Radioactivity
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Radioactivity
The spontaneous breaking up of unstable nuclei with the emission of one or more types of radiation
Non-ionising radiation
Ultraviolet ,visible ,infrared ,microwaves, radio and TV
Ionising
More dangerous ,radiation capable of producing ions (bonds broken) when interacting with matter ,x-rays ,alpha ,beta Gamma ,cosmic rays
Pierre and Marie curie
Purified pitchblende
Discovered Polonium and Radium
Studied radiation to uranium
Which elements are radioactive?
Most elements have radioactive isotopes but any element with an atomic number greater than 83 consists entirely of radioactive isotopes
Uranium is the heaviest natural occurring element. Most elements above 92 are artificially created in nuclear research facilities.
3 types of radiation
Alpha beta gamma
Alpha particles
Consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons —helium nucleus
Attracted to - charge so positive
Thrown out by unstable radioactive nuclei until they become stable
Relatively large mass -slow -not very penetrating -stopped by air or a sheet of paper -not dangerous as they can’t penetrate skin
Americium-241 is used in smoke alarms
Beta particles
Attracted to + charge so negative
Fast moving/high energy electrons
Formed when a neutron is changed into a proton and electron ,and electron is ejected from the nucleus
More penetrating -pass through paper and up to 5mm of aluminium
Carbon-14 emits beta particles so is used for carbon dating
Gamma rays
High energy electromagnetic radiation-similar to x-rays
Passed straight through electric and magnetic fields so not charged
very penetrating -only stopped by tick layer of lead
very dangerous carcinogenic
Can be used to cure cancer and sterilise surgical instruments
Cobalt 60 is used in radiotherapy/killing tumours
Nuclear reaction
Radiation emitted from the nucleus. Completely different from chemical reactions.
Difference between chemical and nuclear reactions
