Biochemistry - Chapter 7 -
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Enzymes
Protein catalysts that can accelerate the rate of a reaction by factors of as much as a million or more.
Substrates
Reactants in enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Proteolytic enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of what?
Peptide bonds
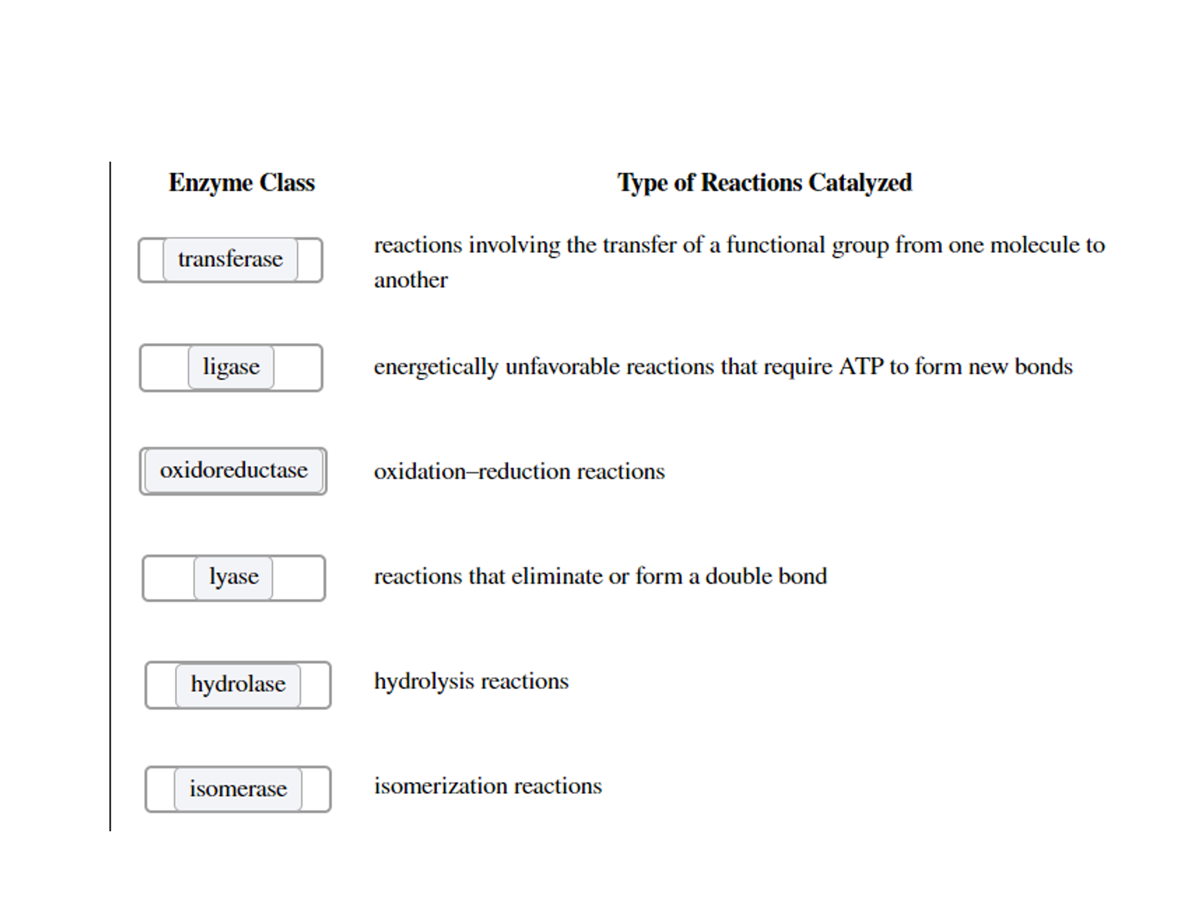
What are the six major classes of enzymes? What do they do?
Oxidoreductases catalyze oxidation–reduction reactions.
Transferases move functional groups between molecules
Hydrolyases cleave bonds with the addition of water.
Lyases remove atoms to form double bonds or add atoms to double bonds.
Isomerases move functional groups within a molecule.
Ligases join two molecules at the expense of ATP.
