Physiology: Salivary Gland and Saliva Formation
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
what are the 4 stages of food processing?
ingestion
digeation
absorption
egestion
what is ingestion?
taking in nutrients (proteins/amino acids, carbohydrates/glucose and fats/triglycerides)
what is digestion?
using physical and chemical means to break down complex organic molecules into smaller usable parts
what is absorption?
pulling in digested molecules into the cells of the digestive tract, then into the blood
what is egestion?
the removal of waste food materials (e.g. cellulose = fiber) from the body
what are the 3 phases of digestion?
cephalic (reflex) phase
gastric phase
intestinal phase
what is the cephalic (reflex) phase of digestion?
begins prior to food entry. Salivary gland secretion is the major component of the cephalic phase
what is the gastric phase of digestion?
Begins with the arrival of food in the stomach
what is the intestinal phase of digestion?
Begins as partially digested food enters the duodenum
cephalic phase: purpose
To prepare the body for a meal
cephalic phase: stimuli
Thoughts, site, sound, smell of food
cephalic phase: response
increase Parasympathetic Outflow
cephalic phase: effect
Salivation, gastric and pancreatic secretion and release of bile to the GI tract
how much liquid is ingested and secreted throughout the GI tract?
2 L ingested
7 L secreted into GI tract
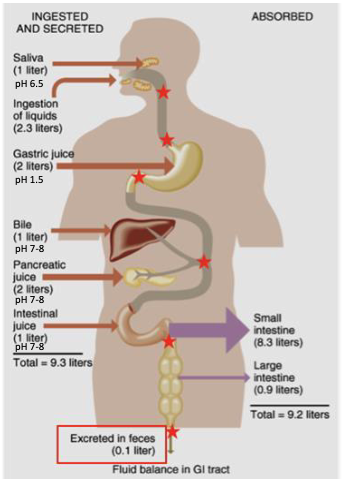
what are some stimulants for secretion?
Local effect of luminal contents
Autonomic stimulation
Parasympathetic: usually increases
Sympathetic: usually decreases
Hormonal and paracrine stimulation
which CNs are responsible for salivation?
VII and IX
which CNs are responsible for foregut outflow?
X
Oral homeostasis is dependent upon …?
saliva and its content of proteins
what are some positive regulators of saliva production?
• Thought of Food
• Smell of Food
• Sight of Food
• The Act of Chewing
• Nausea
what are some negative regulators of saliva production?
• Dehydration
• Sleep
• Fear
• Anticholinergic drugs
t/f; Reflex salivary flow occurs at a low 'resting' rate and for short periods during the day more intense taste or chewing stimuli evoke a ≥ ten-fold increases in salivation
true
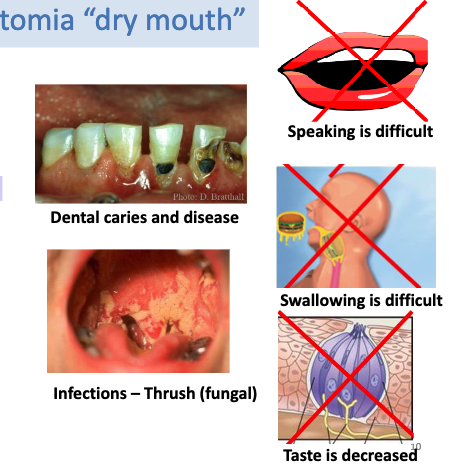
what are some causes of xerostomia?
• Medications, especially anticholinergics
• Nerve damage
• Autoimmune destruction (Sjogren’s)
• Infection (HIV)
• Radiation
• Severe dehydration
what are some effects of xerostomia?
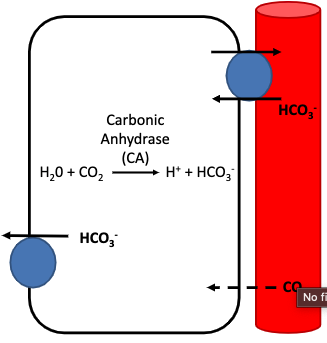
bicarbonate is essential in the GI tract for…?
• Buffering pH fluctuations
• Neutralizing gastric acid and providing optimal pH for digestive enzymes in duodenum
• Helps solubilize macromolecules (mucin, bile acids)
• HCO3- source: plasma, CA, GI lumen
what enzyme is involved in bicarbonate transport to/from blood circulation + lumen of small itntestine?
carbonic anhydrase
what are the 3 pairs of salivary glands that produce the majority of our saliva?
parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands
what duct drains the parotid gland opposite to the upper second molar?
