Titration terminology, and Ksp, Ka, Kb, and Kf.
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
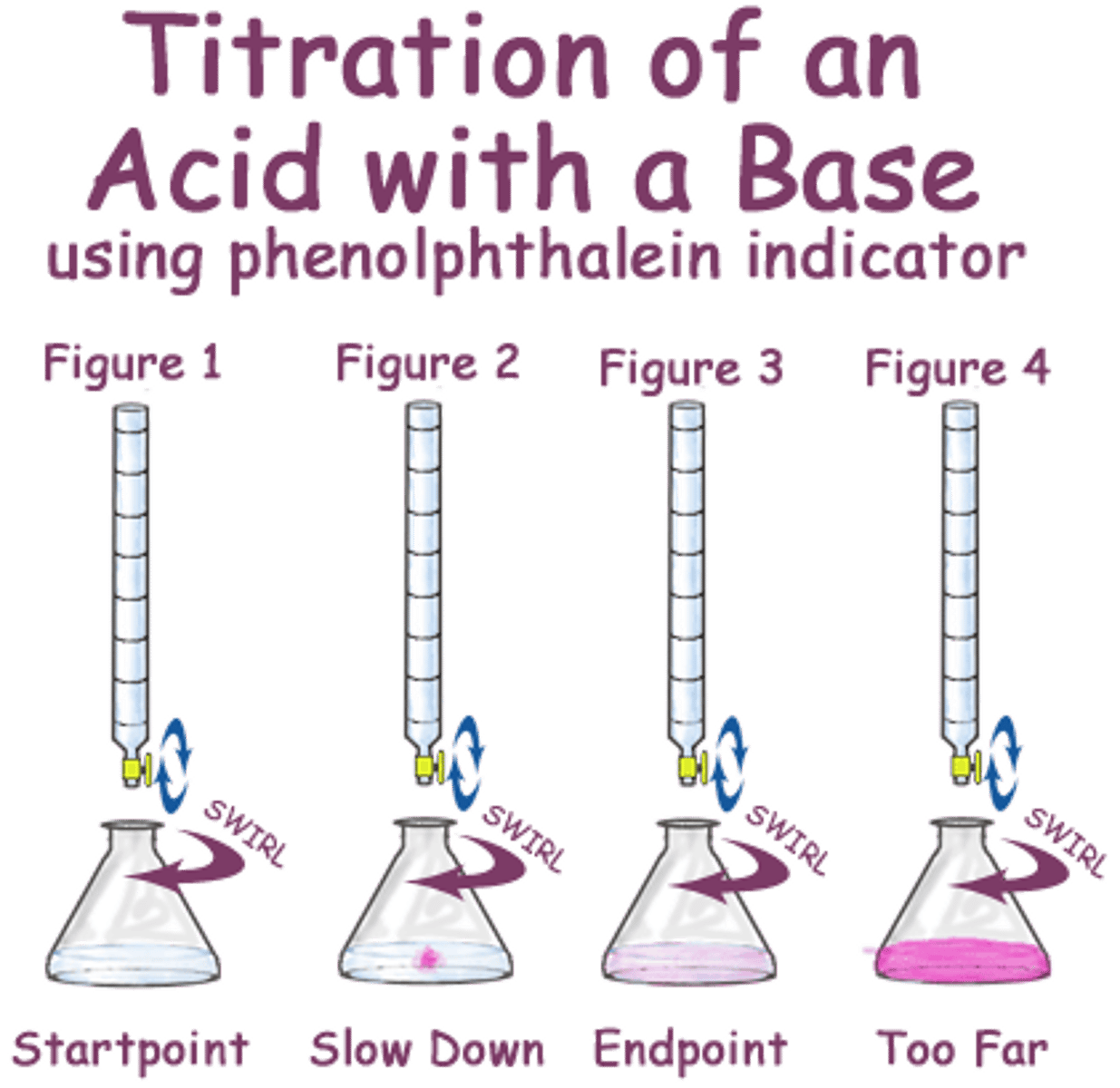
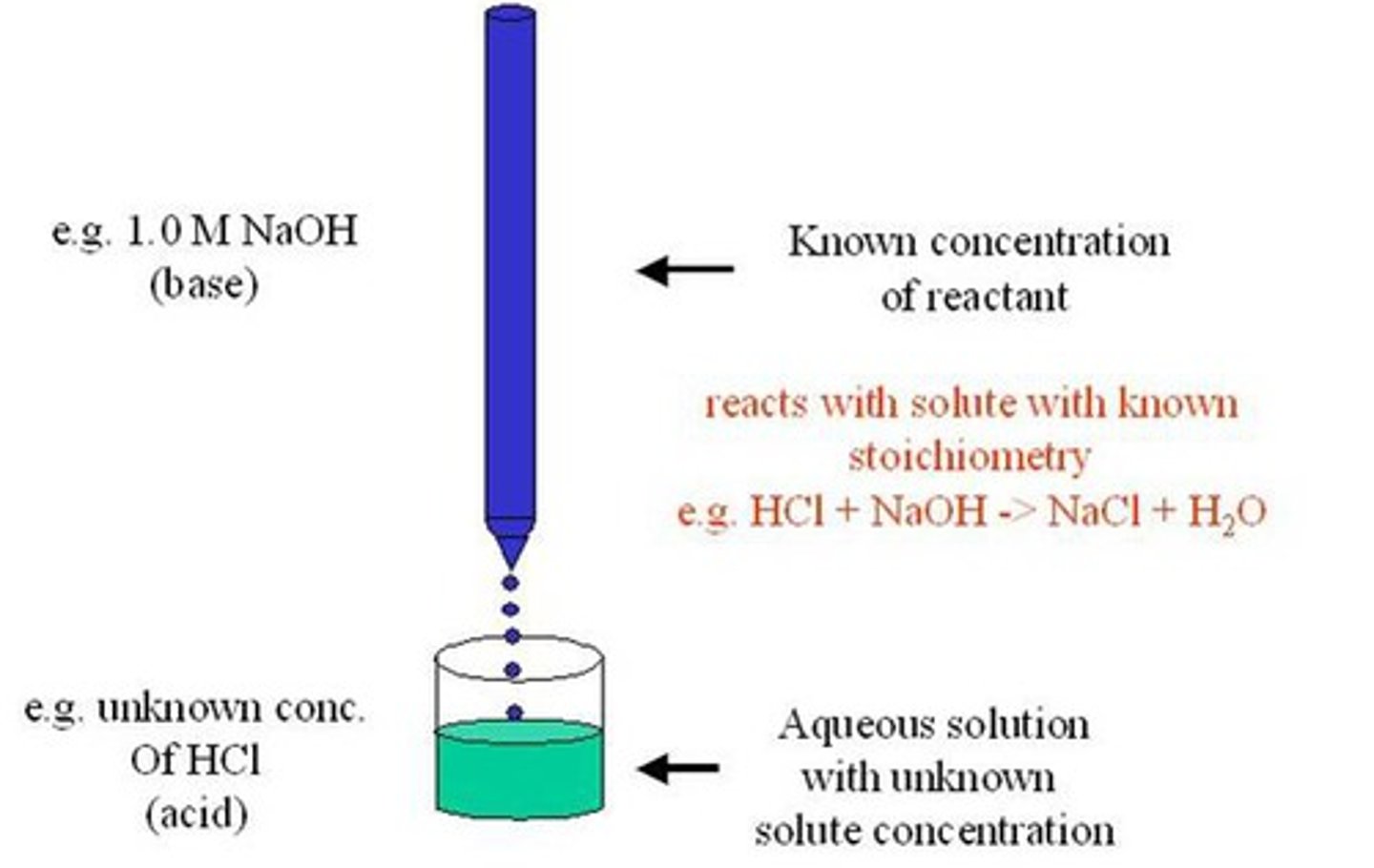
Titration