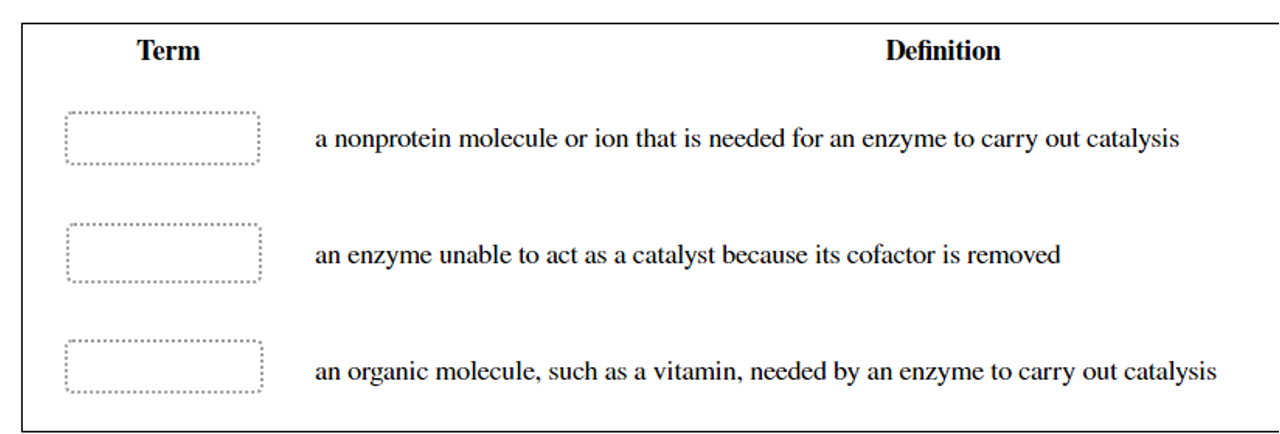
What are cofactors? What are the two main classes of cofactors?
Small molecules that some enzymes require for activity.
Two main classes of cofactors are
Coenzymes (Organic molecules derived from vitamins)
Metals
Prosthetic groups
Tightly bound coenzymes
Holoenzyme
An enzyme with its cofactor
Apoenzyme
An enzyme without its cofactor.
Oxidoreductases do what? What is an example?
Transferring an electron from one molecule to another.
Dehydrogenase
Dehydrogenase
An enzyme that takes a hydrogen off of something and puts it onto something else.
Transferases do what?
Move functional groups between molecules. An example is peptidyl transferase.
Hydrolases do what?
Cleave bonds with the addition of water.
