Protozoan Parasites
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 34, 35, 36, and 37
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
The following general features match which type of parasite:
single celled organisms
small scale (microscopic)
parasitic in all vertebrate hosts
parasitic in all host tissues/systems
variable life cycles
reproduction based on asexual, sexual, combination/alernation involving both modes, and allelic sequence heterogeneity
protozoan
What is the living, motile form of protozoan parasites?
Trophozoite
What is the environmental transmission form of protozoan parasites?
cyst/oocyst
How do protozoan parasites cause disease?
feed on solid tissues directly or after liquefying them
compete with the host for ingested food
destroy host cells by growing in them
production of various toxic substances (hemolysins, histolysins, anticoagulants) that aid in their ability to enter host tissues, feed, or reproduce
cause various host reactions such as allergic, inflammatory, hyperplasia, thrombocytopenia
reduce host resistance to other diseases and parasites
What are the major protozoan groups?
flagellates and coccidia
Which species is described by the following:
single cell, flagellate protozoan parasite
First described in 1681 by Antoine van Leeuwenhoek in his own diarrheic stool
significant confusion with naming the parasite by different parasitologists
ICZN review to determine its “real” identity
Primarily associated with waterborn outbreaks
occupational risk for veterinarians and techs
Giardia spp
What are the three species of Giardia?
G. lamblia
G. duodenalis
G. intestinalis
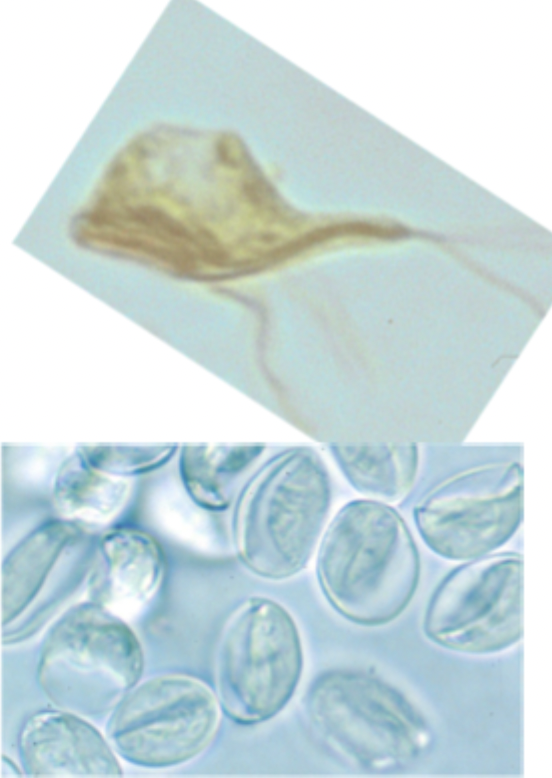
These images match which species?
Giardia sp
The following lifecycle matches which species:
direct lifecycle
trophozoites live free (extra cellular) or attach via ventral sucking disk in lumen of proximal small intestine
Multiply by binary fission with genetic diversity by allelic sequence heterogeneity
Cysts passed in the feces following a 7 to 14 day incubation period
Host infection/re infection via fecal oral contamination and ingestion of immediately infective cysts
Giardia spp
Describe a syptomatic infection of giardia spp in dogs and cats.
watery diarrhea in acute phase (5 days post infection)
voluminous, maldorous stools with mushy consistency
gas, flatulence
cysts appear in stools 7 to 14 days post infection
Clinical signs may persist for 2 to 6 weeks before resolution in immunocompetent animals
Describe a symptomatic infection of giardia spp in humans.
voluminous watery diarrhea
gas, flatulence, greasy stools that float
abdominal discomfort, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, fatigue
symptoms appear 7 to 14 days post infection
illness duration 2 to 6 weeks, may be self limiting if immunocompetent
What is the host range of genotype assemblage A within Giardia duodenalis/intestinalis?
humans, livestock, dogs, cats, beavers, guinea pigs
What is the host range of genotype assemblage B within Giardia duodenalis/intestinalis?
humans, dogs, beavers
What is the host range of genotype assemblage C and D within Giardia duodenalis/intestinalis?
