Unit 4 Phys Part E, Anerobic Respiration and the Cori Cycle
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Cellular respiration
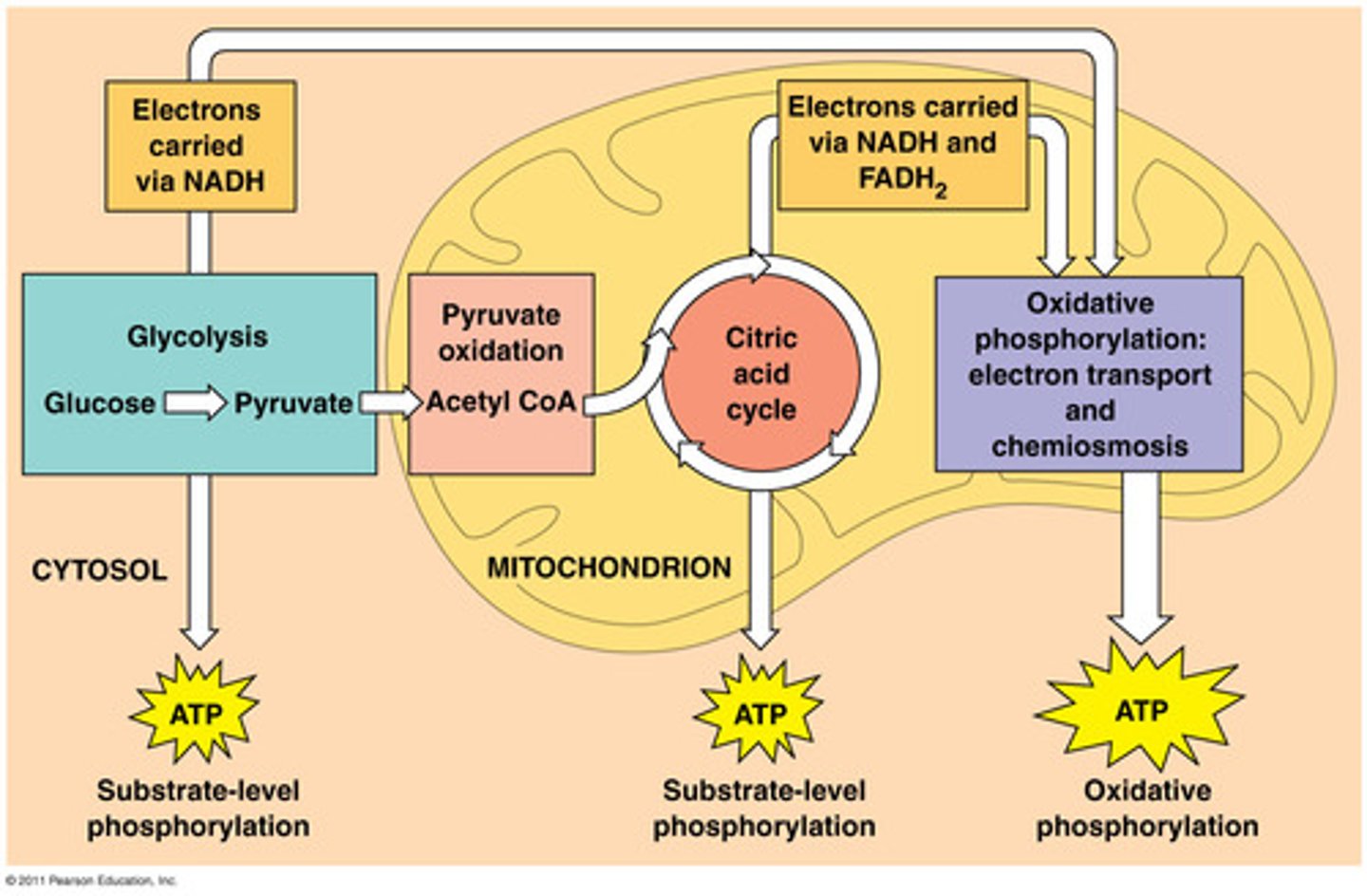
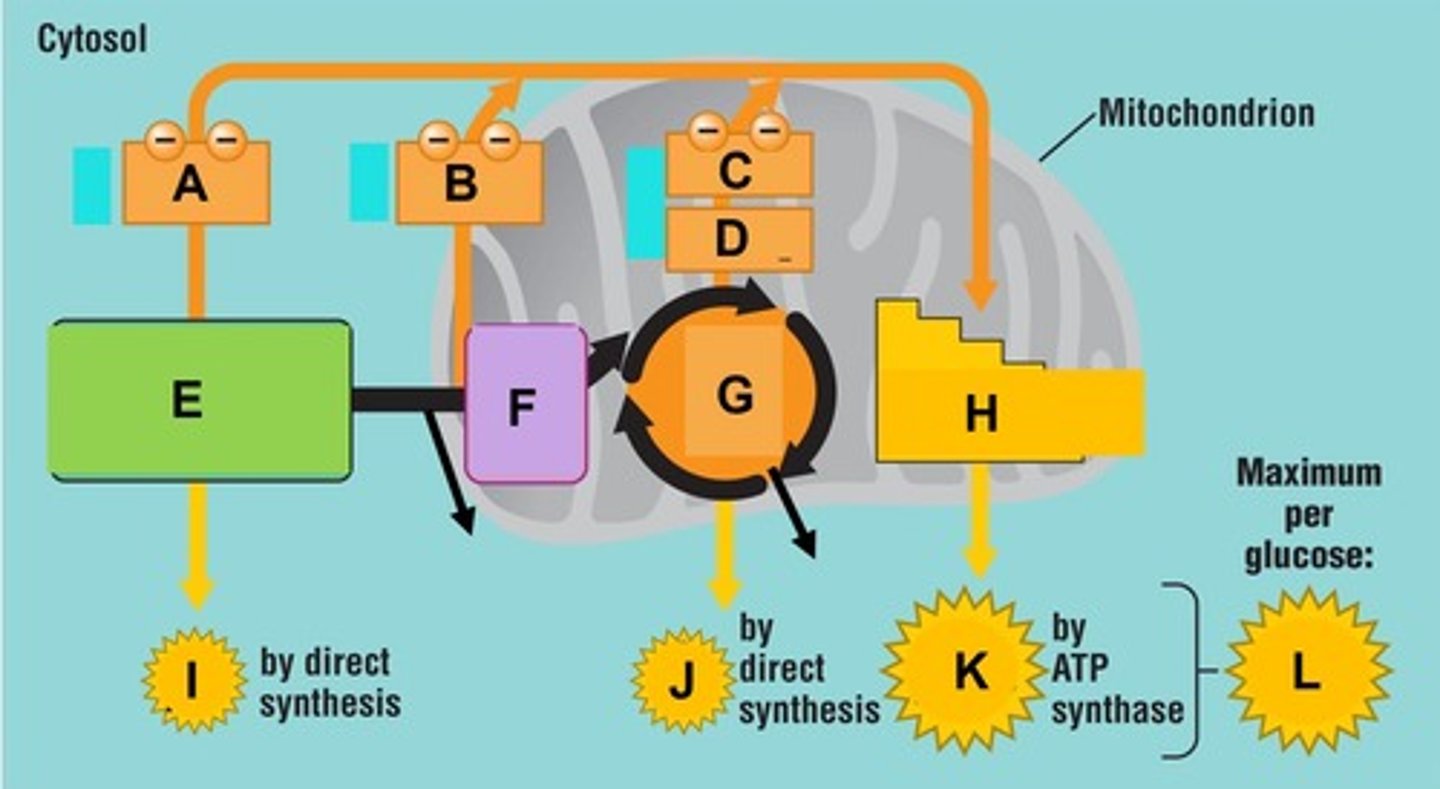
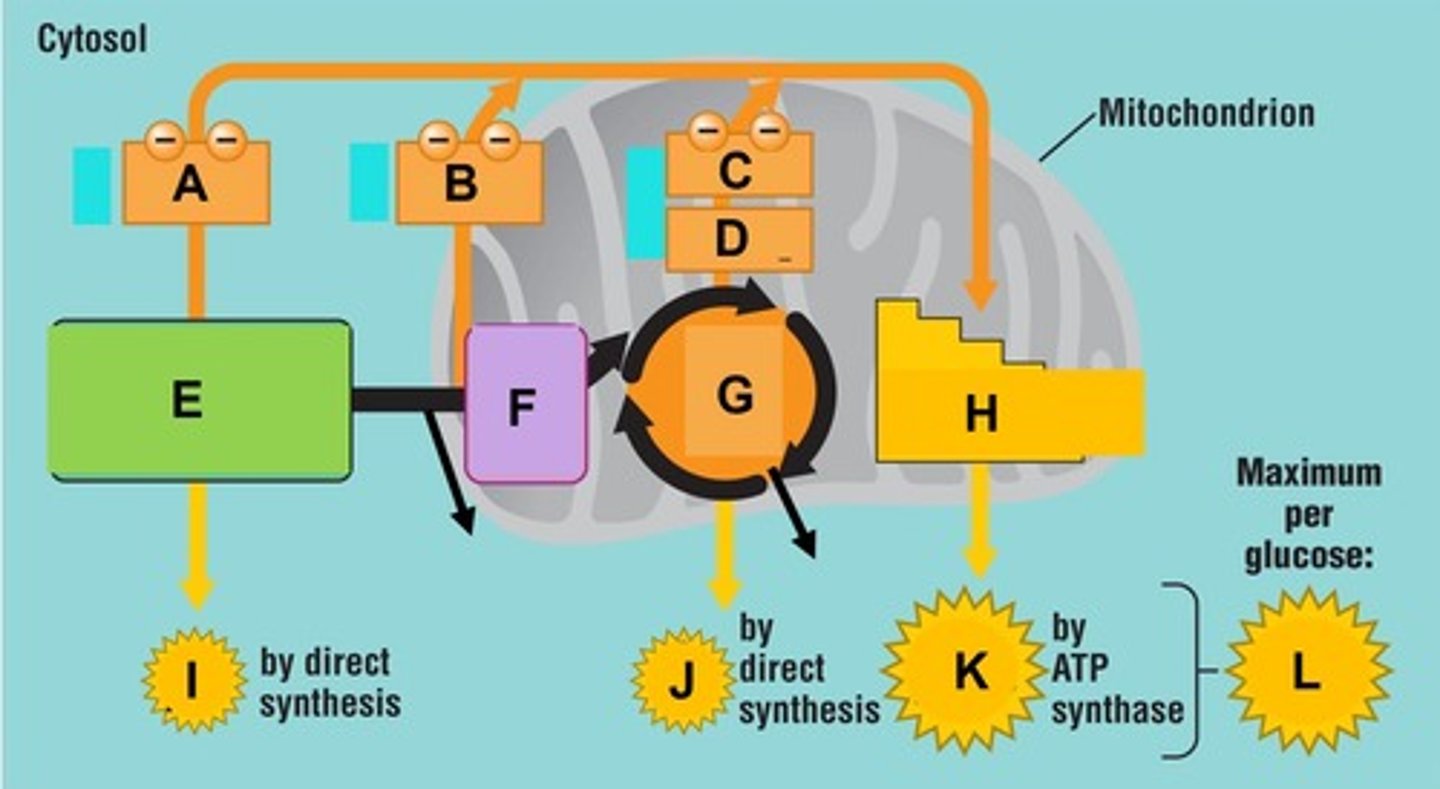
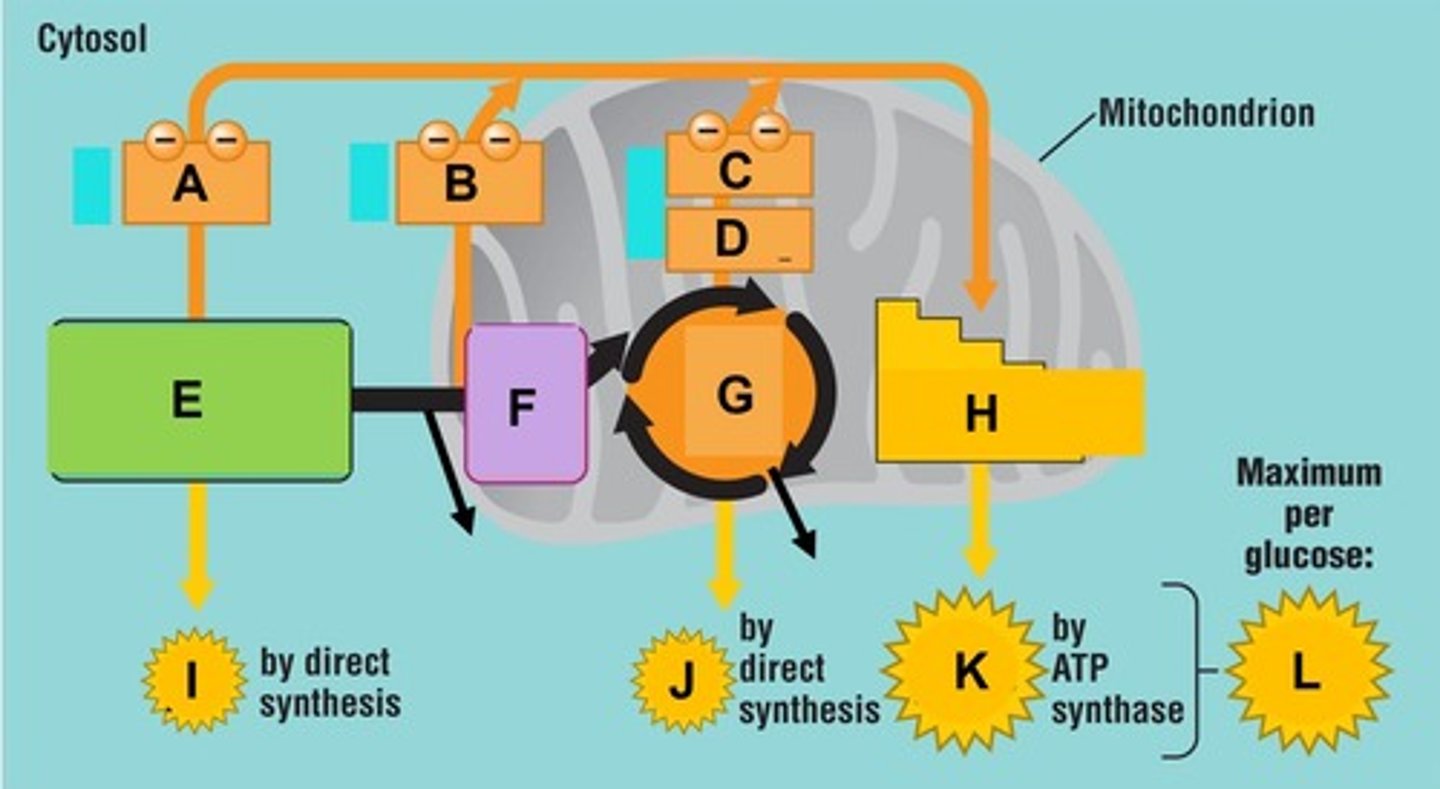
Term for the process that utilizes food energy to generate ATP and occurs by two mechanisms: aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration
Term for the cellular respiration pathway that does not use oxygen to generate ATP. Occurs in the cell's cytoplasm and generates ATP by glycolysis.
