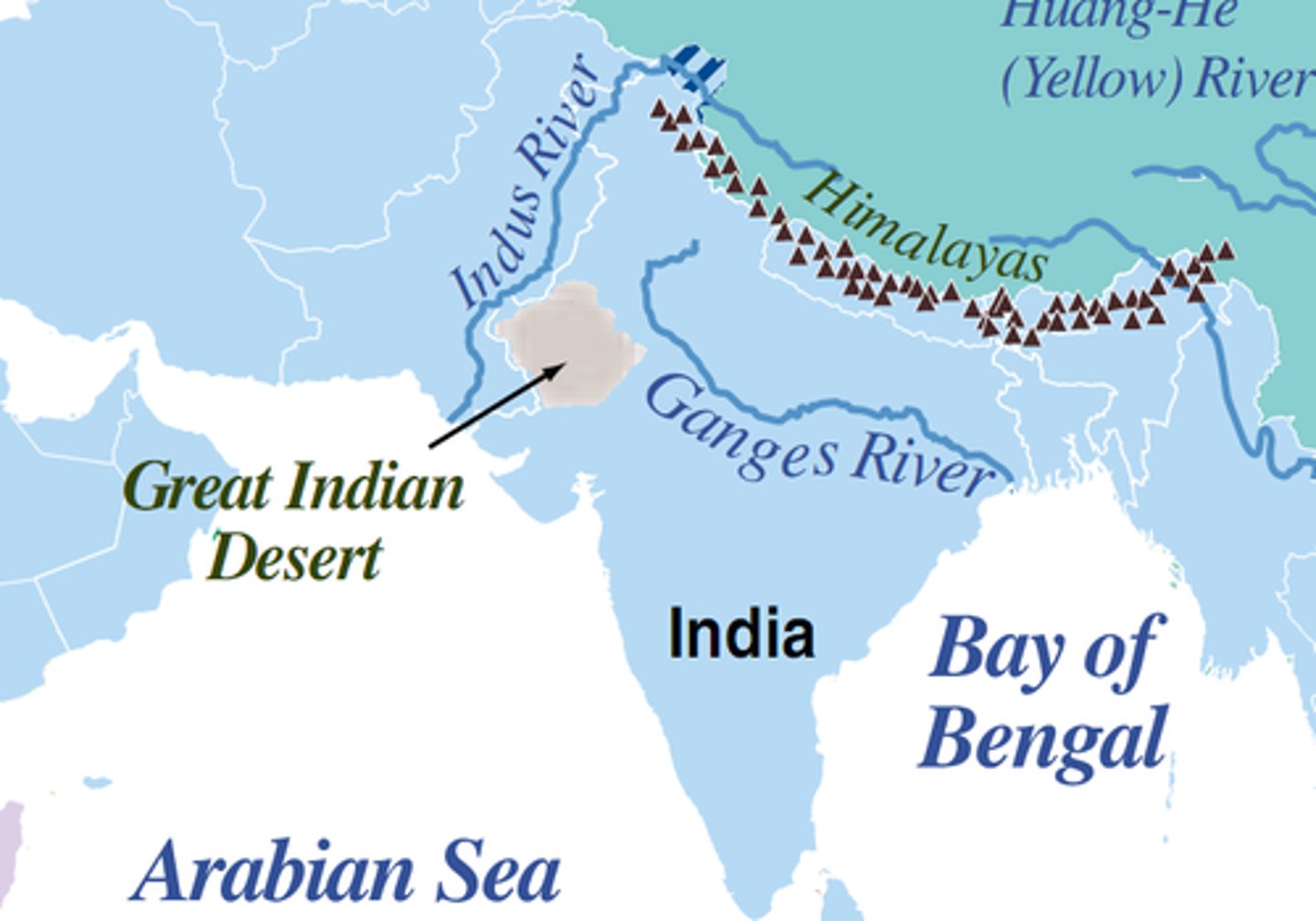
Indus River
A river in South Asia that flows from the Hindu Kush + the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea. Less predictable than the Nile but not as bad as the Yellow River.
Dravidians
The original people of the Indus River Valley.