Stensen's duct
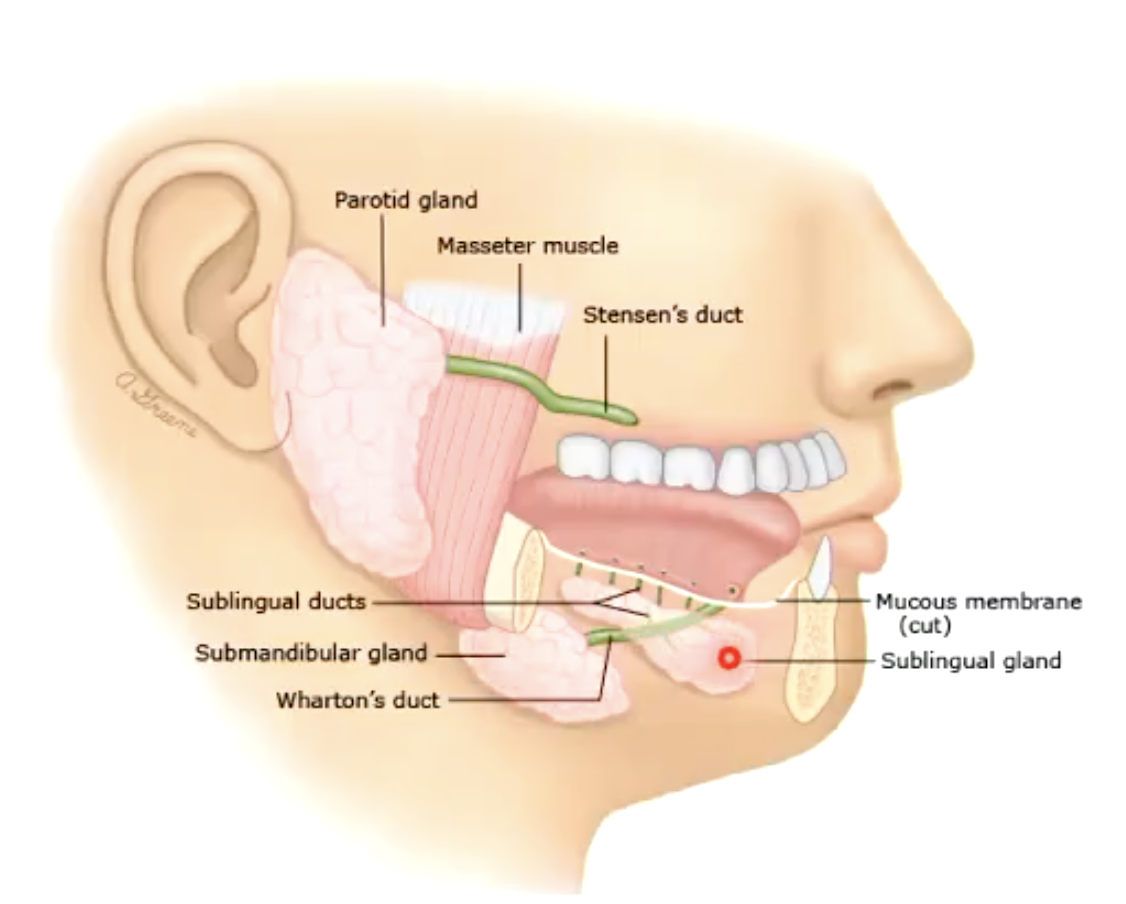
what duct drains the submandibular and some of the sublingual glands into the floor of the mouth near the frenulum of the tongue?