Cytoplasm
Anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen to generate ATP. Occurs in the cell's ________________ and generates ATP by glycolysis.
Glycolysis
Anaerobic respiration does not use oxygen to generate ATP. Occurs in the cell's cytoplasm and generates ATP by the process of ________________
Aerobic respiration
Term for the cellular respiration pathway that requires oxygen to generate ATP and usually occurs in three phases: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
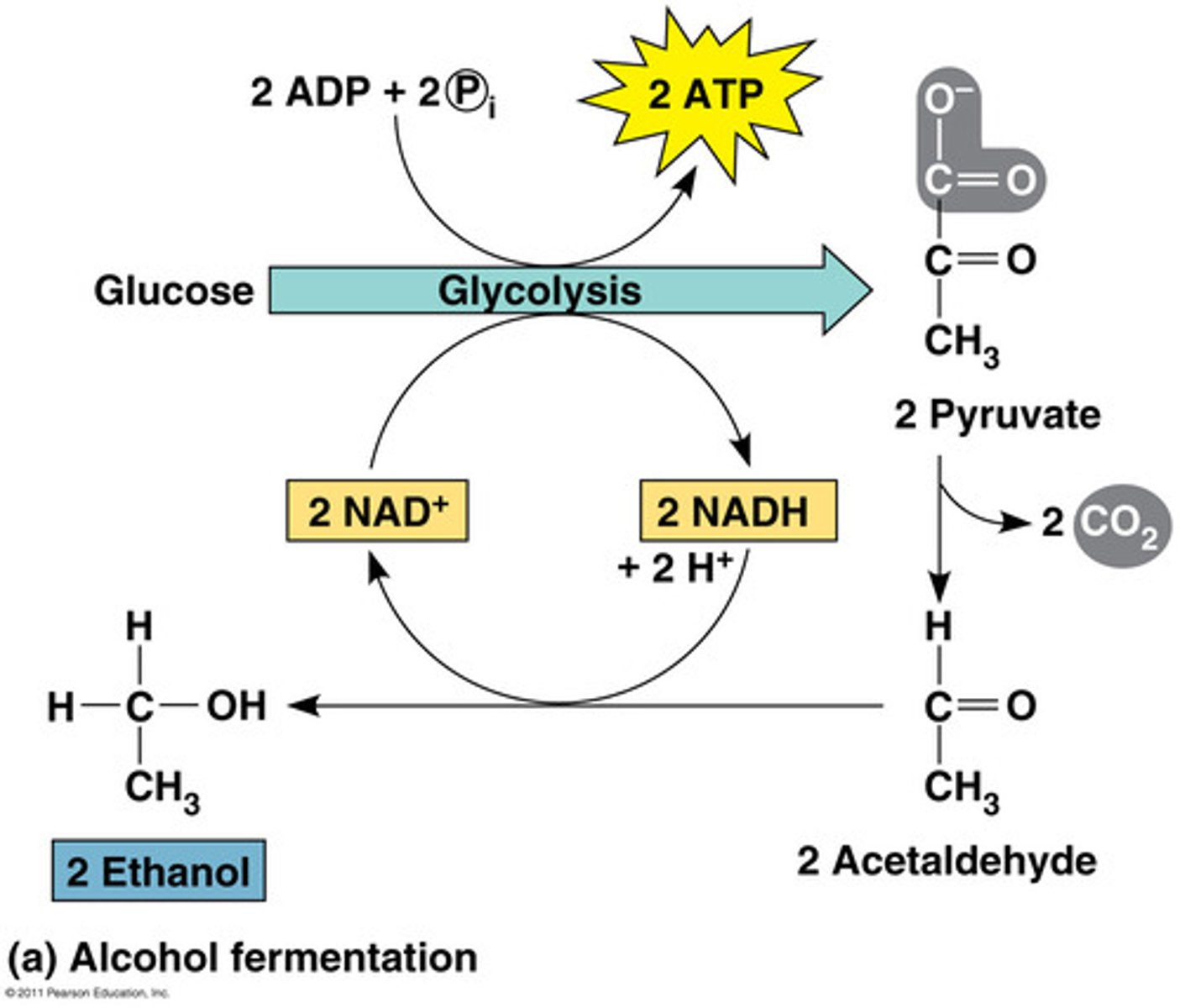
Fermentation
Anaerobic respiration is also called ______________
Glycolysis
Unfortunately, without O2, we cannot generate ATP by the oxidative phosphorylation and can only generate small amounts with anerobic respiration by ____________________
Oxygen
Anaerobic respiration occurs when ______________ levels are not sufficient.
