Bio 2 Exam 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
diffusion
Countercurrent exchange in the fish gill helps to maximize
2
New cards
true tissues and no tissues
The most ancient branch point in animal phylogeny is that between having
3
New cards
method of reproduction
There are three major groups of mammals, categorized on the basis of their
4
New cards
they are required for animal diets, but these animals are not able to synthesize the nutrients.
Certain nutrients are considered "essential" in the diets of some animals because
5
New cards
the bilaterians
Which of the following clades contains the greatest number of animal species?
6
New cards
amniotic egg
What is a primary, common evolutionary feature of all reptiles, mammals, and birds?
7
New cards
lophotrochozoans
Which clade does NOT include humans?
8
New cards
nervous conduction and muscular movement
Which of the following is unique to animals?
9
New cards
birds
Which of the following are the only extant animals that descended directly from dinosaurs?
10
New cards
Multicellularity probably arose independently in fungi and animals.
Select the correct statement(s) about the origin of fungi
11
New cards
salamander
Which of the following is NOT an amniote?
Salamander
Lizard
Turtle
Dinosaur
Dr. McNeal
Salamander
Lizard
Turtle
Dinosaur
Dr. McNeal
12
New cards
Ray-finned Fish
What is the most diverse group of vertebrates? (highest # of extant species)
13
New cards
A - Owl
B - Salamander
C - Goldfish
D - Butterfly
E - Jellyfish
B - Salamander
C - Goldfish
D - Butterfly
E - Jellyfish
Match the letters to the organism that belongs in that place on the phylogenetic tree
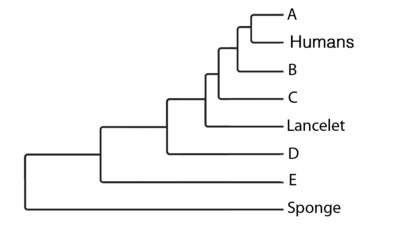
14
New cards
Swim Bladder/Lungs
Which of these characteristics evolved at node C?
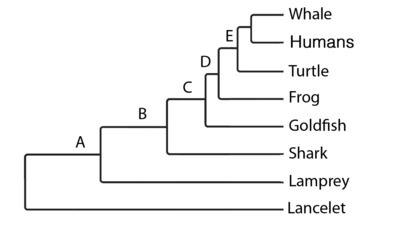
15
New cards
B
At which node did paired appendages homologous to arms and legs evolve?
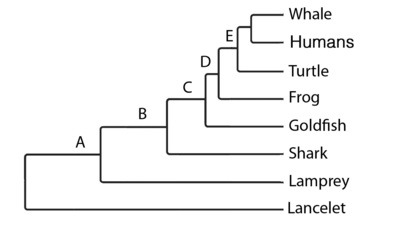
16
New cards
Nematode (Caenorhabditis elegans)
What was the first animal to have its complete genome sequenced?
17
New cards
earthworm
Which of the following is NOT an arthropod?
Butterfly
Earthworm
Millipede
Spider
Crab
Butterfly
Earthworm
Millipede
Spider
Crab
18
New cards
backbone
Which of the following is NOT one of the ancestral defining features found across chordates?
Notochord
Backbone
Dorsal hollow nerve chord
Muscular tail
Pharyngeal gill slits
Notochord
Backbone
Dorsal hollow nerve chord
Muscular tail
Pharyngeal gill slits
19
New cards
Amniotic egg < Swim Bladder/Lungs < Jaws < Notochord < Mesoderm
Put the following characteristics in the order they evolved in your ancestors (Most recent)
Notochord
Swim Bladder/Lungs
Jaws
Mesoderm
Amniotic egg
Notochord
Swim Bladder/Lungs
Jaws
Mesoderm
Amniotic egg
20
New cards
alligator
Which of the following is not a Lepidosaur?
Gila Monster
Snake
Tuatara
Alligator
Gecko
Gila Monster
Snake
Tuatara
Alligator
Gecko
21
New cards
Porifera
- Spicules
22
New cards
Cnidaria
- Zooxanthellae
23
New cards
Platyhelmenthes
- Tapeworm
24
New cards
Mollusca
- Cephalopods
25
New cards
Annelida
- Chemoautotrophic symbionts
26
New cards
Platyhelmenthes
Out of the list below, which phylum is most closely related to you?
Porifera
Cnidaria
Ctenophora (comb jellies)
Platyhelmenthes
Placozoa
Porifera
Cnidaria
Ctenophora (comb jellies)
Platyhelmenthes
Placozoa
27
New cards
Mesoderm
Which feature evolved on the same branch of the phylogenetic tree as bilateral symmetry?
28
New cards
Both involve a photosynthetic organism donating carbon skeletons to a chemoheterotrophic organism in exchange for inorganic nutrients
What do coral reefs and lichens have in common?
29
New cards
Echinodemata
Which phylum below is most closely related to you?
Platyhelminthes
Porifera
Cnidaria
Echinodemata
Arthropoda
Platyhelminthes
Porifera
Cnidaria
Echinodemata
Arthropoda
30
New cards
8
How many haploid spores eventually form from a zygote in Ascomycota species?
