Neuroanatomy
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Head and Brain + Cranial Blood Supply & Cranial Nerves + Extremity Nerves
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Cranial Meninges
3 membranes encloses the brain and spinal cord
three layer:
Dura mater = tough mother. periosteal and meningeal
Arachnoid mater= spider web like
pia mater - pia= tender
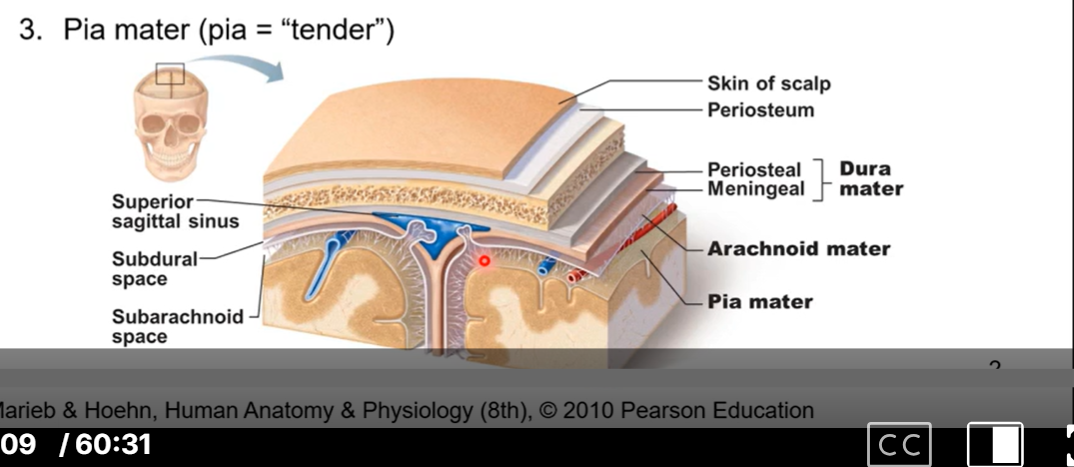
Function of cranial meninges
protect brain
supporting framework for vessels & venous sinuses
enclose fluid filled space (subarachnoid) vital for normal function of brain.
1st layer of the cranial meninges - dura mater
adherent to internal surface of skull
two layered membrane
external periosteal layer
same as periosteum lining of calvaria
internal meningeal layer
strong fibrous layer
continuous at foramen magnum with spinal dura mater
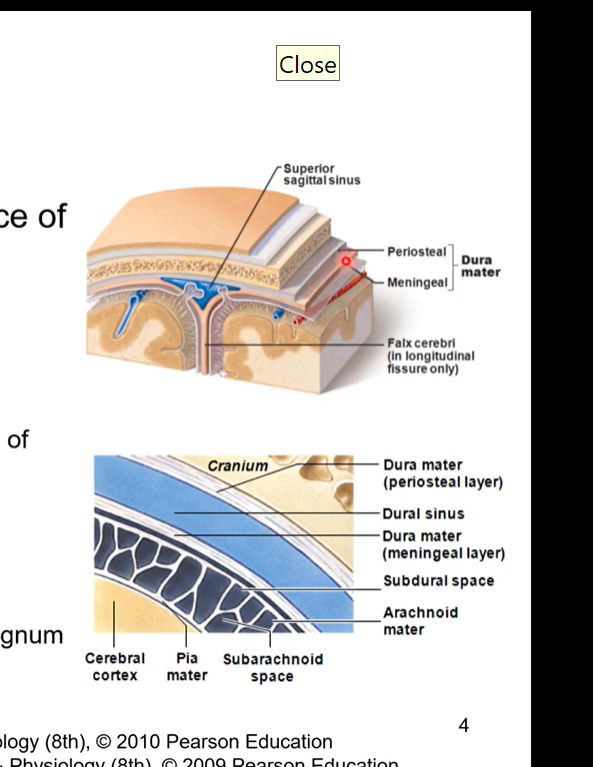
Dura mater meningeal layer and cerebri and cerebelli
Meningeal layer draws away from external layer to form dural infoldings
largest is the falx cerebri which divides cranial cavity and cerebral hemispheres
falx cerebelli separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
tentorium cerebelli separates occipital lobes and cerebellum
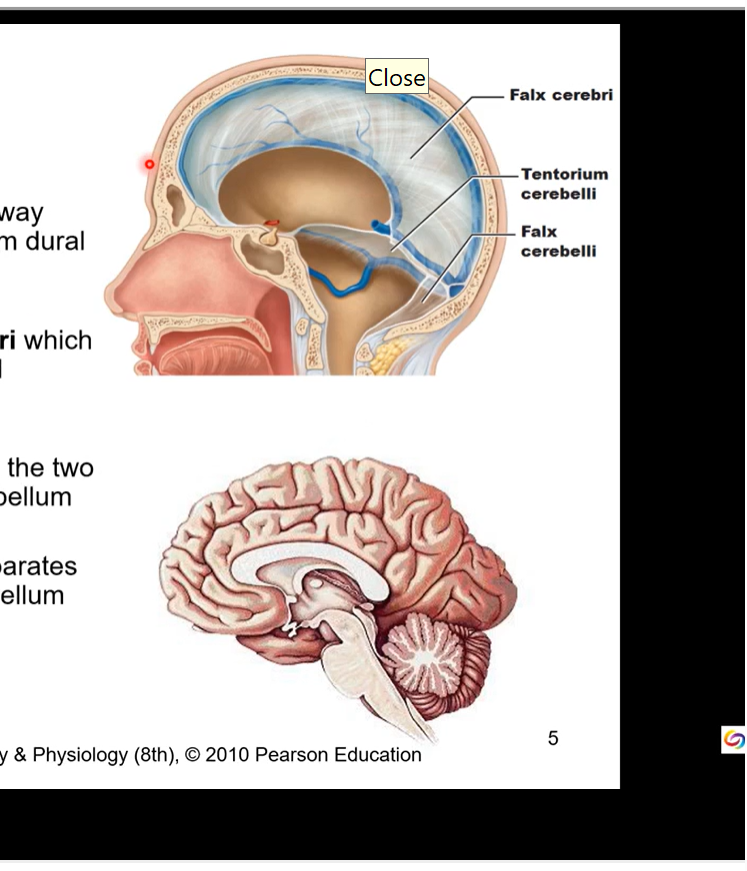
Dura Mater Spaces
dural infoldings spaces= sinuses
venous drainage via sinuses
large veins from brain drain into there sinuses
superior sagittal sinuses lies within the falx cerebri
begins at crista galli and ends at occipital protuberance
all join at confluence of sinuses
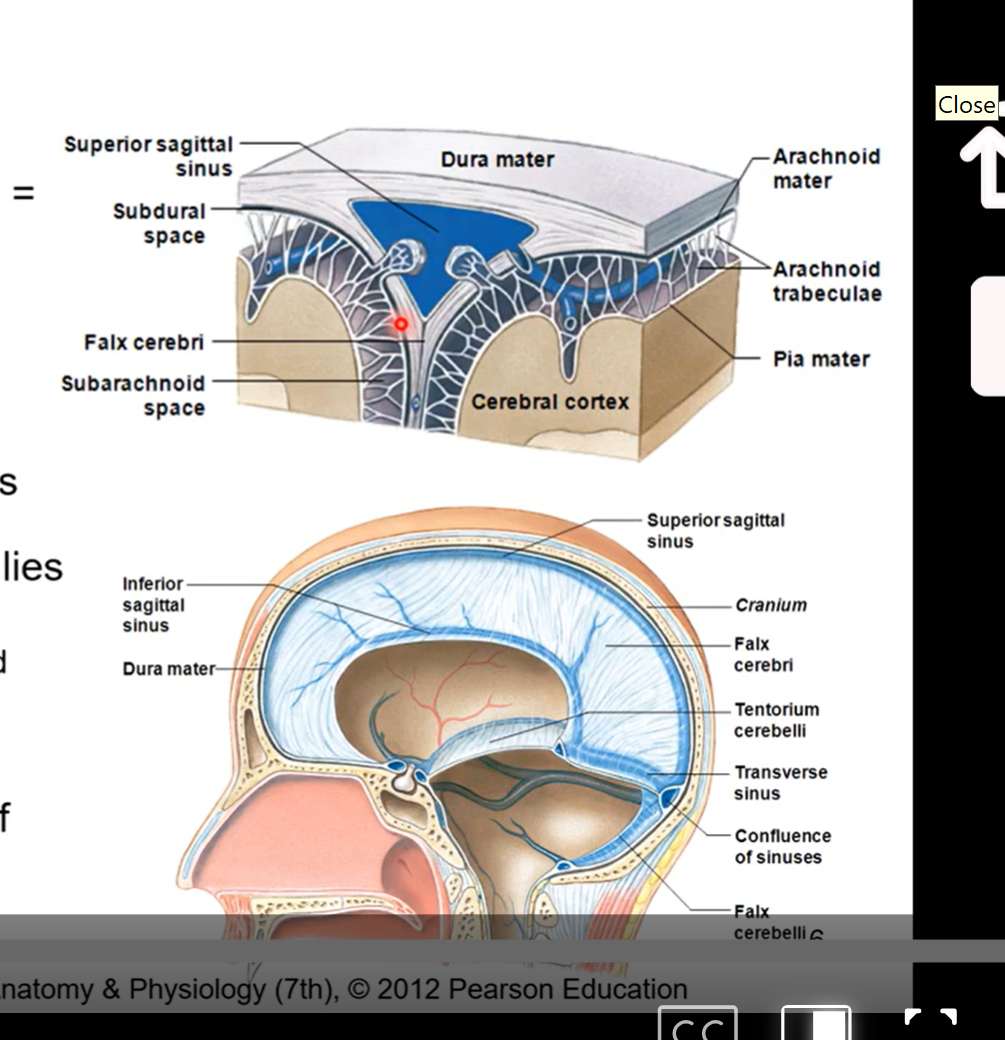
2nd layer of the cranial meninges - arachnoid mater
the meningeal layer of dura mater lines on top of this
it is separated from dura mater. the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid pushes the meningeal layer of dura mater and the arachnoid mater closer together
with no cerebrospinal fluid arachnoid layer would collapse down and stick to the pia mater
arachnoid mater contains fibroblasts, collagen fibres, and some elastic fibres
avascular in nature ( no blood is being supplied to the arachnoid mater. but there are blood vessels going through the arachnoid trabecula.