Dog
How do we manage giardia infections in companion animals?
diagnosis by ZnSO4 flotation
supportive care to restore electrolyte imbalances
Treatment with Panacur or Metronidazole
Bathe pet at beginning and end of treatment protocol to remove imediately infective cysts
disinfection os pet reisdential environment usin chlorine bleach at a high concentration, lysol, or quaternary ammonia compounds
What do we have to worry about when treating giardia infections with prolonged use of metronidazole?
neurotoxicity
The following description matches which species:
flagellate protozoan parasite in large intestine of cats
causative agent of chronic diarrhea (long duration, cats otherwise healthy)
Lymphoplasmacytic/neutrophilic colitis, crypt abscess, increased mucous production, generalized erosionof colonic mucosa
Tritrichomonas blagburni
Which species was formerly known as T foetus until molecular genetic confirmed identity as a distinct species?
Tritrichomonas blagburni
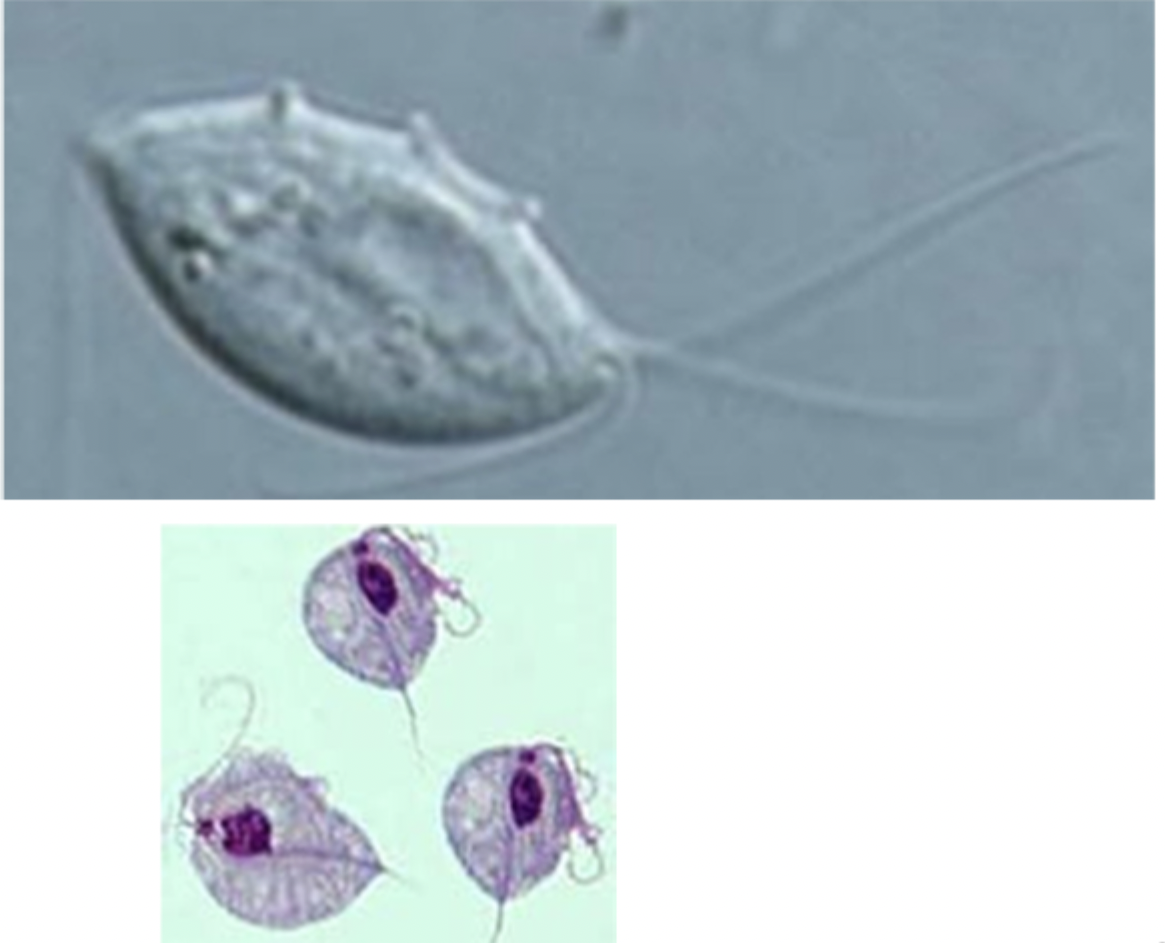
These images match whcih species?
