sleep & biological rhythms
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
animals have a sense of time
-dogs wait for their owner to come home
-pigs know if they have been in crates for short/long periods of time
-chimps & ability to exhibit delayed gratification
-big cats & elephants in zoos pacing before meal time
biological rhythm
-”a cyclic change in behavior or internal physiological process that occurs at a regular rate in an organism”
-exogenous rhythms
-endogenous rhythms
exogenous rhythms
rhythms that depend on external stimuli in order to persist regularly
endogenous rhythms
rhythms that are independent of external stimuli & rely on internal clock mechanisms
internal clock mechanism
“self-regulating, self-sustaining neural signals that occur at regular intervals”
different rhythms frequencies
-high frequency
-ultradian
-circadian
-diurnal
-infradian
-annual
high frequency rhythm
occur in short periods → <30 mins
heart rate high frequency example
-conservative within species and age groups
-adult cows → 60-80 bpm
-calves → 80-100 bpm
-adult horses → 28-40 bpm
ultradian rhythm
period between 30 mins to 24 hrs
growth hormone ultradian example
-GH production from pituitary gland in cattle
-~every 3.5 hours
feeding behavior ultradian example
-if feed is ad lib
-every 2-3 hrs → dogs, cats, sheep, pigs, cattle
circadian rhythms
-repeat approx every 24 hrs
-common to see behaviors and hormones expressed
infradian rhythm
longer than 24 hrs
cyclicity of polyestrous animals infradian example
-~21 days for cow & sow
-~17-24 days for mare
-~16-17 days for ewe
-repro hormone levels & behavior
-activity monitors on cows can detect when to breed
annual rhythm
-repeats annually
-seasonal breeders
seasonal breeders annual example
-horses = long day breeders
-sheep/goats = short day breeders
-goal → spring births for high prob of offspring survival
zugunruhe
-anxious behavior that migratory animals exhibit when unable to migrate
-in captivity
what do you see when zugunruhe is displayed?
increased activity around/after dusk → wing flapping, restlessness
circadian rhythm
-most well-studied
-period ~24 hrs
-influences by Zeitgeber → “time giver;” “entertainment”
circadian examples
-sleep/wake cycles
-hormone secretion in most mammals
-body temp
sleep/wake cycles
-depends on whether nocturnal or diurnal
-will have a reg period of wakefulness & sleepiness that repeats every ~24 hrs
hormone secretion in mammals
-peak cortisol early in the day
-various zeitgebers → depends on hormone → food, light, activity, other hormones
body temp
-peak in afternoon, lowest in early morning
-common across many species
circadian properties
1.must be ~24 hr period
2.must be endogenous rhythm
3.must persist (at least for a time) in constant conditions → “free running” rhythm
4.must be able to reset or “entrain” to an environmental factor
internal clock mechanism
-suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
-paired nuclei that regulates circadian
-lives above optic chiasm
-each cell is its own clock, w own electrical signals
-cells in nuclei work together to create ~24 hr rhythm
diurnal rhythm
-~24 hr rhythms that rely on external cues in order to persist
-ex → foraging & hunting, stereotypies in many species, poultry perching behavior
foraging & hunting diurnal example
-foragers alter behavior depending on temp to conserve energy
-hunters alter behavior based on prey
stereotypies in many species diurnal example
bar-biting in pigs → peak ~2 hr after feeding
poultry perching behavior diurnal example
depends on amount of light (photoperiod) & timing of darkness
sleep
-4 levels of alertness
1.alert wakefulness
2.drowsiness
3.quiet sleep
4.active sleep
-measured via EEG
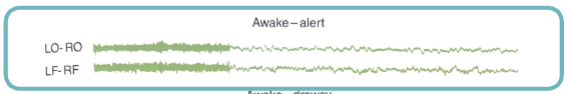
alert wakefulness
-eyes fully open
-EEG → low voltage, fast activity output
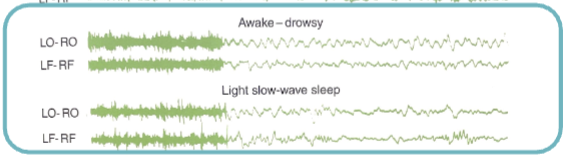
drowsiness
-relaxed upper eyelids
-high arousal threshold/reduced alertness
-EEG → combo low voltage/high activity and high voltage/low activity
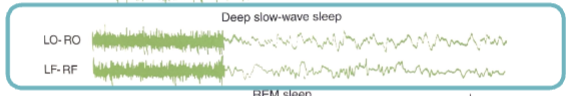
quiet sleep
-eyes closed or nearly closed, even more required to arouse
-EEG → all high voltage/slow activity
active sleep (REM sleep)
-eyes fully closed
-EEG → low voltage/fast activity (like wakefulness) → “paradoxical sleep”
-REM → rapid eye movement
dogs relative sleep behaviors and positions
-~50% of time spent sleeping → 20% of that in REM
-dependent on housing & schedule
cats relative sleep behaviors and positions
~45-65% of time sleeping → 20% in REM
cattle relative sleep behaviors and positions
-~25% of time sleeping
-sleep lying down, but rarely lateral
horses relative sleep behaviors and positions
-~20% of time sleeping
-sleep standing up majority of time
-must be in recumbency for REM → usually only ~5 mins at a time
pigs relative sleep behaviors and positions
-~30% of time sleeping
-many bouts of REM if in stress-free environment
poultry relative sleep behaviors and positions
-very dependent on light cycle
-definite difference in resting vs sleeping posture (head neutral vs head tucked)