held against dura mater by pressure of cerebrospinal fluid. ( not direct attachment)
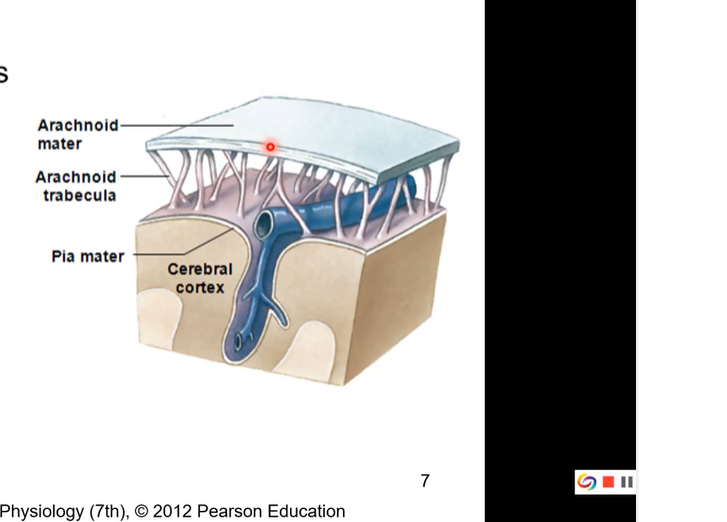
3rd layer of the cranial meninges - pia mater
thinner than arachnoid
high vascularized ( lots of blood going though it)
gives brain shiny appearance
invests within all folds and contours of the brain
adds layer of protection and vascularization to the skin of brain
hard to dissect away cause lots of folds
everyone has a unique pattern to their cerebrum and everyone’s folds and contours are different
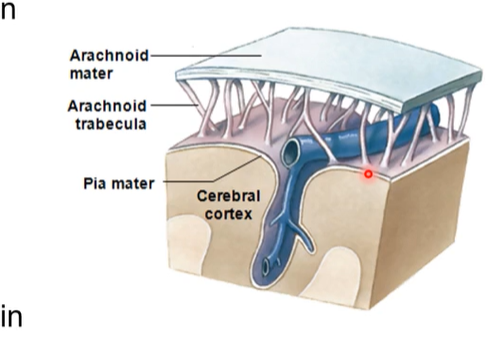
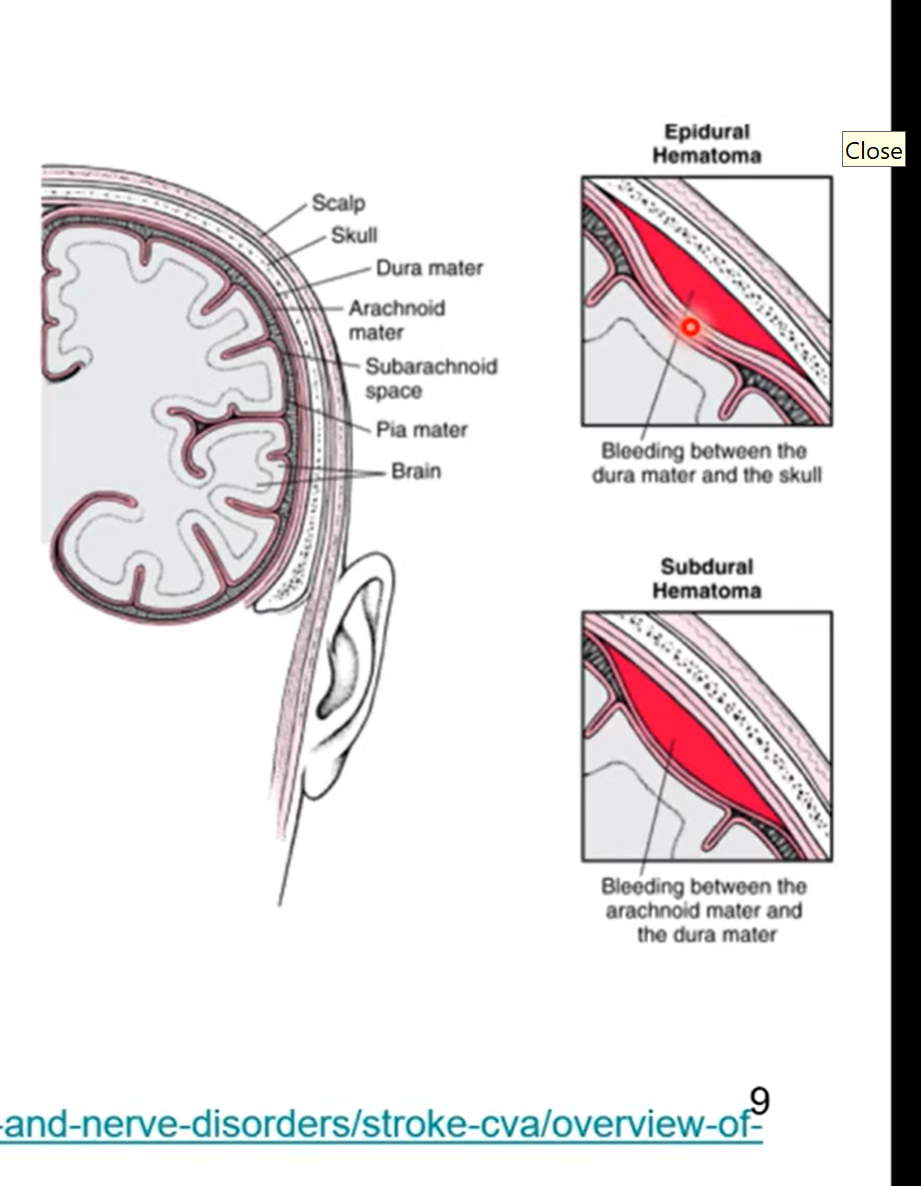
Meningeal spaces
3 spaces
subarachnoid
actual space- contains cerebral spinal fluid, arteries, and veins. healthy space
epidural space
occurs with some sort of injury
potential space- observed with injury
hematoma - blood leak from vessel in brain
Subdural
potential space with injury
what is the brain made of, parts of the brain
cerebrum
various lobes and diencephalon
cerebellum- most posterior and inferior part of the brain
brainstem ( parts moving from superior to inferior)
pons
midbrain
medulla oblongata
cerebrum part of brain
lots of lobes responsible of higher order thinking/ reasoning
principal part of brain
made up of various lobes divided into cerebral hemispheres
