Chapter 11 - Chemical Equilibrium
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What occurs during dynamic equilibrium?
Rate of forward reaction will occur at the same rate as that of the reverse reaction
Once equilibrium is reached, do the forward and reverse reactions stop?
No, it is still ongoing such that the rate of production formation is equal to the rate of reactant formation
Do concentrations of reactants and products have to be equal at the time of equilibrium?
Not necessarily, but they can be
What is the formula for equilibrium constant given this formula, aA + bB ⟷ cC + dD?
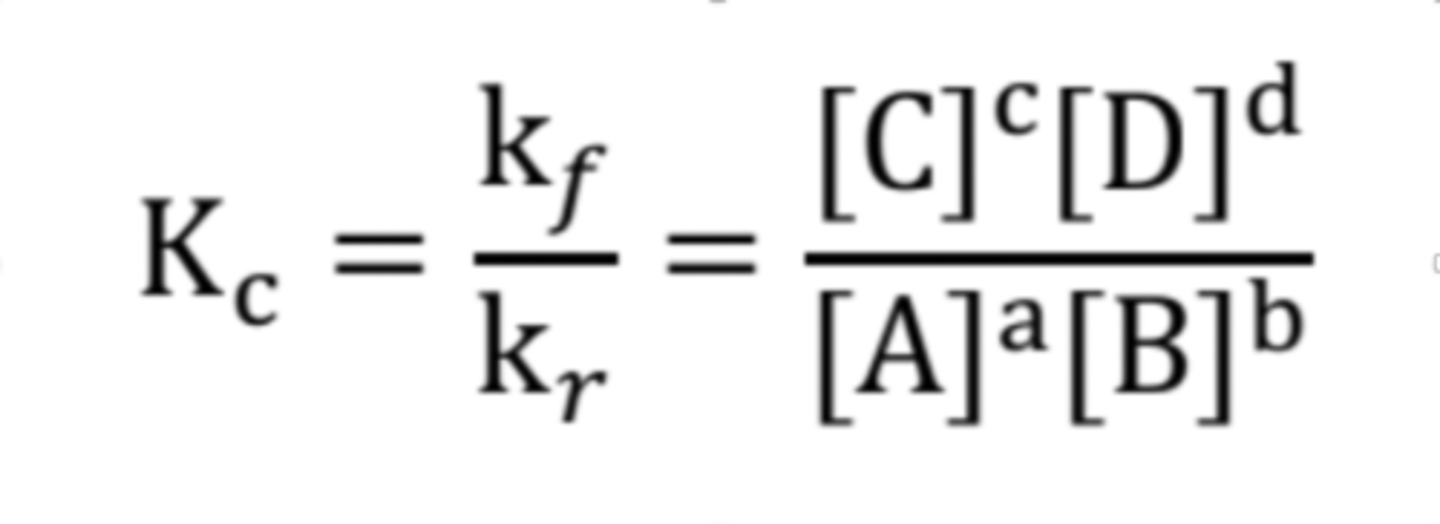
What is the Gibbs' free energy formula with the inclusion of equilibrium constant?
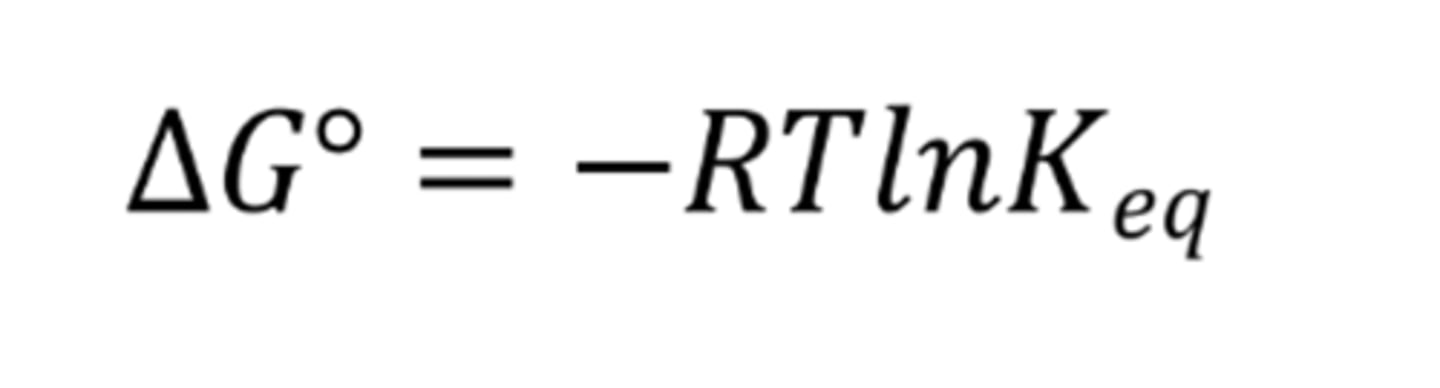
A Keq < 1 suggests what about the ratio of reactants and products at equilibrium?