Lysase does what?
This enzyme catalyze the cleavage of various chemical bonds using a different method not like hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction.
Lyases cleave bonds by doing addition and removing groups directly to the substrate
Lyases catalyze reactions by removing atoms to form double bonds or adding atoms to double bonds or a new ring structure
Various types of Lyase: Decarboxylases and Aldolases,
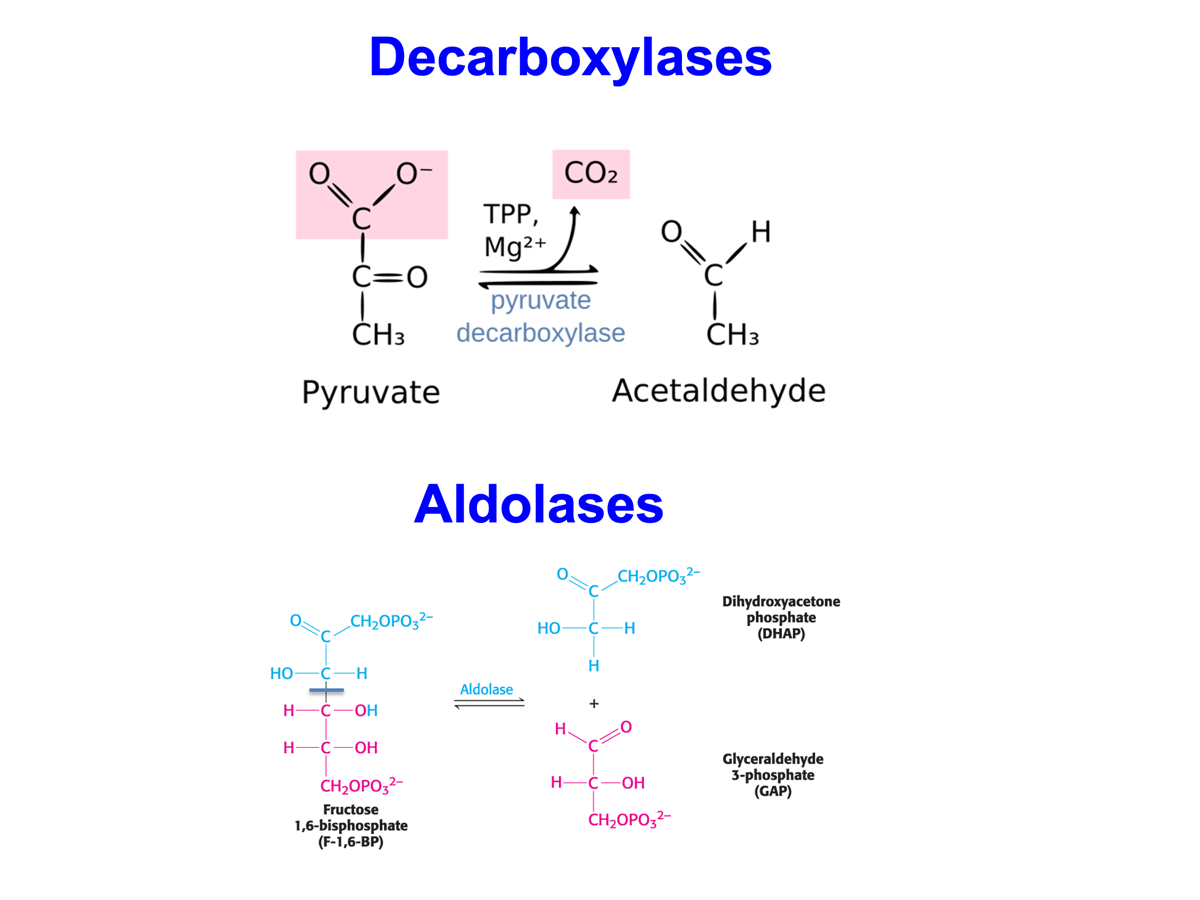
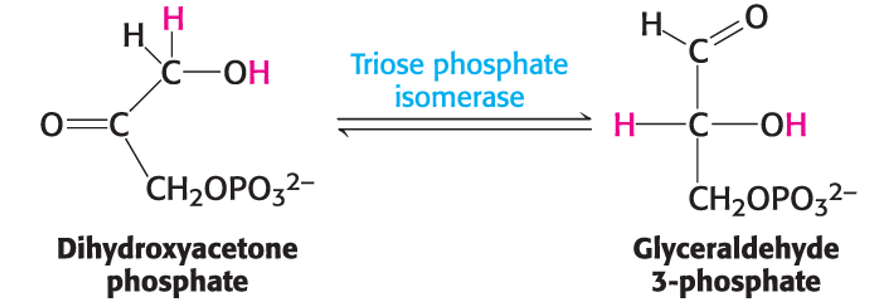
Isomerases do what?
Move functional groups within a molecule
Ligases do what?
Join two molecules at the expense of ATP
Ligase enzymes are a class of enzymes that play a crucial role particularly in DNA and RNA metabolism.
