Lecture 15- Metabolism Catabolism Part 2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
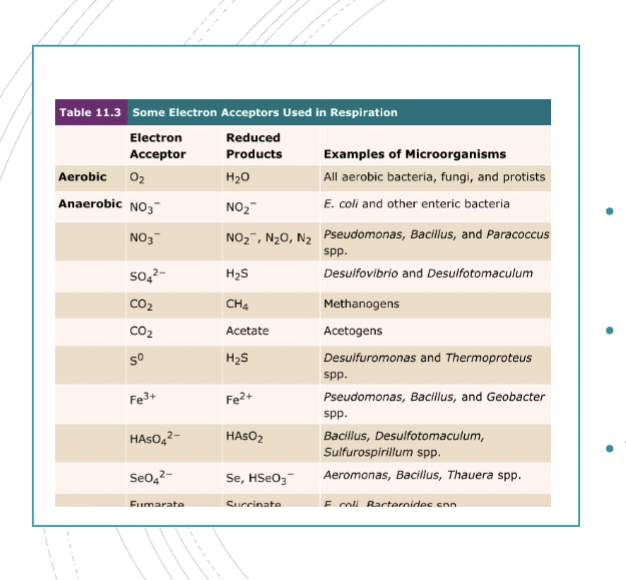
Anaerobic Respiration
Organisms that use electron acceptors other than O₂ carry out glycolysis, the TCA cycle, and electron transport.
NADH and FADH₂ still donate electrons, but ATP yield is lower since O₂ is not the terminal acceptor.
This is common in many bacteria and archaea
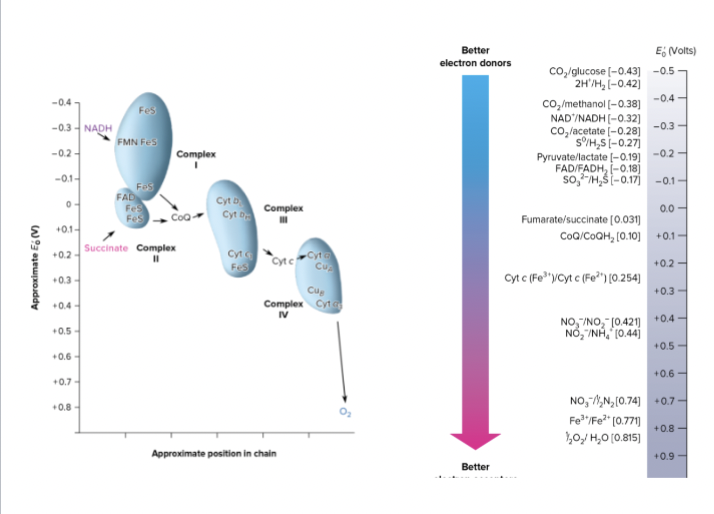
Why is there Less energy production in Anaerobic respiration?
This is because the electron acceptors are less positive than the O2.
Results in a shorter ETC and fewer protons transported.
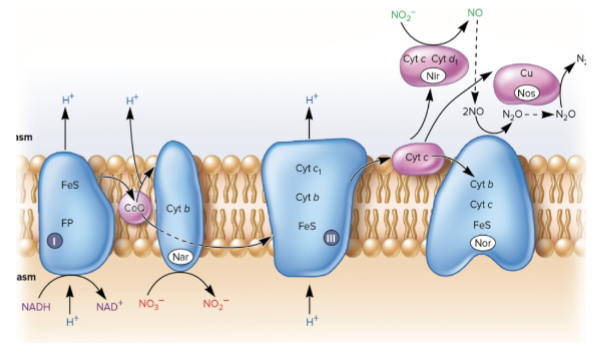
Consequence of using alternate electron acceptor
Using nitrates as a final electron acceptor removes nitrates from the soil.
Depletion results in poor crop outcome.
Causes farmers to use nitrogen-containing soil fertilizer which can ultimately leach into well water.
Fermentation occurs in some organisms
In these organisms, they can undergo glycolysis but can’t undergo ETC or generate an electron motive force.
Takes place in the absence of oxygen or other electron acceptors. Those that can’t undergo respiration, do not have the proteins to complete the process.