Harappans
Early agrarian people of the Indus River Valley Civilization. We don't know much about them because most remains are under the water table and their written records are in an indecipherable (Dravidian) script. They were a very peaceful people with no weapons/warfare. Had an advanced sewage system & it's thought that each city ruled itself. They traded with surrounding civilizations (exported cotton), had a surplus of food, standardized weights & measures, and more.
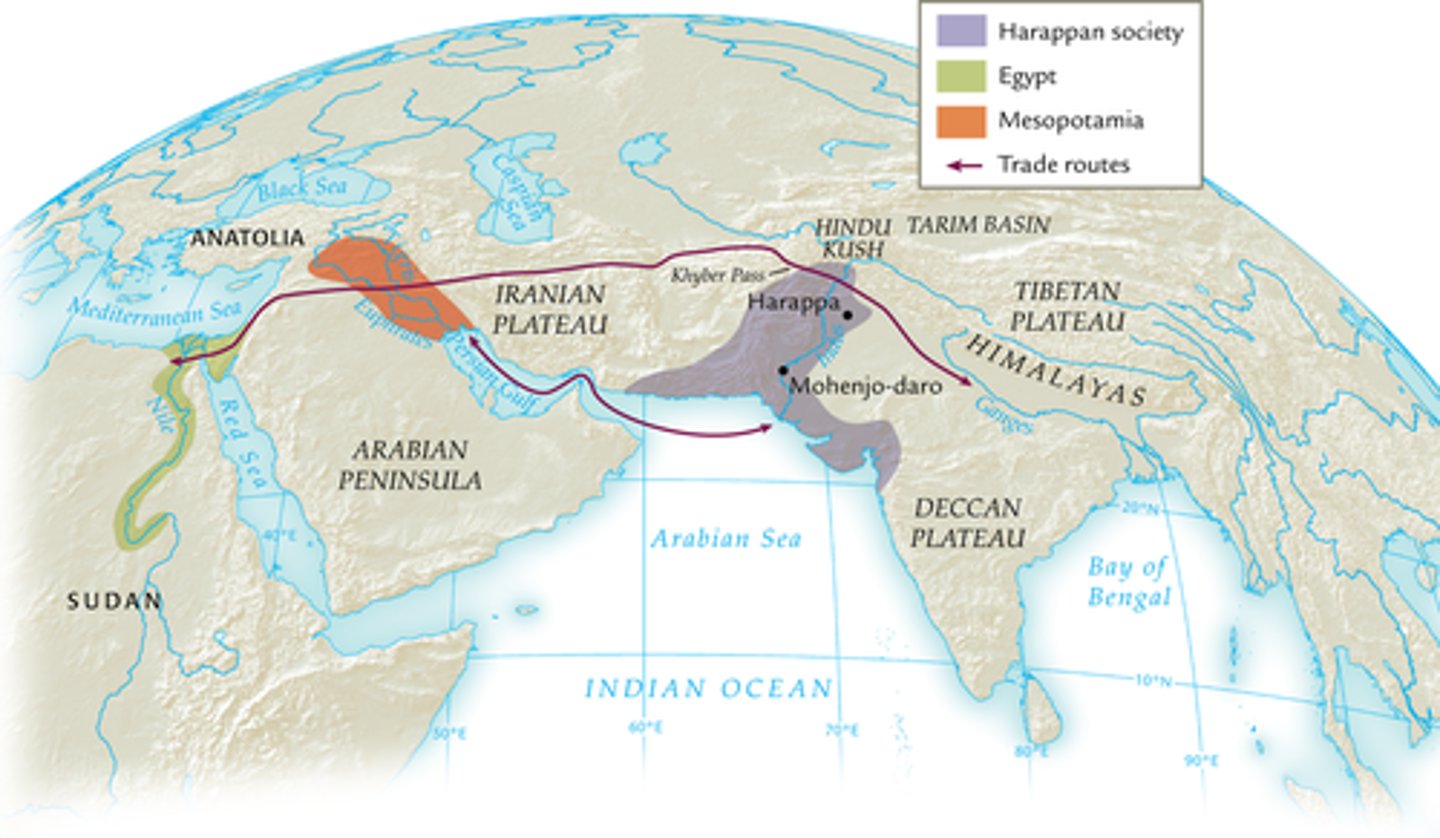
Mohenjo-Daro
Largest city of the Indus Valley civilization. It was centrally located in the extensive floodplain of the Indus River. Home of the Great Bath.