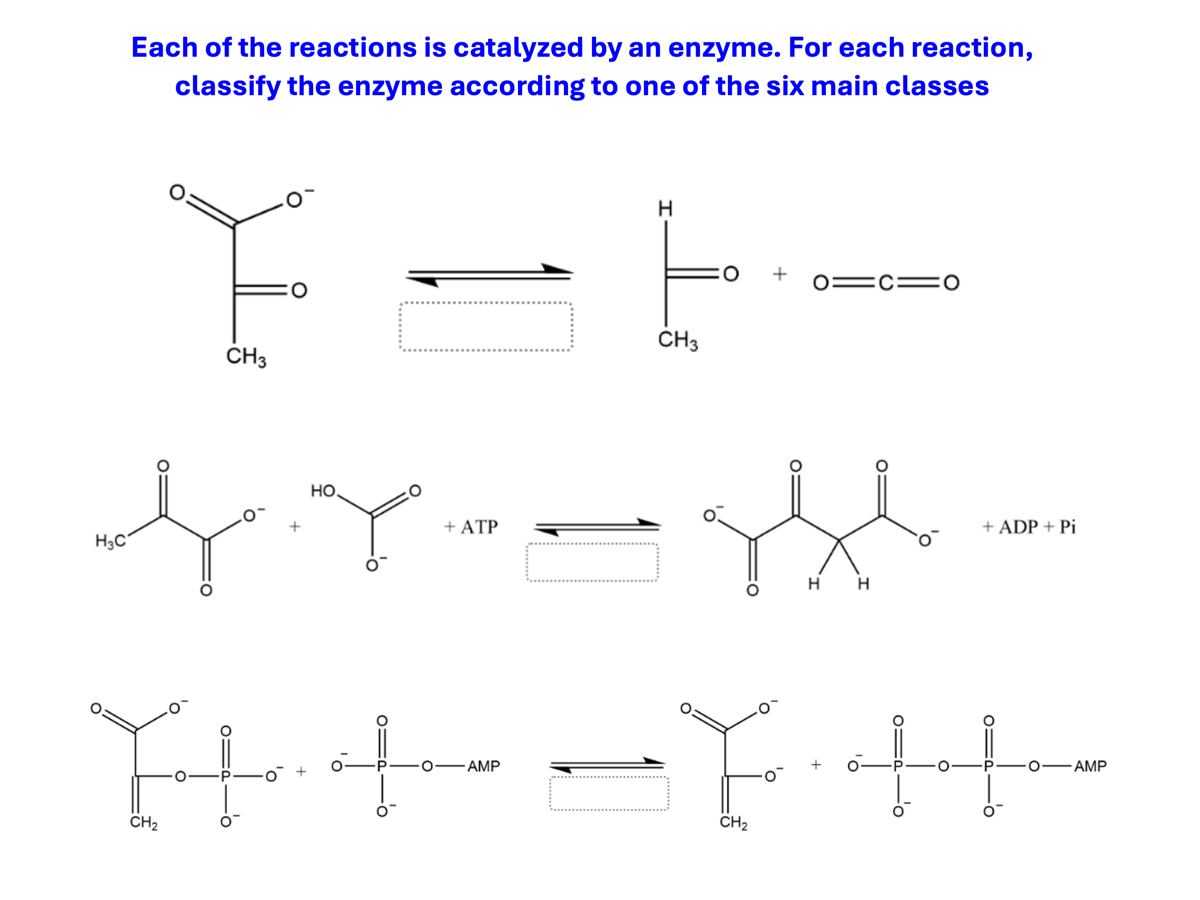
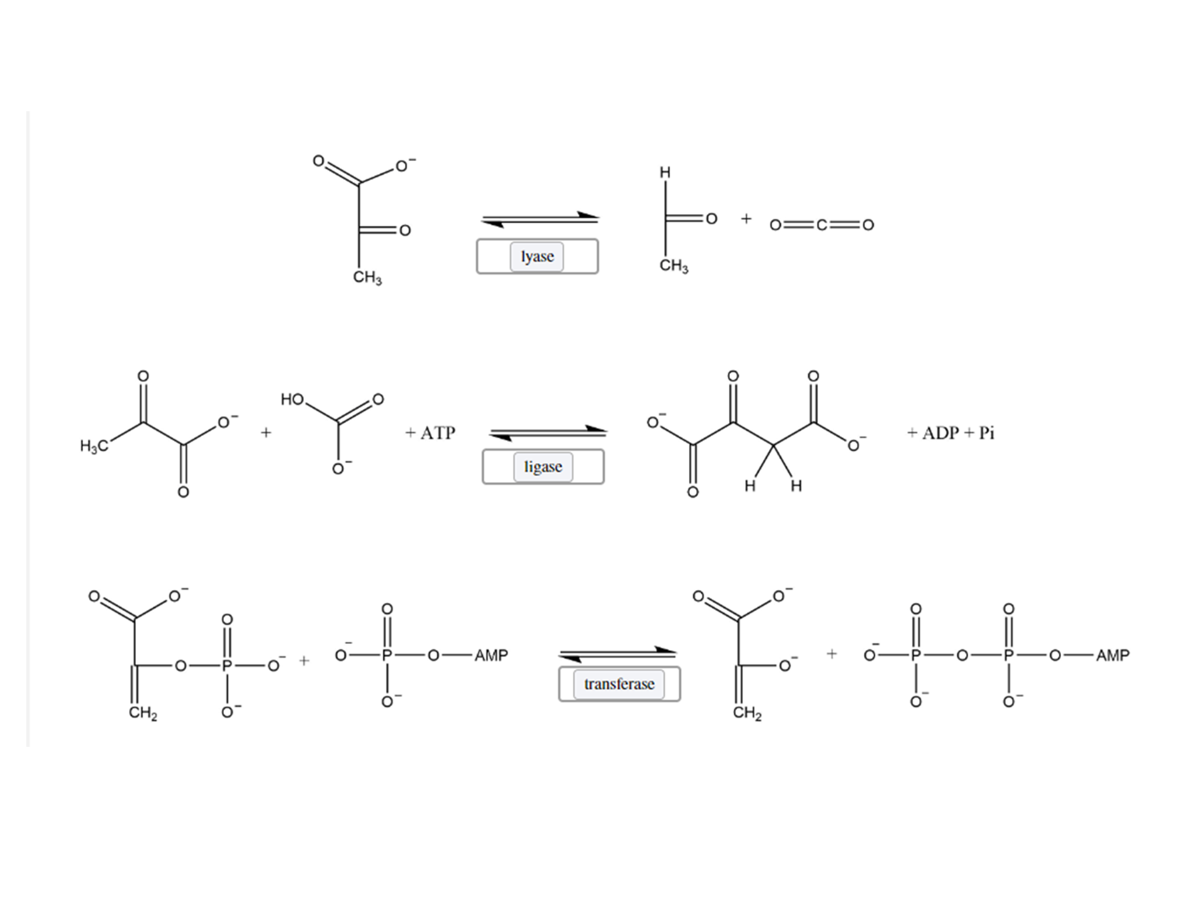
Follow the directions of the picture.

Gibbs Free Energy (G)
A measure of energy capable of