Chapter 3 - Cells: The Living Units
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Selectively (semi) permeable
Determines which substances enter/exit the cell
Diffusion
The movement of molecules or ions from a high concentration to lower concentration
Osmosis
The diffusion of a solvent through a semi-permeable membrane (high concentration to low concentration)
Isotonic
Cells retain their normal size and shape; equal amount of water inside and outside of the cell
Hypertonic
Cells are shrunken and spiky; more water is outside of the cell than the inside (will undergo crenation)
Hypotonic
Cells are big and swollen; too much water is in the inside of the cell than the outside (will burst! aka lysis)
Facilitated diffusion
Certain molecules that can’t cross the semi-permeable membrane will do it with the help of carrier/channel proteins
Active transport
The cell provides the metabolic energy (usually ATP) needed to move substances against the concentration gradient
Endocytosis
Brings specific substances from the extracellular fluid into the cell
Exocytosis
Substances are ejected from the interior of the cell to the extracellular fluid
Phagocytosis
Engulfs large particles and combines with the lysosome to digest its contents
Pinocytosis
Drinks/slurps in extracellular fluids containing solutes into tiny vesicles
Plasma membrane
Semi-permeable membrane that separates 2 of the body’s major fluid compartments — intracellular and extracellular
Cytoplasm
The intracellular fluid that is packed with organelles
Nucleus
The “control center” organelle — controls the cellular activities
