Types of sugars 2.3 (copy)
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Fructose
Monosaccharides Found in fruits, honey and in some vegetable
galactose
Monosaccharides a simple sugar found in breaking of lactose in the milk and diary products
Sucrose
Disaccharides made up of one glucose and fructose together Sugar that we add to our food when baking is sucrose
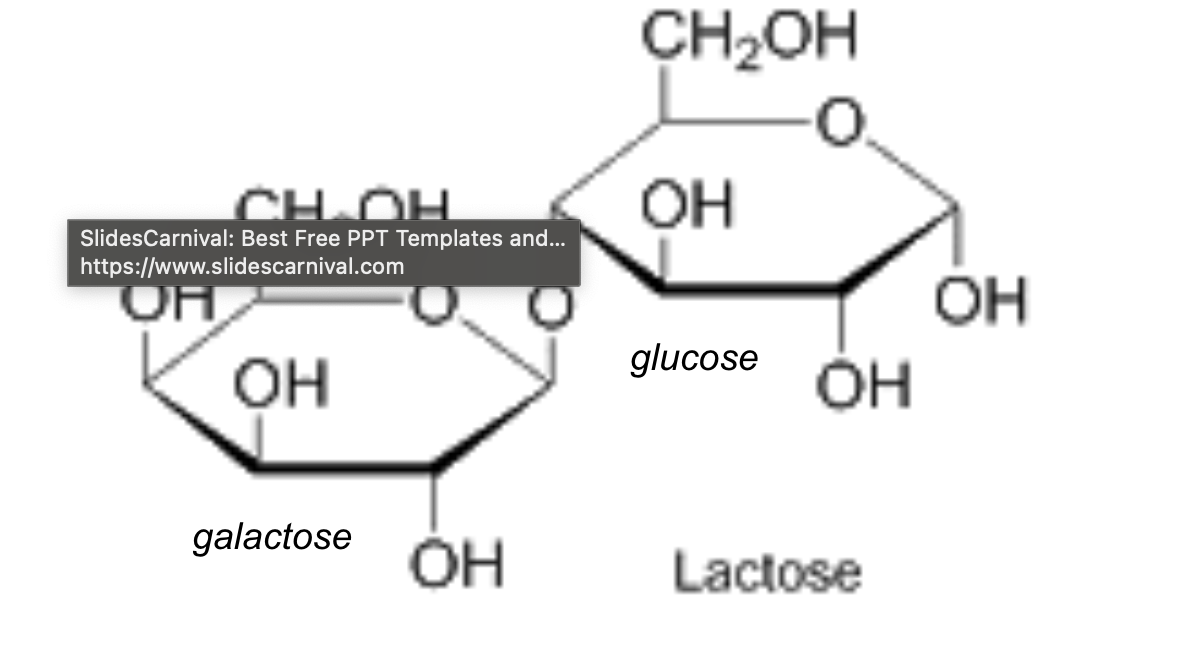
Lactose
disaccharides made up of one molecule of glucose and galactose Milk sugar because it is found in milk and diary products Lactose intolerance: This means that your body has hard time digesting diary products such as milk because of lactase deficiency. Lactase is the enzyme that breaks down the lactose into galactose and glucose in the small intestine
Maltose
Disaccharides made up of two glucose wheat and barley and beverages
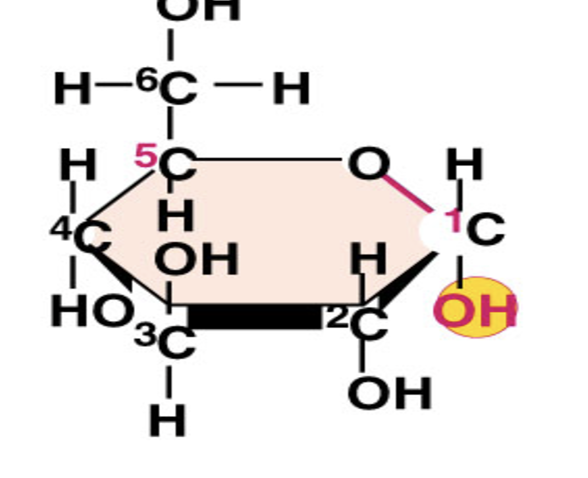
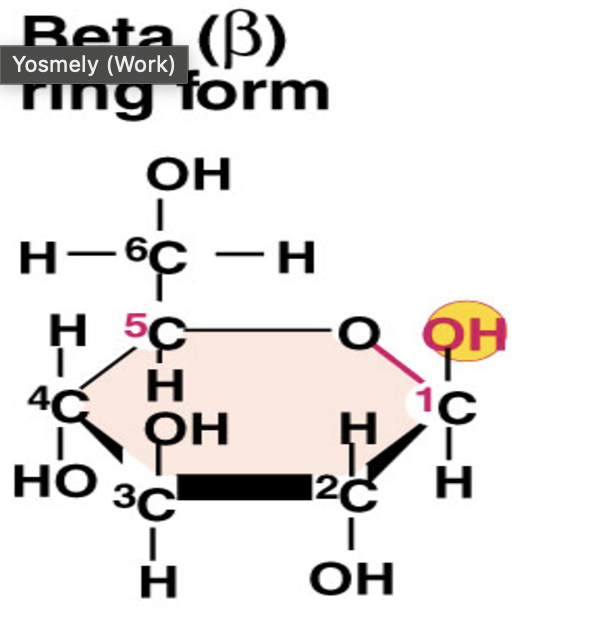
Alpha Glucose/ Beta Glucose
A product of photosynthesis, serving as the basis of the food web.