hemispheres separated by longitudinal fissure and joined by corpus callosum (highway of info that send info between left and right side so hemispheres talk to each other)
pic has sagittal view
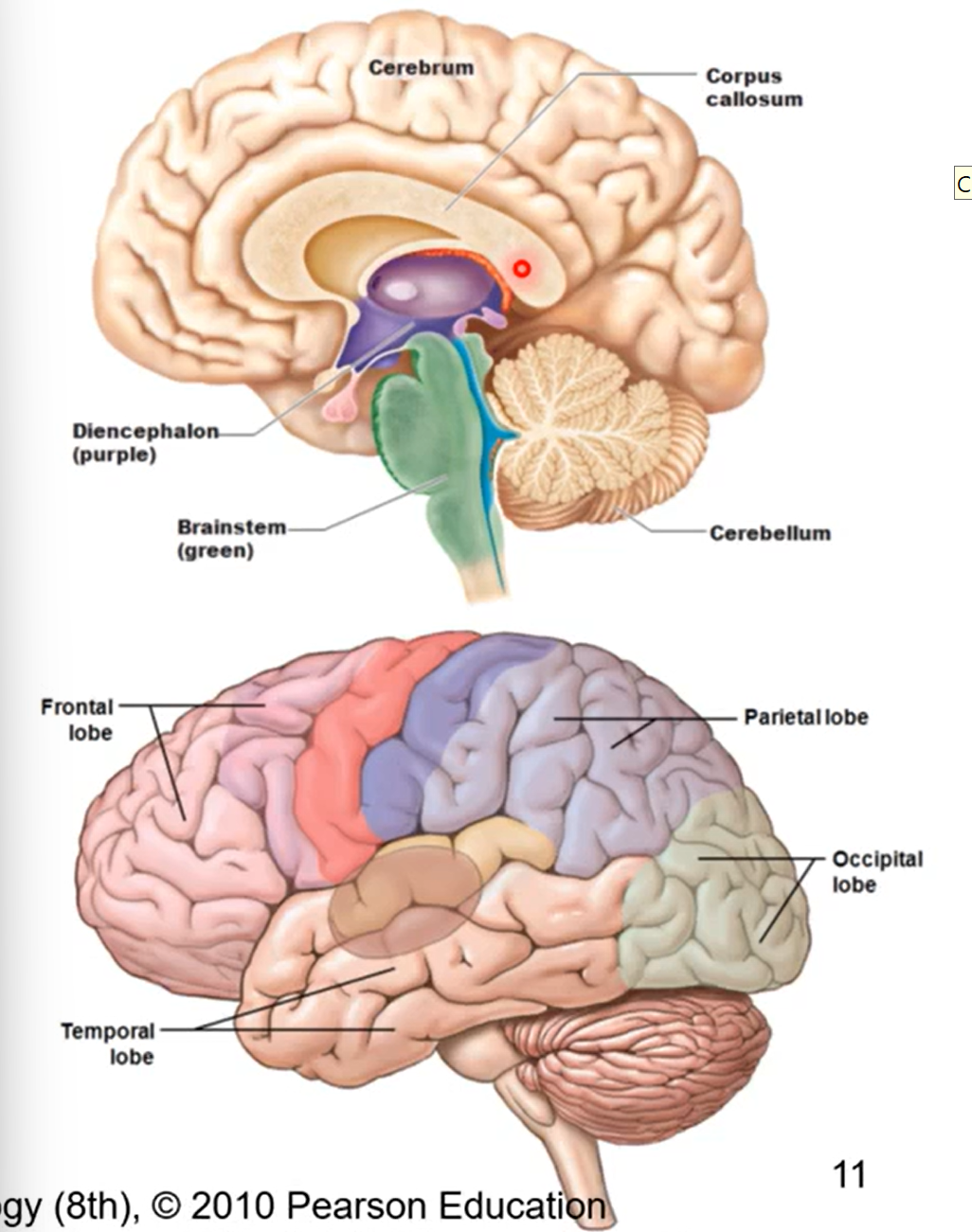
Lobes of cerebrum
frontal (most anterior lobe), parietal, (dorsal to frontal lobe) occipital (posterior and inferior to parietal), and temporal lobes (on lateral side of cerebrum)
frontal and parietal lobes separated by central sulcus
temporal and parietal lobes separated by lateral sulcus
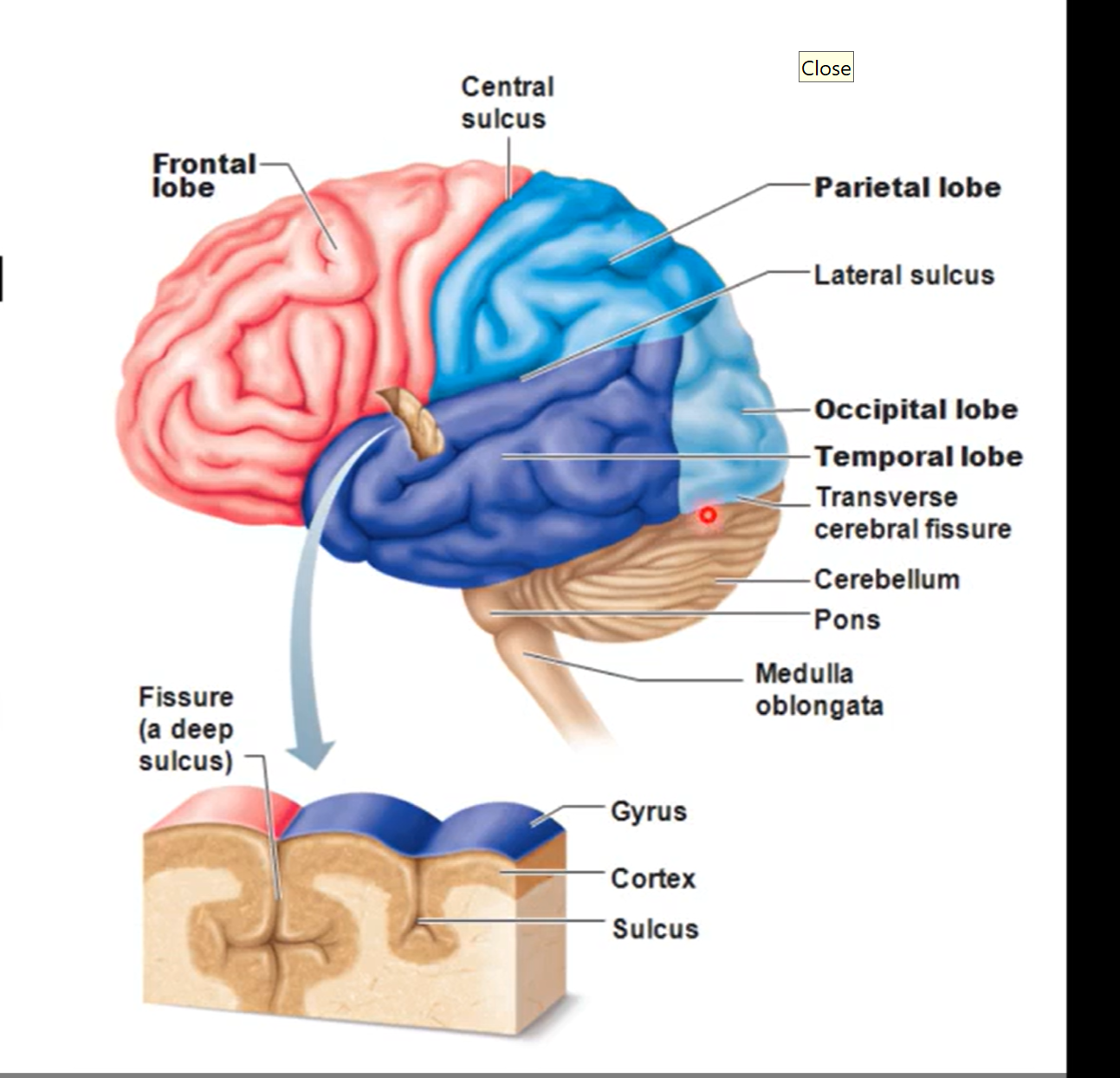
functions of each of the cerebrum lobes
frontal
pre-frontal area (personality) also most anterior
pre-central area (motor activities)
temporal lobe
smell and hearing
parietal lobe
sensory interpretation
occipital lobe
vision
diencephalon
core of brain and surrounds 3rd ventricle
Formed form right and left halves
joined together via intermediate mass
composed of right and left thalamus and hypothalamus
controls equilibrium, vison, facial sensation, hearing, phonation, respiration, salivation, swallowing, smell, taste
diencephalon is purple in pic
Midbrain
inferior to thalamus
first most superior part of the brainstem
controls most autonomic functions
vision, hearing, alertness, temperature
cavity forms cerebral aqueduct
conduct cerebrospinal fluid 3rd (other side of thalamus) to 4th ventricle (posterior to pons).
