Psych Unit 1- Biological Basis of Behavior & States of Consciousness
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Natural Selection
organisms with traits that better enable them to survive and reproduce in their environment are more likely to pass those traits on to future
nature vs nurture
nature: heredity, how passed down physical or mental traits affects a person
nurture: environmental factors and how they affect a person
Eugenics
improving genetic quality of human population by selectively breeding for desirable trait and discouraging reproduction among those with traits considered undesirable
Epigenetics
focuses on how environment and a person’s behavior affect a person’s genes and how they work
how a persons’s body reads a DNA sequence
can help explain how even twins can be completely different ppl despite having the same genes
evolutionary psychology
study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles such as natural selection. (how are ppl alike/different because of out shared biology and natural history?)
behaviour genetics
study of how environment and genetics affects behaviour
Twin studies
compare identical twins to one another
Monozygotic (identical twins) vs dizygotic (fraternal twins)
Adoption Studies
compare twins who have been separated and adopted by different families
Family studies
researchers assess hereditary influence by examining blood relatives to see how much they resemble each other on a specific trait
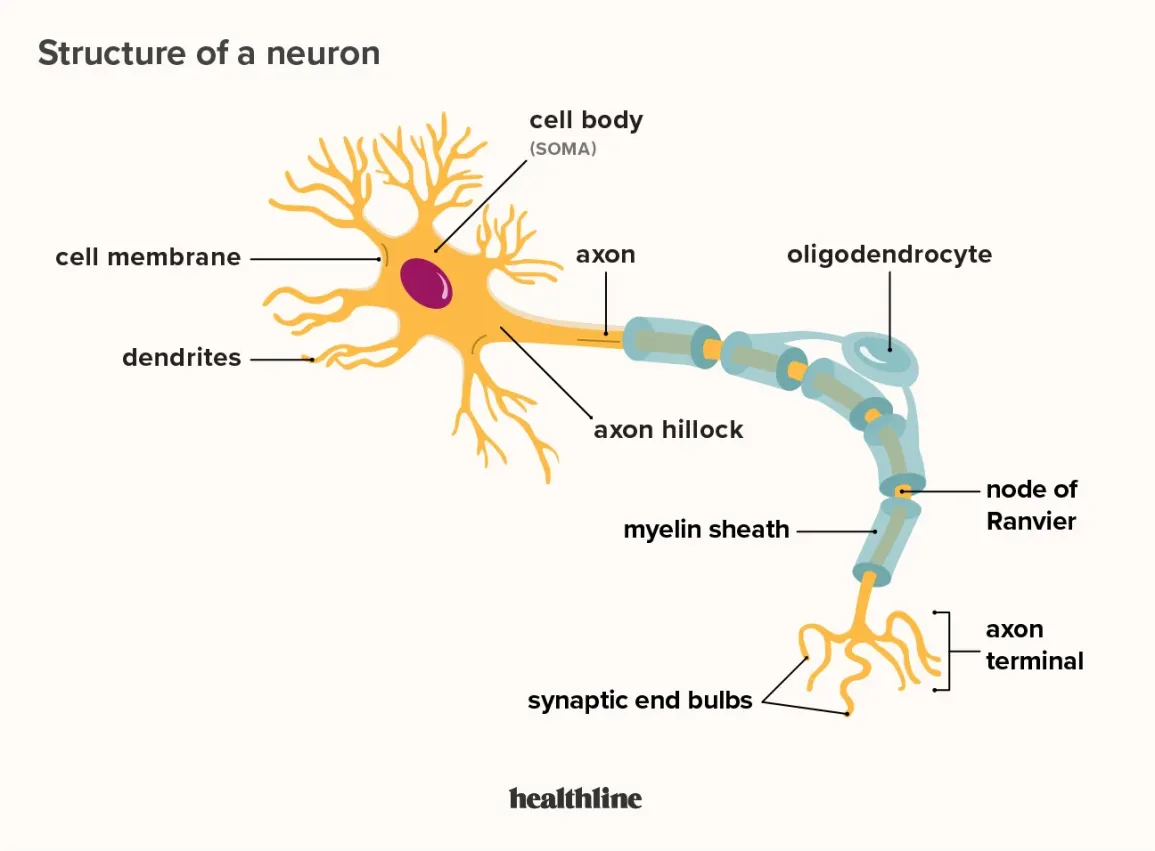
Neurons (know the parts)
Dendrite
Cell body/soma
Axon
Myelin Sheath
Axon terminals/terminal buttons
synapse/synaptic cleft
glia cells
form basis of the nervous system and are building block of all behavior and mental processes
most abundant cell in nervous system
do not send any messages or signals in the body
provide structural support and insulation; 1 to 5 million
reflex arc
neural pathway that allows body to respond to stimulus without thinking
includes sensory, inter, and motor neurons
receptor activation, sensory neuron transmission, interneuron transmission, motor neuron transmission, and effector response.