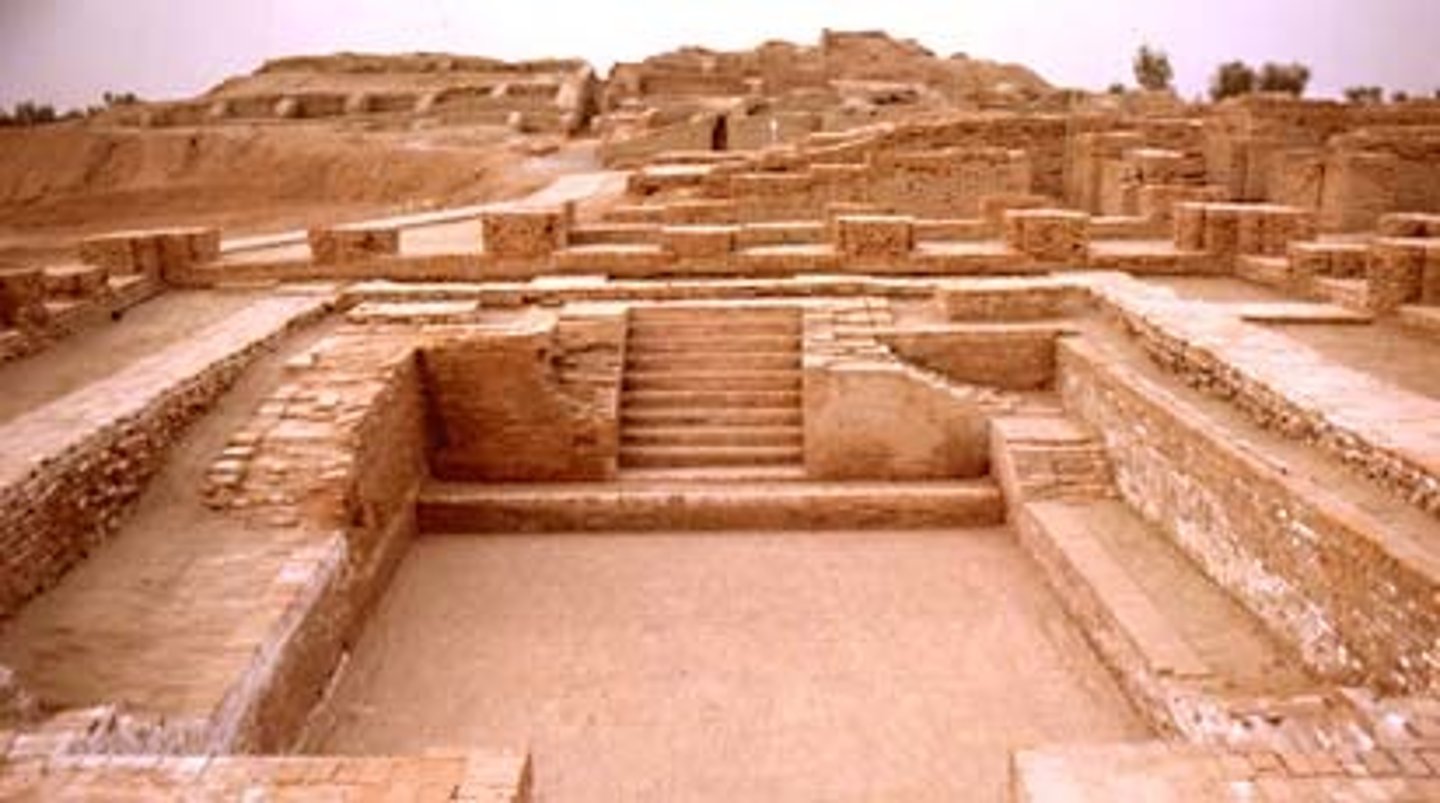

Harappa
A large ancient city of the Indus civilization, created in present-day Pakistan
Aryans
Nomadic/pastoral people from Iran (Eurasia) who migrated and settled in India. Also known as "Vedic People" and started the Vedic Age in India.
Sanskrit
The most important language of ancient India.
