13.2 Family and Kinship
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What is the most basic unit for Anthropologists?
family
What does family determine?
our identities, our life chances, who you spend your time with
What is family directly related to?
economics
To understand a society, what must we understand about them?
how they organize their families
What do families form in all societies?
the basic social and economic unit of all societies
What can we discover by studying families and households?
some of the fundamental differences between various cultures
What is family generally defined by?
“kinship”
What does consanguineous mean?
being related by blood
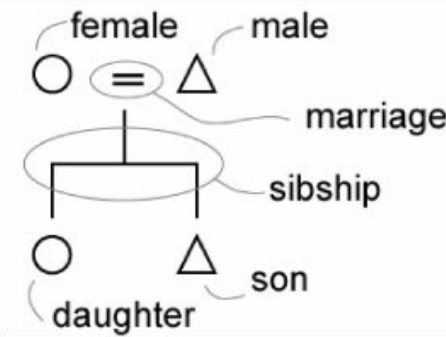
What do anthropologists use to talk about family structures?
kinship charts
What does ego mean on kinship charts?
you
What are many of the rules about marriage based on?
who you are related to; but those relations are defined in different ways by different cultures
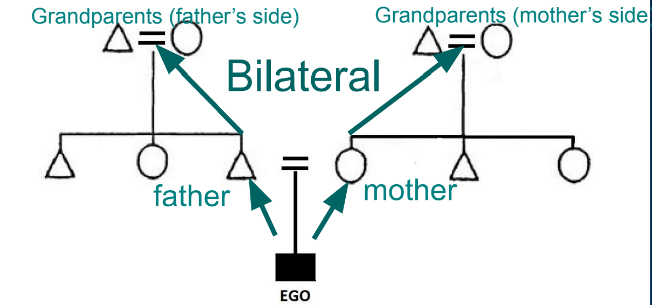
What are bilateral kinship systems?
you are related to both your mother’s and your father’s side; how many of us see the world
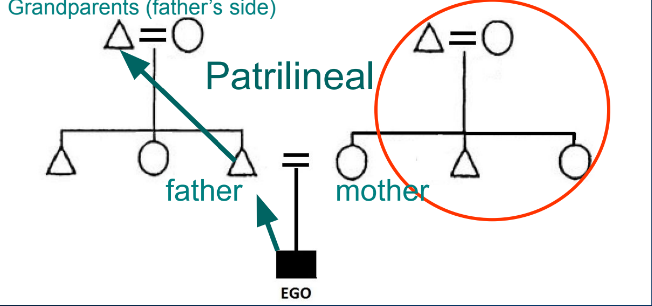
What are patrilineal kinship systems?
descent through the male line; these may or may not be your “relatives” since you do not trace descent through them; the chart doesn’t change, but how we read it does
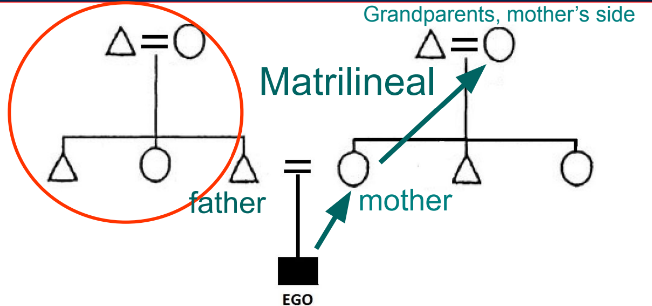
What are matrilineal kinship systems?
descent through the female line
What does affinal mean?
marriage
The ideal of marriage is universal, but the form it takes varies between what?
societies based on cultural norms, religion, economic strategies, etc.
Because marriage is universal, what does it enable?
gendered divisions of labor which makes deciding who does what work more efficient (though not always fair)
Because marriage is universal, what does it allow us to do?
take care of our infants; human infants require so much more care and attention than the infants of other species
Because marriage is universal, what does it create for children?
role models for children to learn about gender roles and expectations (gender stratification)
Because marriage is universal, what does it minimizes?
sexual competition; we can spend less time dating and more time doing other things
Because marriage is universal, what can it be part of?
an economic exchange and alliance formation
While marriage is universal, different societies have different norms. What two kinds of marriages do we tend to think of?
arrange marriages and “love” marriages

Marriage is a continuum from _____ to ______ ______
arranged; couple’s choice

The role of “love” and money in marriages is a continuum from _____ ______ to _____-_______ _______
love marriages; socio-economic marriages
What is monogamy?
marriage between two
What is polygamy?
marriage between several
What is polygyny?
one man marries several women
What is polyandry?
one woman marries several men
What does mono mean?
one
What does poly mean?
many
What does gamy mean?
marriage
What kind of marriage restriction is incest?
restrictions against marrying “close” family, but “close” is defined differently between culture
What is exogamy?
only allowing marriages “outside” of the group
What is endogamy?
only allowing marriages “inside” of the group
What does exo mean?
outside
What does Endo mean?
within
In the USA, how many states allow first cousin marriages?
21
In the USA, how many states DO NOT allow first cousin marriages?
23
In the USA, how many states set conditions on first cousin marriage?
6
Can you marry your cousin in Illinois?
yes, but under certain circumstances
Worldwide what percentage of marriages are between first or second cousins?