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell; transforms food into glucose, and produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Golgi complex
Packages and exports the proteins made by the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to its destination
Peroxisomes
Very active in detoxing potential hazards in the body, also breaks down/synthesizes fatty acids
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Synthesizes & metabolizes lipids, and can also detoxify drugs
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Imbedded with ribosomes and manufactures integral proteins
Flagella
Tail-like projection that propels the cell
Cilia
Tiny hairs that propel substances across the surface of the cell
Ribosome
Granules that make proteins — they can either be free or membrane bound
Microfilaments
Semi-flexible strands of actin protein that is involved in cell motility and shape
Lysosome
Power enzyme containing vesicles with super low pH digestive enzymes that clean, recycle, and rid of unwanted waste through exocytosis
Microvilli
Foldings or finger-like extensions of the plasma membrane; maximizes surface area for absorption
Mitosis
The division of the nucleus to replicate 2 identical daughter cells
Transcription
Transfers information from a DNA sequence to its complementary RNA sequence
Translation
The base sequence is translated into an amino acid sequence
What is labeled “F”?
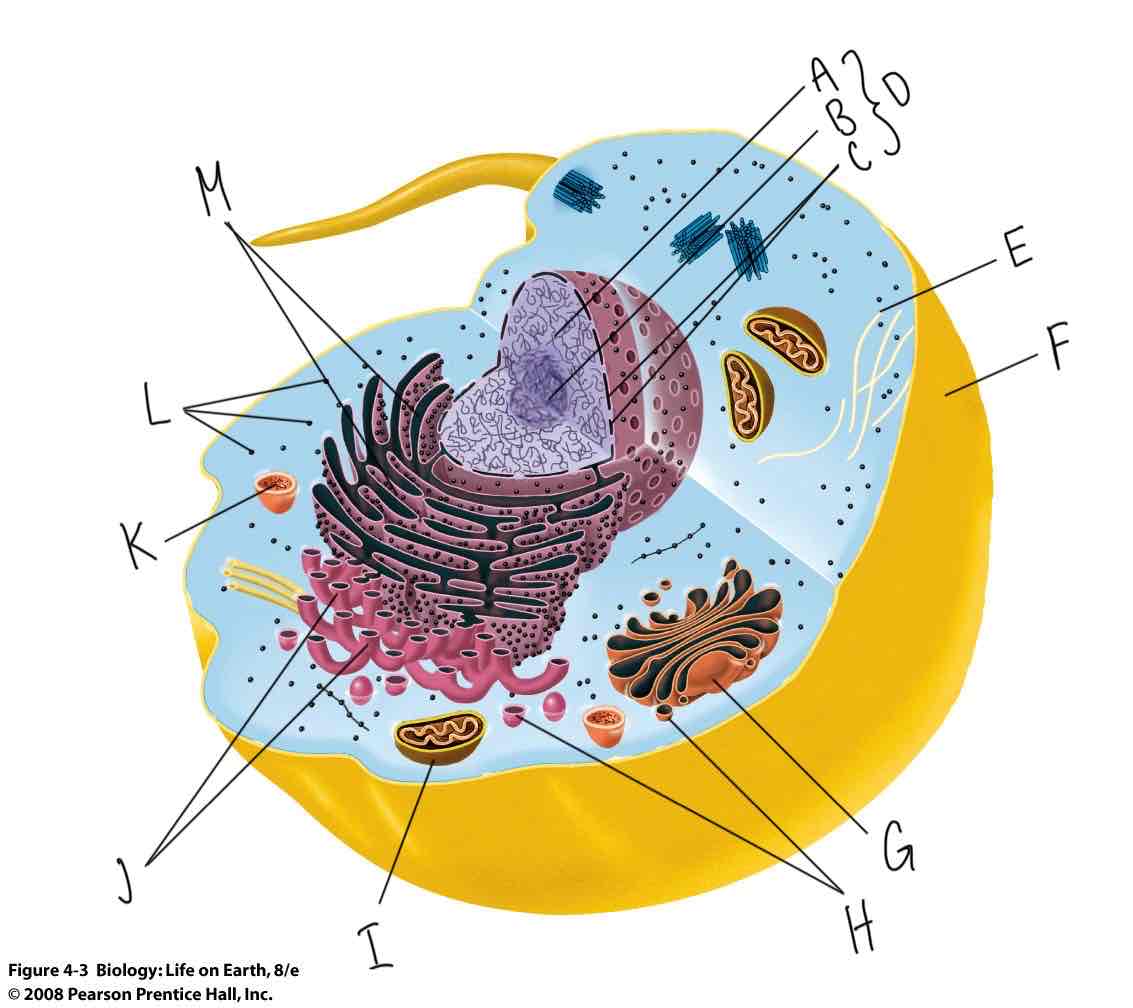
Plasma membrane
What is labeled “D”?
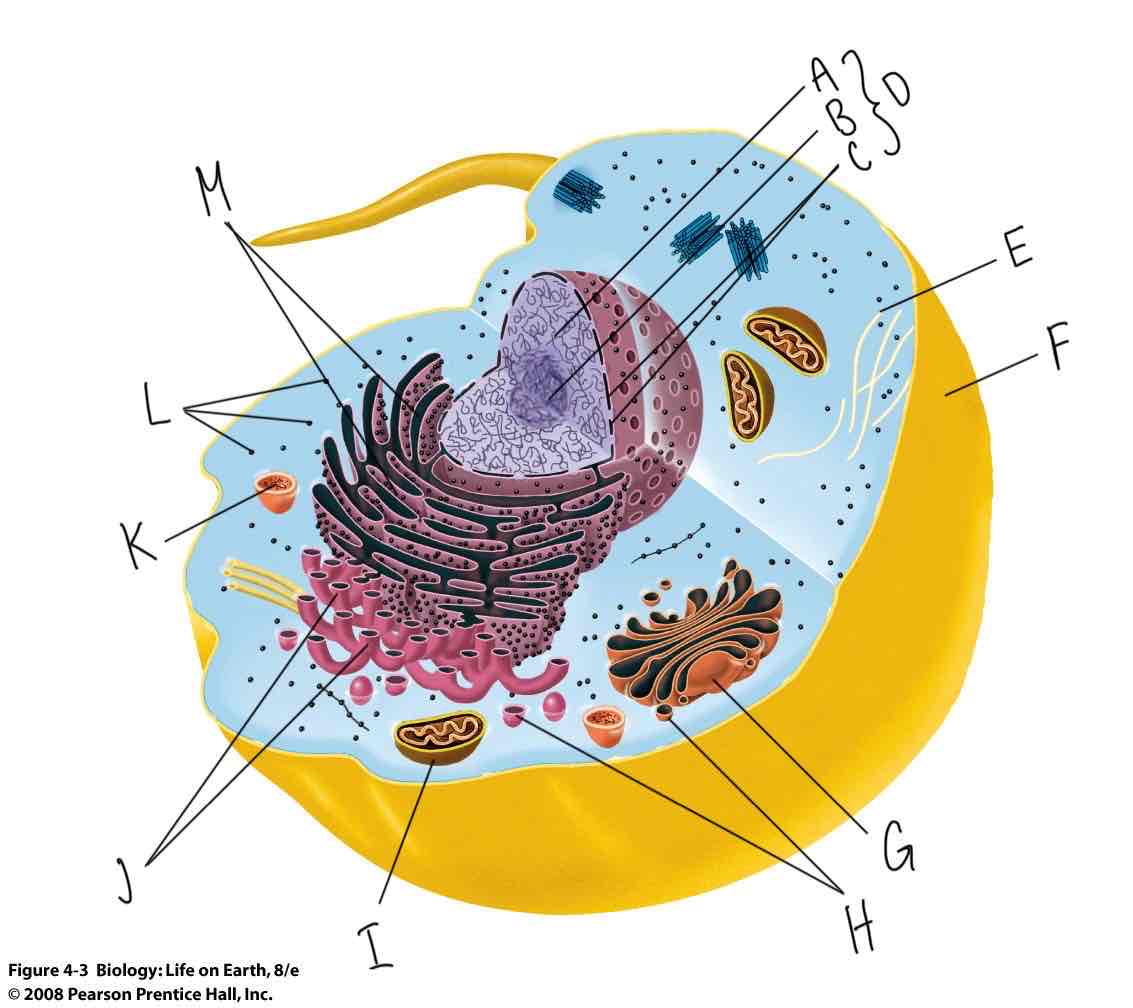
Nucleus
What is labeled “G”?
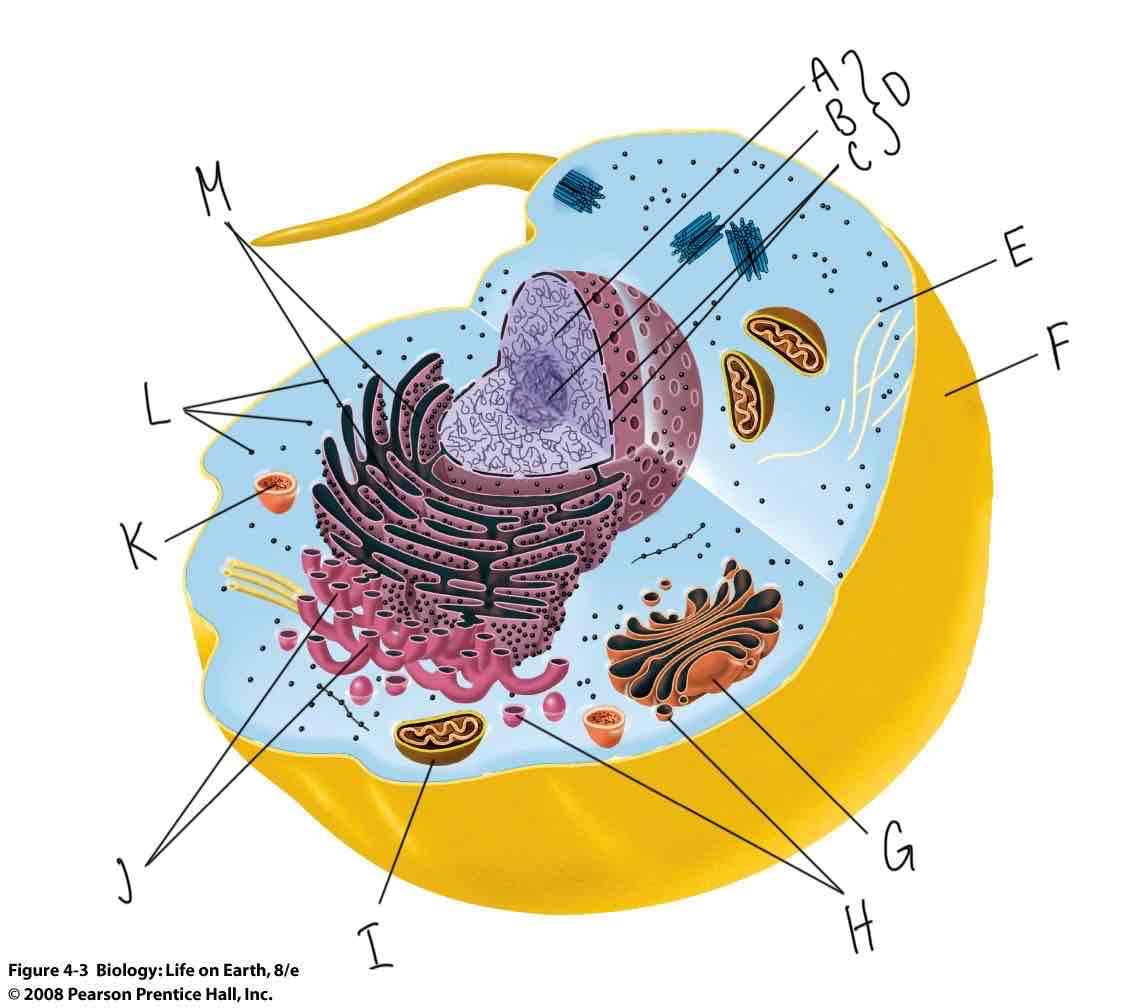
Golgi complex
What is labeled “K”?
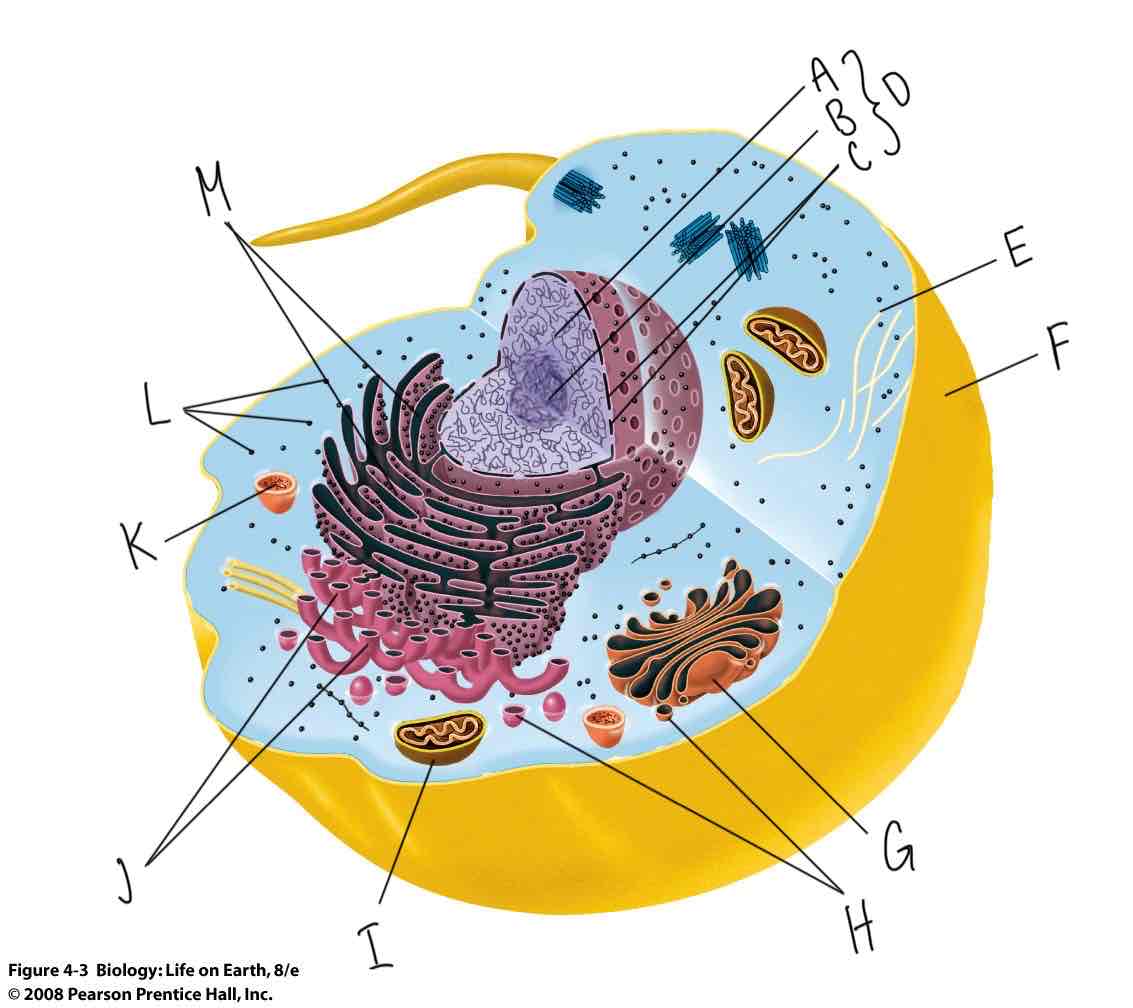
Lysosome
What is labeled “I”?
