Colour vision
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
1. Define the term trivariance of vision. (3 marks)
Individual cones though are also colour blind. As a single cone absorbs the photon of light, it cannot determine the wavelength=univariance
Only when information from the 3 classes of cone photoreceptor are combined, that colour vision is possible. = 3-channel system
2. Describe the colour ordering system proposed by Munsell.
Briefly define each category in the system. (6 marks)
Munsell system is a colour ordering system based on three variables
1. Dominant wavelength- hues specify colour
2. Excitation purity - chroma specifies saturation
3. Luminance - value specifies the reflectance of the wavelength of light
3. Compare additive colour to subtractive colours highlighting the differences between the two. (4 marks)
Diff colour lights = added together
Use 3 additive primary colours =other colours
Basis of RGB monitors (TVs) etc
Mixing colour so that wavelengths of light are selectively absorbed
CMY
when 2 of these subtractive primary colours are mixed, a primary (additive) colour is produced.
Basis of colour printing, mixing paint, as it is the reflected light that we perceive
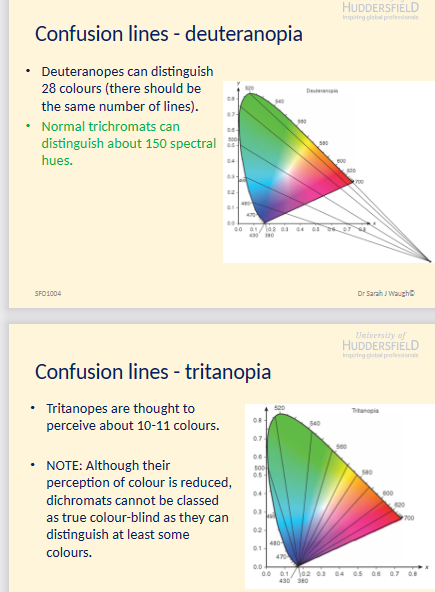
4. Draw a schematic CIE Chromaticity diagram and add confusion lines for a protanope (deuteranope or tritanope). (6 marks)
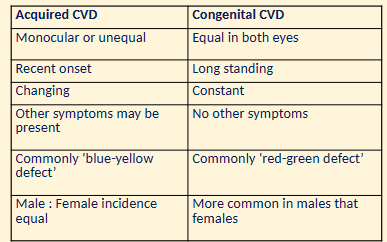
5. Give reasons when you would suspect a patient has an acquired colour vision defect rather than a congenital colour defect. (4 marks)
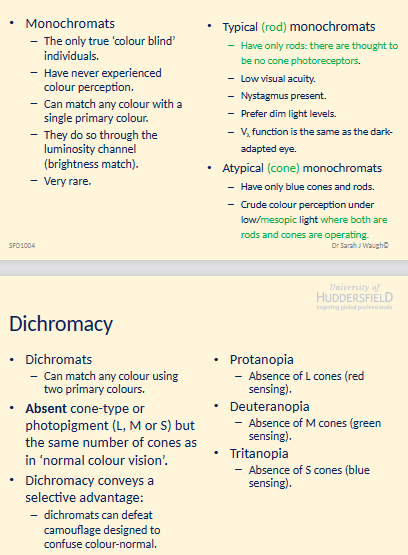
6. Explain the key differences between monochromat and a dichromat. (4 marks)
Aspect | Monochromats | Dichromats |
|---|---|---|
Color Perception | Completely color blind; no experience of color. | Limited color perception; can match colors using two primary colors. |
Primary Colors | Match any color with a single primary color. | Match any color using two primary colors. |
Visual Receptors | Typically have only rods, no cone photoreceptors. | Absent cone-type photopigment (L, M, or S), but same number of cones as in normal vision. |
Selective Advantage | None; no selective advantage related to color vision. | Can defeat camouflage designed to confuse color-normal individuals. |
Common Variants | Typical (rod) monochromats and atypical (cone) monochromats. | Protanopia (absence of L cones), Deuteranopia (absence of M cones), Tritanopia (absence of S cones) |
7. Explain why the central fovea has a specific type of colour vision defect even in patients with otherwise normal colour vision. (2 marks)
The S cones are absent from the central 20 mins of arc of the fovea.