Without the ETC, there needs to be an alternative pathway to recycle the reduced NADH. Without oxidation of NADH, the organism will run out of NAD+ molecule to reduce during glycolysis and organism will die
While it doesn’t generate much ATP, it is critical in recycling the reduced NADH molecules into NAD+ so that they can be act as continue to act as electron acceptors.
Indirectly contribute to energy production by keeping glycolysis active.
butyric-butylic fermentation occurs in…
Clostridium species that cause tetanus and botulism
5 Unifying facts in all fermentation pathways
1) O2 is not used.
2) Electron acceptor is pyruvate or pyruvate derivative.
3) NADH must be oxidized to NAD+
4) Decrease in ATP yield as a result of no ETC.
5) Sugar is not completely oxidized to CO2.
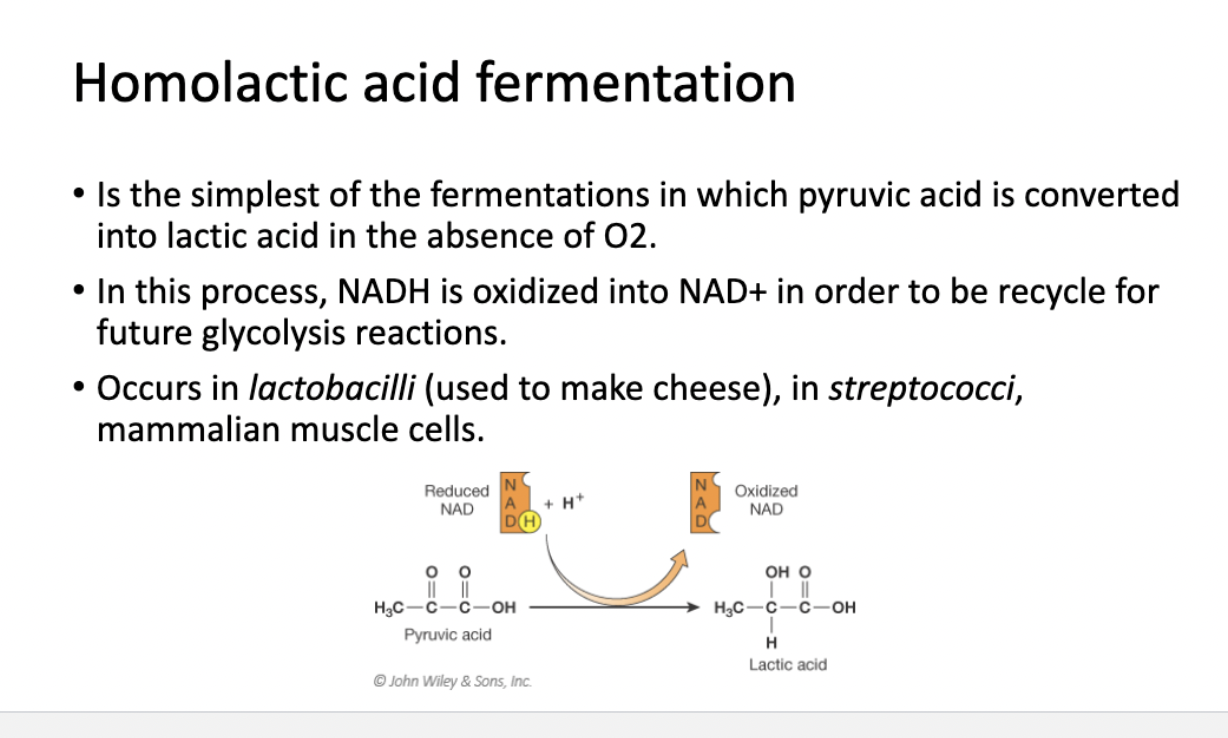
Homolactic acid fermentation
Is the simplest of the fermentations in which pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the absence of O2.
Process of Homolactic acid fermentation
In this process, NADH is oxidized into NAD+ in order to be recycle for
future glycolysis reactions.
Where does Homolactic acid fermentation occur
Occurs in lactobacilli (used to make cheese), in streptococci,
mammalian muscle cells.
Alcohol Fermentation
CO2 is released from pyruvic acid resulting acetaldehyde.
Process of Alcohol Fermentation
The acetaldehyde is reduced to ethyl alcohol using the H on NADH.
Allows the recycling of NADH.
Where does Alcohol Fermentation occur?
Not common in bacteria, but common in yeast and used for making bread and wine.