doing work. The change in free energy when a reaction occurs is symbolized by ΔG
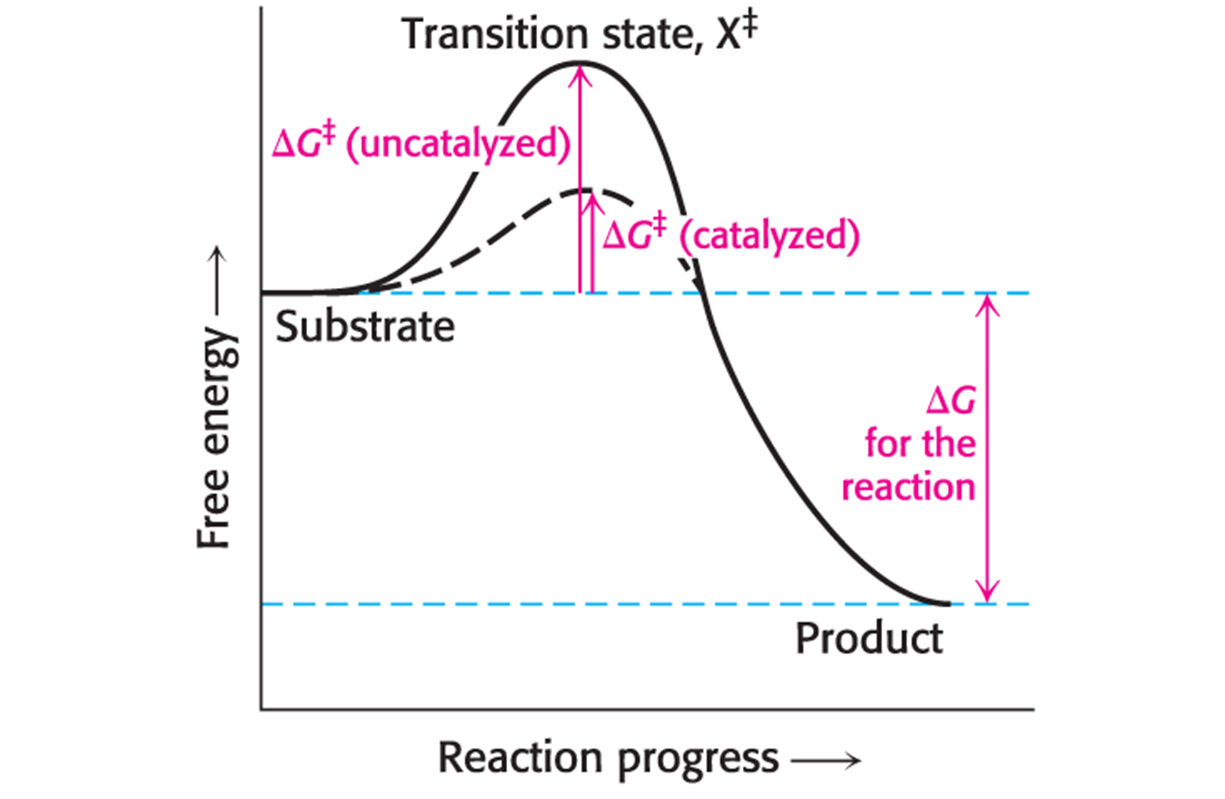
How do enzymes alter the ΔG of a reaction? Do they?