Tritrichomonas blagburni
How do we diagnose infection with Tritrichomonas blagburni ?
microscopically by direct smear to differentiate from Giardia
PCR specific assay to identify organism isolated from infected animals
Fecal culture and isolation in commercially available media will increase sensitivity
How do we treat infections of Tritrichomonas blagburni?
No FDA approved treatment but can use Ronidazole or Metronidazole despite neurotoxicity (although reversible) has been reported with use of both drugs
How do we prevent infection of Tritrichomonas blagburni?
suspected transmission between hosts by fecal oral route
no environmentally resistant cyst stage
trophozoites may survive outside of host for variable times
segregate infected cats, separate litter boxes
not known to be zoonotic
The followng description matches which species:
flagellate protozoan parasite in the reproductive tract of cattle
morphologically indinstinguishable from T. blagburni and other Trichomonad protozoa
causative agent of bovine genital trichomoniasis
bulls are generally symptomatic and responsible for herd level infections
diagnosis by PCR and culture methods
Tritrichomonas foetus
What are the symptoms of bovine genital trichomoniasis?
infertility
spontaneous abortion in first trimester
generalized reproductive tract infection
Blood and tissue flagellates are broadly classified as what?
Trypanosomes
The following description matches which type of protozoan parasite:
family members wekk known as causative agent of Affrican Sleeping Sickness and Chagas Disease
Flagellate trophozoite stage circulating in blood/lymph known as Trypomastigote, which is infective for the vertebrate host
classified by mode of transmission (anterior station vs posterior station)
Blood and Tissue Flagellates (Trypanosomes)
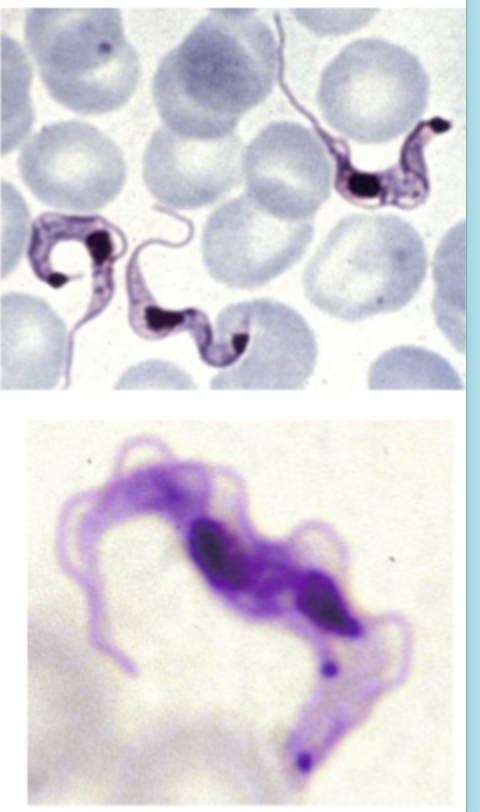
These images match which type of protozoan parasite?
Blood and Tissue Flagellates (Trypanosomes)
These general lifecycle features match which type of protozoan parasites:
arhtropods intermediate host and are infected during blood meal
epimastigotes divide and multiply in intermediate host
develop into Trypomastigotes in intermediate host
tansferred to human/animal host
multiplication in human/animal host
Blood and Tissue Flagellates (Trypanosomes)
Which disease is decribed by the following:
T brucei and T gambiense
live in blood, invade lymph nodes, intercellular spaces
generally produce anemia from imune mediated processes and mechanisms (depressed erythropoiesis, hyperplasia bone marrow and spleen, erythrophagocytosis because trypanosome antigens attach to RBCs)
animal production limited to areas where disease is not prevalent
African Trypanosomiasis
Which species is the causative agent of Chaga’s Disease or American Trypanosomiasis?
Trypanosoma cruzi
What are the obligate intermediate hosts for Trypanosoma cruzi?