process in which a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of another unknown solution
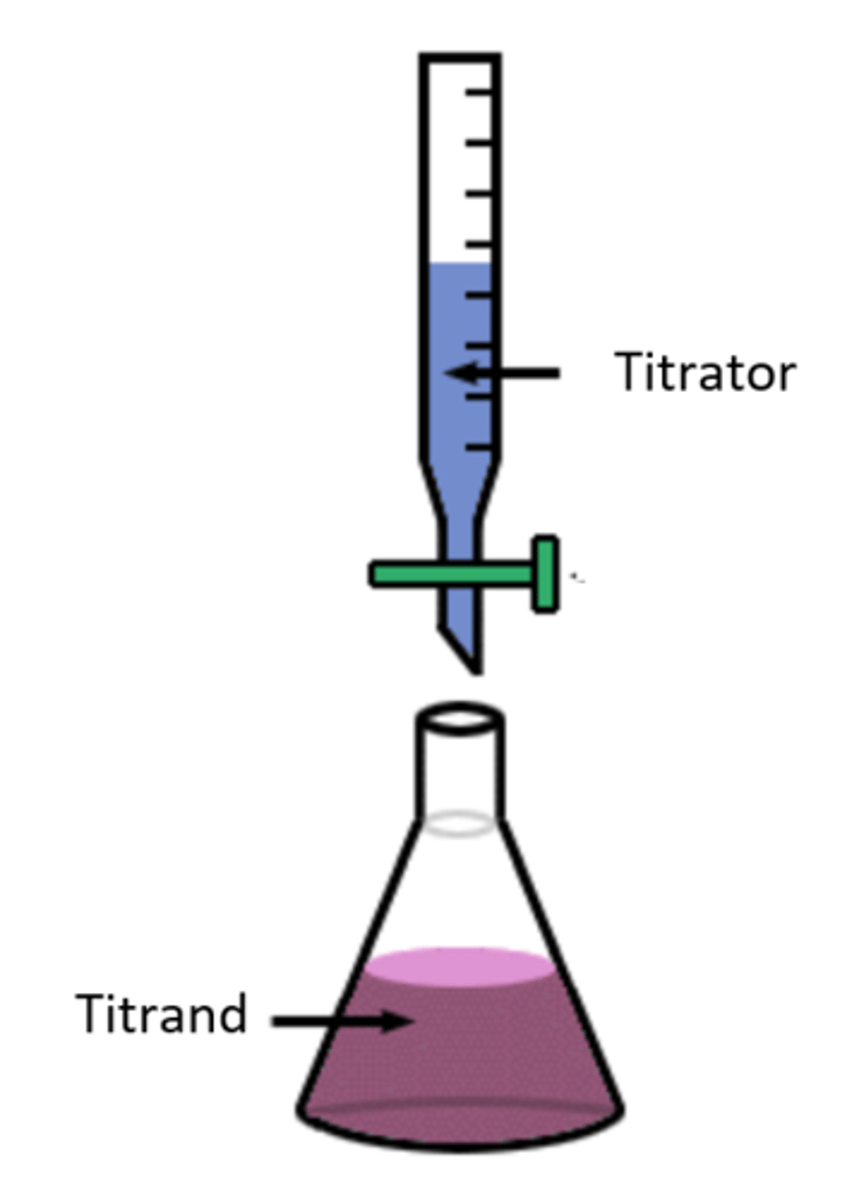
Titrant
A solution of known concentration that