allows body to respond to a threat before processing what’s going on
sensory neurons (afferent neurons)
send signals from sensory receptors to CNS
motor neurons (efferent neurons)
send signals from CNS to PNS
interneurons
connect sensory neurons to motor neurons in CNS
mirror neurons
fire both when an individual perform and action or observes the same action being performed (when watching smth ur brain processes it as if you’ve done it too)
dopamine
neurotransmitter
Functions:
Movement
Rewards and addiction
Pleasurable emotions
Condition related to excess/deficit:
Oversupply: Linked to schizophrenia
Undersupply: Leads to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson’s disease
serotonin
neurotransmitter
Functions:
Mood regulation
Hunger/appetite
Sleep
Condition related to excess/deficit:
Undersupply: Linked to depression
Some antidepressants work by raising serotonin levels
norepinephrine
neurotransmitter
Functions:
“Fight-or-flight” response: increases heart rate, circulation, and respiration
Slows down appetite and digestion during fight-or-flight
Condition related to excess/deficit:
Undersupply: Can depress mood
GABA
neurotransmitter
Functions:
Inhibits excitation and anxiety (calming effect)
Primary inhibitory neurotransmitter
Condition related to excess/deficit:
Undersupply: Linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
glutamate
neurotransmitter
Functions:
Primary excitatory neurotransmitter
Learning and memory
Condition related to excess/deficit:
Oversupply: Can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures
substance p
neurotransmitter
Functions:
Excitatory neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting pain signals
Condition related to excess/deficit:
Oversupply: Can lead to chronic pain
acetylcholine
neurotransmitter
Functions:
Voluntary movement
Memory
Learning
Condition related to excess/deficit:
In Alzheimer’s disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorat
endorphins
neurotransmitter
Functions:
Pain relief and feelings of pleasure
Stress reduction
“Natural opiates”
Condition related to excess/deficit:
Oversupply: Can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures
resting potential
stable, negative charge when the cell is inactive (polarized)
action potential
rapid, electrical impulse that travels down a neuron's axon to transmit signals
all the same size
send signal down the axon to other neurons. then, neuron goes through process of depolarization which brings neuron back to resting potential
absolute refractory period
minimum time which another impulse can not occur (1-2 milliseconds)
all-or-nothing principle
a neuron either fires or it doesn’t
synapse
small pocket of space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrite of another neuron
chemical synapse: uses neurotransmitters for slower communication
electrical synapse: for messages that need to be send ASAP
inhibitory neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that reduce the likelihood of a neuron firing an action potential
excitatory neurotransmitters
chemical messengers in the nervous system that increase the likelihood of a neuron firing an action potential
reuptake
the process where a cell reabsorbs excess substance left in the synaptic gap, such as a neurotransmitter
synaptic pruning
unnecessary connection between neurons are eliminated in the brain for efficiency
neuron firing process
action potential send a signal down axon of neuron to the presynaptic terminal
channel in axon terminal are opened and neurotransmitters are released into synaptic gap
neurotransmitters diffuse through synaptic gap, and bind to receptors in postsynaptic terminal
neurotransmitters unbind with receptors, some (neurotransmitters) are destroyed and some go through reuptake process
agonist drugs
increases effectiveness of neurotransmitters by mimicking them
bind to receptors in synapse that are meant for neurotransmitters,
antagonist drugs
decrease effectiveness of neurotransmitters
either blocks neurotransmitters from being released, or connects to receptors and blocks neurotransmitters from binding
central nervous system
body’s main processing center
Brain: receives and processes sensory info, initiates responses, stores memories, generates thoughts and emotions
Spinal cord: conducts signals to and from the brain control reflex activities
peripheral nervous system
includes all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, acting as the body's communication network between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
autonomic nervous system
controls involuntary responses. makes sure ur heart’s beating, stomach’s digesting, ur breathing, etc
sympathetic division
mobilizes body and gets it ready for action. pulls dilate, increases breathing, etc '
fight or flight
parasympathetic division
relaxes body. slows heart rate, increases digestion, helps focus and saving and storing energy
somatic nervous system
responsible for voluntary muscle movements and sensory perception from the skin and muscles. happens consciouslyand voluntarily
fight-flight response
a physiological reaction that occurs in response to perceived stress or danger.