Chemical
No new element formed
No release of nuclear radiation
Chemical bonds broken and formed
Nuclear reaction
A new element is formed
Nuclear radiation is released
No new chemical bonds broken or formed
What happens to radium 226 when it emits an alpha particle
Ie. Loses 2P and 2N
Mass number decrease by 4 to 222 because 4 nucleons lost
Atomic number decrease by 2 to 86 because 2 protons lost
Changes to element two places before it
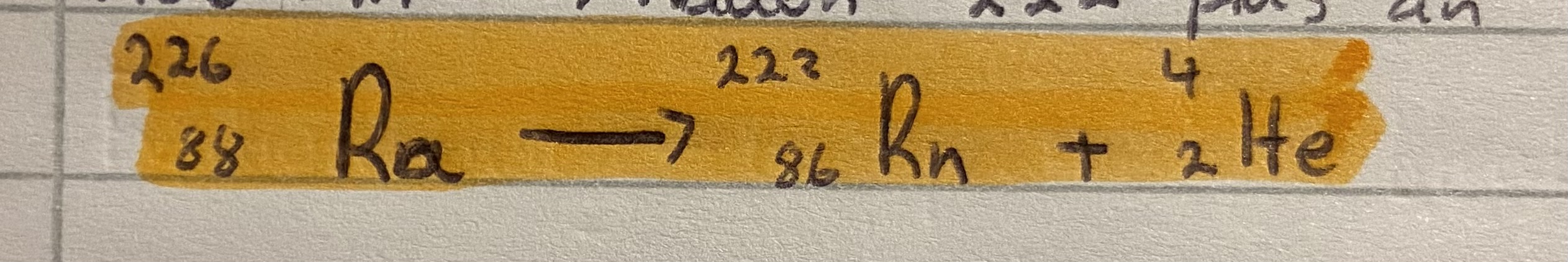
What happens to carbon 14 when it loses a beta particle
Mass stays same
Atomic number decreases by 1
Changes to an element 1 after it in the periodic table
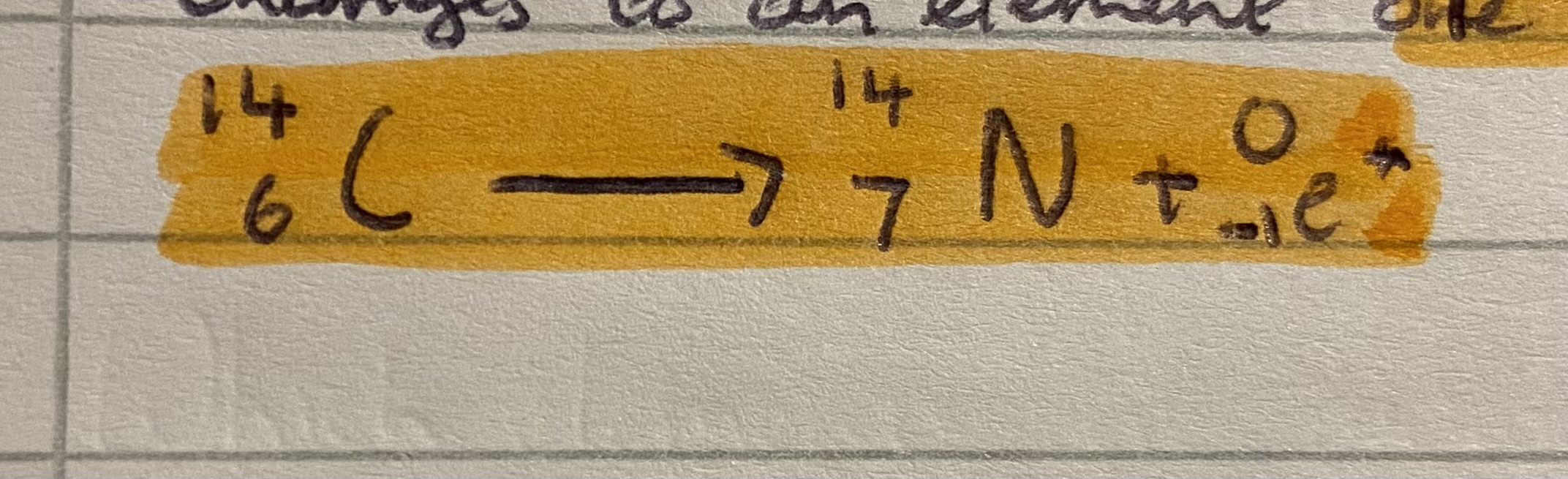
Eg alpha
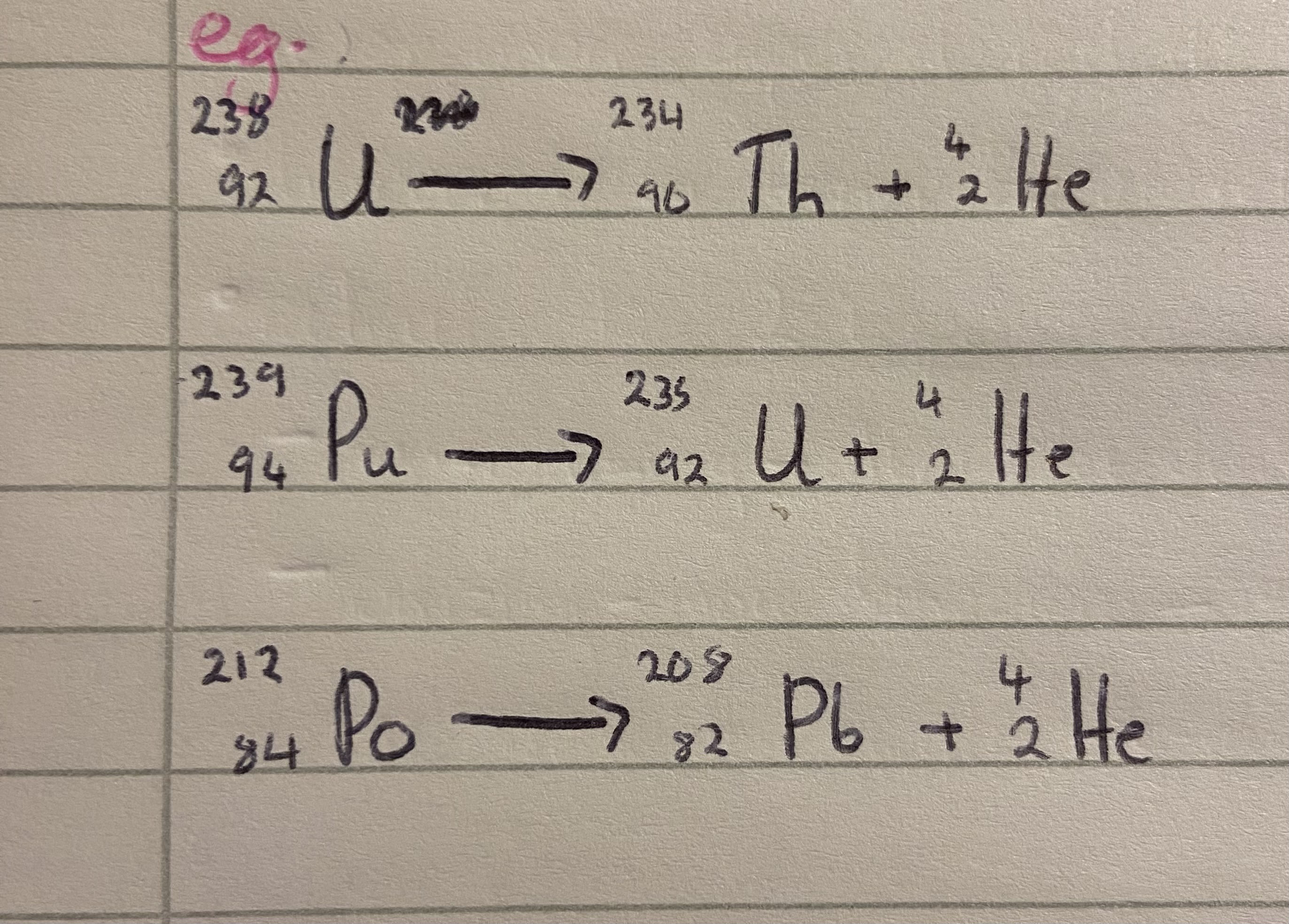
Eg beta
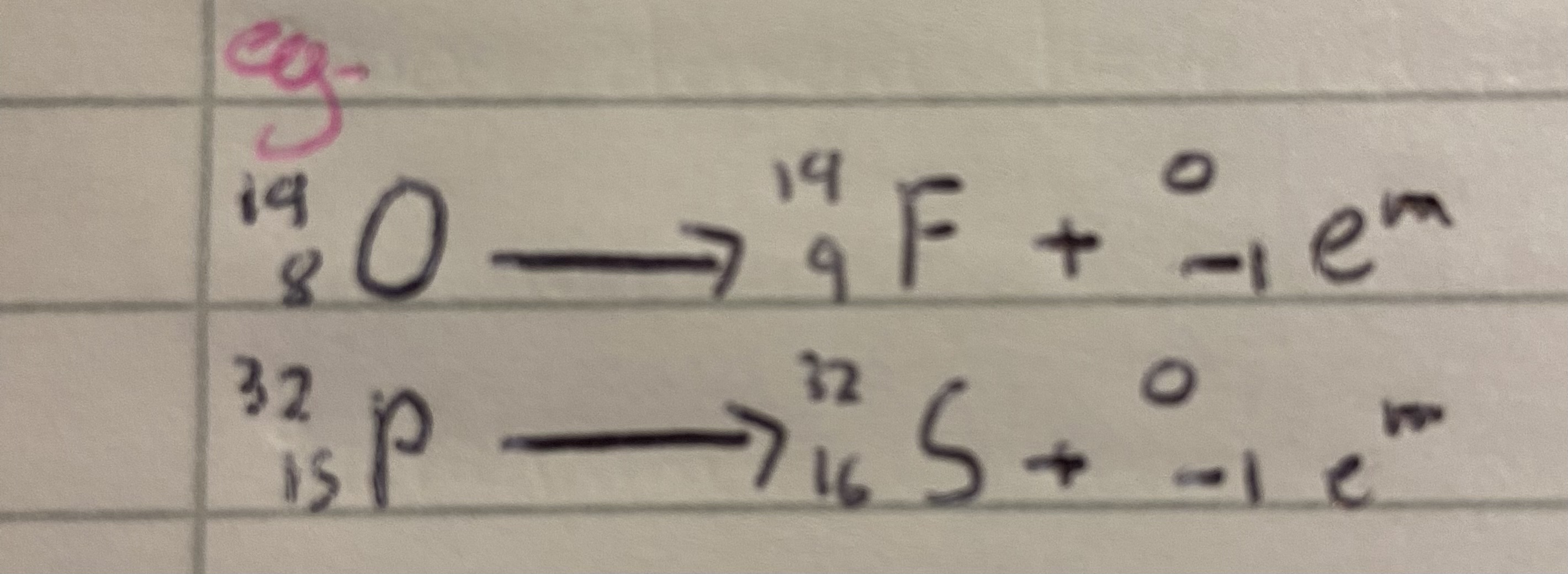
Transmutation
The changing of one element to another
Half-life
The time taken for half of the nuclei of an element to decay
Radioisotope
Radioactive isotope eg. Americium 241, Carbon 14, Cobalt 60