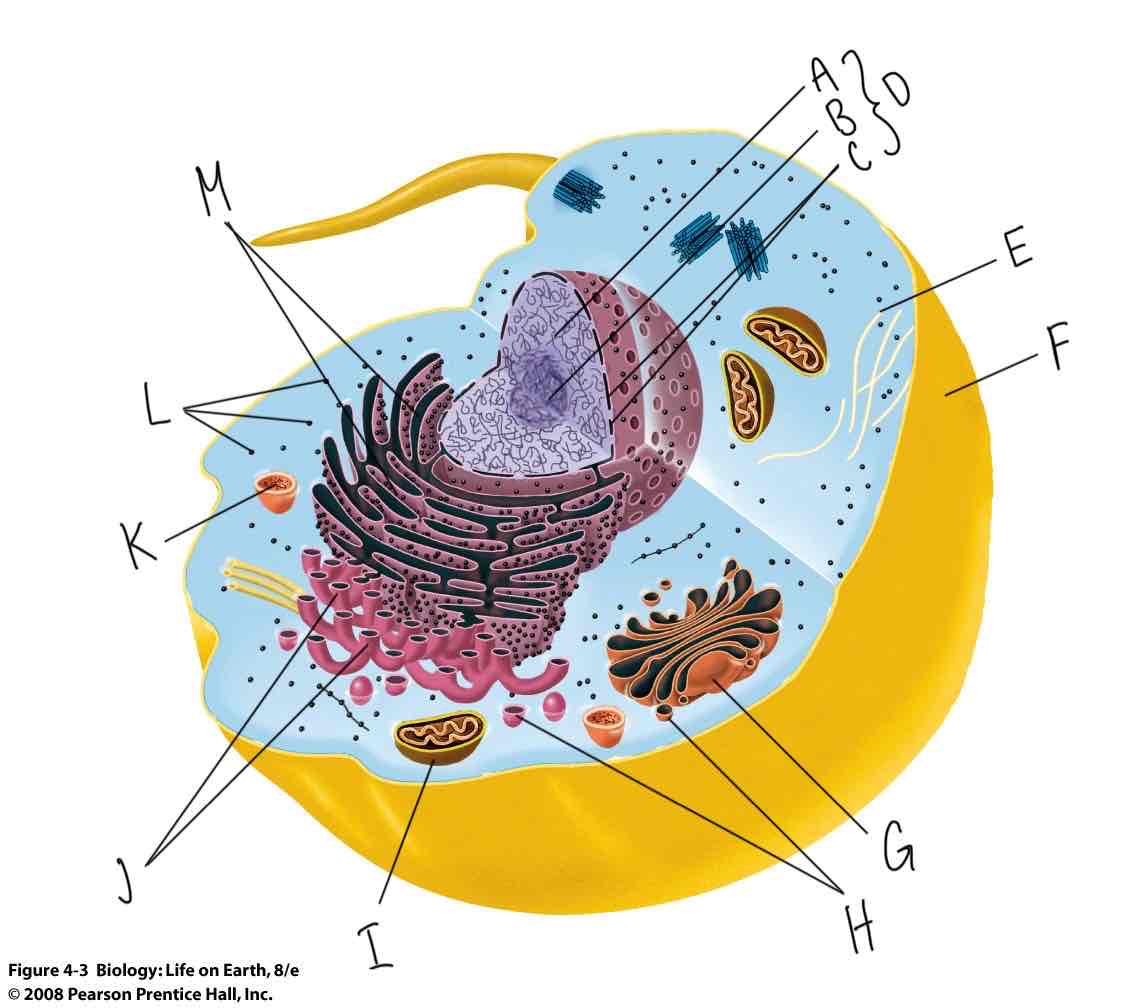
Mitochondria
What is labeled “J”?