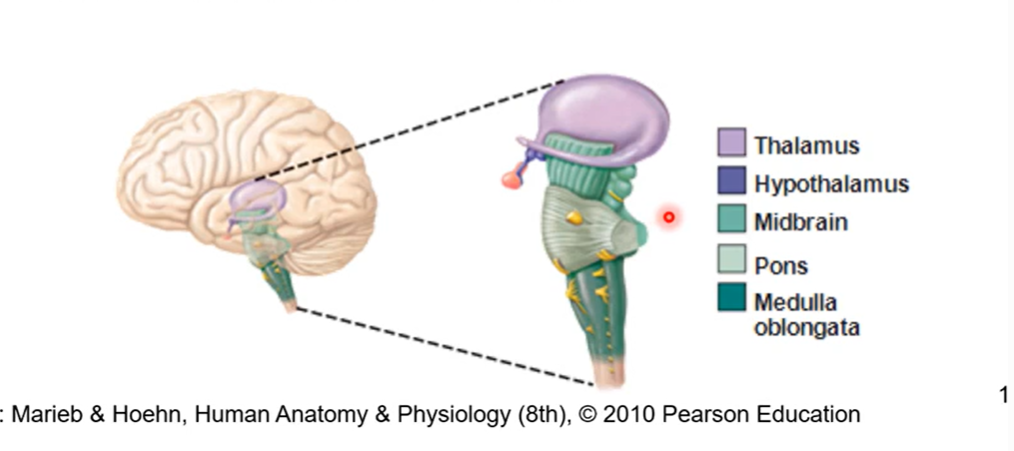
Pons next inferior part of brain stem
part of brainstem between midbrain and medulla oblongata
forms superior part of 4th ventricle
control sleep and arousal
midbrain is superior to the pons
inferior to that is the medulla oblongata
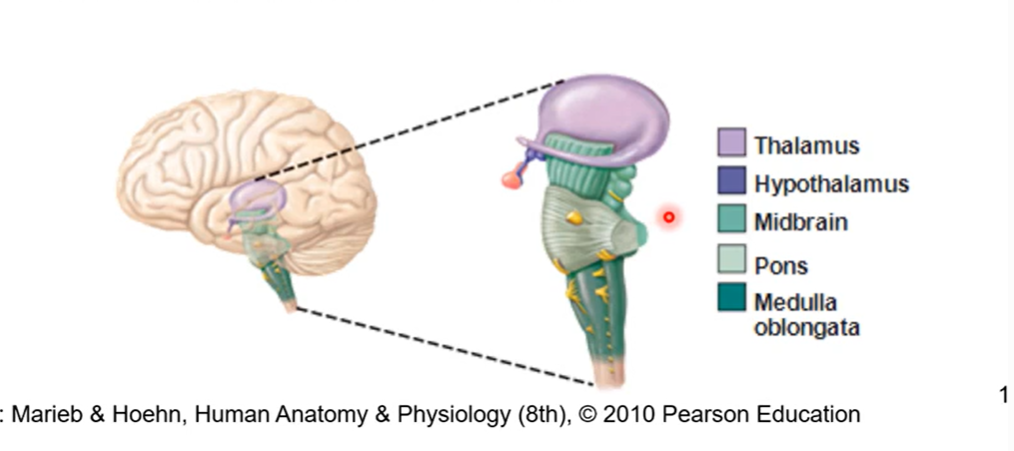
Medulla oblongata-most inferior part of the brain stem
inferior to pons
continuous spinal cord
controls autonomic functions (breathing and heartbeat)
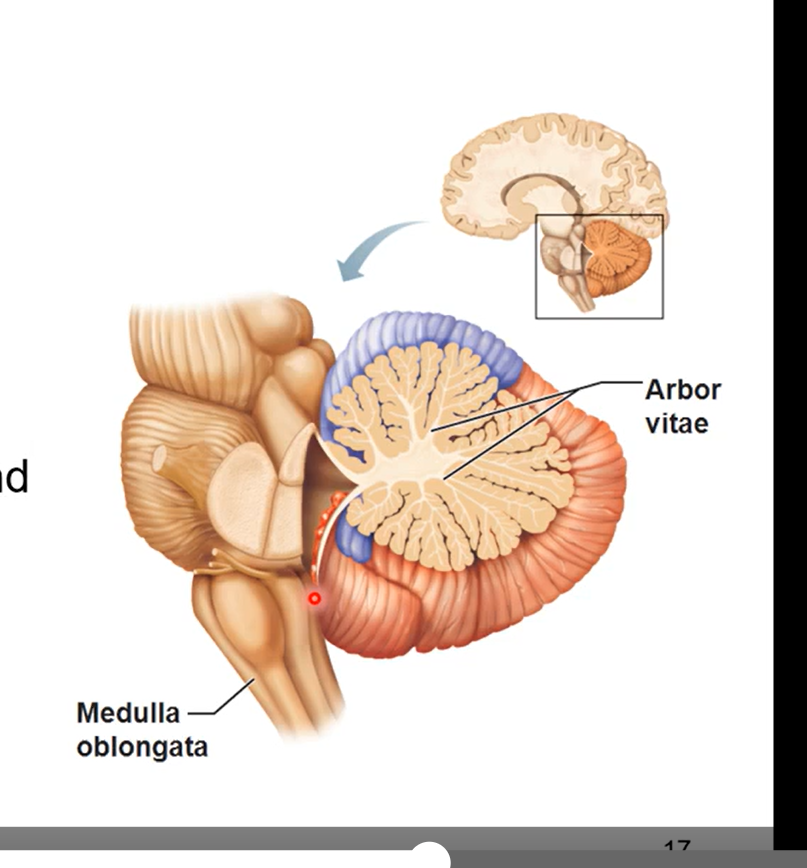
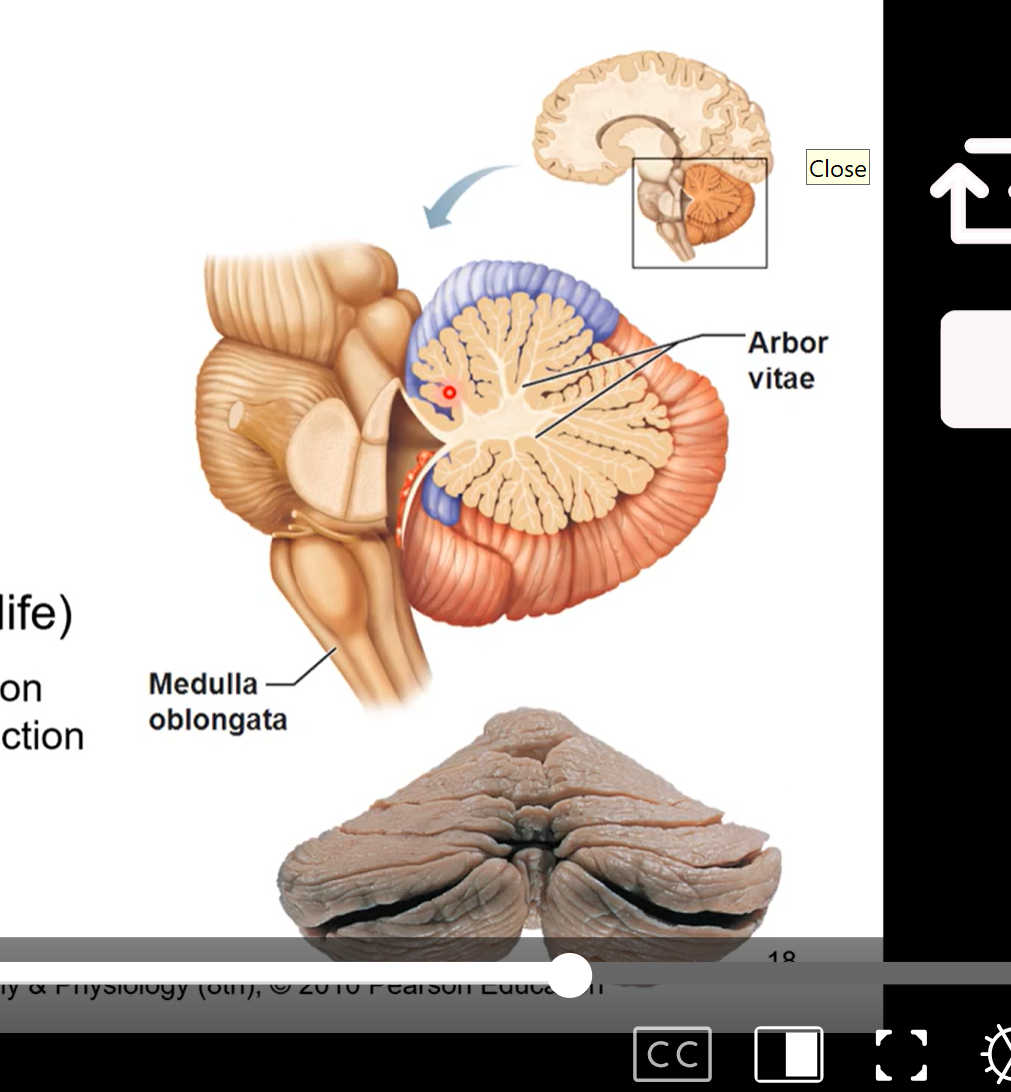
Cerebellum
a mini brain
dorsal to pons and medulla oblongata
controls fine motor coordination
fine tunes motion like throwing a ball or catching
arbor vitae (tree of life)
tree like configuration seen in a sagittal section of cerebellum
relays sensory information
pic is sagittal section of cerebellum
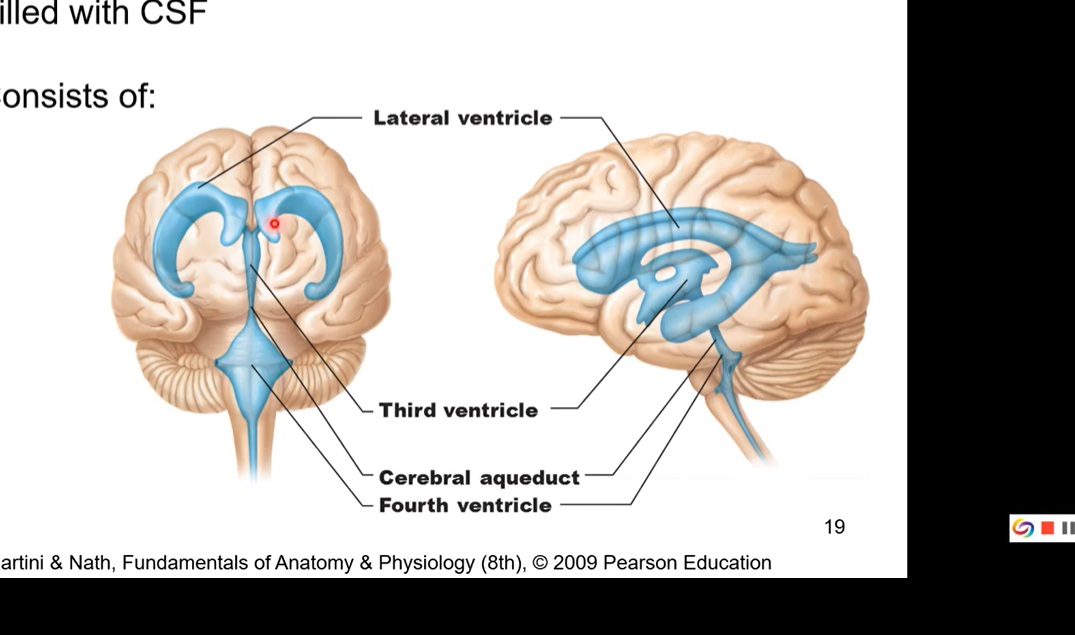
ventricles of the brain
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
consisted of
lateral ventricle
sit on cerebrum on each side. there’s a left lateral ventricle and a right
also called the 1st and second ventricle
third ventricle (sit in between thalama and same shape)
cerebral aqueduct
fourth ventricle
pic has frontal plane and sagittal plane
Lateral ventricles
also called 1st and 2nd ventricles. doesn’t matter if left or right is the first
largest cavities
separated by septum pellucidum (separates each ventricle so each one has its own space) which sits inferior to corpus callosum (corpus callosum is a mass that communicated between left and right?)
