practical 3 review
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
diarthrosis is a __ joint
freely movable
syndesmosis which is between the tibia and the fibula is an example of a ___ joint and a ___ joint
fibrous, amphiarthrosis
intervertebral disc is an example of what type of joint
cartilaginous
intervertebral disc are classified as cartilaginous joints but what are their structural classification
synchondrosis
synovial joints are all ___ joints
diarthrosis
true or false there are 6 types of joints
true
examples of hinge joints include the ___, _____ and interphalngeal joints
elbow, ankle
the hip is an example of what joint
ball and socket joint
true or false, the radio-carpal joint is an example of a pivot joint
false
true or false, the thumb is an example of a saddle joint
true
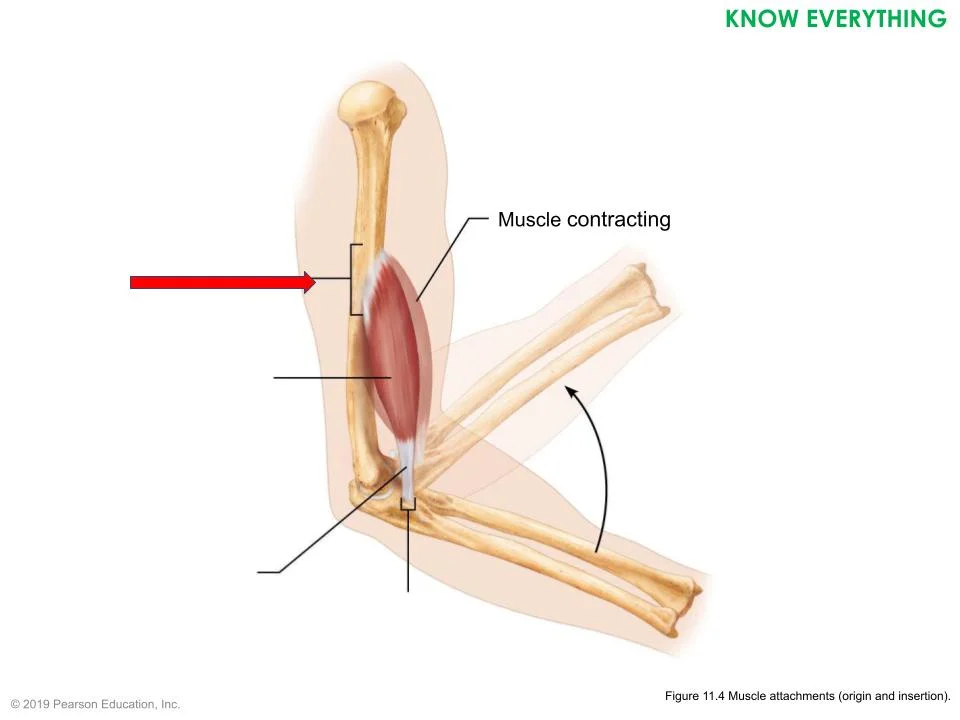
the red is an example of the ___
origin
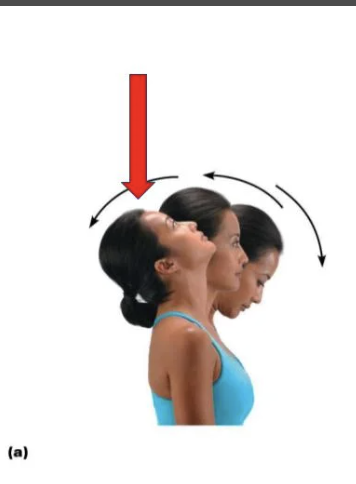
the red indicates
hyperextension
if you were to work out on the hamstring curl machine, the movement you are doing is an example of what?
flexion
a calf raise would be an example of what
plantar flexion
true or false, inversion is the movement of the foot laterally
false
the ACL and PCL help to prevent what?