They do not.
The changes in Gibbs free energy (DG) or simply change in free energy allow us to predict what?
Spontaneity by focusing on the system only.
What is the formula for Gibbs Free Energy
ΔG° = ΔH° – TΔS°
What do the different signs of ΔG° mean?
The sign of DG indicates if a reaction will be spontaneous or not.
If ΔG < 0, the reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction.
If ΔG > 0, the reaction is nonspontaneous in the forward direction
If ΔG = 0, the system is at equilibrium
The ΔG of a reaction depends only on…
…the free energy difference between reactants and products and is independent of how the reaction occurs.
For the reaction A + B ⇌ the free energy change is given by what formula?
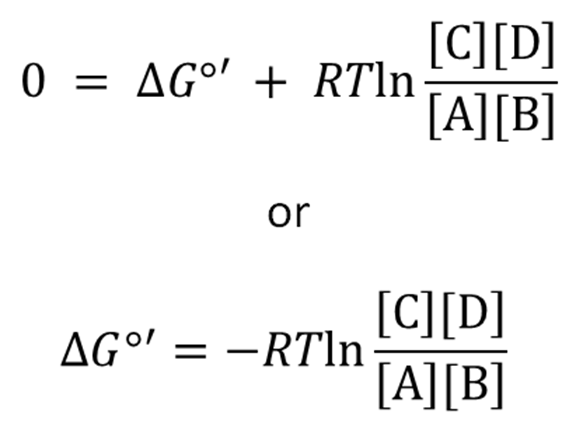
ΔGo = Standard free energy
R = Gas Constant ((8.314 J.K-¹. mol-¹ or 0.008314 kJ.K-¹. mol-¹ )
T = 298 K (Add 274k + Celsisu)
