naming compounds for exam 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
methane
2 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
ethane
3 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
propane
4 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
butane
5 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
pentane
6 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
hexane
7 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
helptane
8 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
octane
9 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
nonane
10 carbon in parent chain (alkane)
decane
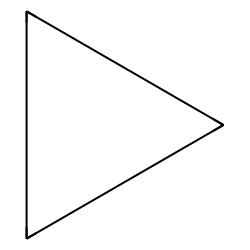
cyclopropane
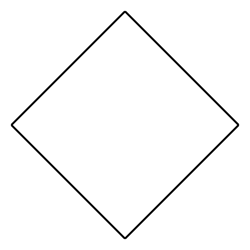
cyclobutane
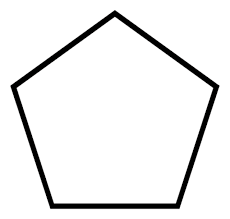
cyclopentane
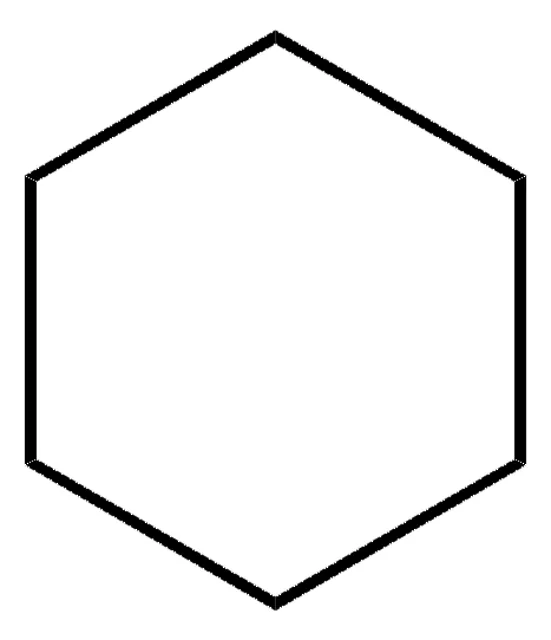
cyclohexane
1 carbon substituent
methyl
2 carbon substituent
ethyl
3 carbon substituent
propyl
4 carbon substituent
butyl
5 carbon substituent
pentyl
6 carbon substituent
hexyl
7 carbon substituent
heptyl
8 carbon substituent
octyl
9 carbon substituent
nonyl
10 carbon substituent
decyl
order of functional groups from least to most important in terms of naming (6)
amine
alcohol
ketone
aldehyde
ester
carboxylic acid
suffix for compound with carboxylic acid
-oic acid
suffix for compound with ester
-oate
suffix for compound with aldehyde
-al
suffix for compound with ketone
-one
suffix for compound with alcohol
-ol
suffix for compound with amine
-amine
what wavenumber range do H-X bonds correspond to? (X=any non H element)
2900 to 4000 cm^-1
what wavenumber range do C triple bond X correspond to? (X=any non H element)
2100 to 2400 cm^-1
what wavenumber range do C double bond X correspond to? (X=any non H element)
1500 to 1900 cm^-1
what are enantiomers?
stereoisomers that are non-superimposable, mirror images of each other
what are diastereomers?
stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other
what are stereoisomers?
molecules with the same chemical formula and connectivity but different arrangements of atoms, so do not line up perfectly
aka superposition
difference between cis and trans substituents:
cis indicates substituents are on same side of compound (both on dash or both on wedge)
trans - on opposite sides (so one on wedge, one on dash)
CIP rules for configuration of chirality centers
locate chirality center
assign bonds on chirality center (#1-4 for each group branching off, 4 is lowest atomic number, 1 is greatest atomic number)
rotate lowest priority (4) bond away from you
assign R configuration if top 3 priority bonds rotate clockwise
R configuration
top three priority bonds rotate clockwise
S configuration
top three priority bonds rotate counter clockwise