joint over-flexion and joint hyperextension
the Medial Collateral Ligament is also known as the
Tibial Collateral Ligament
true or false, bursa is a type of synovial fluid
true
true or false, actin and myosin are known for shortening muscle through the sliding theory
true
true or false, in a bicep curl the bicep is known as the antagonist
false
true or false, in a leg extension the quads are known as the antagonist
false
classifications of naming skeletal muscles include
number of origins
shape of muscle
action of muscle
maximus correlates to naming of a muscle in what way
size
the bicep femoris has an origin of
2
what is the direction of a rectus muscle
straight
which of the following isnt a quadricep muscle
semitendinosus
true or false, the adductor muscle breaks up into two categories
false
true or false, the gastrocnemius is known as the calf muscle
true
the origin refers to
the “fixed” attachment
insertion point refers to
the attachment that moves with the contraction
action is..
a particular movement of a muscle
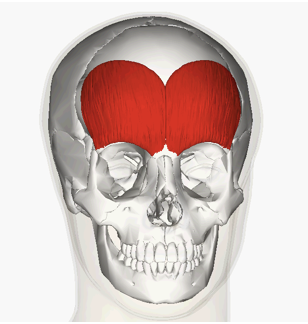
ORIGIN of Frontalis
Aponeurosis
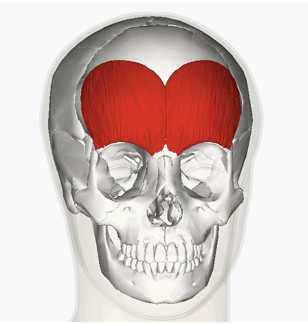
INSERTION of frontalis
eybrows
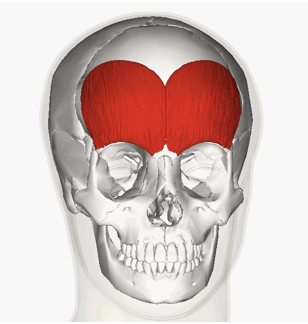
ACTION of frontalis
raising eyebrows, wrinkling forehead (ex:when confused or low key judging some1)
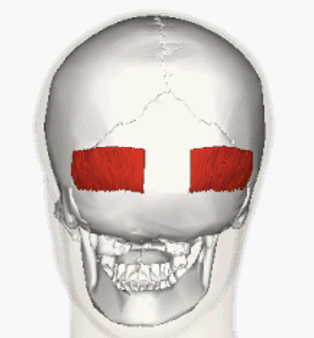
ORIGIN of occipitalis
occipital bone
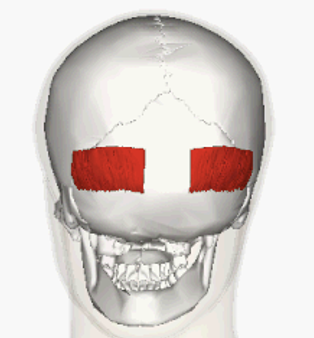
INSERTION of occipitalis
Aponeurosis
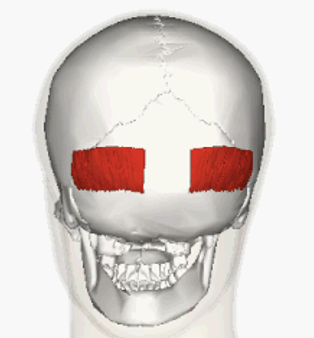
ACTION of occipitalis
pulls scalp backward
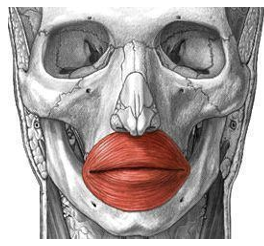
ORIGIN of orbicularis oris
maxilla and mandible
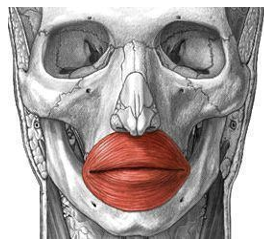
INSERTION of orbicularis oris
skin around the lips
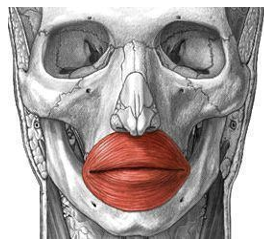
ACTION of orbicularis oris
pucker and close lips
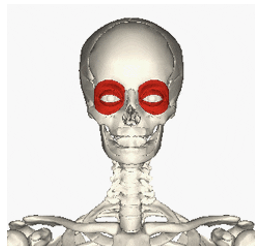
ORIGIN of orbicularis oculi
maxilla and frontal bone
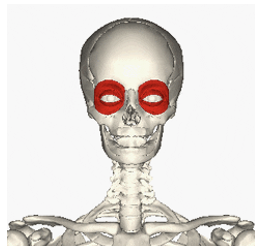
INSERTION of orbicularis oculi
eyelids
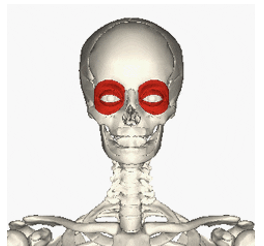
ACTION of orbicularis oculi
closing eyelids, blinking and squinting
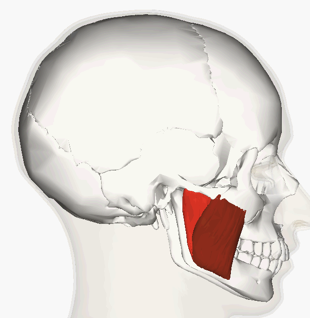
ORIGIN of masseter
zygomatic arch and maxilla