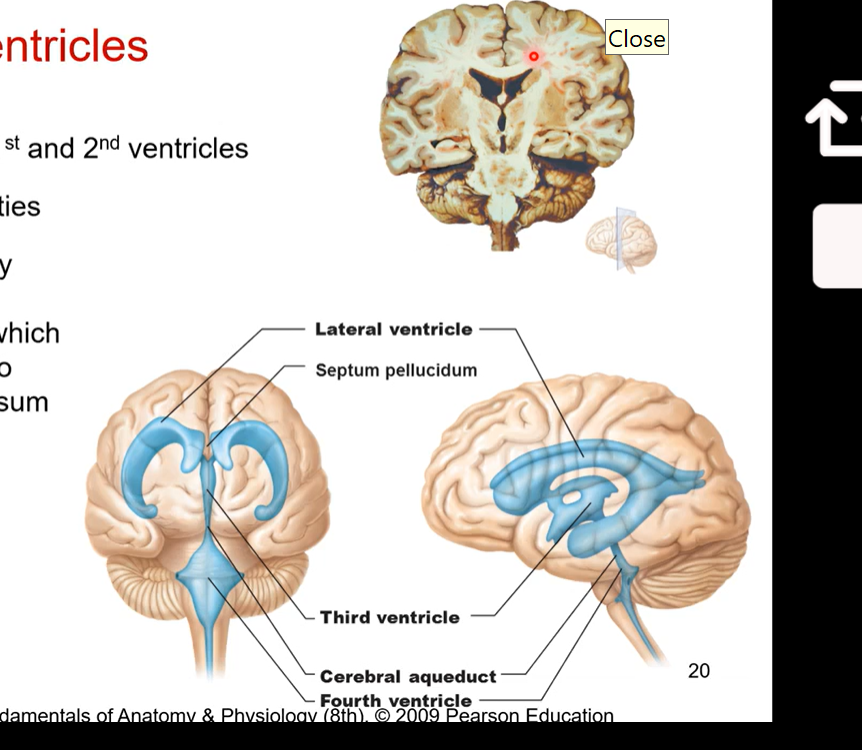
3rd and 4th ventricles
3rd ventricle is between the two halves of the diencephalon
intermediate mass lies within
3rd and 4th connected via cerebral aqueduct so cerebrospinal fluid can also pass through there
4th ventricle is posterior to pons and medulla oblongata
continuous with central canal of spinal cord
Septum pellucidum
Septum pellucidum separates the two lateral ventricles - roof is corpus callosum
intermediate mass lies within 3rd ventricle - lateral borders are diencephalon
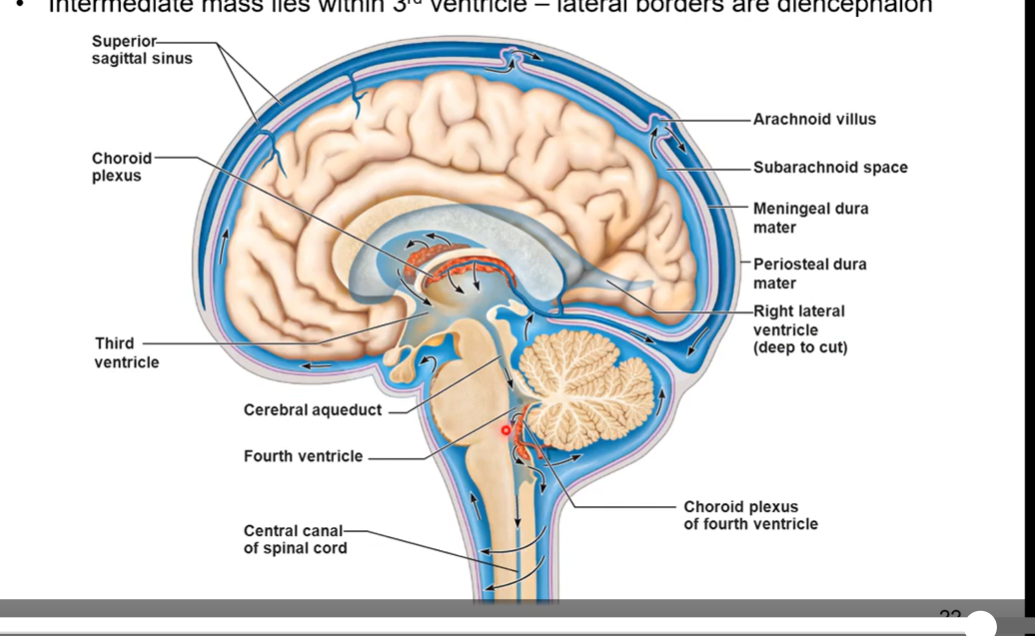
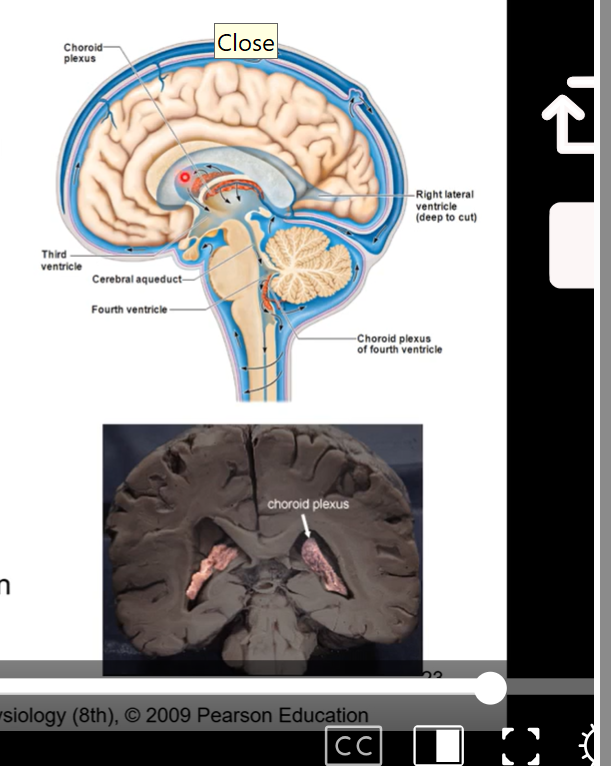
Cerebrospinal fluid
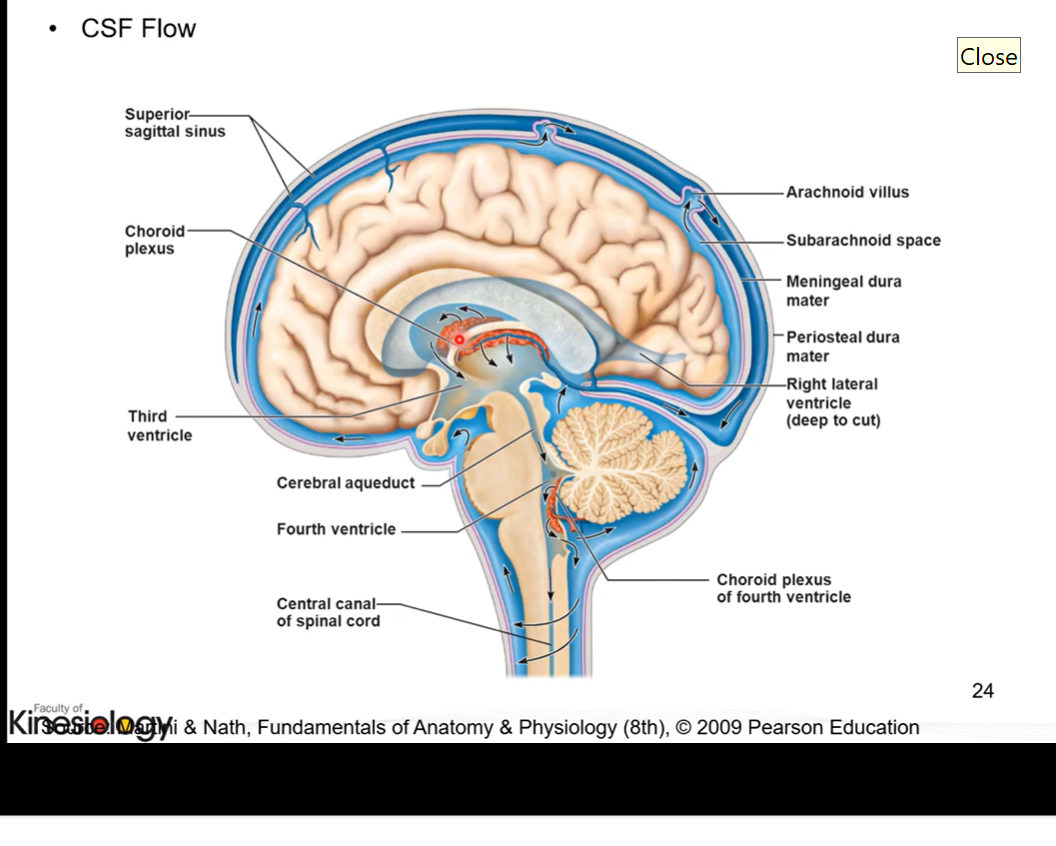
produced by choroid plexus found within each ventricle and travels throughout brain
circulates throughout central nervous system
old cerebrospinal fluid and fluid that is used up is absorbed into venous system through heart after by sinuses
functions:
protection
buoyancy
excretion of waste products
endocrine medium for the brain
Cerebrospinal fluid flow
CRANIAL BLOOD SUPPLY AND CRANIAL NERVES BELOW
The two main blood vessels
arteries - take oxygenated blood away from heart to its destination
