Chapter 9: Synovial Joints and Joint Injuries
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
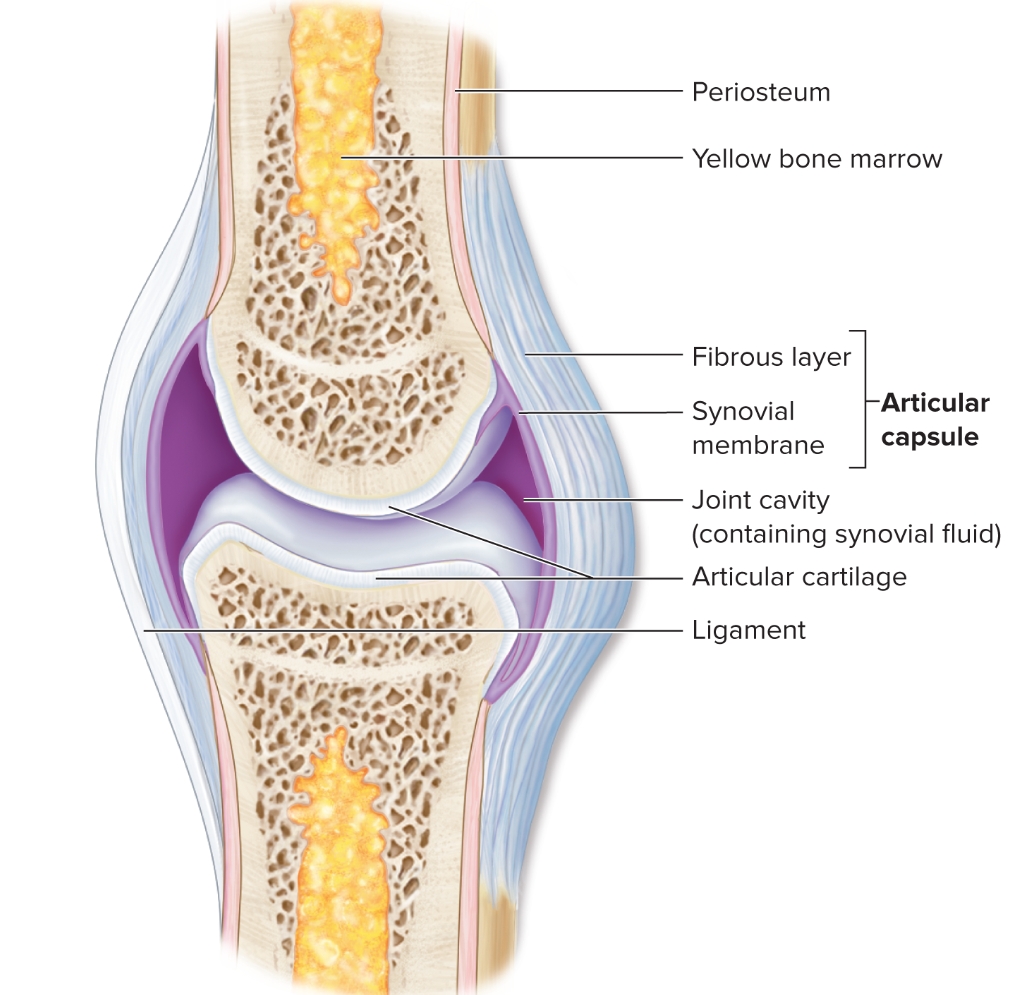
What are synovial joints?
bones separated by a joint cavity
include most joints in body
diarthroses (free mobile)
basic features?
articular capsule and joint cavity
synovial fluid
articular cartilage
ligaments, nerves and blood vessels
What is the double layered articular capsule (joints capsule)?
outer fibrous layer
DRCT
strengthen joints prevent bones pulled apart, hold in synovial fluid
inner synovial membrane
areolar connective tissue
covers internal joint surfaces not covered by cartilage
produce synovial fluid
What is the articular cartilage?
hyaline cartilage on bone surface at joint
function
reduce friction during movement
acts as cushion absorb joint compression
prevents damage to articulating ends of bones
avascular
What is the joint cavity?
space between articulating bones
lines by synovial membrane secreting fluid
viscous, oily substance
functions:
lubricates articular cartilage
nourishes the chondrocytes
acts as shock absober
What are the ligaments?
DRCT
connect bone to bone
stabilize, strengthen and reinforce synovial joints
What are the sensory receptors and blood vessels?
numerous
detect painful stimuli, report on movement and stretch
What are the tendons?