The more exergonic a reaction is, the ______ the equilibrium constant will be. The more endergonic a reaction is, the ______ the equilibrium constant will be.
Larger
Smaller
Predict how a graph model of how enzymes accelerate the reaction rate would look like (Product vs Time)?
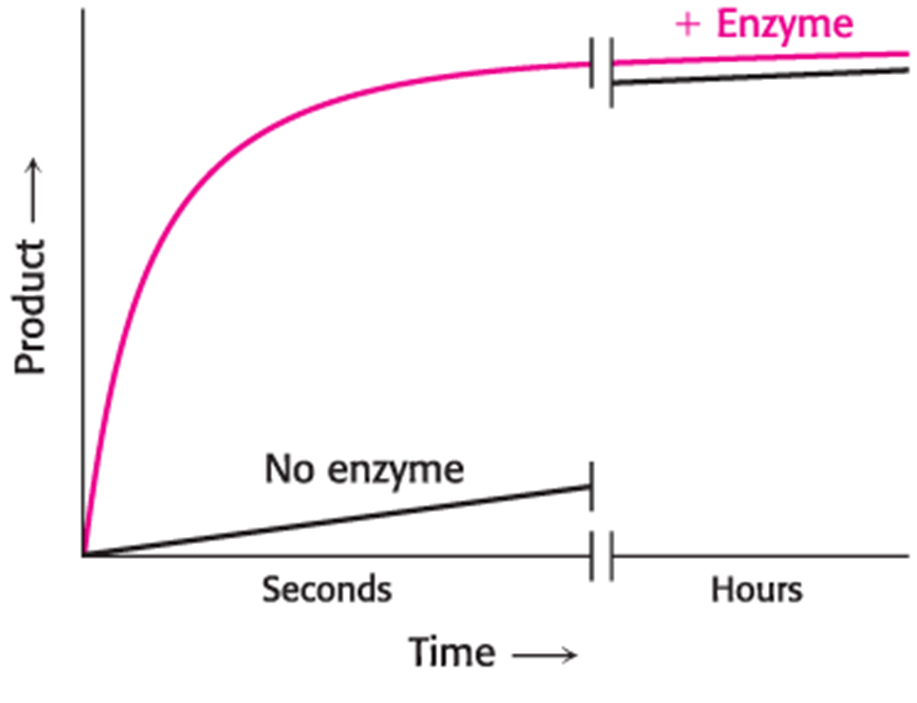
Graph Model of How Enzymes Decrease the Activation Energy
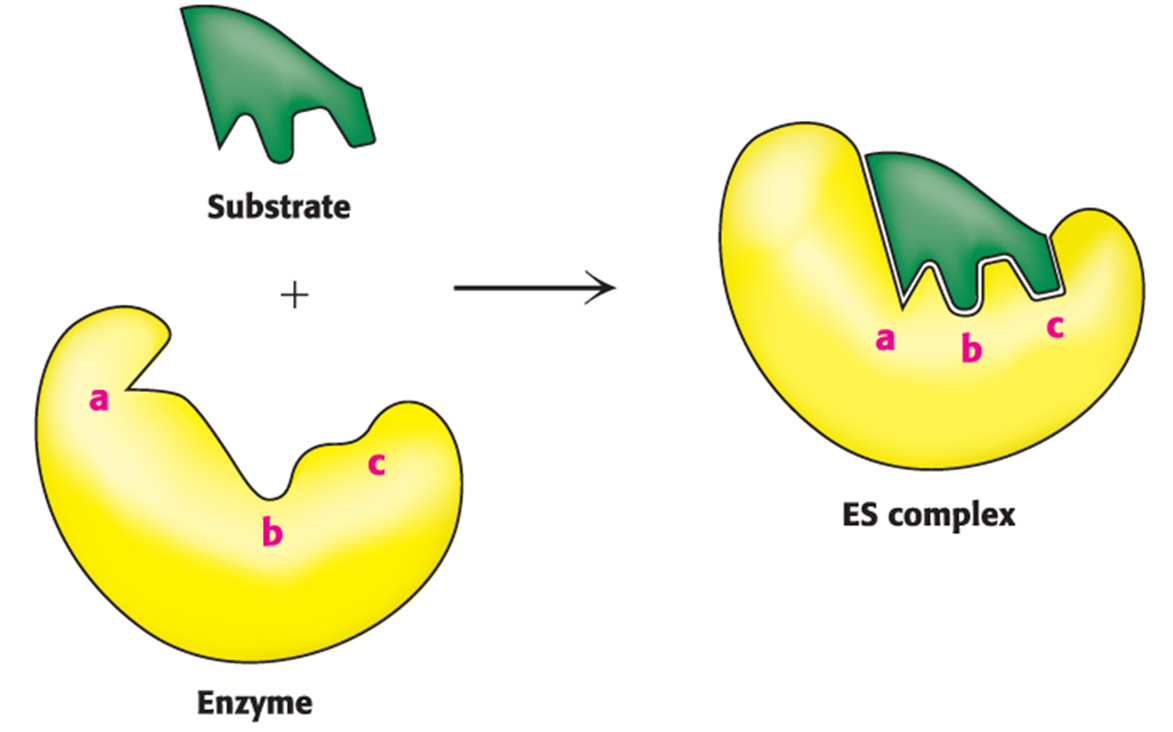
Active Site
Enzymes bring substrates together to form an enzyme–substrate complex on a particular region of the enzyme called this.
The interaction of the enzyme and substrates at the active site promotes the formation of what?
Transition state
Enzymes do not interact with their substrates like a lock and key. Rather, the enzyme changes shape upon substrate binding, a phenomenon called…
induced fit.
Binding energy
The free energy released upon interaction of the enzyme and substrate; it is greatest when the enzyme interacts with the transition state, thus facilitating the formation of the transition state.