=CV defect for targets of 20 mins of arc or less.
8. Give two key advantages and two key disadvantages of the Ishihara colour vision test. (4 marks)
Advantages
Detects presence of defect
1st plate=demonstration – everyone should see the number
Disadvantages
No information about severity of defect.
Not useful at separating protan – deutan defects.
9. Briefly describe the key elements of the Farnsworth D15 test. When should this test be performed? (5 marks)
Perform under daylight conds
rearrange colours in orderly sequence of changing hue.
Instructions should be to arrange in what patient thinks is the natural order beginning with the fixed cap.
Record results according to number sequence of caps in order.
Pass the test by having no ‘crossing’ errors
10. Give two examples where a patient with a dichromatic colour vision defect may experience ‘real world’ difficulties. (4 marks)
Difficulty in distinguishing the colour of traffic signal lights,e.g R/G -could misinterpret signal + cause accident
Difficulty in determining when fruit + veg are ripe -can’t tell based on colour cues alone
(both mainly affects dichromats)
11. How does the Vanishing Plate of the Ishihara test work? (3 marks)
Ishihara exploits the confusion lines of CVD.
Small coloured discs that vary in luminance
Arranged to form a figure and background
normal people will see the number, people with cvd won’t see any number

transformation plates
individuals with CVD should see a different figure from individuals with normal color vision
hidden digit plates
only individuals with color vision defect could recognize the figure.
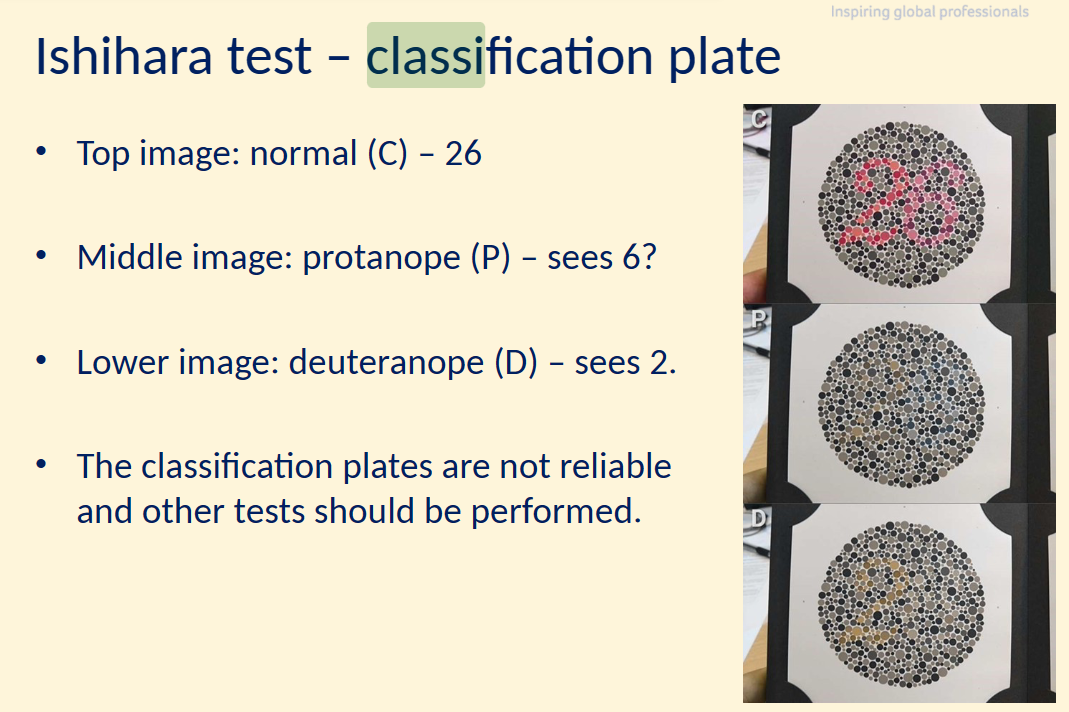
classification plates
not reliable + other tests should be performed
helps to know if they have a cvd and can kind of tell which cvd but you can’t rely on just that