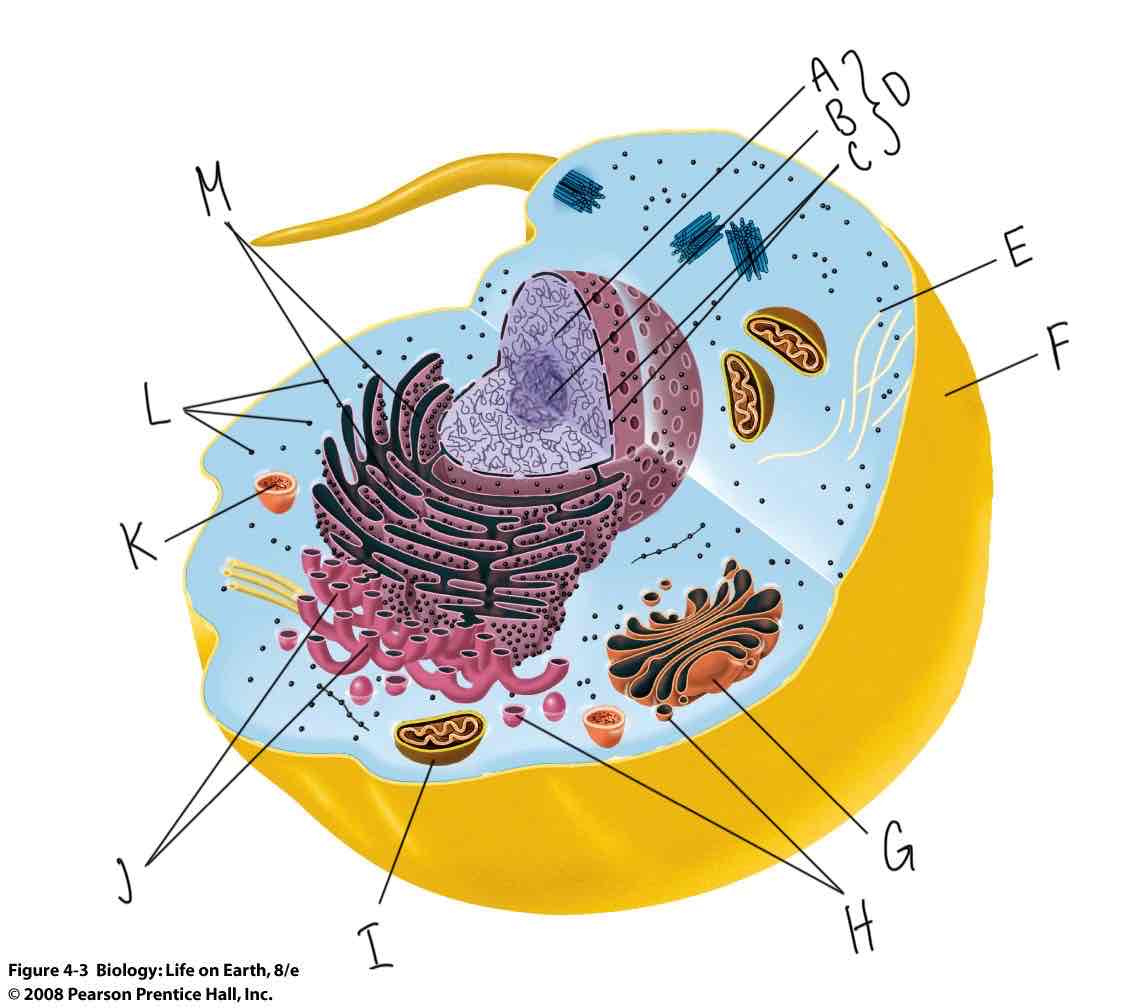
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth ER)
What is labeled “M”?