Hinduism
The oldest world religion (polytheistic) that was influenced and shaped by both Aryans and Dravidians.
Essential Belief: Humans are reincarnated beings whose experiences in this life are shaped by previous lives.
Brahman
The power which supports and upholds everything (not a god in the same sense as monotheism).
Trimurti
Holy trinity (creation, preservation, destruction).
Samsara
Reincarnation; a cycle of repeated lives.
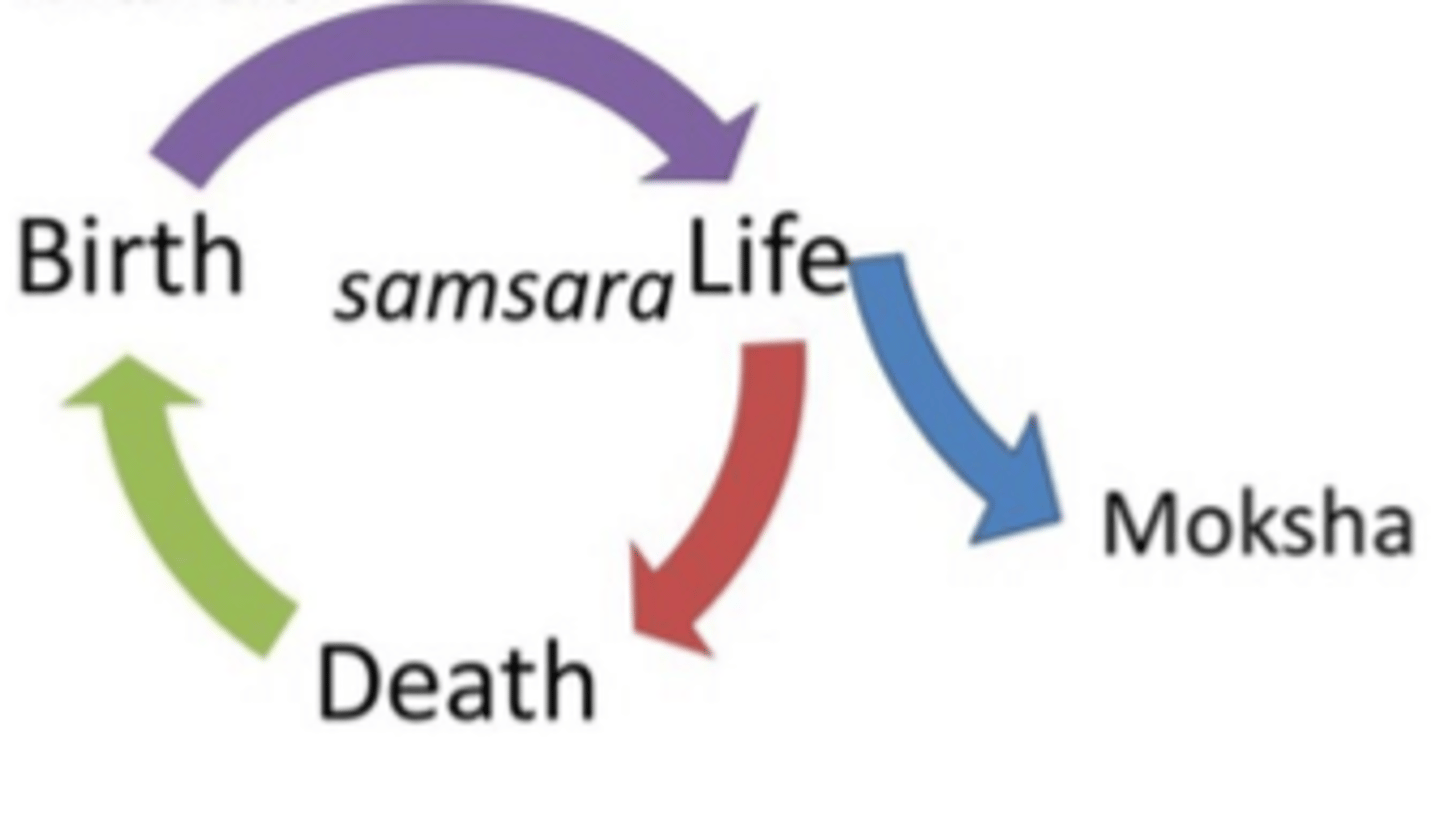
Dharma
The religious and moral duties of an individual.