Needed to make ATP during cellular respiration.
Monomer of the polymer cellulose.
Alpha Glucose (Structure)
(Pic)

Beta Glucose Structure
pic
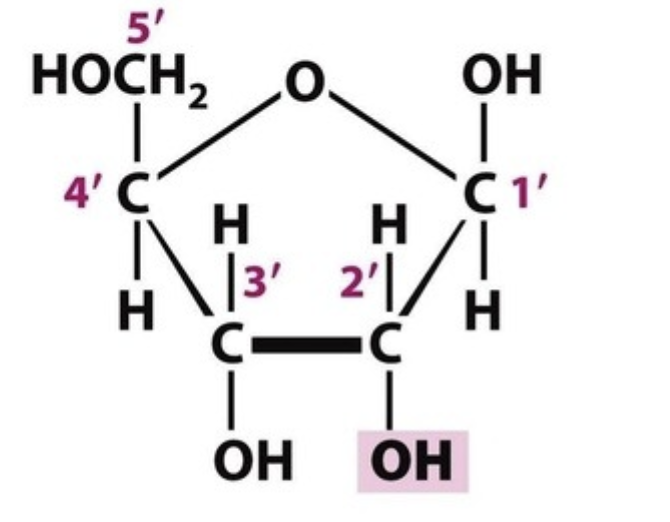
Ribose structure
pic
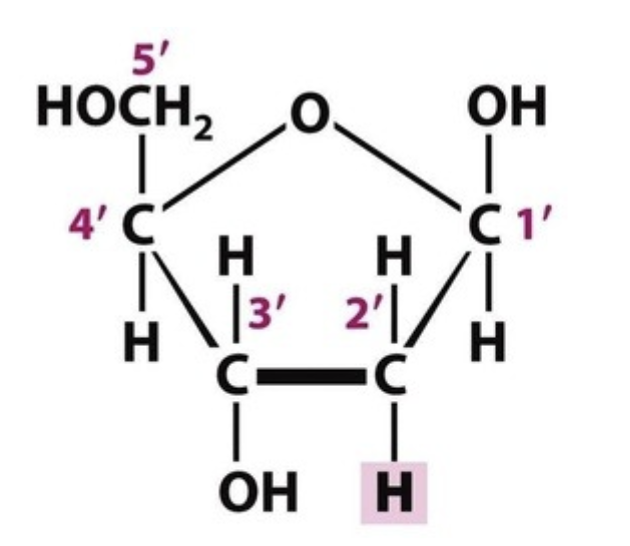
Deoxyribose sturcture
Maltose Structure
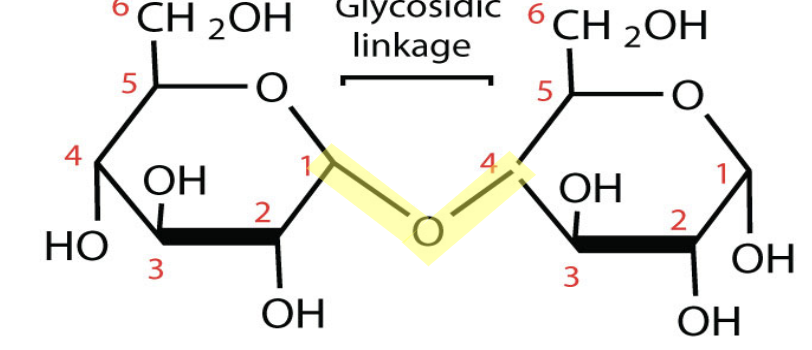
Maltose
Maltose is primarily used as an intermediate molecule in the formation and/or digestion of the larger polysaccharides starch and glycogen.