Triatomin/Reduviid bugs
What are the reservoirs for Trypanosoma cruzi?
armadillo, monkeys, dogs, cats, opossum, rodents, raccoons
How is Trypanosoma cruzi transmitted by vectors?
active defecation by intermediate host
ingestion of intermediate host
How is Trypanosoma cruzi transmitted by something other than vectors?
blood transfusion
organ/tissue transplantation
congenital
lab exposure
fecal contamination of food items
How does genotypic variation affect Trypanosoma cruzi?
geographics
host associations
transmission
disease potential
response to treatment
What is Romana’s sign?
edema and inflammatory response resulting from trypomastigotes defecated on host and rubbed into eye
Trypomastigotes proliferate asexually in histocytes as what?
amastigote stage organisms
How do we diagnose Chaga’s disease?
serology and PCR
What are clinical signs of Chaga’s disease in dogs?
lymphadenopathy
myocarditis
pale mucous membranes
tachycardia
splenomegaly
Which protozoan parasite species is described by the following:
parasites infecting macrophages of vertebrate hosts
Amastigote stages only and transmitted by sand fly bite
Associated with visceral disease, mucocutaneous disease, cutaneous disease depending on species
Leishmania sp
Which species of Leishmania sp are associated with visceral disease?
L. donovoni
L infantum (L. chagasi)
Which species of Leishmania sp are associated with muco-cutaneous disease?
L mexicana
Which species of Leishmania sp are associated with cutaneous disease?
L. tropica
T cruzi infection should be on the differential diagnosis for dogs presenting with symptoms of what?
cardiac disease including lymphadenopathy, tachycardia, ascites, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