veins- take deoxygenated blood ( venous blood) from muscle, brain, bone etc back towards heart so it can get oxygen
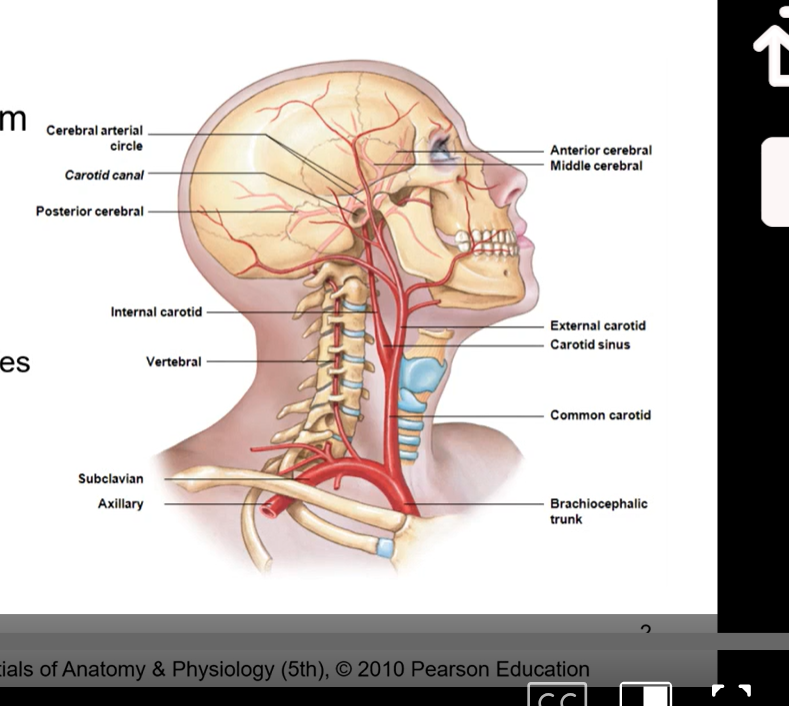
brain receives arterial blood ( oxygenated blood) from heart via 2 sources:
internal carotid arteries
branches off heart with the brachiocephalic trunk and then splits into external carotid which goes to outer part of face and the internal carotid artery which goes through the carotid canal and then to cerebralarterial circle
vertebral arteries
go up brachiocephalic trunk then go up the subclavian axillary then to the vertebral arteries
vertebral arteries tied into our axial skeleton cuz these are the ones that go thru the transverse forename in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. then goes to cerebralaterial circle/circle of Willis
in diagram we want to from heart ( behind sternum) and go up towards the brain so it has oxygenated blood and then the venous blood can go back towards heart
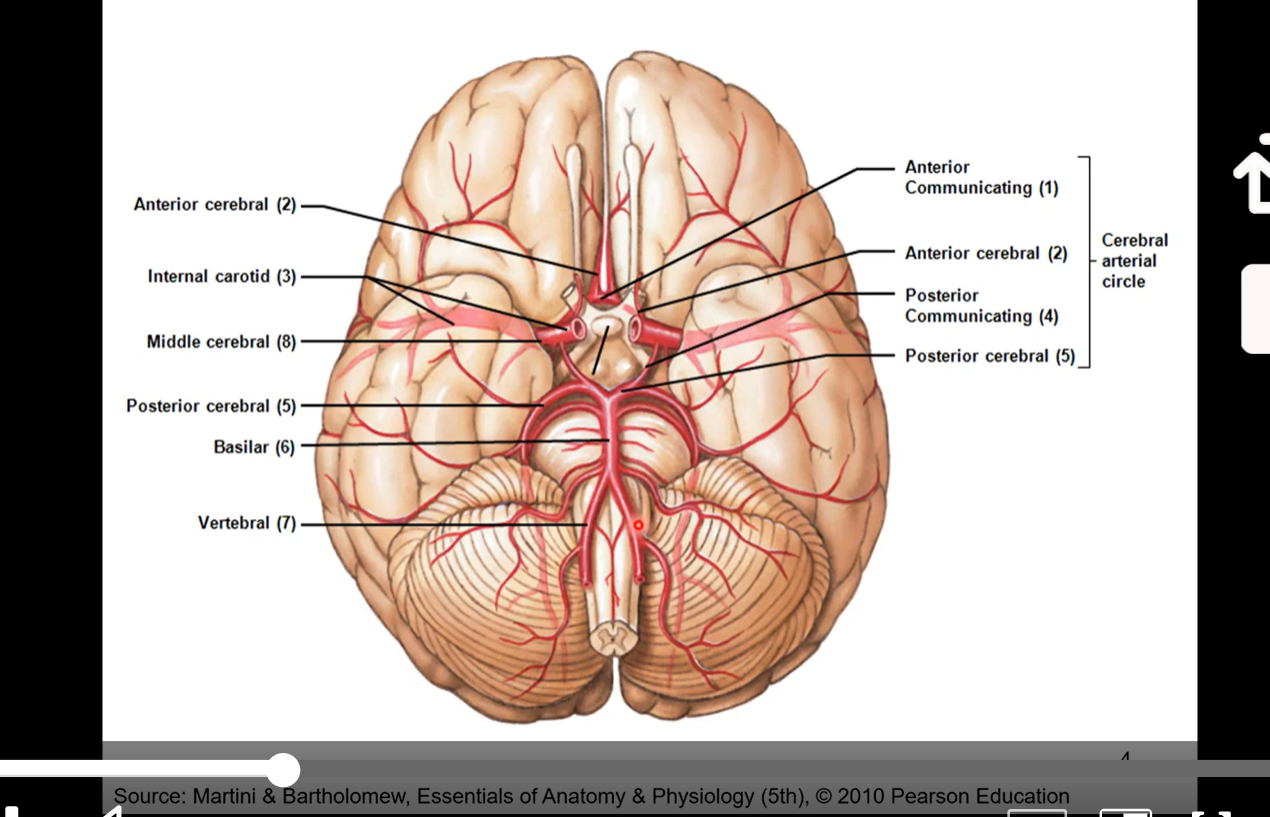
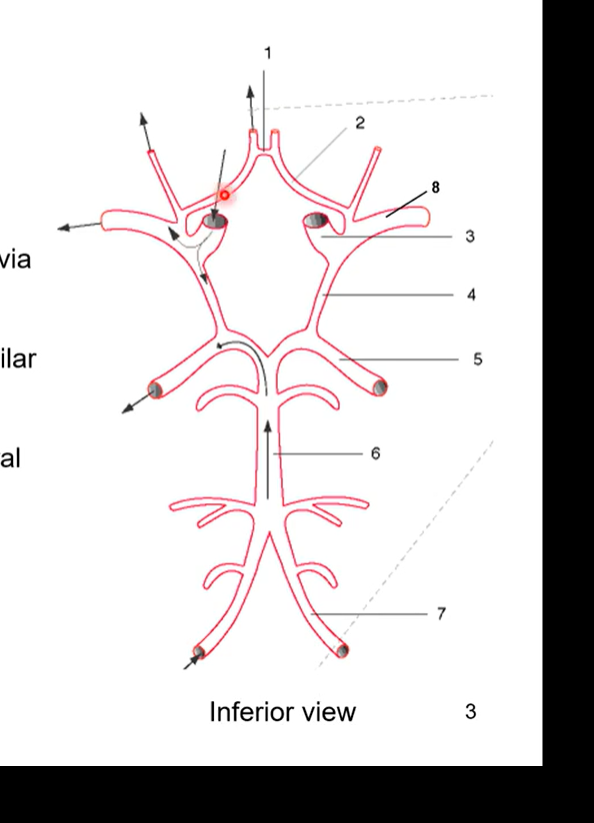
Cerebralarterial Circle/ Circle of Willis
pic also the same as below pic