31
New cards
Choanoflagellates
Which lineage is most closely related to animals?
32
New cards
False
(True or False) Fungi directly have killed more humans through disease and poisoning than they have saved by other means.
33
New cards
Blastula
What is the name of the "hollow ball of cells" developmental stage shared by all animals
34
New cards
Both involve a photosynthetic organism donating carbon compounds to a fungus in exchange for inorganic nutrients
What do fungi and mycorrhizal interactions have in common?
35
New cards
Chemoheterotrophic
Photoautotrophic
Photoautotrophic
What nutritional mode is this plant? (mistletoe)
36
New cards
True
(True or False) Plants are easier to genetically modify than animals because reproductive tissues or entire plants can often be grown from a single transformed meristem cell.
37
New cards
Glomeromycota
Which group of fungi can actively grow inside plant root cell walls to exchange nutrients?
38
New cards
Dikaryotic
The mushrooms you buy in a grocery store are what type of tissue?
39
New cards
GMO pros
increased crop yields, less pesticides necessary, healthier produce
40
New cards
GMO cons
genes escaping into wild populations
41
New cards
why plants are amenable to genetic transformation
Undifferentiated meristematic cells can often be transformed and induced toregrow into a full plant
•Transformed apical meristem cells give rise to flowers and seeds which will growinto a transgenic plan
•Transformed apical meristem cells give rise to flowers and seeds which will growinto a transgenic plan
42
New cards
Carnivorous Plants
Photoautotrophic,
43
New cards
Mycotrophic Plants
chemoheterotrophic
44
New cards
Parasitic Plants
photoautotrophic/ chemoheterotrophic
45
New cards
5 major lineages of Fungi
Chytridiomycota, Zygomycota, Glomeromycota, Ascomycetes, and Basidiomycetes
46
New cards
Chytridiomycota characteristics
Live in water and make flagellated haploid spores
47
New cards
Zygomycota characteristics
Very resistant spores made from the zygote that can survive in outerspace/microwave
48
New cards
glomeromycota characteristics
Form specialized mycorrhizal hyphae that actually grow inside plant root cells (penetrate the cell wall but not the cell membrane) to donate inorganic nutrients in exchange for sugars
49
New cards
Ascomycetes characteristics
Hyphae from 2 different individual haploid fungi come together and join into onehypha, but nuclei do not fuse: Dikaryotic= cells with 2 haploid nuclei The haploid nuclei fuse into one diploid nucleus (zygote) for recombination only in reproductive cells, each of which becomes the Ascus, a sac containing 8 haploid ascospores produced through meiosis
50
New cards
Basidiomycetes characteristics
Sexual life cycle similar to Ascomycetes: hyphae from 2 different individual haploid fungi grow together, but nuclei do not fuse: Dikaryotic= each cell with 2haploid nuclei- a mushroom is made of dikaryotic mycelium Nuclei fuse for recombination in a diploid cell that becomes the basidium (zygote), which makes 4 dangling haploid spores through meiosis.
51
New cards
Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes
_________ and ________ account for the vast majority of described fungispecies.
52
New cards
Ascomycetes Have 8 spores Basidiomycetes have 4
Ascomycetes Vs. Basidiomycetes
53
New cards
Bad ways fungi affect humans
Athlete's Foot, Ringworm, and Jock Itch, dandruff, nail fungus, and yeast infections
54
New cards
good ways fungi affect humans
mycorrhizae, antibiotics, bread yeast
55
New cards
lichens
photosynthetic organism donates carbohydrates in exchange for inorganic nutrients from the fungus
56
New cards
choanoflagellates
Sister group to animals are single-celled, sometimes colonial organisms called __________
57
New cards
Characteristics of Animals
Ingest food and digest it internally with enzymes
Multicellular with no cell walls- held together by proteins
Formation of a blastula/gastrula
Origin probably ~770 million years ago
first fossils at 560 million years ago
Multicellular with no cell walls- held together by proteins
Formation of a blastula/gastrula
Origin probably ~770 million years ago
first fossils at 560 million years ago
58
New cards
Cambrian Explosion (~542 million years ago)
most modern animal phyla appear during _________
59
New cards
Phylum Porifera
sponges
60
New cards
Phylum Porifera characteristics
-no specialized tissues
-filter water to catch food
-often have silica or calcium carbonate Spicules
-basal branching lineage
-filter water to catch food
-often have silica or calcium carbonate Spicules
-basal branching lineage
61
New cards
Phylum Ctenophora
comb jellies
62
New cards
Phylum Ctenophora characteristics
Superficially similar to true 'jellyfish' (Phylum Cnidaria) and used to be grouped with them, but Ctenophores differ in locomotion by rows of cilia. Similar to a big gastrula
63
New cards
Phylum Placozoa
Simple, pancake-like animals
64
New cards
Phylum Placozoa Characteristics
1mm that behave like multicellular amoeba and move with cilia. Probably branched off after Porifera and Ctenophora and are a result of simplification/reduction of an ancestor that probably had tissues
65
New cards
Phylum Cnidaria
jellyfish, sea anemones, corals
66
New cards
Phylum Cnidaria characteristics
-2 tissue layers
-radial symmetry
-gastrovascular cavity functions as both mouth and anus
-radial symmetry
-gastrovascular cavity functions as both mouth and anus
67
New cards
Bilateral Symmetry evolved
after Sponges and Cnidarian
68
New cards
Bilateral animals have
- A dorsal (top) side and a ventral (bottom) side
- A right and left side that is approximately symmetrical
- Anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends
- Having a distinct mouth often leads to cephalization, the development of a head
- 3 tissue layers
- A right and left side that is approximately symmetrical
- Anterior (head) and posterior (tail) ends
- Having a distinct mouth often leads to cephalization, the development of a head
- 3 tissue layers
69
New cards
the ancestor of bilateral animals would have been....