Leishmania infections should be on the differential diagnosis doe dogs presenting with symptoms of what?
dermatologic disease and infection including lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
A SNAP test for giardia tests for what?
fecal antigen
Which species of protozoan parasite does not have a cyst stage?
Tritrichomonas blagburni
The following general features match which type of protozoan parasite:
intracellular parasites of intestinal epithelium, endothelium blood vessels, organs, and other tissues
gliding locomotion
tropozoites with apical complex
asexual and sexual replication in vertebrate and invertebrate hosts
1 host lifecycles are monoxenous and may use a paratenic host
2 host lifecycles are heteroxenous and can be obligate or facultative indirect
Coccidia
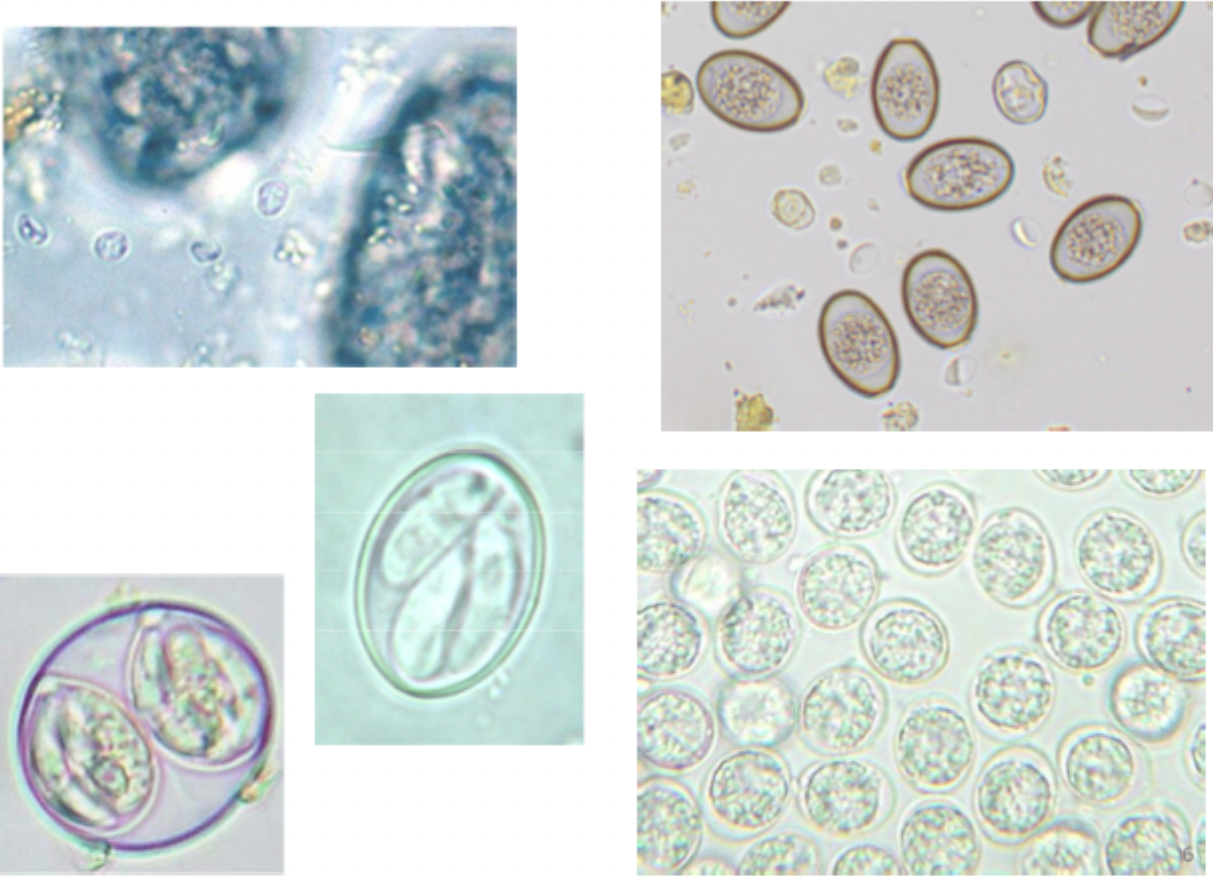
These images match which type of protozoan parasite?
Coccidia
Which species of coccidia are intestinal?
cryptosporidium
eimeria
cystoisospora
Which species of coccidia are found in tissues?
toxoplasma
neospora
sarcocystis
Which species of coccidia are found in blood?
hepatozoon
babesia
cytauxzoon
Which coccidia species matches the following description:
primarily associated with waterborne outbreaks
foodborne outbreaks can be ue to homemade, natural unpasteurized apple cider or from bottled water for pediatric colic
occupation risk
metabolically divergent from other Apicomplexa (Lack Krebs cycle so unable to synthesize fatty acids, lack plastid bodies for mannufacturing food, unresponsive to drugs)
host specificity is variable
oocysts passed in feces, are immediately infective, and morphologically indistinguishable
able to survive in the environemtn and water treated with chlorine
Cryptosporidium spp
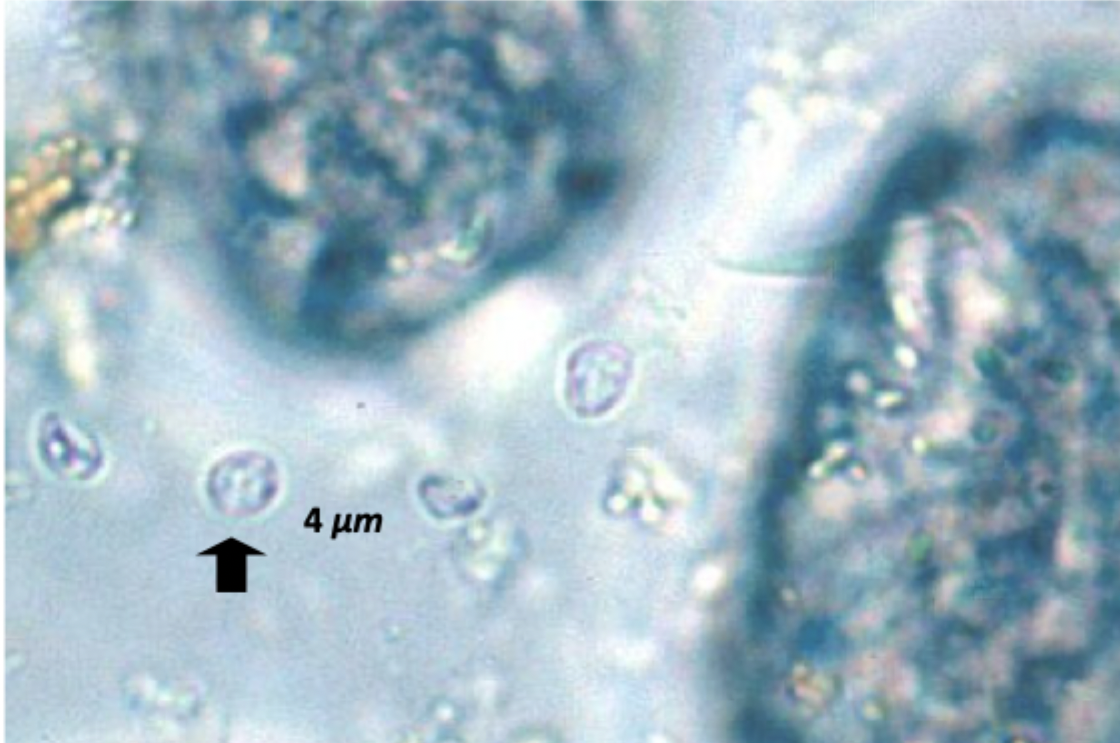
This image matches which species?