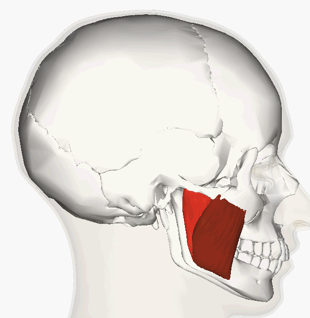
INSERTION of masseter
mandible
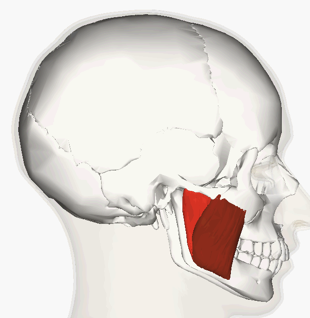
ACTION of masseter
raises mandible, chewing
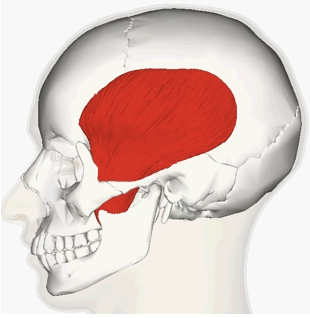
ORIGIN of temporalis
temporal bone
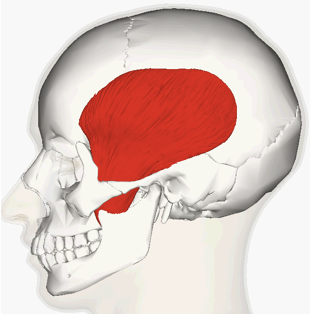
INSERTION of temporalis
mandible
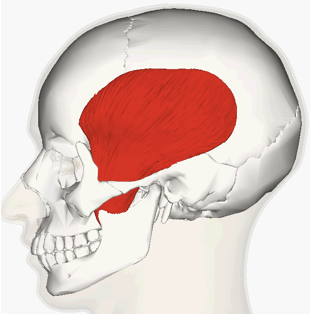
ACTION of temporalis
raises mandible, chewing
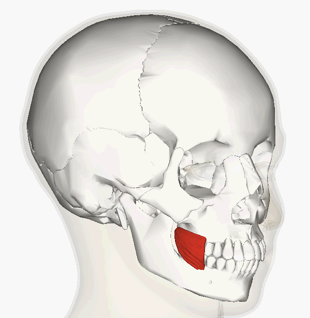
ORIGIN of buccinator
maxilla and mandible
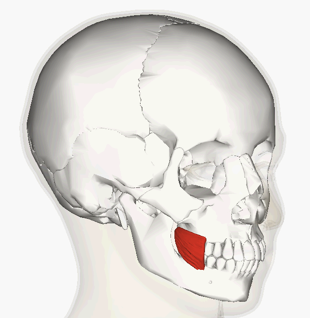
INSERTION of buccinator
orbicularis oris
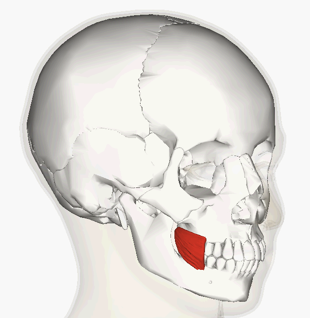
ACTION of buccinator
compresses cheek to hold food in, sucking in cheek
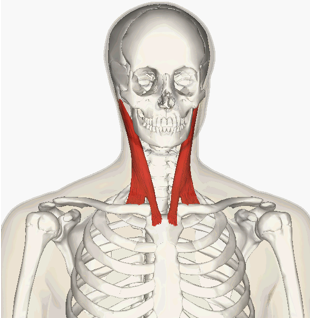
ORIGIN of Sternocleidomastoid
manubrium of sternum and clavicle
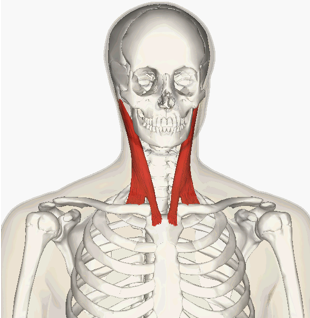
INSERTION of Sternocleidomastoid
mastoid process of temporal bone and occipital bone
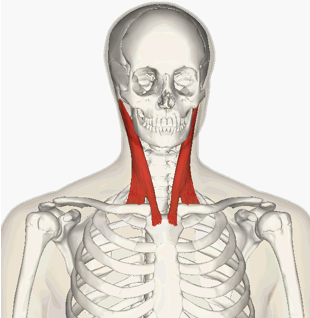
ACTION of Sternocleidomastoid
flexion of neck, rotation of head toward shoulder
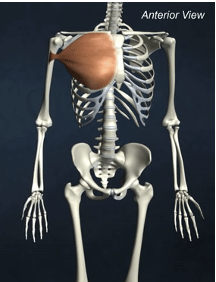
ORIGIN of pectoralis major