is used to titrate a solution of unknown concentration
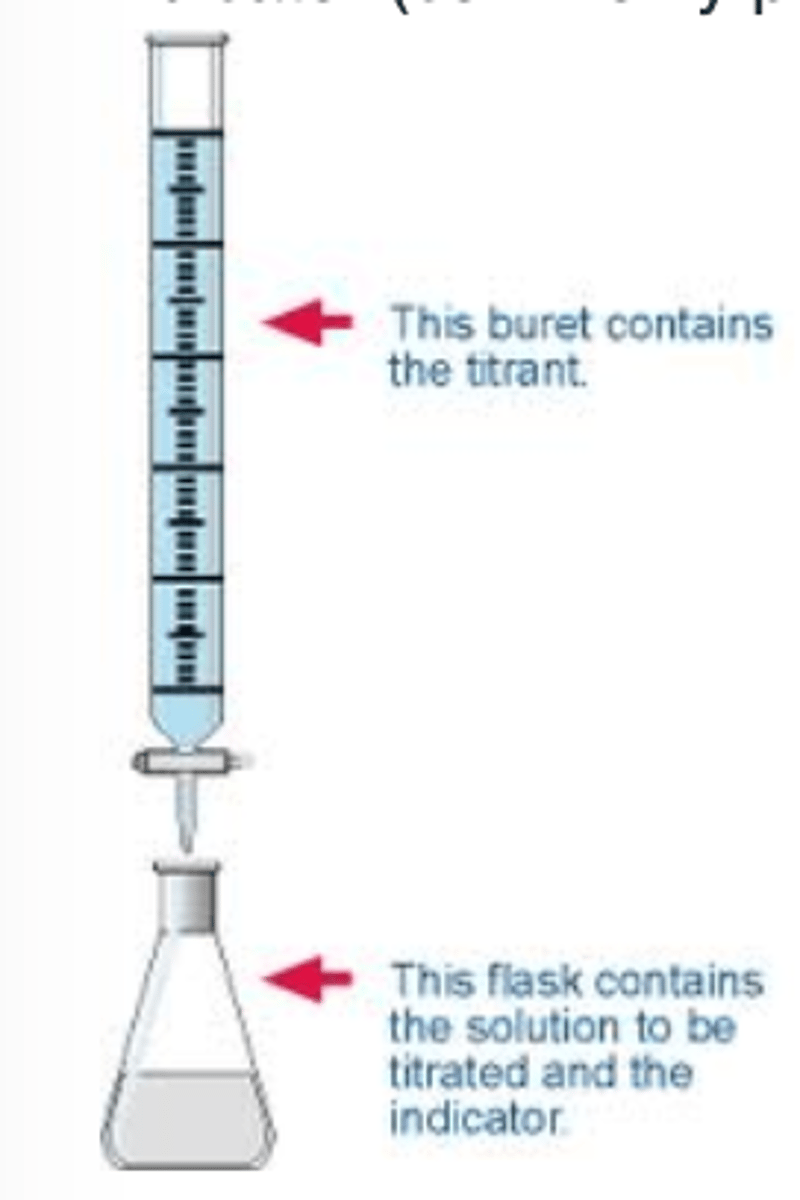
Titrand
A solution of unknown concentration to which small volumes of a solution of known