BIO - Ch 7 Cellular Respiration
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
what is aerobic cellular respiration
when oxygen is present
what molecules does aerobic cellular respiration result in
carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O) and energy (ATP)
what is oxidation
the loss of electrons
what is reduction
the gain of electrons
what does OIL RIG stand for
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
what are electron carriers
molecules that carry electrons from one set of reactions to another
is NAD+ oxidized or reduced
NAD+ oxidized
is NADH oxidized or reduced
NADH reduced
NADH and FADH2 are what
electron carriers
NAD+ and FAD are what
electron acceptors
what is the first stage of cellular respiration
glycolysis
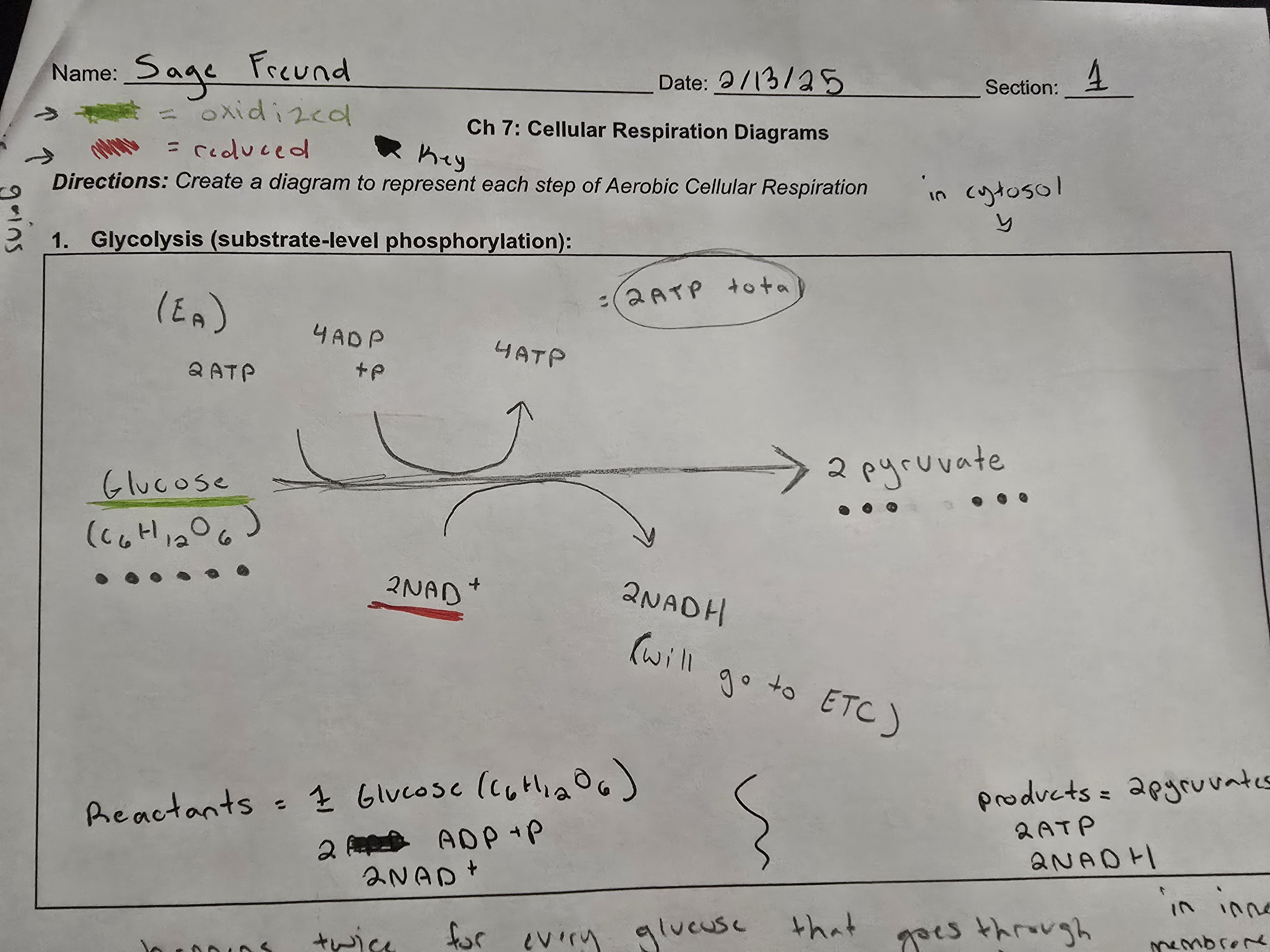
where does glycolysis take place
the the cytosol - liquid of cell
what does glycolysis do
breaks down glucose into two pyruvates
how much ATP does glycolysis produce & through what
2 ATP, through substrate level phosphorylation
what is anaerobic cellular respiration
can proceed without oxygen (doesn’t need oxygen to work)
what energy molecules are produced in glycolysis
2 pyruvates, 2 ATP and 2NADH
what is oxidized in glycolysis
glucose is oxidized in glycolysis
what is the chemical equation for glucose
C6 H12 O6
what is reduced in glycolysis
NAD+ is reduced in glycolysis and converts to NADH
what are the reactants in glycolysis
1 glucose (C6H12O6) 2 ADP (and a phosphate) and 2 NAD+