clavicle and sternum
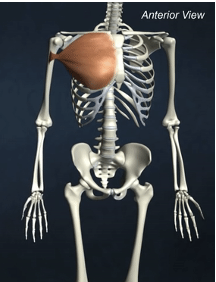
INSERTION of pectoralis major
greater tubercle of humerus
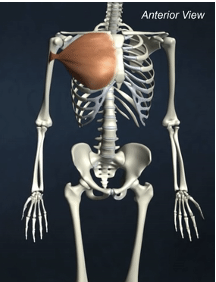
ACTION of pectoralis major
shoulder flexion, adduction of arm, medial rotation
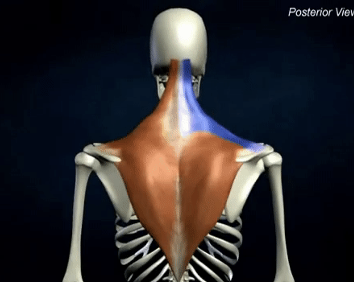
ORIGIN of trapezius
occipital bone and spinous process of C7-T12
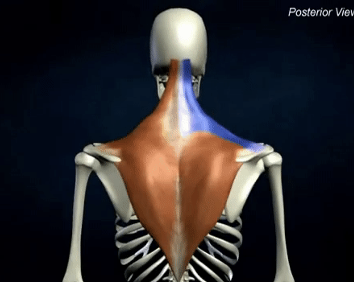
INSERTION of trapezius
lateral clavicle, acromion process and spine of scapula
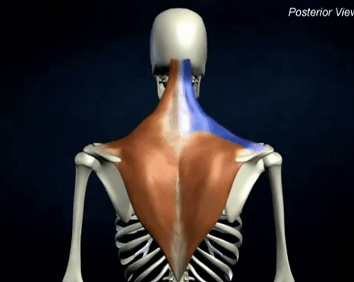
ACTION of trapezius
scapular stabilization, elevation, depression, retraction, and rotation
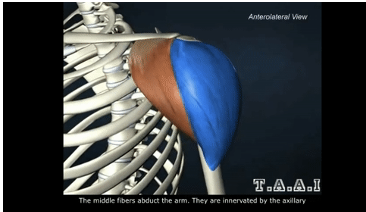
ORIGIN of deltoid
lateral clavicle, acromion process and spine of scapula
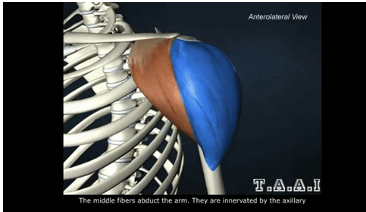
INSERTION of deltoid
deltoid tuberosity of humerus
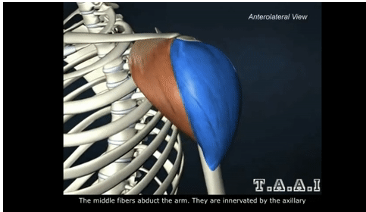
ACTION of deltoid
shoulder abduction
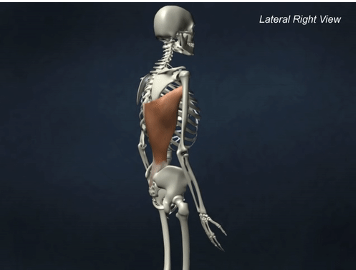
ORIGIN of Latissimus dorsi
spinous process of T6-T12, and lumbar vertebrae, lower ribs, illium
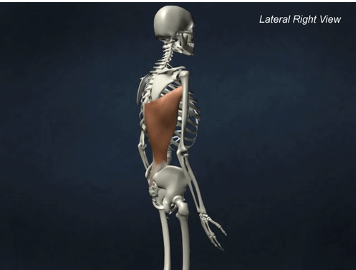
INSERTION of Latissimus dorsi