concentration are added to reach the equivalence point.
Analyte
A substance that is being identified or measured in a laboratory test.
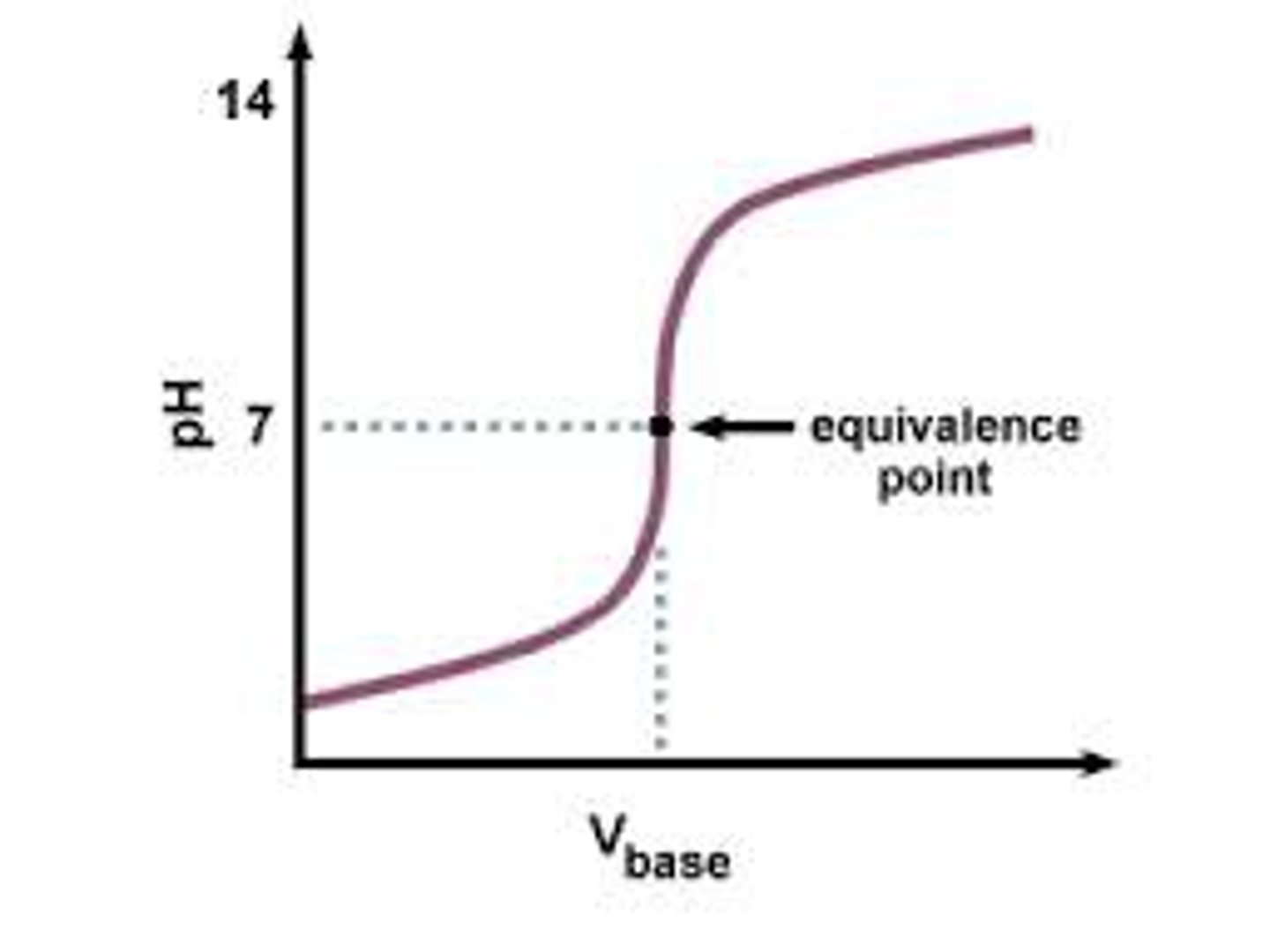
titration curve