lesioning
destroying a piece of the brain
Insert electrode into a brain structure and pass a high electrical current which burns tissue
brainstem
connects brain to spinal cord, and helps regulate involuntary body functions (breathing, heart rate, etc)
medulla, pons, midbrain
hindbrain: medulla, cerebellum
medulla: Lowest part of the brain stem that controls autonomic movements like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, sneezing, swallowing.
cerebellum: Part of the hindbrain responsible for coordinating voluntary movements, balance, and posture
midbrain: reticular activating system
Network of neurons in the brainstem that regulates wakefulness and alertness
forebrain: cerebrum, cerebral cortex
cerebrum: largest part of brain, controls voluntary actions, responsible for cognitive functions (thinking, learning, reasoning, memory)
cerebral cortex: wrinkled outermost layer of the brain. center for higher-level functions (memory, language, consciousness). divided into 4 lobes
limbic system- thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala
Thalamus: Located right above brain stem and acts as the brain’s “sensory control center” by relaying sensory information to cerebral cortex
hypothalamus: helps regulate autonomic nervous system (endocrine system) by regulating things like thirst, hunger, temperature
hippocampus: Structure in the limbic system critical crucial for memory formation, spatial navigation, and consolidating short-term memories into long-term ones
amygdala: Located in temporal lobe responsible for processing emotions (especially fear and anger). Helps trigger fight-or-flight mode, forming emotional memories, moderating emotional responses.
occipital lobe- visual cortex
Part of the occipital lobe that analyzes basic visual stimuli like orientation and movement, laying the foundation for higher-level processing of visual information from the eyes, enabling us to perceive shapes, colors, and movements.
parietal lobe- somatosensory cortex
Processes sensory input from the skin, muscles, and joints. This area detects and interprets information on touch, temperature, pain, and pressure, and allows us to perceive the size, shape, and texture of an object via touch.
temporal lobe- auditory cortex
Found within the temporal lobe, it is responsible for processing sounds and interpreting auditory stimuli, allowing us to recognize different pitches, tones, and rhythms
frontal lobe- prefrontal & motor cortex
prefrontal cortex: part of the frontal lobes at the very front of the brain. It's involved with executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning & abstract thought.
motor cortex: part of the cerebral cortex involved in planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
brain plasticity
the brain's ability to change and adapt its structure and function throughout life. It allows the brain to reorganize itself in response to experiences, learning, and even injuries.
neurogenesis
the process of creating new neurons from neural stem cells, which contributes to brain functions like memory, learning, and mood regulation.
broca’s area
Located in the frontal lobe, it is essential for speech production and language processing, enabling us to formulate and articulate spoken language.
wernicke’s area
Located in the temporal lobe, it is critical for language comprehension, allowing us to understand spoken and written language effectively
aphasia
inability (or impaired ability) to understand or produce speech, as a result of brain disease or damage.
left hemisphere
Analytics thought, logic, language, science and math
Controls right side of the body
right hemisphere
Holistic thought, intuition, creativity, nonverbal expressions (body language, facial expression, etc), art and music
Controls left side of the body
corpus callosum
a thick bundle of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, allowing them to communicate and share information.