10%
In the US, what is greatly exaggerated in popular culture to place constraints on the behavior?
the increased risks of genetic disorders between cousin marriage
The increased risks of genetic disorders between cousin marriage being exaggerated in the US is an example of what?
how “science can be exaggerated to encourage a specific cultural norms
What qualifies as a cousin in the US?
children of your mother’s brothers and sister or your father’s brothers and sisters
What are parallel cousins?
children of your mother’s sister or your father’s brother
What are cross cousins?
children of your mother’s brother or your father’s sister
What is one of the most common forms of marriage in the world and throughout human history involving cousins?
cross cousins marriages
What is the advantage of cross-cousin marriage?
it allows you to marry someone who is technically outside of your immediate family, but whose family know very well, and you can probably trust; family resources remain in a smaller circle of people who can be counted on to help out in times of crisis
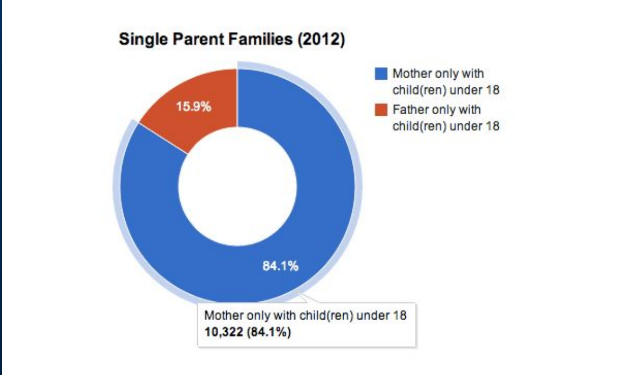
What are single parent families?
one parent and their unmarried children
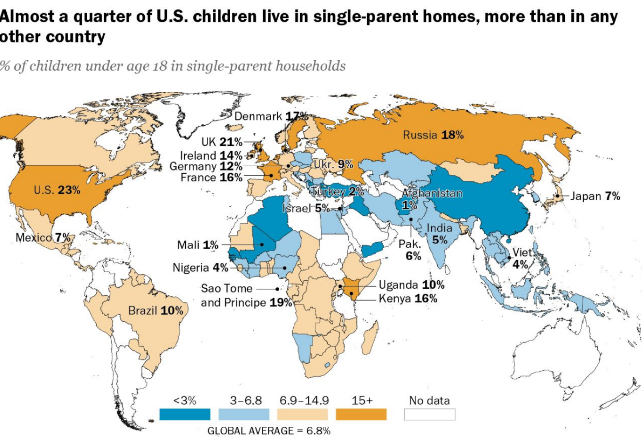
What is the smallest defined family and frequently female-led?
single parent families
What are nuclear families?
two parents and their unmarried children
What are some characteristics of nuclear families?
common in the US
rare in the world and almost non-existent in the past
our idea of nuclear family = household is a 20th century creation
in most common areas of the world both the concepts of families and households are far more complex
What are extended families?
one or two parents and their unmarried children plus one or more additional family members (often elderly)
What are some characteristics of extended families?
often involves the grandparents
common in 20% of American households
it is extremely common elsewhere
What are joint families (eg. patrilocal)?
two parents, their sons, their sons’ wives, and all of the unmarried children of their sons
What is the difference between joint families and extended families?
joint families include multiple generations
Where are joint families very common?
South Asia
What are some residence patterns?
patrilocal, matrilocal, neolocal
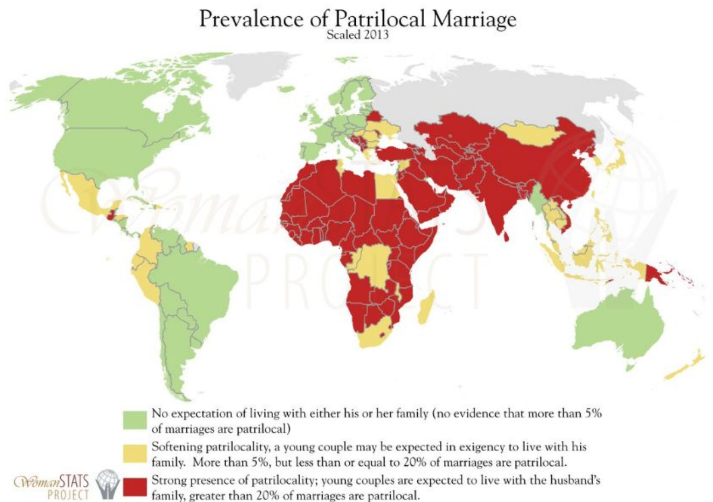
What does patrilocal mean?
a married couple lives with the husband’s parents
What are patrilocal residences made up of?
fathers, sons and brothers and their unrelated wives
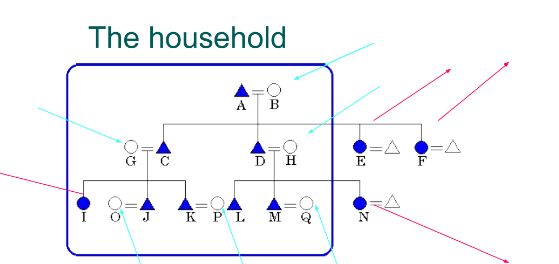
In a patrilocal residence, if a husband and wife have four children, two sons and two daughters, who stays and who marries outside? What happens in the next generation?
The sons stay in the household while the daughters marry outside. In the next generation all the sons stay in the household while all the daughters leave
What does matrilocal mean?
a married couple lives with the wife’s parents
What does neolocal mean?
married couple finds a new residence separate from both parents’ households (this is a very new idea)
In the US, what are the few rules about residency after marriage largely determined by?
economics; this is very rare among other cultures and across history
What may determine the amount of power, prestige and wealth you have access to and control the most important aspects of your life?
who you live with
What does fictive mean?
neither marriage nor blood (social)
What social position in society do females tend to hold?
females tend to hold extremely poor social positions in societies that are organized with male descent groups (patrilineal) and where they must live with their husbands’ family (patrilocality)