a graph of the pH of a solution as a function of the volume of the added titrant
Titre (Titration)
the concentration of a solution as determined by titration
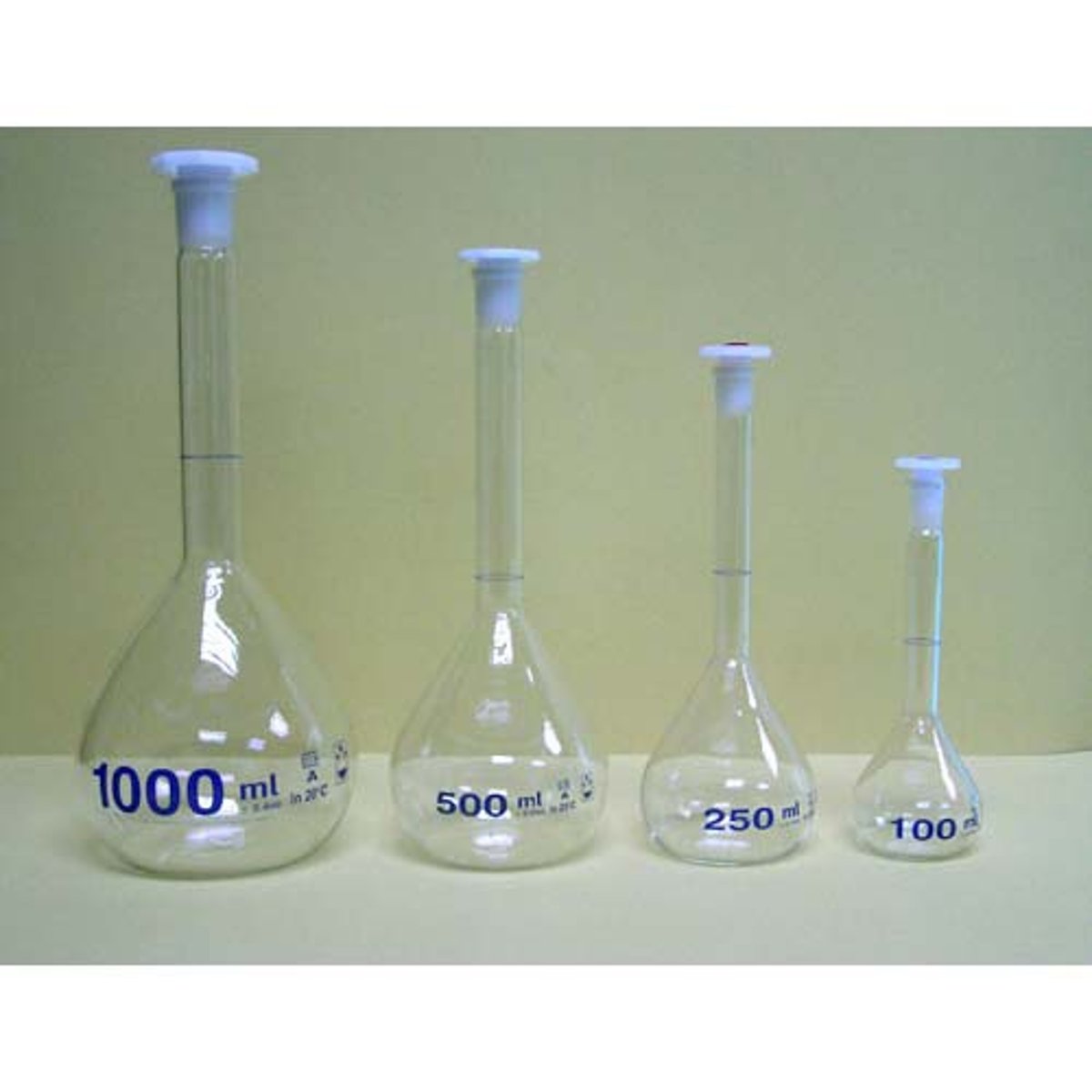