Cryptosporidium spp
The following lifecycle matches which species:
direct lifecycle
sexual and asexual replication occur in the small intestinal epithelium (inter-cellular)
oocysts passed in the feces following 3-5 day incubation period
immediately infective
host infection via fecal oral contamination and ingestion of oocysts
infectious dose with as few as 9 oocysts
infections can be asymptomatic or symptomatic
Cryptosporidium spp
What are the clinical features of a symptomatic infection with Cryptosporidium spp?
voluminous watery diarrhea
mucous present, rarely blood/leukocytes
abdominal discomfort, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, fatigue, fever
mean illness duration 12 days but may be self limiting if immunocompetent
In which animals do we usually see apparent infections of Cryptosporidium?
Dairy calves 1-3 weeks of age
What can act as a persistent source of reinfection for Cryptosporidium in animals?
oocyst contamination of bedding environment
Are Cryptosporidium infections seen in companion animals zoonotic?
Only in immunocompromised persons
How do we diagnose Crypotsporidium infection?
Sucrose fecal flotation focused immediately below the coverslip
What is the therapy protocol for animals infected with Cryptosporidium spp?
no consistently effective, approved pharmaceutical for use in animals
not cost effective for use in cattle/calves
supportive care to restore electrolyte imbalance from diarrhea
What is the therapy protocol for humans infected with Cryptosporidium spp?
Nitazoxanide which interferes with anaerobic energy metabolism of parrasite
How do we disinfect areas where Crptosporidium spp have been found?
ammonia compounds, ethylene oxide, methyl bromide, and ozone appear to be most effective
hydrogen peroxide and formaldehyde containing compounds show promise with increased contact times
oocysts in milk and water killed by commercial pasteurization
chlorine not effective
Which species of coccidia matches the following description:
intestinal
direct lifecycle (ingestion of sporulated oocysts, 4 sporocysts each with 2 sporozoites)
domestic livestock, birds, and grazing wildlife are definitive hosts
asexual replication in small intestine
diarrhea associated with destruction of enterocytes by developing oocysts sexual reproduction in fresh uninfected cells of large intestine
Eimeria sp
What is the term for disease that is associated with onset of sexual replication in host tissues and causes mechanical disruption of mucosal cells by gametes (sexual stage)?