Roger Sperry & Michael Gazzaniga’s split brain research- Contralateral hemispheric organization
demonstrated contralateral hemispheric organization, where each side of the brain controls the opposite side of the body and has specialized functions. Because the corpus callosum was severed in split-brain patients, the hemispheres could not communicate, revealing how each side processes information independently.
adrenaline
hormone
Functions:
Activates the sympathetic nervous system
Involved in the fight-or-flight response
Released from:
Adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys)
leptin
hormone
Functions:
Provides information about the body’s fat stores
High levels: Signal fullness
Low levels: Increase feelings of hunger
Released from:
Adipose tissue (body fat) — proportional to amount of body fat
oxytocin
hormone
Functions:
Social bonding (“love hormone”)
Childbirth
Released from:
Produced by the hypothalamus, then stored and released by the pituitary gland
melatonin
hormone
Functions:
Regulates the sleep-wake cycle
Increased levels: Cause drowsiness
Released from:
Pineal gland (small cone-shaped endocrine organ in the center of the brain)
ghrelin
hormone
Functions:
“Hunger hormone”
Increased levels: Increase appetite
Released from:
Stomach
pituitary gland
“The master gland” responsible for producing hormones that regulate body functions such as growth, metabolism, stress, and reproduction |
multiple sclerosis
Potentially disabling disease of the brain and spinal cord
Immune system attacks protective (myelin sheath) that covers nerve fibers and causes communication problems between brain and rest of body
Can cause permanent damage or deterioration of nerve fibers
May lose ability to walk independently or ambulate at all
myasthenia gravis
Causes weakness in voluntary muscles, especially those in eyes, mouth, throat, and limbs, double vision and difficulty speaking and chewing
critical period
specific developmental window during which neurons are highly sensitive to environmental stimuli
Consciousness
state of awareness of our mental activity and external stimuli
EEG
uses electrodes that are placed on an individual’s scalp. allows researcher to record electrical signals from neurons firing.
allows to measure brain frequencies
MRI and fMRI
Brain imaging- MRI: persons head is surrounded by a magnetic field and the brain is exposed to radio waves, which cause hydrogen atoms in the brain to to release energy
fMRI: also measures movement of blood molecules (an index of neural activity)
Provides both functional and structural information in the same image
Brain waves: beta, alpha, theta, delta
Beta 15-30 Hz
Awake, normal alert consciousness
Alpha 9-14 Hz
Relaxed, calm, meditation, creative visualization
Theta 4-8 Hz
Deep relaxation, and meditation, problem solving
Delta 1-3 Hz
Deep, dreamless sleep
Sleep stages with EEG patterns
Awake (beta waves)
Drowsy, relaxed (alpha)
Stage N1 sleep (theta)
Stage N2 (sleep spindles)
Stage N3 (delta)
REM sleep (fast, random)
Circadian rhythms
24 hour biological clock
Our body temps and awareness changes throughout the day
Best to take a test or study during circadian peaks
Jet lag
tiredness felt by a person after a long flight across different time zones.