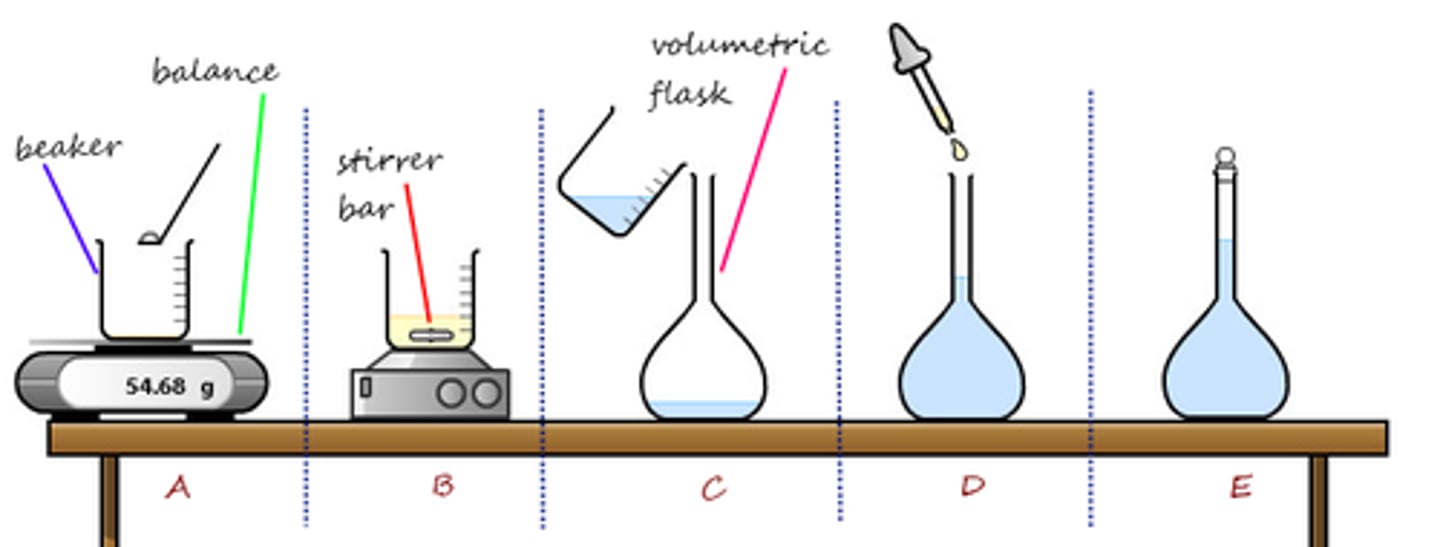
volumetric flask
used for making liquid solutions of precise volumes

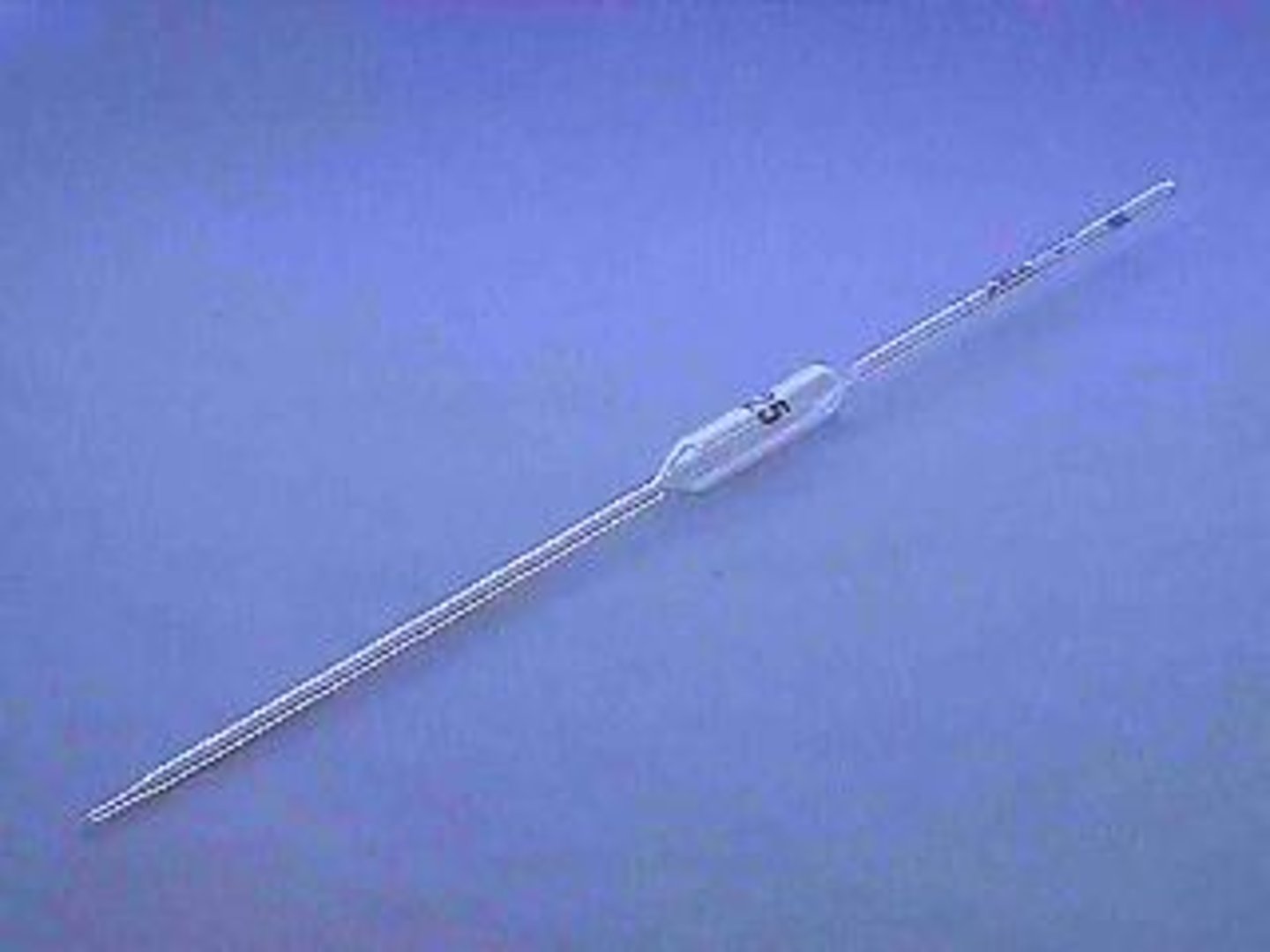
Volumetric Pipet/Pipette
to transfer liquids quantitatively (DELIVERS precise and accurate volumes)

Burette
a graduated glass tube with a tap at one end, for delivering known volumes of a liquid, especially in titrations.