intertubercular sulcus of humerus
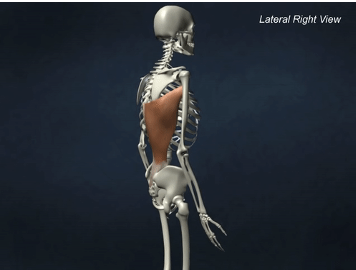
ACTION of Latissimus dorsi
shoulder extension, adduction, and medial rotation
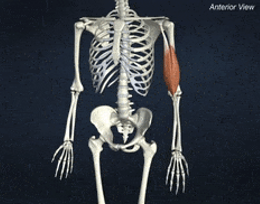
ORIGIN of biceps brachii
Supraglenoid tuberosity and coracoid process of scapula
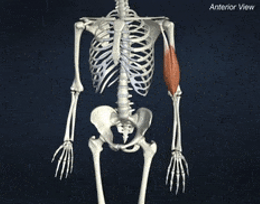
INSERTION of biceps brachii
radial tuberosity of radius
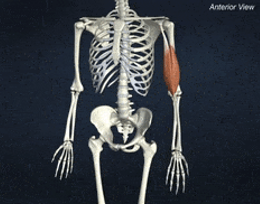
ACTION of biceps brachii
elbow flexion and supination of forearm
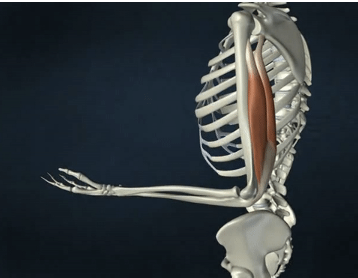
ORIGIN of triceps brachii
Glenoid cavity of scapula, radial groove, and posterior humerus
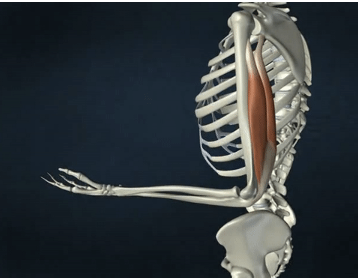
INSERTION of triceps brachii
olecranon process of ulna
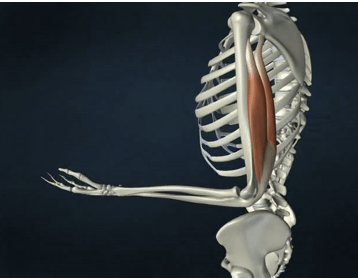
ACTION of triceps brachii
elbow extension
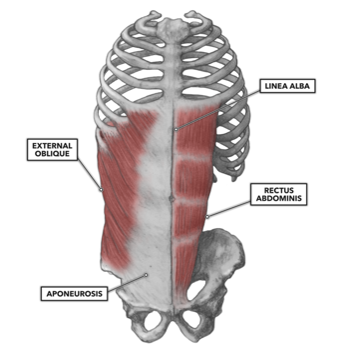
ORIGIN of external oblique
5th to 12th ribs
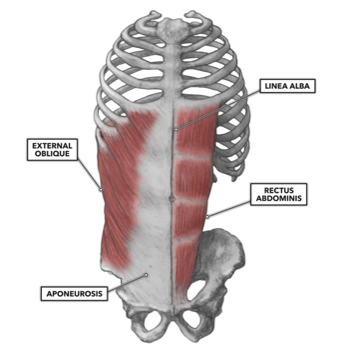
INSERTION of external oblique
pubic crest and tubercles and linea alba
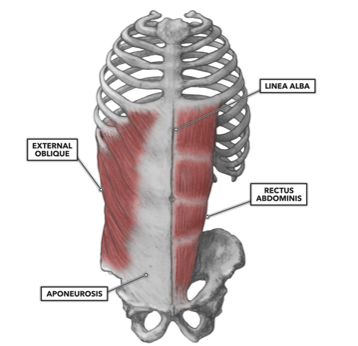
ACTION of external oblique
Compression of abdominal wall, aids in expiration, trunk rotation, lateral flexion