DRCT
not part synovial joint itself
attach muscle to bone
help stabilize
What are the bursae?
fibrous, saclike structures containing synovial fluid
lined internally by synovial membrane
found synovial where bones, ligaments, muscles, skin or tendons rub together
connected to or separate from joint cavity
alleviate friction
What are tendon sheaths?
elongated bursae
wrap around tendon where friction is excessive
common in wrist and ankle
What are the menisci?
deep to articular capsule within knee joint
c-shaped fibrocartilage pads on top of tibial condyles
cushioning between articular surfaces
change shape to conform to articulating surfaces
partially stabilize joint medially and laterally
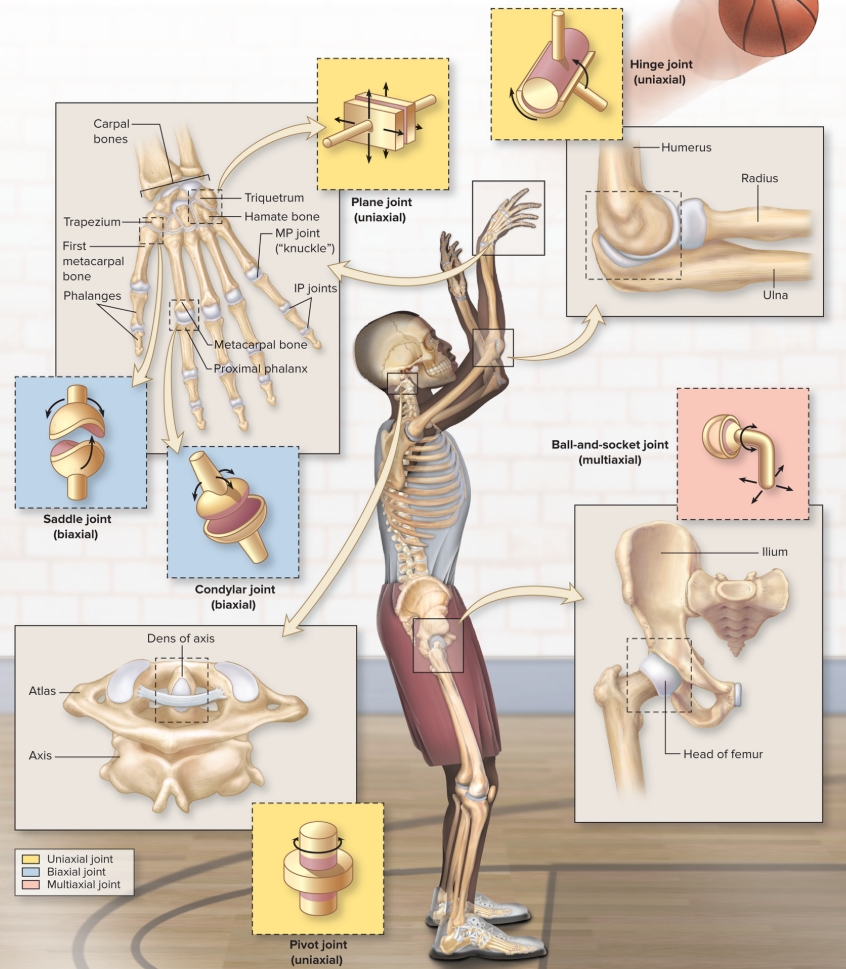
What are the shape classifications?
plane
flat articulation, side-to-side movement in single plane
simple, least mobile
tarsals, carpals, vertebrae
hinge
convex surface within concave depression
hinge of door
elbow, middle phalangeal
pivot
rounded surface sits into ligament ring
rotation longitudinal axis
proximal radius/ulna (elbow)
condylar
oval, convex shape (condyle) articulating with concave surface (fossa)
wrist, ankle, jaw, knee, proximal phalanx
saddle
convex and concave surface resembling saddle shape
thumb
ball-and-socket
spherical head bone fitting into cuplike socket
3 planes of movement, most mobile
hip and shoulder, not a bony socket
What are the movements of synovial joints?
gliding, flexion, extension, hyperextension, lateral flexion, circumduction, rotation, dorsiflexion, plantar flexion, eversion, inversion, protraction, retraction
What is the shoulder joint?
most stability due to rotator cuff muscles
SITS - supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
work as group hold humerus in glenoid cavity
tendons encircle joint and fuse with articular capsule
What are some joint injuries?
tibial collateral ligament - leg forcibly abducted
fibular collateral ligament - medial side of knee struck
ACL - hyper extended
PCL - hyper flexed
Meniscus - trauma and/or overuse
Unhappy triad: tibial collateral ligament, medial meniscus, ACL
lateral blow to knee, abducts and laterally rotates leg
What is a sprain?
stretching/tearing of ligaments without fractur or dislocation
twisting foot, over inversion
fibers lateral ligament stretched or torn
localized swelling and tenderness anteroinferior to lateral malleolus
What are some shoulder dislocations?
common due to instability
shoulder separation - acromioclavicular joint dislocation
pain abducted more than 90
acromion appearing prominent
glenohumeral dislocation - abducted humerus struck hard
shoulder flattened and squared-ff
humeral head anterior and inferior to glenohumeral joint capsule
What is arthritis?
group inflammatory/degenerative diseases of joints
joint swelling, pain and stiffness
What is gouty arthritis?
middle-aged or older males
increased levels or uric acid
What is osteoarthritis?
degenerative joint condition in older individuals
wearing down of articular cartilage
fingers, knuckles, hips, knees, and shoulders most affected
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
younger to middle-aged adults, often women
autoimmune disorder
starts with synovial membrane inflammation