Karma
Action: Good actions lead to a better life in the next round, bad actions lead to a worse life.
Moksha
Release: goal is to be released from the cycle of repeated lives & reunite with Braman. Believed to be ultimate goal of existence.
Caste System
A Hindu social class system that controlled every aspect of daily life. It was passed down through families (some social mobility originally but became more rigid under British) and dictated most aspects of life including jobs, religious duties, and marriage.
Varnas
Another word for the social classes in the caste system.
Brahmins
Top varna; priests and academics
Kshatriyas
Second highest varna; rulers, administrators, and warriors.
Vaishyas
Third highest varna; artisans, tradesmen, farmers, and merchants
Shudras
Fourth highest varna; manual labourers
Dalits
Lowest varna; "Untouchables"; street clearners.
Jati
Sub-varnas in the caste system that was largely determined by occupation.
Vedas
Collection of ancient Sanskrit writings that are the earliest sacred texts of Hinduism.
Yellow (Huang He) River
A river in Northern China. Was super unpredictable & brought devastating floods & destructions. Known as "China's Sorrow".
Chinese Dynasties
Xia (mythical), Shang (developed calendar, modern language, math/astronomy/art/military advances), Zhou (Chinese philosophies + philosophers: Lao-Tzu, Confucius AND Mandate of Heaven), Qin (after Warring States Period; used Legalism)