where arterial blood is distributed to areas within the brain
ICA (3) branch into anterior (2) and middle (8) cerebral arteries
anterior cerebral arteries connected via anterior communication artery (1)
vertebral arteries (7) join to form basilar artery (6)
basilar splits to form posterior cerebral arteries (5)
posterior cerebral arteries joined to circle via posterior communicating arteries (4)
to get to temporal lobe it’ll go through middle cerebral arteries (8)
frontal lobe would be anterior cerebral arteries (2)
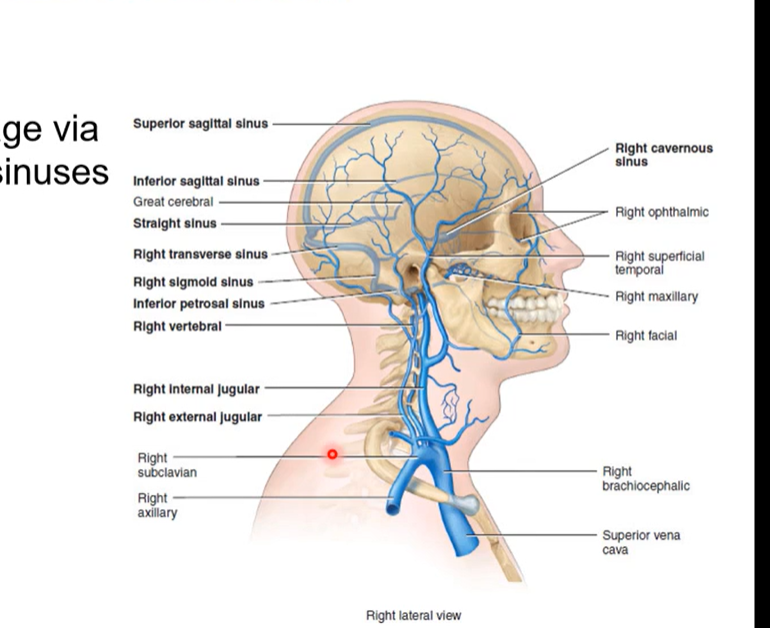
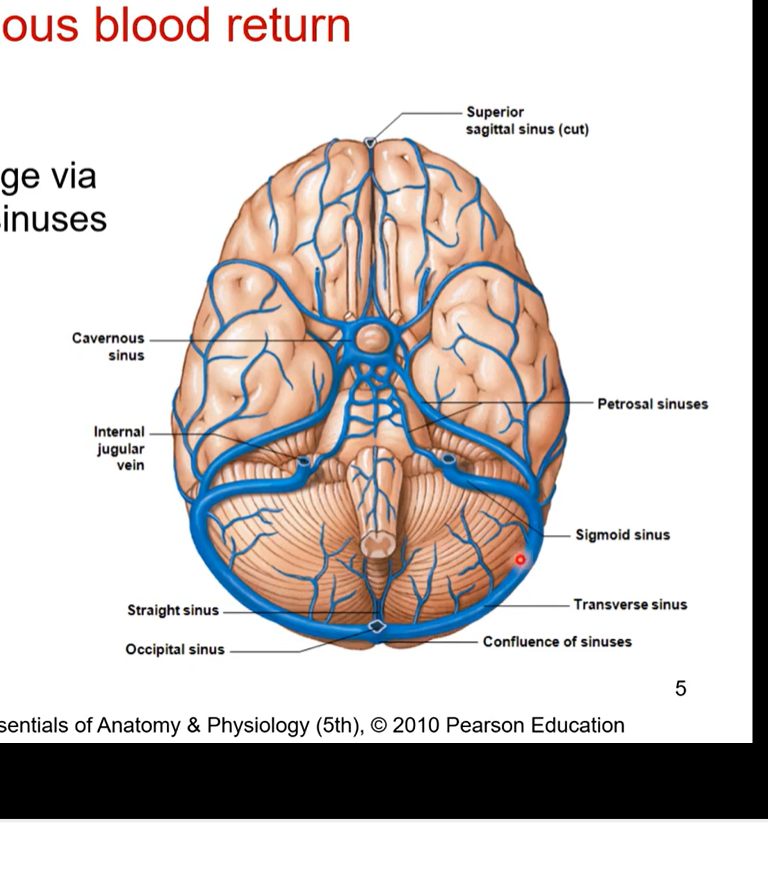
Cerebral Venous blood return
pic is the same as below
once oxygenated blood is received by the brain, the brain will then discard deoxygenated blood so we can go back to heart
cerebral venous blood return refers to veins that are taking deoxygenated blood away
venous blood drained via dural venous sinuses
they drain into internal jugular veins (IJV). This then drains back into heart
Cranial nerves
emerge from foramina in the cranium and go out of skull
contain sensory or motor fibres or combination of both
whether they’re responsible of sensation only or motor only or a combination of both