NREM stages 1-3 (your textbook also has a stage 4)
Stage 1
Lasts between 1-5 min and occupies approximately 2-5% of normal night sleep
Easily awaken
Consists mostly of theta waves (high amplitude, low frequency (slow))
Brief periods of alpha waves
Hypnagogic sensations can occur (ex: feeling of falling)
Stage 2
10-20 minutes
Follows stage 1 and is the “baseline” of sleep
Theta waves and sleep spindles
Occupies approximately 45-60% of sleep
Stage 3 (used to be 3 and 4)
Has delta waves, “slow wave” sleep and may last 15-30 minutes
Brain activity slows down dramatically and hight of waves increase dramatically
Delta sleep is the “deepest” stage of sleep (not REM) and the most restorative
Production of growth hormones
It is delta sleep that a sleep deprived person craves the most
In children, delta sleep can occupy 40% of all sleep time
Stage 4 (REM sleep)
REM = rapid eye movement
Very active stage of sleep (paradoxical sleep)
Composed 20–25% of nights sleep
Vivid dreams can occur
Body is essentially paralyzed
Breathing, heart rate, brain waves quicken
hypnagogic sensations (occur in stage1)
vivid, dream-like experiences that occur during the transition from wakefulness to sleep
REM rebound
tendency for rem sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation
Insomnia
Recurring problem of falling or staying asleep even when the opportunity is presented
1 in 5 adults have insomnia
Nature → some ppl have it genetically
Nurture → stress or drinking caffeine can reduce sleep quality and cause insomnia
Melatonin works in helping regulate it, you can build up a tolerance to it tho. Sleep specialist can help with long term treatments
Symptoms: chronic tiredness, increased depression, hypertensions, arthritic and fibromyalgia pain, obesity
Narcolepsy
Sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. Affected person may lapse directly into REM sleep often at inopportune times
1-2000 adults have it
Nature AND nurture- there is a gene that causes it, in most cases sporadic and environmental triggers like infections and stress likely play a key role in activating disease in genetically susceptible individuals
No cure, but medications such as stimulants and changes to lifestyle can be beneficial
Attacks are usually less than 5 minutes but they tend to happen at the most vulnerable times
Sleep apnea
when an individual has a hard time falling or staying asleep cuz they struggle with breathing
prevents REM since they keep waking up
Somnambulism
(AKA sleepwalk)
Repeated episodes of complex motor behaviour, such as walking while asleep happens in stage theme
most common during stage 3 sleep
1-15 in 100 have it
Nature
Can be treated with stress management and a consistent sleep schedule and here are medications if serious
Most cannot recall their trip the next morning
REM sleep behavior disorder
person acts out their dreams during REM sleep
normally body is paralyzed during sleep, but this disorder causes this paralysis to be absent or incomplete
may be at risk for self injury
Hobson & McCarley’s Activation-Synthesis theory of dreams
Our cerebral cortex is trying to interpret random electrical activity while we sleep
That is why dreams sometimes make no senes
Biological theory
Consolidation dream theory (memory consolidation)
Dreaming is a result of memory consolidation that occurs during sleep
Suggests that the brain reactivates memories during sleep, which then influences the content of dreams
restoration theory
we sleep bcuz we get tired from daily activities and we sleep to restore our energy & resources
stimulants
excite and promote neural activity
gives and individual energy, reduces appetite, causes them to be irritable
Ex: caffeine, nicotine, cocaine
depressants
reduce neural activity
cause drowsiness, muscle relaxation, lowered breathing, and if abused- death
Ex: alcohol, sleeping pills
hallucinogens
cause individual to sense things that are not acc there
can reduce motivation, and cause extreme panic
Ex: marijuana, peyote, LSD
opioids
function as a depressant, but have their own category due to addictive nature
panic relief
Ex: morphine, heroin, oxycotine
Addiction
chronic, relapsing condition characterized by a compulsive need for a substance or behavior, despite harmful consequences.
Tolerance
needing more of smth to produce the same effect
Physical dependence
a condition where a person's body becomes adapted to a substance, and unpleasant physical withdrawal symptoms occur if the substance is suddenly stopped or its dose is reduced.
Psychological dependence
psychological dependancea behavioral and psychological syndrome characterized by loss of control over drug use and compulsive, continuous use despite damage caused to oneself and others.
Withdrawal
physical and mental symptoms that a person has when they suddenly stop or cut back the use of an addictive substance
sensation
process of detecting information from the environment
when taking in outside stimulus, you activate sensory neurons which create sensation (sensory transduction)
sensory adaptation
stimulus is continuous and doesn’t change
Ex: lighting a candle and smelling it initially, but you get used to the smell so you don’t smell it anymore