Mandate of Heaven
A political theory of ancient China in which those in power were given the right to rule from a divine source.
Tian
Heaven; an abstract conception in early Chinese religion; possible the combined spirits of all male ancestors; first appeared during Zhou dynasty.
Oracle Bones
Animal bones carved with written characters which were used for telling the future.
Book of Songs
Earliest collection of Chinese poetry; provides glimpses of what life was like in the early Zhou Dynasty.
Ancestor Worship
Honoring ancestors though rituals, such as offering food and wine to the dead.
Nomad
A person with no settled home that keeps moving from place to place to survive.
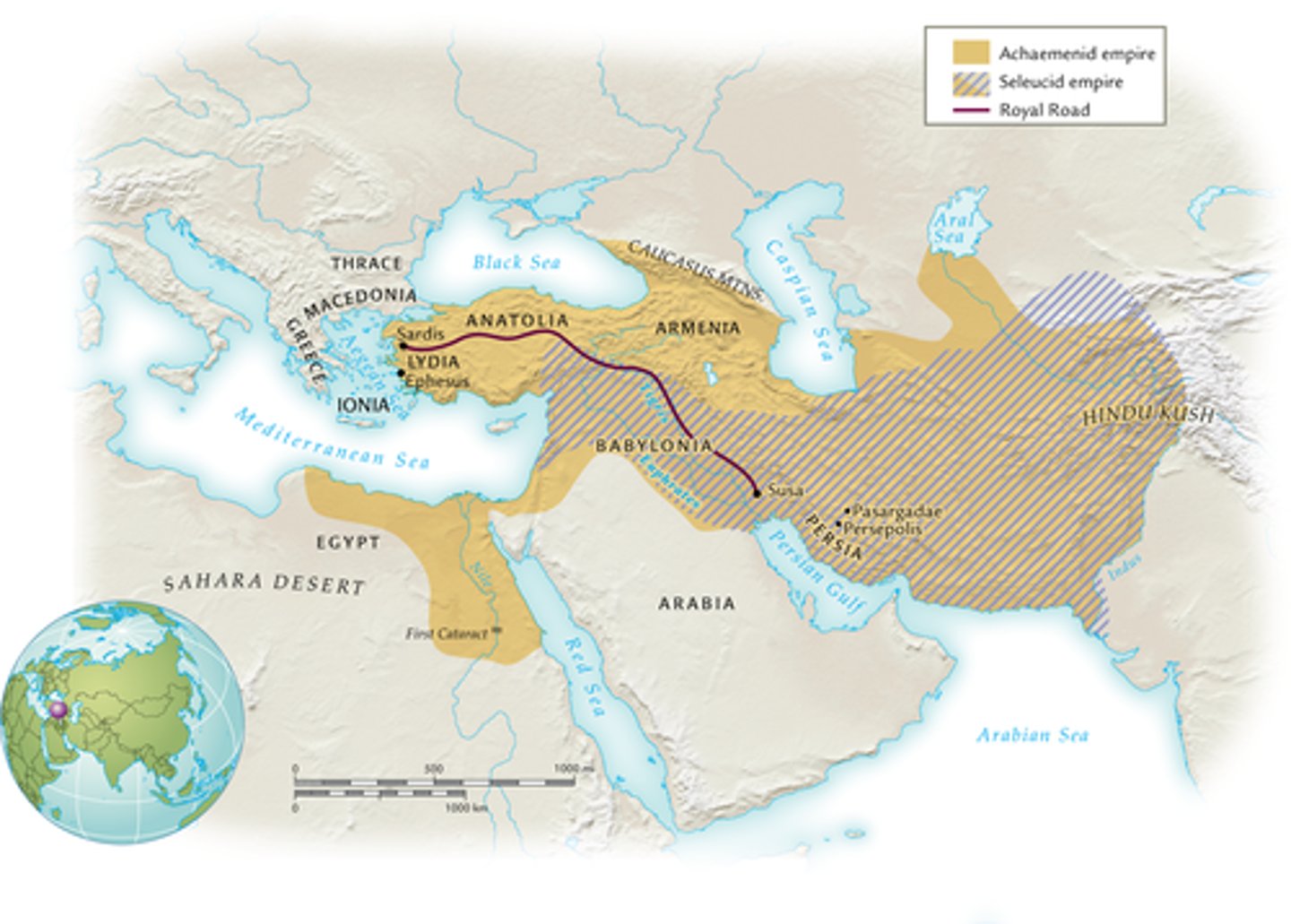
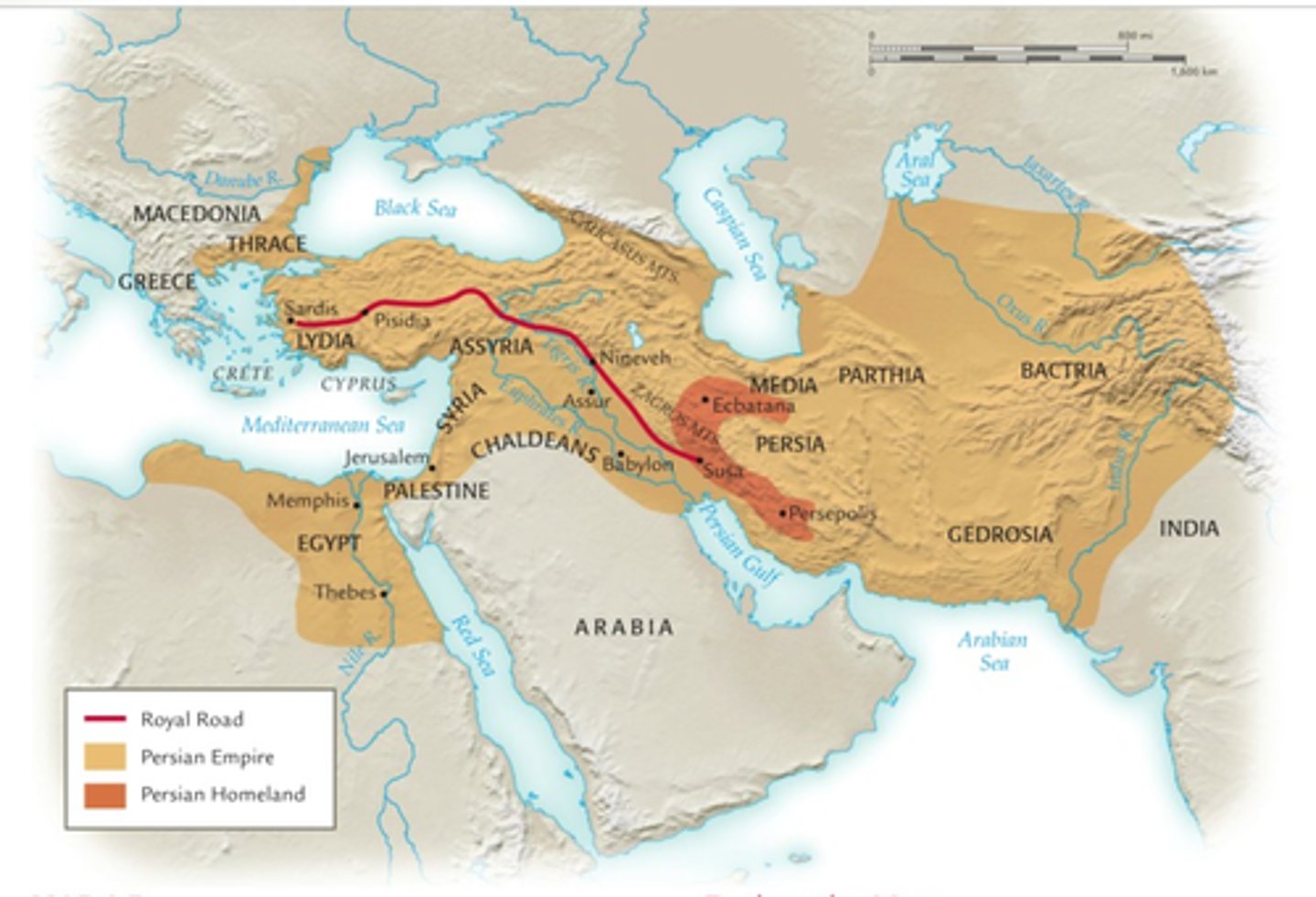
Persian Empire (MAP)
A major empire that expanded in much of Southwest Asia.
Achaemenid Empire (558-330 BCE) -> Seleucid Empire (323-83 BCE) -> Parthian Empire (247 BCE - 224 CE) -> Sassanid Empire (224-651 CE)
Achaemenid Empire
Starts with Cyrus the Great going through the Persian Wars and doesn't end until Alexander the Great (Greece) conquers Persia. Cyrus conquered many regions, eventually holding an empire that stretched from India to the borders of Egypt. After Cyrus, his son Cambyses conquered Egypt. Then Darius continued to expand the empire while also uniting the different ethnic groups under Achaemenid control. The Achaemenids were very tolerant of different cultures (even between monotheistic vs polytheistic).