Coccidiosis
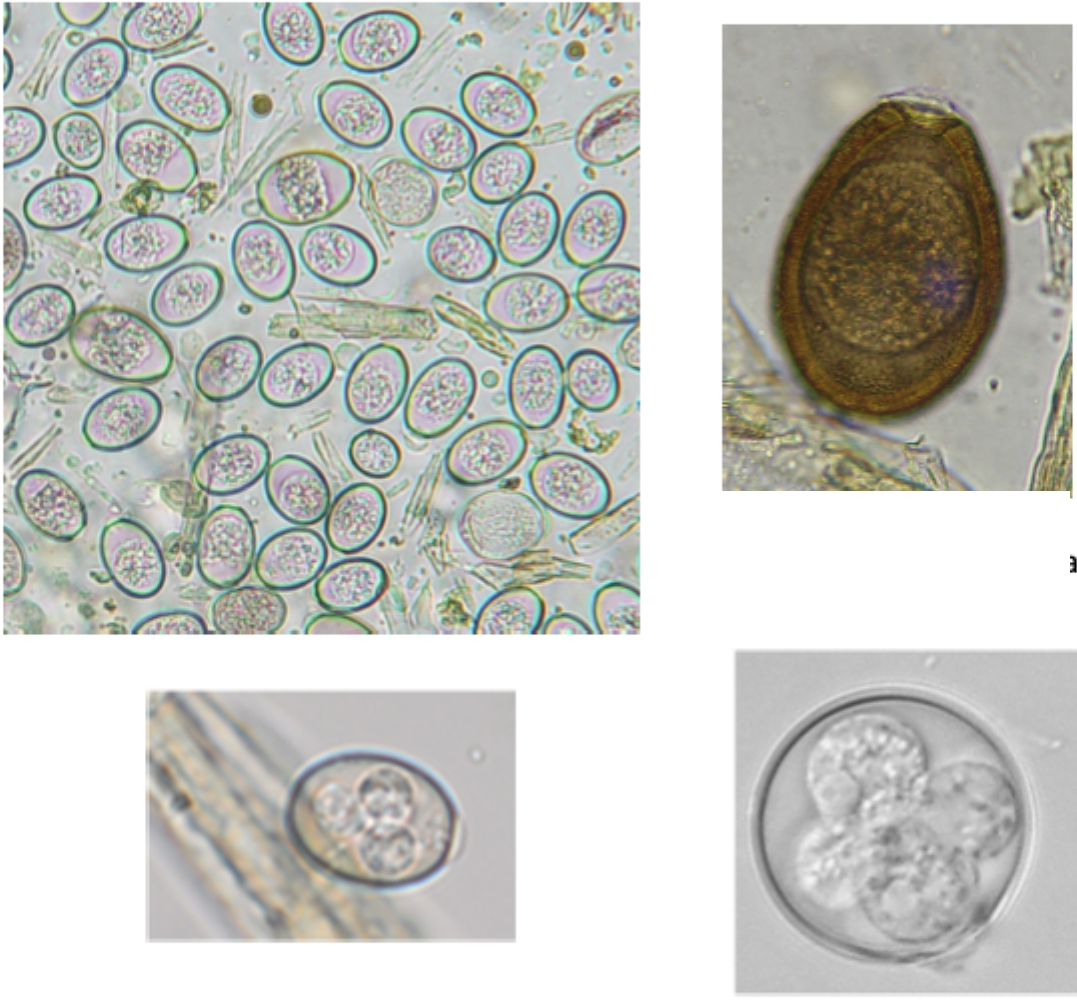
These images match which coccidia species?
Eimeria
Coccidiosis is a function of what?
age
nutrition
stress
sex
season
gestational status
inherent pathogenicity
What species causes coccidiosis in sheep and goats?
Eimeria ovinoidalis
What species cause coccidiosis in cattle?
Eimeria bovis
Eimeria zuernii
Risk of disease with coccidia species is a function of what?
environmental contamination
moderate levels of infection
stress in the host population
How do we prevent coccidiosis?
environmental hygiene (removal of manures, keep surfaces dry and clean)
chemoprophylaxis (targets asexual stage of replication)
All treatment decisions for coccidiosis need to be based on what?
holistic assessment of environmental contamination, health status of herd, risk of exposure to susceptible hosts, and production goals
Which drugs arrest development at specific stages of the lifecycle but allow parasites to remain alive in the tissues so withdrawal of the drug allows the parasite to resume development and completion of the lifecycle?
Coccidiostatic drugs
Which drugs kill or damage the parasite irreversibly so there is no disease relapse following drug withdrawal?
Coccidiocidal drugs
Which drugs may have static and cidal properties depending on dose of the drug and length of parasite exposure to the drug?