what is the second stage of aerobic cellular respiration
pyruvate oxidation/creation of Acetyl coA
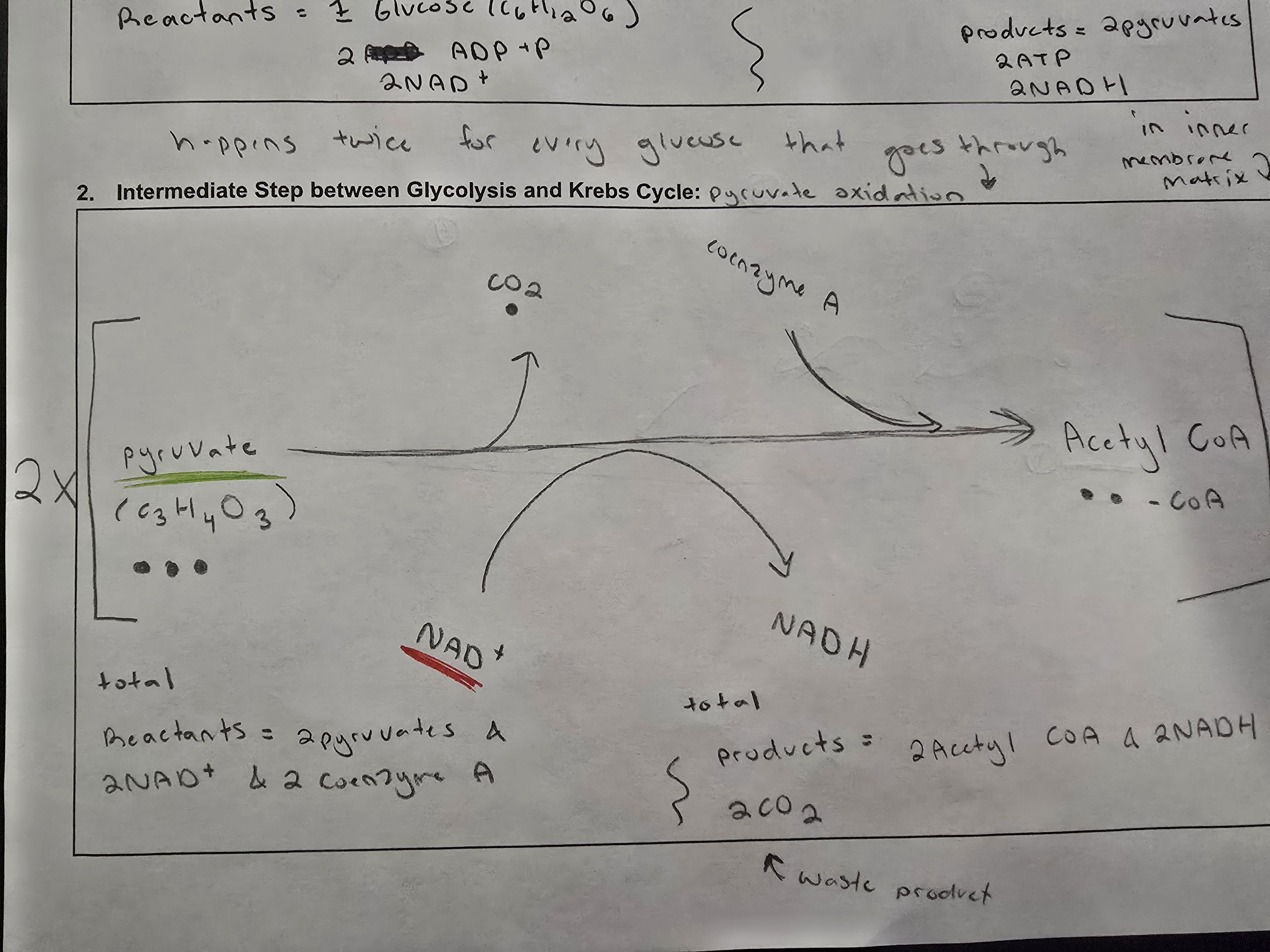
what happens during pyruvate oxidation
pyruvates are broken down into an acetyl group & acetyl joins coenzyme A to become acetyl coA
where does pyruvate oxidation take place
pyruvate oxidation takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria
how much ATP is produced during pyruvate oxidation
none
what electron carriers are produced in pyruvate oxidation
2NADH is produced in pyruvate oxidation
what is oxidized in pyruvate oxidation
pyruvate is oxidized in pyruvate oxidation
what is reduced in pyruvate oxidation
NAD+ which converts to NADH in pyruvate oxidation
what is the intermembrane space
the space between outer and inner membrane
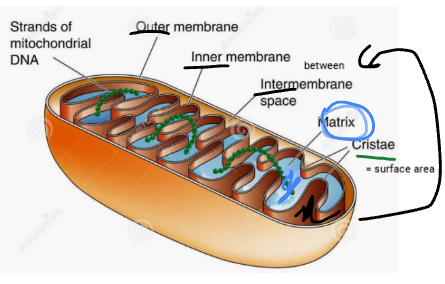
what is the outer membrane
surrounds the cell wall (on the “outside”
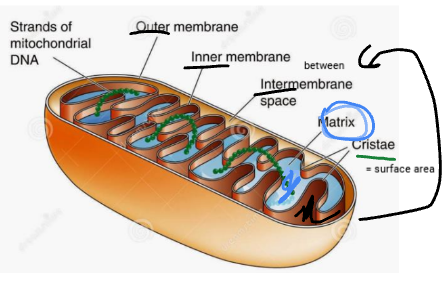
what is the inner membrane
barrier between the outer membrane and intermembrane space, it makes something that looks like a dividing wall between them
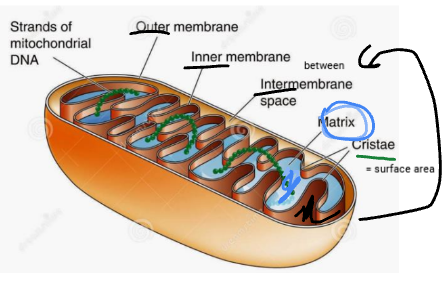
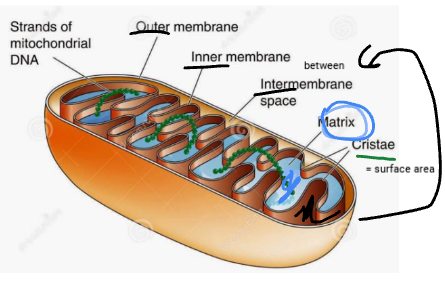
what is the matrix of a mitochondria
the gel like space within the inner membrane
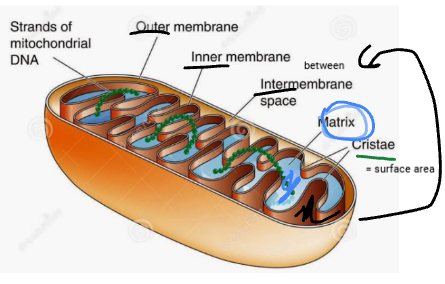
what is the cristae in a mitochondria
the folds in the inner membrane of the mitochondria, it increases surface tension on the membrane
what is the third stage of aerobic cellular respiration
the citric acid cycle, aka the krebs cycle