Satraps
Officials appointed by the King who rule in the name of Persia through the empire. The Persian government had spies who would check on the satraps to make sure they were doing their job properly.
Royal Road
Went across the length of the empire and could move troops and trade quickly + efficiently.
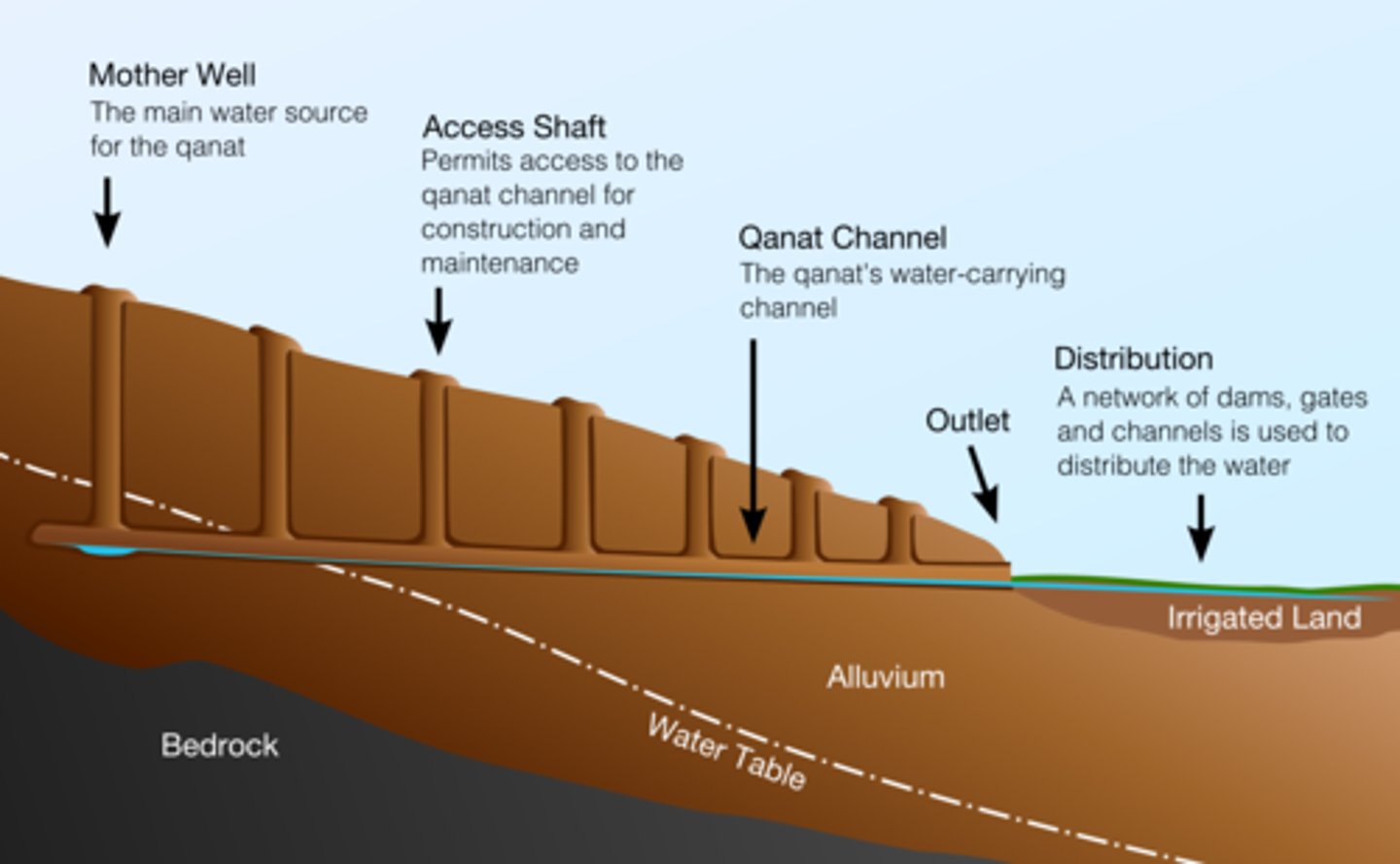
Qanats
Underground irrigation canals that provided a reliable source of water throughout the empire.
Persepolis
The capital of the Achaemenid Empire. It was made to reflect the nomadic origins of the Persians with lofty ceilings and supportive poles like tents. Eventually burned down by Alexander the Great.
Zoroastrianism
A monotheistic religion followed in the Persian Empire. It was about the freedom to choose right or wrong & taking individual responsibility for one's actions. It valued the duality between good and evil with a good god that people worshipped and a bad god (like Satan) that people didn't worship. It had an afterlife based on reward/punishment (seen in later monotheistic religions) and ideas of heaven + hell.
Minoans
An early Greek society on the island of Crete. They built many lavish palaces (acted as center of society) and developed a written script known as Linear A (written symbols stood for syllables instead of words, ideas, vowels, or consonants). They were heavily involved in Mediterranean commerce, influenced by Phoenicia (high maritime trade expertise) and Egypt. Their society declined due to experiencing a series of natural disasters & invaders.
Myceneans
People from mainland Greece who interacted with the Minoans, learning their systems (like adapting Linear A to Linear B). Eventually, they expanded, invading the Minoans on Crete along with other conquests. Later, they took part in the Trojan War, which led to their decline.
Polis
A Greek city-state. They were organized with an urban center & surrounding countryside. They usually had outer walls for protection, central market places (agoras), and temples/government buildings on top of an hill (acropolis).
Monarchy
A government ruled by a king or queen
Aristocracy
A government in which power is in the hands of a hereditary ruling class or nobility
Oligarchy
A government ruled by a few powerful people (not hereditary).
Phalanx
A massive military formation of foot soldiers armed with spears and shields
Athens
A Greek city-state. Governed by a monarchy from 750-550 BCE, then shifted to an oligarchy over time. But after that a couple of factors (phalanx, acropolis, agora, and Solon) led to it becoming a democracy.
Acropolis
"High city". A fortified citadel & sanctuary in Athens. It's where Athena's most sacred temple is.
Agora
"Place of assembly". A place where politics were discussed, merchants traded, and people gathered.