Wharton's duct
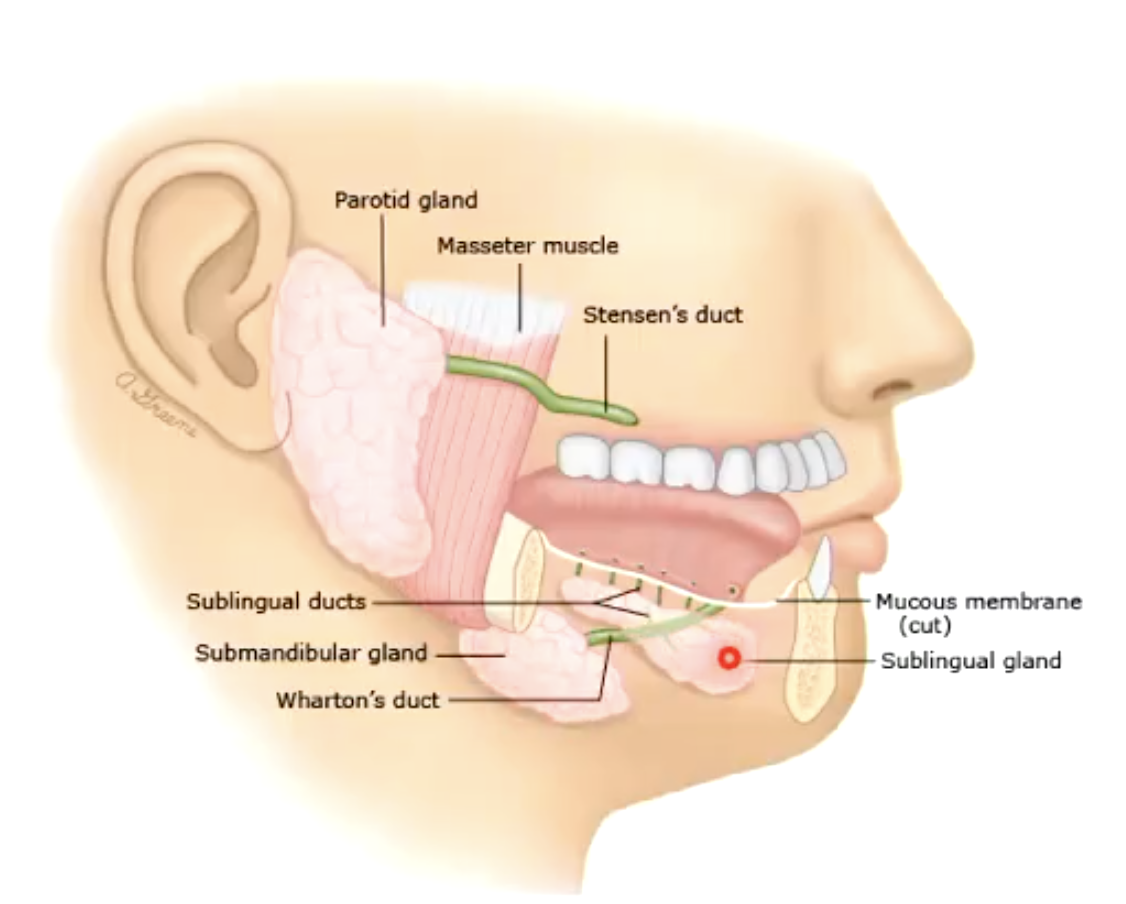
There are approximately ___ minor salivary glands in the mouth
600
Each salivary gland empties saliva into the ___
mouth
% salivary secretion is from the 3 major salivary glands
90%
Salivary Secretions from Acinar Cells include:
alpha-amylase
lipase
mucin
extracellular fluid (similar in ionic composition to plasma)
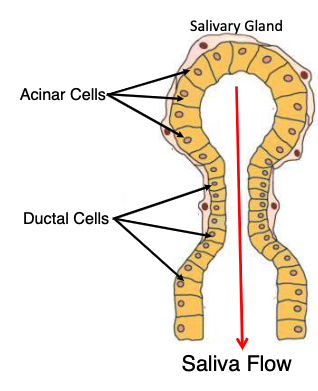
what is the function of alpha-amylase?
begins carbohydrate digestion and is inactivated by low pH
what is the function of lipase?
begins lipid digestion by converting triglycerides to fatty acids and monoglycerides
what is the function of mucin?
important in bolus formation and swallowing food being ingested
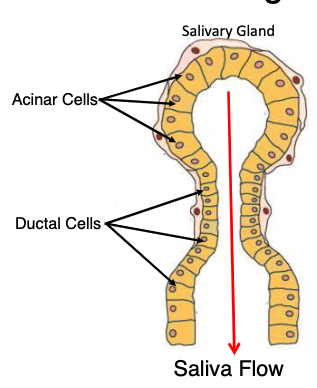
what do ductal cells do?