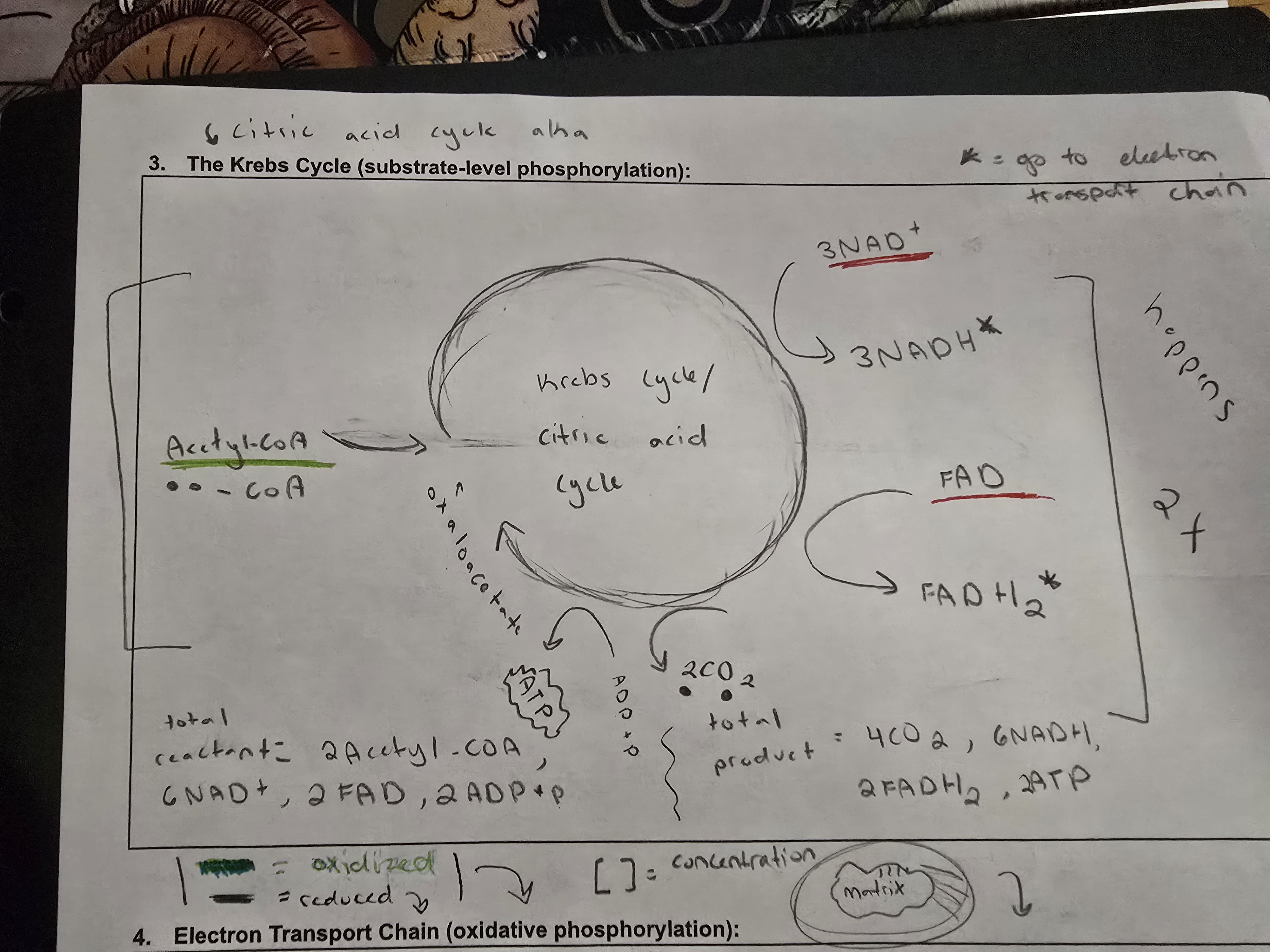
what happens in the citric acid cycle
Acetyl coA gets broken down into CO2 and then makes ALOT of electron carriers (NADH & FADH2)
where does the krebs cycle take place
citric acid cycle takes place in the inner matrix of the mitochondria
what are the reactants of pyruvate oxidation
2 pyruvates. 2NADH+ and 2 coenzyme A
what are the products of pyruvate oxidation
2 acetyl coA, 2NADH and 2CO2
how much ATP is produced through the krebs cycle and what type of production is used
2ATP, substrate level phosphorylation is produced in the Krebs cycle
what electron carriers are produced during the citric acid cycle
6NADH and 2FADH2
what is oxidized in the krebs cycle
acetyl coA
what is reduced in the citric acid cycle
NAD+ and FAD are reduced in the citric acid cycle
what are the reactants in the krebs cycle
2acetyl coA, 2FAD, and 2ADP + P
what are the products of the krebs cycle
4CO2, 6NADH, 2FADH2 and 2ATP
how many times does the krebs cycle occur for one glucose molecule
the krebs cycle occurs twice
how many times does pyruvate oxidation occur for one glucose molecule
pyruvate oxidation occurs twice
what is the fourth stage of cellular respiration
oxidative phosphorylation
what does oxidative phosphorylation do
uses the energy stores in electron carriers to create a proton gradient that will power ATP synthase and make ATP
where does oxidative phosphorylation take place
OX takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria
how much ATP is produced in oxidative phosphorylation, and through what?
28 to 30 ATP, made through oxidative phosphorylation
what electrons carriers are used/produced in oxidative phosphorylation
10NADH & FADG are used (this is where all the energy from our original glucose is stored)
what is oxidized in oxidative phosphorylation
NADH and FADH2
what is reduced in oxidative phosphorylation
O2 is reduced to make H2O
where is the electron transport chain
located in the inner membrane
how does the ETC work
NADH and FADH2 carry their electrons to proteins in the electron transport chain
Electrons are passed until they reach the final electron acceptor, oxygen
when oxygen accepts the electron and pulls it off the ETV, it is reduced to water
where in in stage four is there a high concentration of hydrogen
the intermembrane space
where in stage four is there a low concentration of hydrogen
the matrix of the mitochondria
how much TOTAL ATP is created during cellular respiration per glucose molecule
32 - 34 ATP per glucose molecule
what is chemiosmosis
when ions/molecules move across a semipermeable membrane using an electrochemical gradient
how does ATP synthase work
PE stored in the proton gradient is converted to mechanical (kinetic) energy as protons move down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase
The change in shape of ATP synthase helps catalyze the reaction, converting ADP and P to ATP
what does ATP synthase do
uses protons flowing down gradient to mass produce ATP