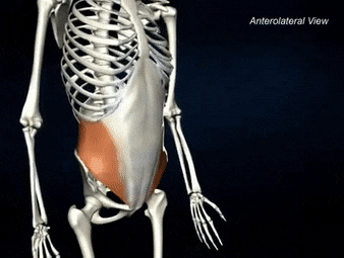
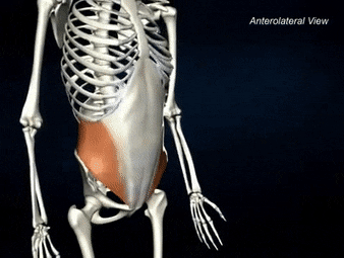
ORIGIN of internal oblique
Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, and lumbar fascia
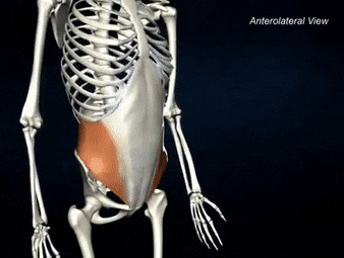
INSERTION of internal oblique
linea alba, pubic crest, and ribs 10-12
ACTION of internal oblique
Compression of abdominal wall, aids in expiration, trunk rotation, lateral flexion
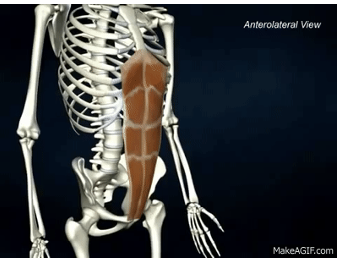
ORIGIN of rectus abdominis
pubic crest and pubic symphysis
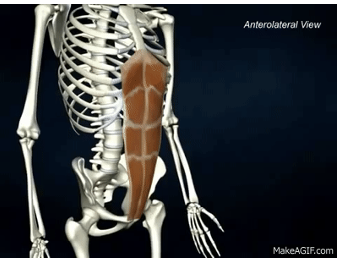
INSERTION of rectus abdominis
xiphoid process and costal cartilage ribs 5-7
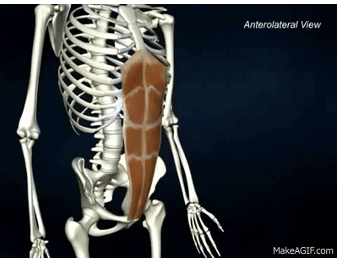
ACTION of rectus abdominis
rotation and flexion of vertebral column (sit up)
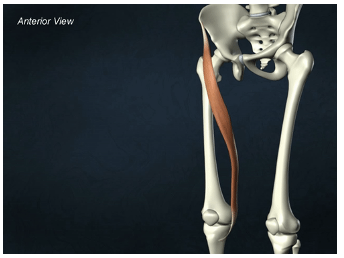
ORIGIN of sartorius
iliac spine
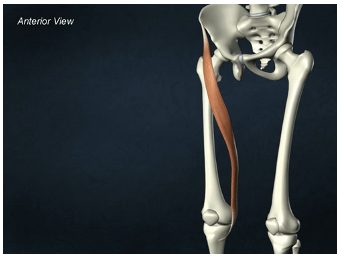
INSERTION of sartorius
proximal tibia
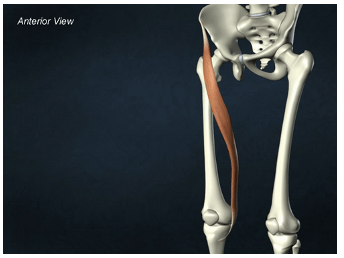
ACTION of sartorius
hip flexion, abduction, and lateral rotation
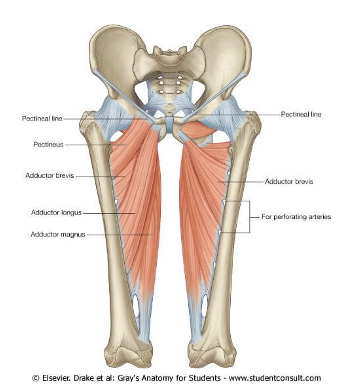
ORIGIN of adductor group
ischium and pubis bone