a simple worm shape with a digestive tract
70
New cards
Phylum Platyhelminthes
flatworms/ lophotrochozoa
71
New cards
Phylum Platyhelminthes characteristics
Simple body plan is probably similar to Acoela & ancestral bilateral animals
•Includes some human parasites (tapeworms, liver flukes)
•Includes some human parasites (tapeworms, liver flukes)
72
New cards
Phylum Mollusca
Snails & Slugs, Oysters & Clams, Octopi & Squid/ lophotrochozoa
73
New cards
Phylum Mollusca characteristics
-largest marine phylum
-head, foot, and mantle
-soft bodies usually w/a hard shell
-head, foot, and mantle
-soft bodies usually w/a hard shell
74
New cards
Phylum Annelida
segmented worms/ lophotrochozoa
75
New cards
Phylum Annelida characteristics
-segmented bodies
76
New cards
Phylum Nematoda
roundworms/ Ecdysozoa
77
New cards
Phylum Nematoda research organism
Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans): 1st animal genome to be completely sequenced
78
New cards
Phylum Arthropoda characteristics
1. means jointed feet
2. jointed appendages
3. exoskeleton: made of chitin
4. open circulatory system
2. jointed appendages
3. exoskeleton: made of chitin
4. open circulatory system
79
New cards
Phylum Arthropoda
jointed animals/ Ecdysozoa
80
New cards
Phylum Arthropoda examples
Crustaceans (crabs, lobsters, shrimp, barnacles, roly-poly/pillbugs),
Chelicerates (horseshoe crab, scorpions, spiders, ticks, mites, etc.),
Myriapods (millipedes, centipedes)
Hexapods (insects)
Chelicerates (horseshoe crab, scorpions, spiders, ticks, mites, etc.),
Myriapods (millipedes, centipedes)
Hexapods (insects)
81
New cards
Phylum Echinodermata
Slow-moving marine animals: includes sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers/ Deuterostomes
82
New cards
Phylum Chordata
Deuterostomes
83
New cards
Major groups of reptiles
turtles, lepidosaurs (tuataras, lizards, snakes), &archosaurs (crocodilians & dinosaurs- including birds)
84
New cards
4 synapomorphies of chordates
notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, muscular post-anal tail, pharyngeal gill slits
85
New cards
Birds
-the only extant lineage of dinosaurs and belong to the Therapod clade
-feathers evolved for insulation
-feathers evolved for insulation
86
New cards
Adaptations of birds for flight
hollow bones, no teeth, no bladder
87
New cards
synapomorphies of mammals
•~ 5,400 species
•Mammary glands produce milk for feeding young
•Hair for insulation
•Differentiated teeth
•Warm-blooded
•Multiple lineages have gone back to the ocean
•Mammary glands produce milk for feeding young
•Hair for insulation
•Differentiated teeth
•Warm-blooded
•Multiple lineages have gone back to the ocean
88
New cards
3 major lineages of mammals
monotremes, marsupials, eutherians
89
New cards
monotremes
Egg laying mammals
90
New cards
marsupials
Mammals whose immature offspring complete their development in an external pouch.
91
New cards
eutherians
Placental mammal; (humans)
92
New cards
Primates (incl. humans) are related to
rabbits, rodents; lab rats, and lab mice are popular as experimental animals because they are the closest living relatives of humans that are small
93
New cards
Primate Phylogeny
lemurs & lorises
Tarsiers
new world monkeys
old world monkeys
orangutans
gorillas
chimpanzees
humans
Tarsiers
new world monkeys
old world monkeys
orangutans
gorillas
chimpanzees
humans
94
New cards
4 tissue categories
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
95
New cards
Hormone
chemical signal secreted into the circulatory system that communicates regulatory messages
96
New cards
nitrogenous wastes
ammonia, urea, uric acid
97
New cards
ammonia
fish
98
New cards
urea
sharks, amphibians, mammals
99
New cards
uric acid
reptiles, insects, land mollusks
100
New cards
nutritional needs for all animals
- fuel for cellular work
- materials for biosynthesis
- essential nutrients
- materials for biosynthesis
- essential nutrients