Glycolysis does not need oxygen to produce ATP, but it does need NAD+ to remove electrons from glucose
NAD+
Anaerobic respiration occurs when oxygen levels are not sufficient.
Glycolysis does not need oxygen to produce ATP, but it does need _________________ to remove electrons and hydrogens from glucose
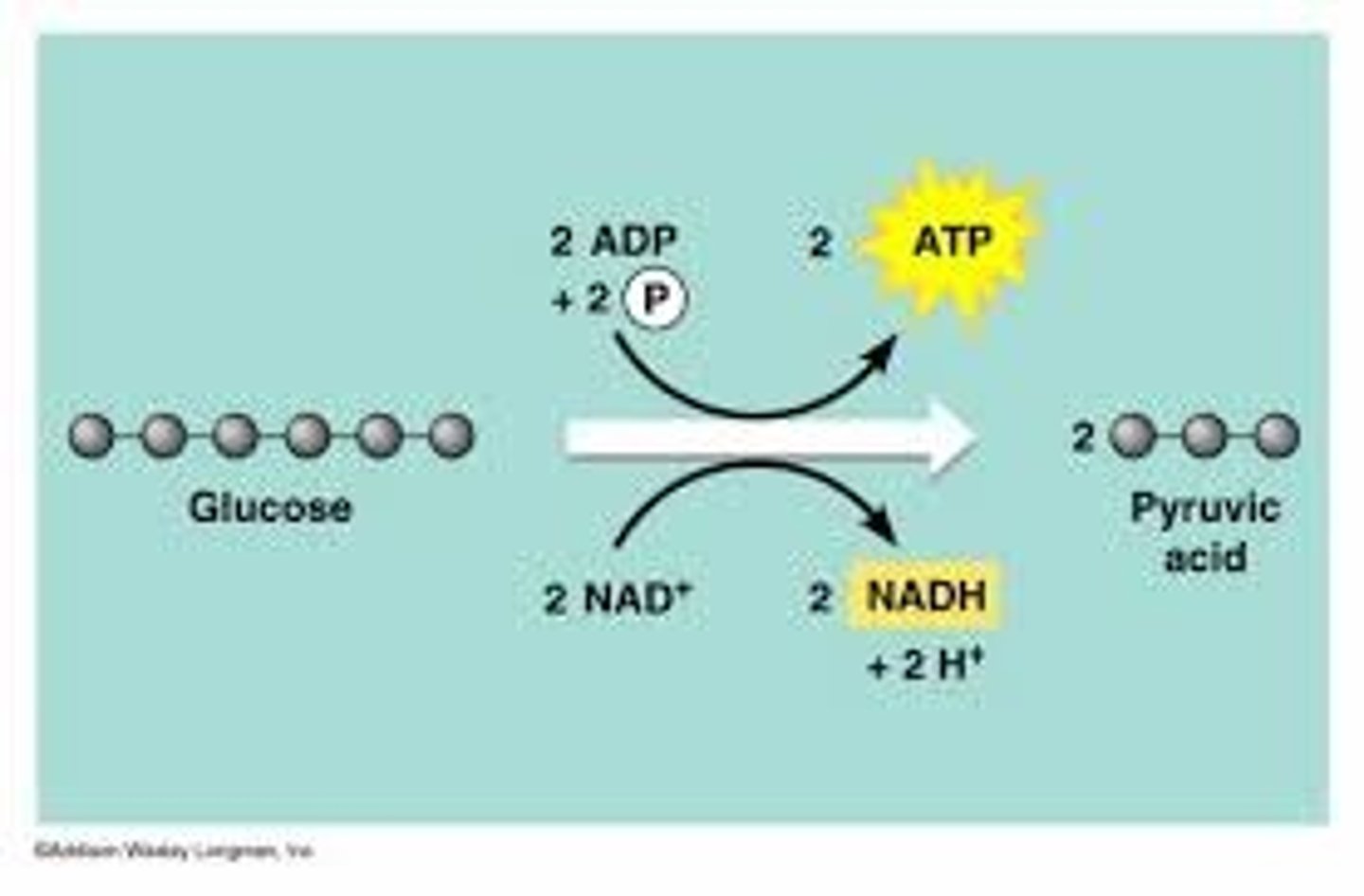
2 ATP
Per glucose molecule, the net end products of glycolysis include 2 pyruvates or pyruvic acid, 2 NADH, and ________________
2 NADH
Per glucose molecule, the net end products of glycolysis include 2 pyruvates or pyruvic acid, _________________, and 2 ATP.
Pyruvate
To regenerate the NAD+, the NADH transfers its electrons to __________________ making it lactate (lactate is the ionized form of lactic acid which is produced at normal pH).
The regenerated NAD+ can then be reused for glycolysis.
Lactate
To regenerate the NAD+, the NADH transfers its electrons to pyruvate making it __________________ which is the ionized form of lactic acid.
The regenerated NAD+ can then be reused for glycolysis.
2 ATP
Anaerobic metabolism is inefficient. There is a net ATP (energy) production of ____________ per glucose molecule. Compare this to the 36 to 38 ATP from aerobic respiration.
Muscle
The temporary accumulation of lactic acid in _____________ cells contributes to the burning feeling during exercise.
Lactate
At normal cell pH, lactic acid is converted to _____________ and then transported to the liver where it is converted back to glucose as part of the Cori Cycle. Note, lactic acid and lactate are often used interchangeably in physiology.
Lactate