actively modify the ion content of saliva by absorption and secretion
t/f: Most salivary ductal cells express aquaporin (water) channels in their apical membrane.
false. The majority of salivary ductal cells do not express AQP channels and are impermeant to water. Without this feature it would be impossible to produce hypotonic saliva
______- condition (<Na+) of saliva entering the mouth aids the detection of salt in the diet
Hypotonic
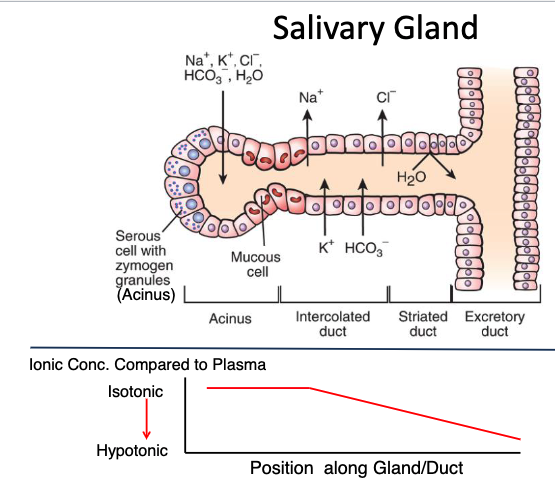
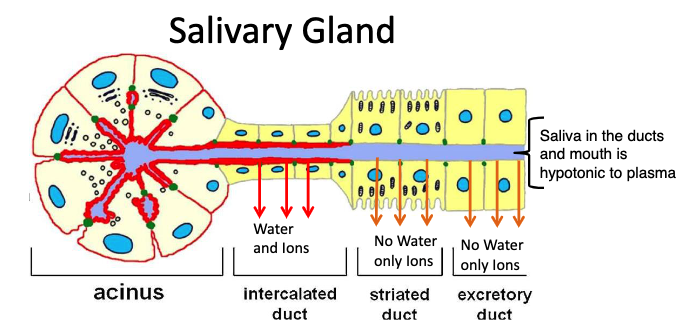
Apical membrane (red) shows those cells expressing ______ channels
aquaporin (AQP, water)
t/f: Saliva in the ducts and mouth is hypotonic to plasma
true
Parasympathetic stimulation of the salivary glands results in …?
increased secretion of fluid and ions from the acinar and ductal cells
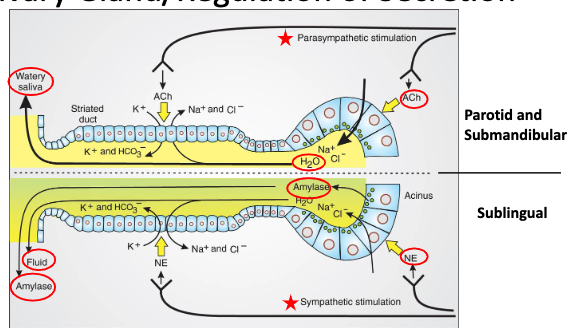
which nervous system controls the majority of salivary secretion?
PNS
t/f: Sympathetic stimulation of the salivary glands increase fluid, ion and protein secretion but is a minor contributor to increase in fluid volume
true
do GI hormones play a role in the regulation of salivary secretion?
GI hormones play NO role in the regulation of salivary secretion
Relative saliva contribution of the major salivary glands is as follows:
UNSTIMULATED
1) Submandibular gland=69%
2) Parotid gland=26%
3) Sublingual gland=5%
Relative saliva contribution of the major salivary glands is as follows:
STIMULATED
1) Parotid gland=69%
2) Submandibular gland=26%
3) Sublingual gland=5%
WHAT IS the most common disorder of the major salivary glands?
STONES (SIALOLITHS)
what are some diseases of the salivary gland?
• Stones (sialoliths)
• Bacterial infection (sialadenitis)
• Viral infection (ie. Mumps and flu)
• Sjögren's syndrome
• Benign pleomorphic adenomas
• Cancerous tumors
______ secretion is important in protecting the mouth from pH shifts and maintaining a pH neutral environment where amylase and lipase are active
Bicarbonate
what is responsible for the hypotonic saliva that enters the mouth?
The lack of aquaporin channels (AQP) in the apical membrane of most of the ductal cells
__________ stimulation of the salivary glands results in increased secretion of fluid and ions from the acinar and ductal cells.
Parasympathetic (Controls the majority of salivary secretion (volume))