Sucrose Sturcture
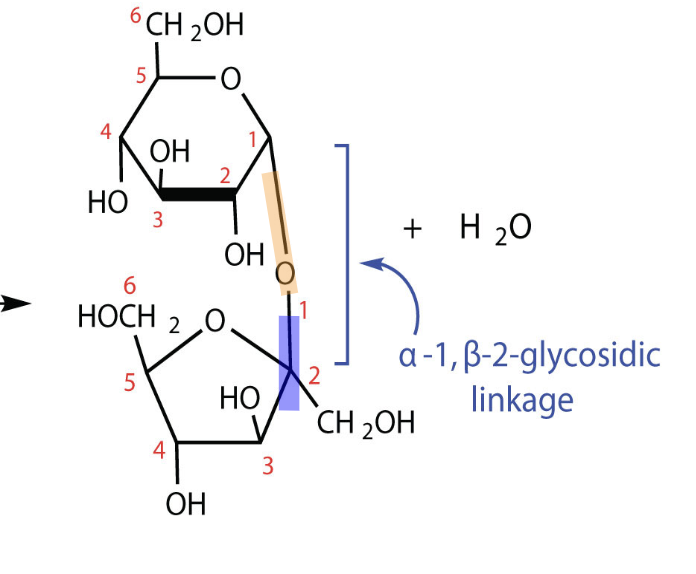
Sucrose Structure
Sucrose is known simply as sugar. Sucrose is produced by many plants (usually in roots, fruits and nectars) because it serves as a way to store energy. Many mammals, birds, insects and bacteria feed on the sucrose in plants and for some it is their main food source.
Lactose Structure
Amylose (Starch) Structure (made of alpha)

Amylopectin (Starch) Structure (Made of alpha)
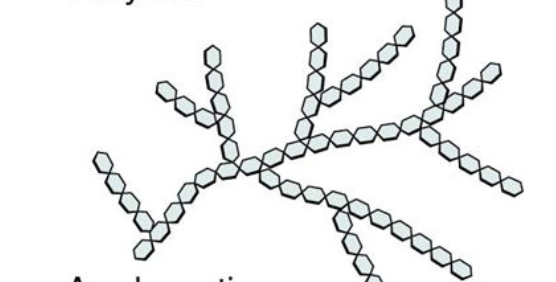
Glycogen Structure
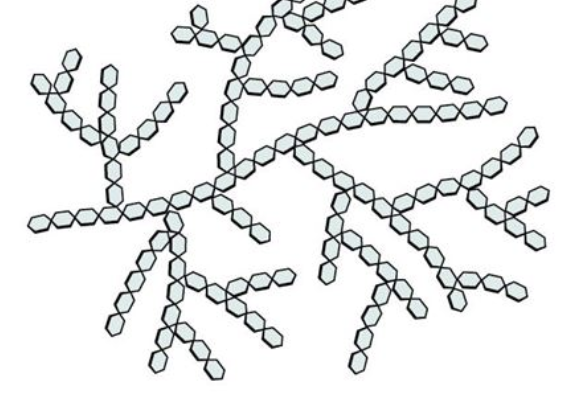
Cellulose Structure
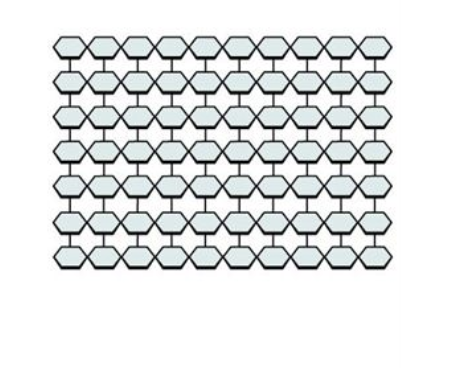
Starch
Starch* is the storage form of carbohydrates in plants. it is made out of a glucose
Plants are able to synthesize glucose in photosynthesis, and the excess glucose, beyond the plant’s immediate energy needs, is stored as starch in different plant parts, including roots and seeds. PLANT MADE
Cellulose
Cellulose is made up of 𝛽-glucose monomers linked by β 1-4 glycosidic bonds.
Cellulose does not branch. The cell wall of plants is mostly made of cellulose; this provides structural support to the cell. (FIBER!!!) PLANT MADE The monomers are packed tightly as extended long chains held adjacent to each other by hydrogen bonding. This gives cellulose its rigidity and strength.
Glycogen
Glycogen is made up of 𝛼-glucose monomers.
Glycogen is a highly branched molecule, with α 1-4 linkages and α 1-6 linkage at the branch points. Glycogen is the storage form of carbohydrates in humans and other vertebrates. (LIVER!!) glucose is stored as glycogen in liver and muscle cells.
When blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen is digested to release glucose into the blood so the cells can continue doing cellular respiration.
Does Amylopectin Branch?
Yes, 1,4 and 1,6 bonds