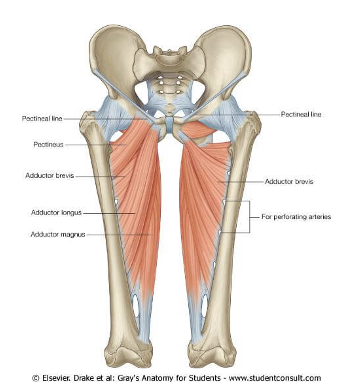
INSERTION of adductor group
linea aspera, and tubercle of femur
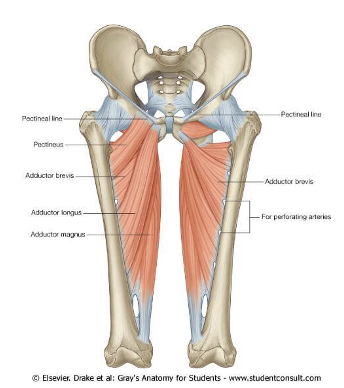
ACTION of adductor group
hip adduction, medial rotation, and flexion
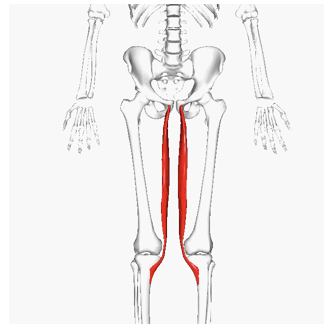
ORIGIN of gracilis
pubis bone
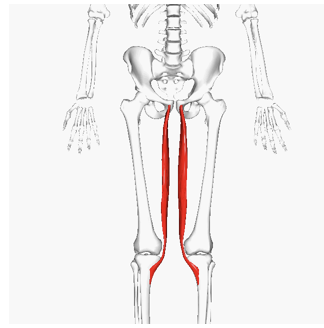
INSERTION of gracilis
tibia, below medial condyle
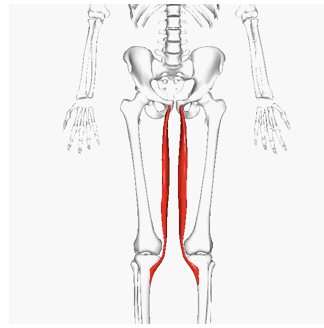
ACTION of gracilis
hip adduction, medial rotation, and flexion
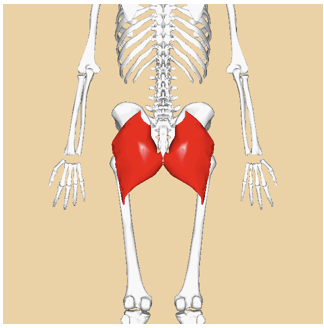
ORGIN of gluteus maximus
illium, sacrum, and coccyx
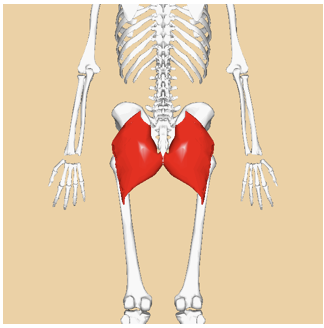
INSERTION of gluteus maximus
gluteal tuberosity
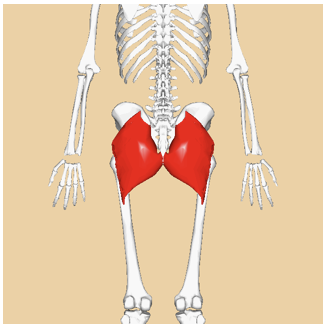
ACTION of gluteus maximus
hip extension, lateral rotation, and abduction
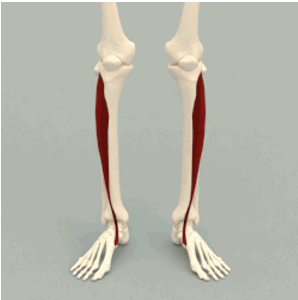
ORIGIN of tibialis anterior
lateral condyle and proximal tibia
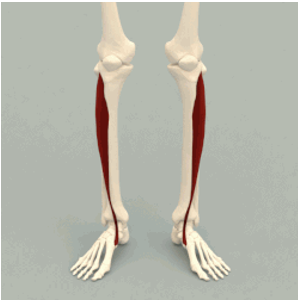
INSERTION of tibialis anterior
1st cuneiform and metatarsal
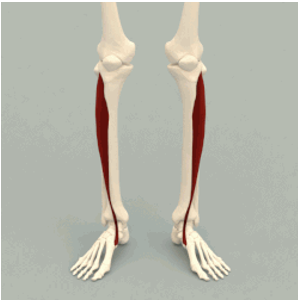
ACTION of tibialis anterior
dorsiflexion of ankle (toes pointing upward)