Greater concentration of reactants than products at equilibrium
A Keq = 1 suggests what about the ratio of reactants and products at equilibrium?
Ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium is equal
When Keq < 1, is ΔG° positive or negative?
When Keq < 1, ΔG° is positive and so the reactants are lower in energy and more stable than the products (there are more reactants)
When Keq = 1, is ΔG° positive or negative?
When Keq = 1, ΔG° is zero and so the ratio of products to reactants is equal
When Keq > 1, is ΔG° positive or negative?
When Keq > 1, ΔG° is negative and so the products are lower in energy and more stable than the reactants (there are more products)
What is different between reaction quotient (Q) and the equilibrium constant (K)?
Equilibrium constant is based off of concentrations once reaction has reached equilibrium. Reaction quotient uses concentrations at any point in time during a reaction other than equilibrium
If Q < Keq, what does this suggest about the concentration of reactants and products?
There is a higher concentration of reactants than there would be at equilibrium, as such the system shifts more towards the forward reaction to reach equilibrium
If Q = Keq, what does this suggest about the reaction?
The reaction is in dynamic equilibrium
If Q > Keq, what does this suggest about the reaction?
There is a higher concentration of products than there there would be at equilibrium, as such the system more towards the reverse reaction to reach equilibrium
What type of reactants and products are excluded from calculating equilibrium constant?
Liquid and solid state reactants or products
What does Le Châtelier's principle describe?
A system will shift in a direction that restores the equilibrium state in the presence of changes in concentration or in the temperature of the system
If reactants are added, what direction would the reaction shift?
Reaction would shift towards the forward reaction until Q = Keq again
If reactants are removed, what direction would the reaction shift?
Reaction would shift towards the reverse reaction until Q = Keq again
If products are added, what direction would the reaction shift?
Reaction would shift towards the reverse rearction until Q = Keq again
If pressure is added to a system resulting in a decrease in volume, how would the equilibrium shift?
The equilibrium will shift towards the side of the reaction with a lower total number of moles of gas
If pressure is removed from a system resulting in an increase in volume, how would the equilibrium shift?
The equilibrium will shift towards the side of the reaction with a greater total number of moles of gas
If a reaction is endothermic in the forward direction, would heat be considered a reactant or a product?
Reactant
If a reaction is exothermic in the forward direction, would heat be considered a reactant or a product?
Product
If you lower the temperature in an endothermic forward reaction, what direction would the system shift?
Reaction will shift left as there is a decrease in heat, a reactant.
If you increase the temperature in an exothermic forward reaction, what direction would the system shift?
Reaction will shift left as there is now more heat, a product.
What is the solubility product constant, Ksp, used to figure out?
Used to figure out direction in which reaction will proceed, but also the saturation of the solution and whether or not precipitation will occur
What relationship between Q and Ksp would suggest a saturated reaction mixture?
Q = Ksp
What relationship between Q and Ksp would suggest a supersaturated reaction mixture?
Q > Ksp
What relationship between Q and Ksp would suggest an unsaturated reaction mixture?
Q < Ksp
What relationship between Q and Ksp would suggest precipitation of a solute will occur?
Q > Ksp. Reaction is currently supersaturated and will proceed in reverse reaction to result in precipitation
What does the term amphoteric mean?
A substance that can act as both an acid and a base, depending on what it is reacting with
What is the general formula for the acidic dissociation constant, Ka?
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
What is the general formula for the basic dissociation constant, Kb?
Kb = [OH-][HB+]/B]
How would the following reaction shift if HCl is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
HCl is a strong acid and dissociates completely into H3O+. As such, more products than reactants so the reaction will shift left.
How would the following reaction shift if NaOH is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
NaOH is a strong base and would immediately react with H3O+ and reduce the concentration. As such, the reaction will shift right
How would the following reaction shift if HA is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
With more HA, there is more reactants than products. Reaction will shift right
How would the following reaction shift if A- is added? HA (aq) + H2O (l) ⇄ H3O+ (aq) + A- (aq)
With more A-, there is more products than reactants. Reaction will shift left