At normal cell pH, lactic acid is converted to lactate and then transported to the liver where it is converted back to glucose as part of the Cori Cycle. Note, lactic acid and ____________ are often used interchangeably in physiology.
Cori Cycle
At normal cell pH, lactic acid is converted to lactate and then transported to the liver where it is converted back to glucose as part of the _______________. Also known as the Lactic acid cycle
Liver
Name the organ most responsible for converting lactate or lactic acid back to glucose as part of the Cori cycle.
Oxygen debt
Term for the amount of oxygen needed to recover after strenuous activity. Provides O2 for the conversion of lactic acid to glucose and other vital processes. Reason a person continues to breath heavily after an activity.
Glucose
Oxygen dept is the term for the amount of oxygen needed to recover after strenuous activity. Provides O2 for the conversion of lactic acid to _________________ and other vital processes. Reason a person continues to breath heavily after an activity.
Glycolysis
The Cori cycle (also known as the Lactic acid cycle), refers to the metabolic pathway in which lactate produced by ___________________ during anaerobic respiration in the muscles moves through the bloodstream to the liver and is reconverted to pyruvate and then to glucose by the gluconeogenesis. The glucose can then return back to the muscles and be converted back to lactate if needed.
lactate
The Cori cycle is a way to prevent _______________ from accumulating in the muscle and to process it back to glucose to be used as an energy source. The glucose can then return back to the muscles and be converted back to lactate if needed.