Burette Clamp (test tube clamp)
Used to hold burettes onto the ring stand

Concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent
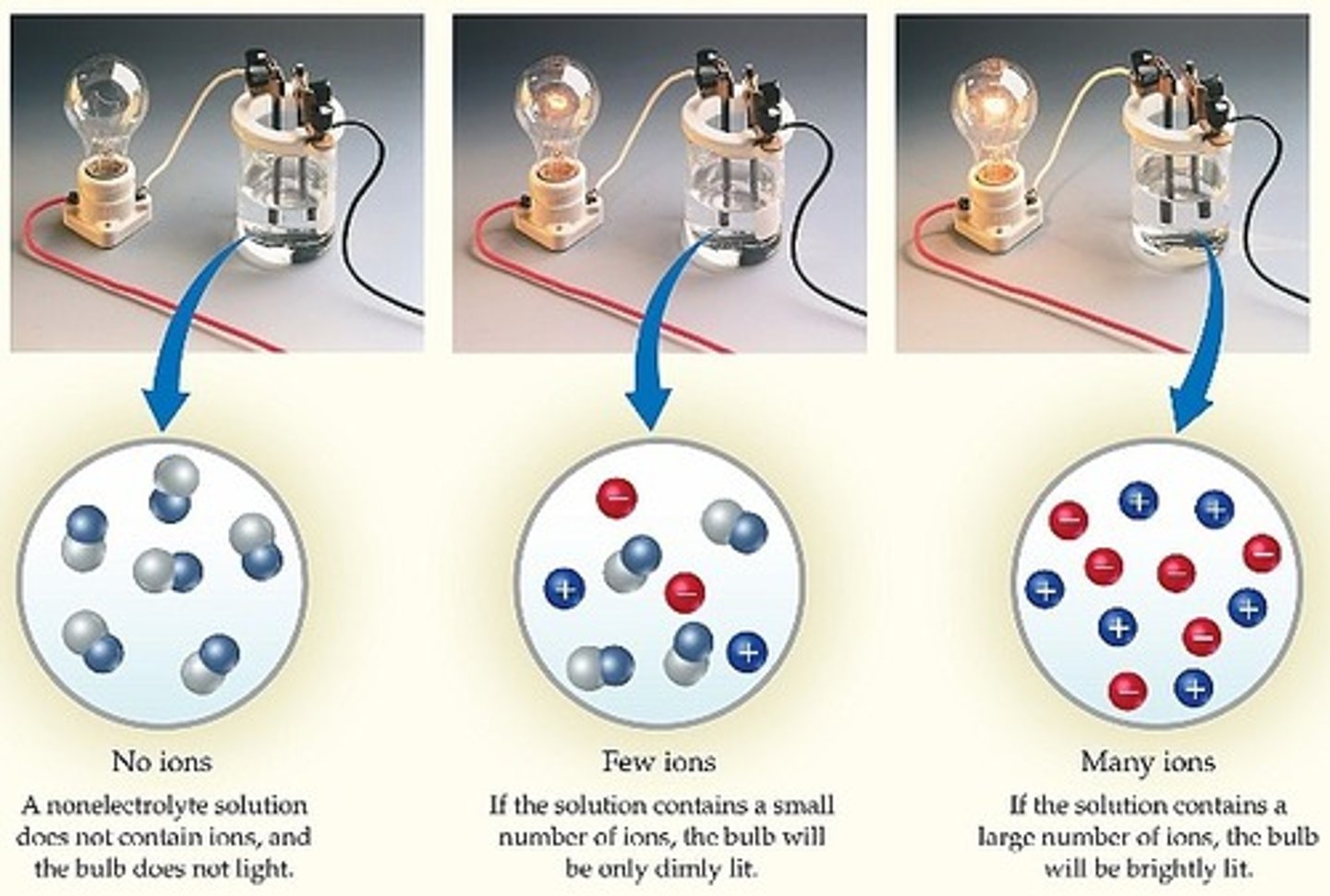
Conductivity of ionic compounds
conduct electricity when dissolved in water because the dissociated ions can carry charge through the solution
Standardised solution
A solution whose concentration is known, having been found by titration against another solution of known concentration
Primary standard solution
A solution prepared from a solid that:
- Is water-soluble.
- Has a high purity.
- Has a known formula.
- Is stable in air.
Equivalence point
theoretical point where the amount of titrant added is stoichiometrically equal to the amount of analyte
Endpoint
Point where visual or instrumental change signals a complete reaction. Often near the equivalence point.
Indicator
Substance that changes color or other physical aspect when at specific PH or concentration.
Ksp
Solubility product constant, or Eq constant for a solid substance for the dissolution of a sparingly soluble ionic compound in a solvent, typically water.
Ka
Acid dissociation constant.
Calculating it is Ka = [H+] [A-] / HA. A- is the concentration of the conjugate base.
Kb
calculate it by, kb = [BH+][OH-] / [B]
kf
molal freezing point depression constant
Amphoterism
acts as both an acid and base
solubility
max amount of substance that can dissolve in a solvent at given temperature
ksp
Eq constant for dissolution of a kinda soluble ionic compound