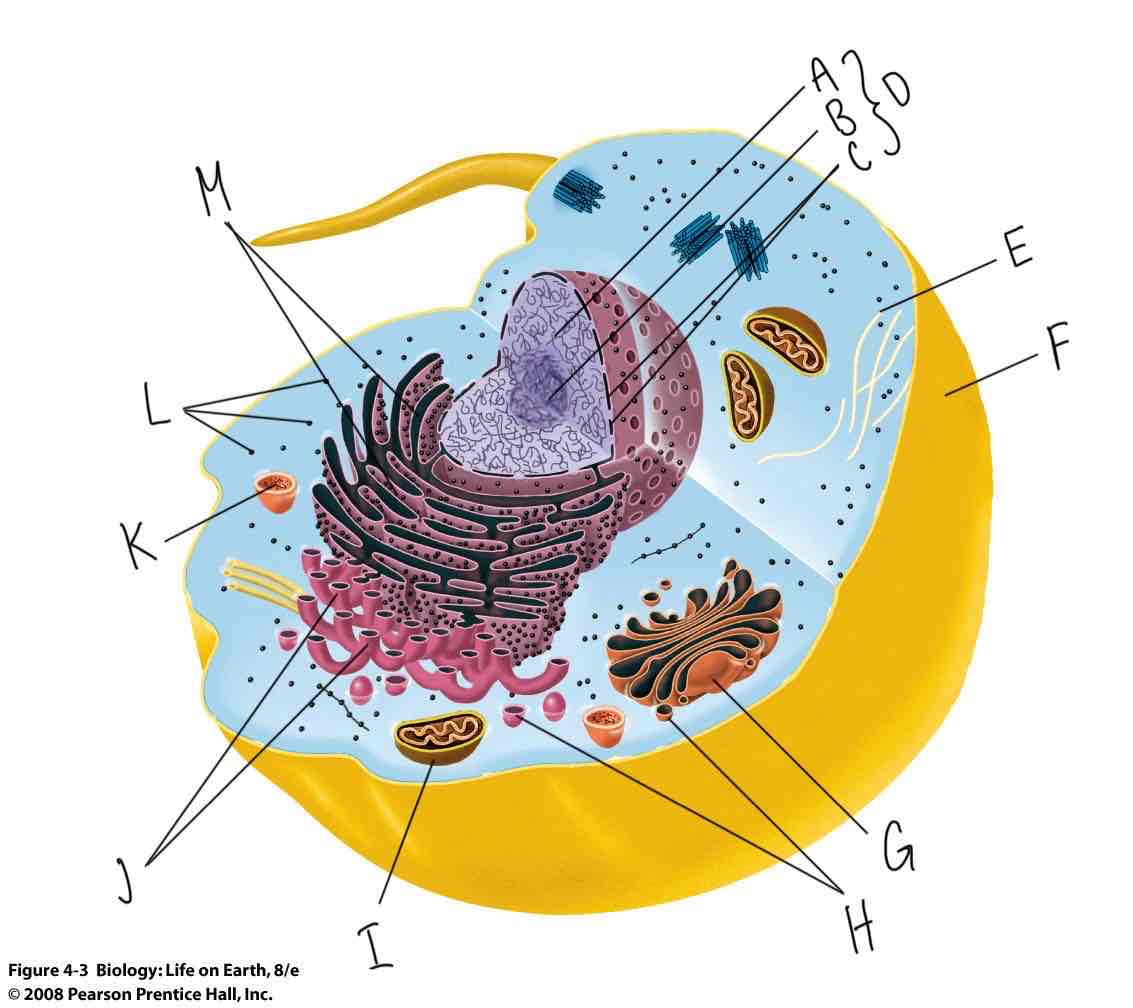
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)