Anticoccidial drugs
Which drug is decribed by the following:
coccidostatic activity
administered as feed additive for 28+ days for prevention of coccidiosis
acts on sporozoite stage
no activity against adult parasites
not approved for lactating cattle, laying poultry
Decoquinate (Deccox)
Which drug is decribed by the following:
coccidiostatic activity
administered in drinking water for 21 days at 5mg/kg for PREVENTION of coccidiosis
administered in drinking water for 5 days at 10mg/kg for TREATMENT of coccidiois
acts on first generation schziont in the intestinal cell wall to prevent differentiation into metrozoites
has ability to suppress sexual stages and sporulation of ocysts
not approved for lactating cattle, laying poultry
more effective as preventative than treatment
Amprolium (Corrid)
Which drug is decribed by the following:
coccidiocidal activity
FDA approval for prevention of coccidiosis in poultry
extra label use for control in cattle, sheep, goats dogs, and cats
acts on “apicoplast” organelle involved in biosynthesis of fatty acids and amino acid metabolism
has ability to suppress sexual stages and sporulation of oocysts
not approved for lactating cattle, laying poultry
Diclazuril (Clincox)
Which drug is decribed by the following:
coccidiocidal activity
FDA approval for prevention of EPM (Sarcocystis neurona) in horses; neosporosis (Neospora caninum) in cattle
acts on “apicoplast” organelle involved in biosynthesis of fatty acids and amino acid metabolism
has ability to suppress sexual stages and sporulation of oocysts
not approved for lactating cattle, laying poultry
Ponazuril (Marquis)
Which drug is decribed by the following:
coccidiocidal activity
Not available in US with FDA approval
acts on “apicoplast” organelle involved in biosynthesis of fatty acids and amino acid metabolism
has ability to suppress sexual stages and sporulation of oocysts
not approved for lactating cattle, laying poultry
Totazuril (Baycox)
Which drug is decribed by the following:
coccidiostatic and coccidiocial actviity
active against folic acid pathway and interfere with folate biosynthesis
significant negative effects on gut microbiota
TMS potentially teratogenic so must weigh benefit vs risk adverse effects
Sulfonamides (Sulfadiazene, Sulfadimethoxine aka Albon, Trimethoprim/Sulfaiazine aka TMS, Tribrissen)
Watery diarrhea in a SINGLE young animal at 1-4 weeks of life with emaciation is suggestive of what?
cryptosporidiosis
What are the usual differential diagnosis for older animals with diarrhea?
coccidia (Eimeria spp) in animals 21 days and older or Ostertagia (anorexia, poor growth) in animals <2 years of age and having chronic presentation
What is your differential diagnosis for 1-4 day old calves presenting with acute and lethal hemorrhagic diarrrhea?
colibacilliosis
What is your differential diagnosis for multiple cases of viral diarrhea?
rotavirus if animals are 5 days to 2 weeks of age
coronavirus if animals are 4 to 30 days of age
Which species of coccidia is described by the following:
intestinal
faculative direct/indirect lifecycle (ingestion of sporulated oocysts, 2 sporocysts each with 4 sporozoites)
cats, dogs, pigs and some birds are definitive hosts
mice, birds, rodents are paratenic hosts
sexual/asexual replication in small intestine
diarrhea associated with destruction of enterocytes
prepatent period 6-12 days
Cystoisospora spp (synonymous with Isospora spp)
Which Cystoisospora spp affect dogs?
C canis
C ohioensis
Which Cystoisospora spp affect cats?
C felis
C rivolta
Which Cystoisospora spp affecting the dog is teardrop shaped and 40 × 30 micrometers?
C canis
Which Cystoisospora spp affecting the cat is teardrop shaped and 40 × 30 micrometers?
C felis
Which Cystoisospora spp affecting the dog is round and 25 micrometers in diameter?
C. ohioensis
Which Cystoisospora spp affecting the cat is round and 25 micrometers in diameter?
C rivolta
How do we manage intestinal coccidia infections in companion animals?
diagnosis by centriful ZnSO4 or sucrose flotation
supprtive care to restore electrolyte balances
Treat dogs with Albon
Treat cats with Trimethoprim sulfadiazene
bathe pet at beginning and end of treatment protocal to remove immediately infective cysts
remove feces daily
Which species is an unequivocally zoonotic parasite, immediately infective, and is associated with waterborne outbreaks?
Cryptosporidium
How do intestinal coccidia cause disease?
by invasion and mechanical destruction of cells in the intestinal tissues of their host species
Which species is tiny with 4 naked sporozoites, immediately infective?
Cryptosporidium
Whcih species is characterized by 4 sporocysts each with 2 sporozoites?
Eimeria
Which species is characterized by 2 sporocysts each with 4 sporozoites?
Cystioisospora
Sporulated oocysts must be ingested via what route to infect the host?
fecal oral
What is a function of limited asexual replication and a single generation of sexual replication in their hosts?
Expression of disease