twelve pairs
Goes anterior to posterior to inferior as we make our way down the brainstem
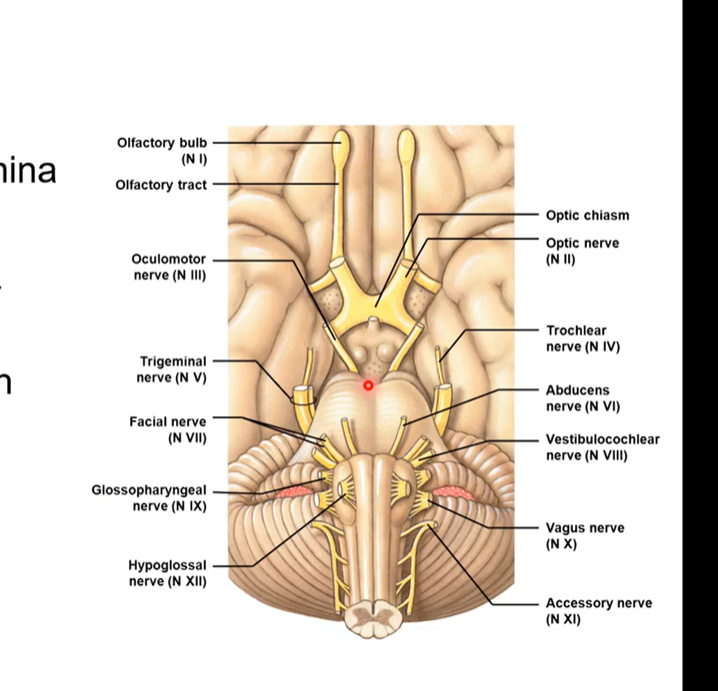
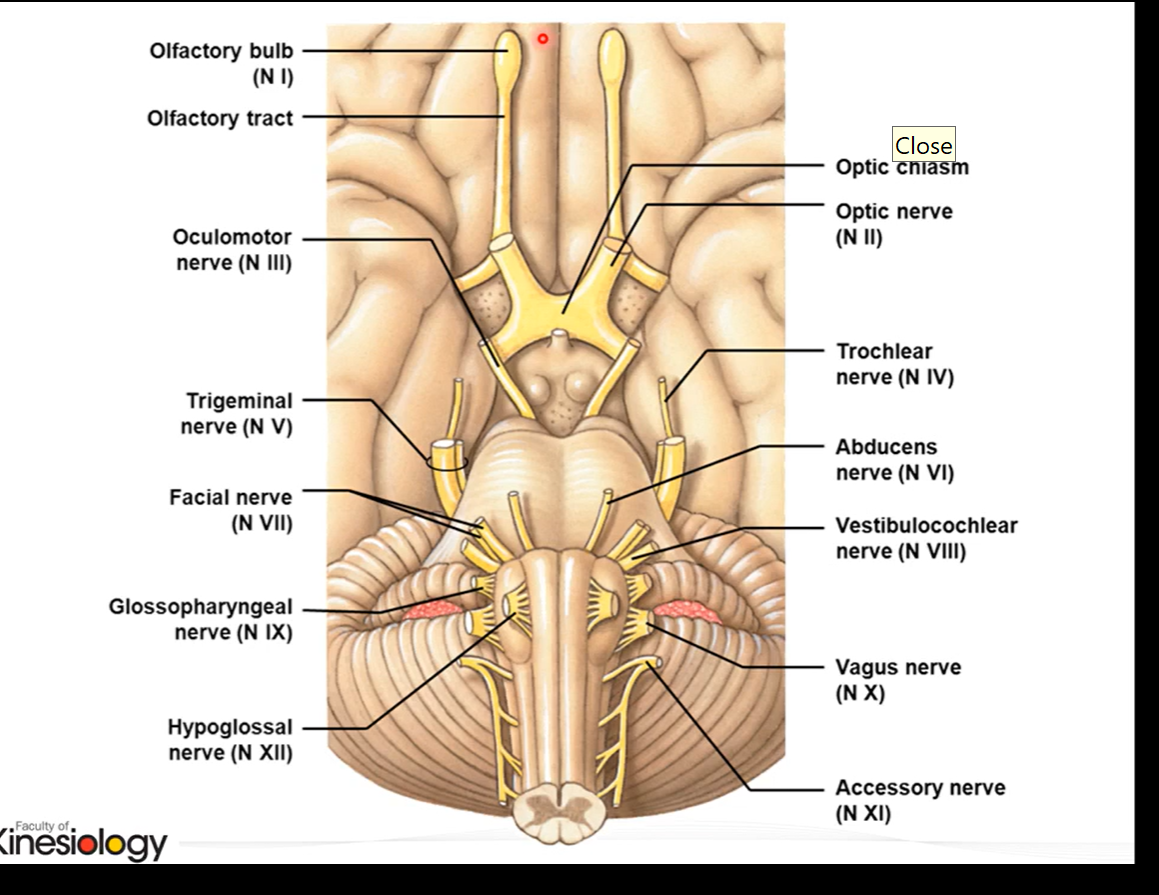
12 pairs of cranial nerves
CNI- olfactory (sensory)
CN II - optic (sensory)
CN III - oculomotor (motor)
CN IV - Trochlear (motor)
CN V - Trigeminal (both sensory and motor)
CN VI abducens (motor)
CN VII - facial (both sensory and motor)
CNVIII - Auditory/ Vestibulocochlear (sensory)
CN IX - Glossopharyngeal (both sensory and motor)
CN XI - accessory (motor)
CN XII hypoglossal (motor)

CN I - olfactory
olfactory bulb rests on cribriform plate
pure sensory nerve ( only function is sensory)
sense of smell and induce visceral response (salivation)
most anterior nerve
combination of olfactory nerve and nerve fibres
all the olfactory nerves are coming through the ethmoid bone
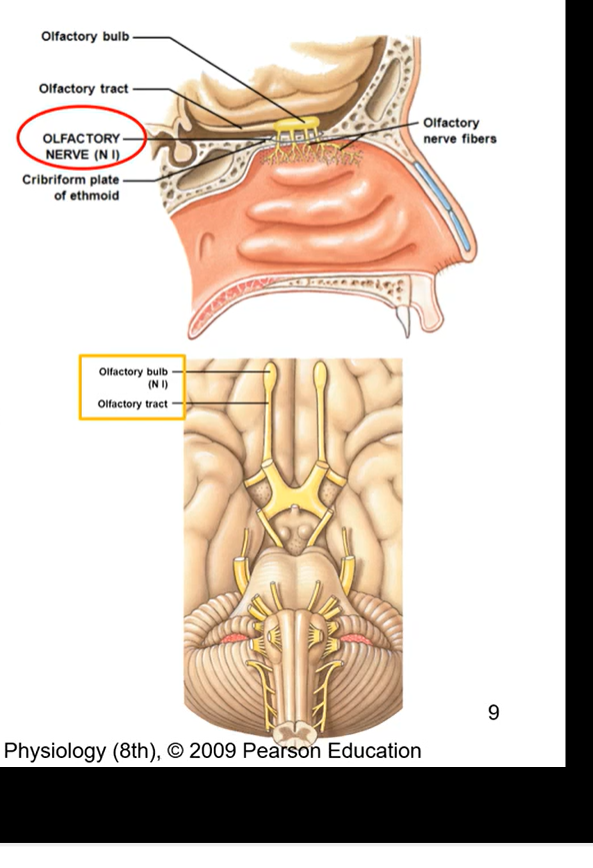
CN II - optic (sensory)
formed from axons of retina ganglion cells from eyeballs
fibres from each nerve run from to each hemispheres at optic chiasm then make its way back to occipital love
allow for 3D vision (sensory)
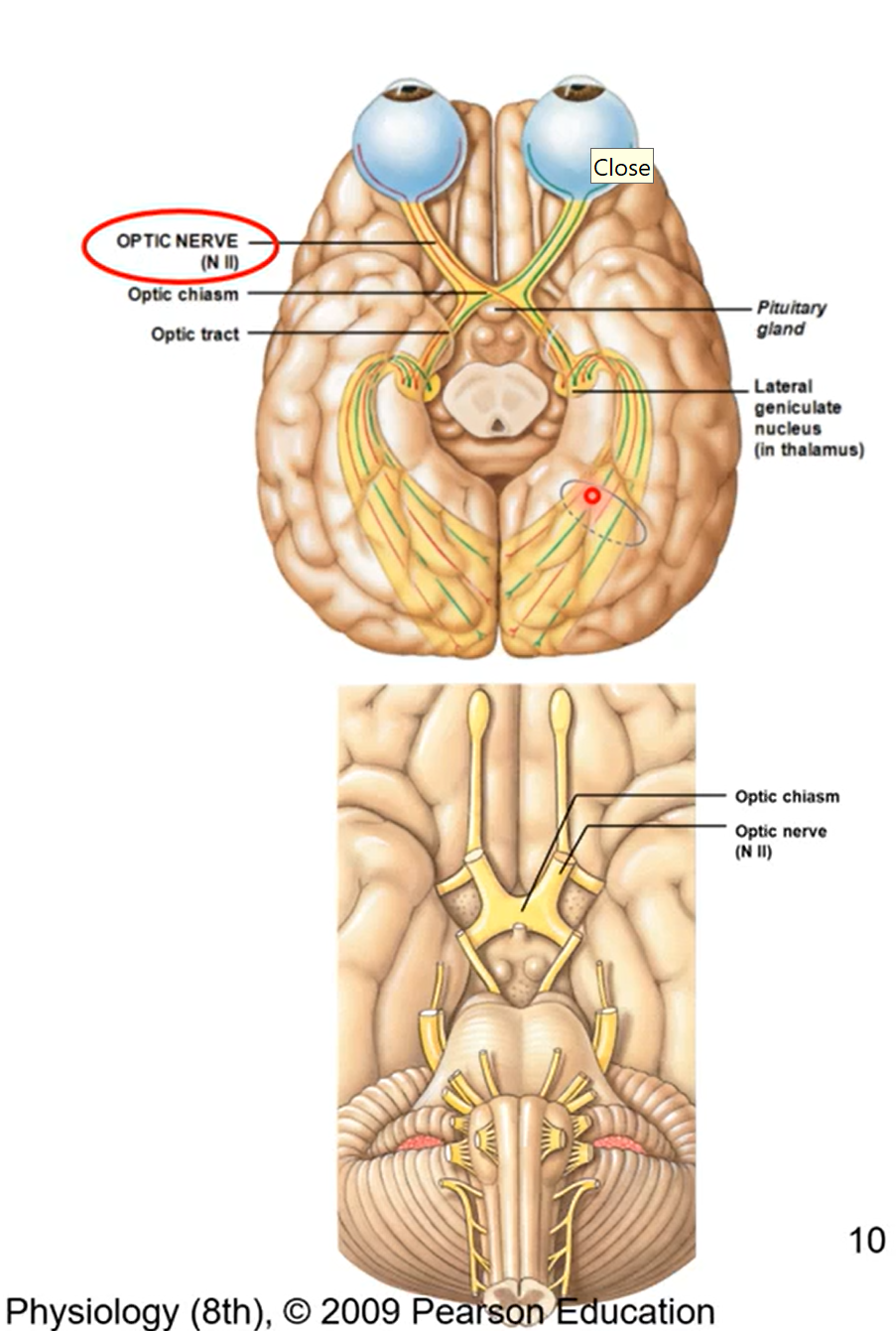
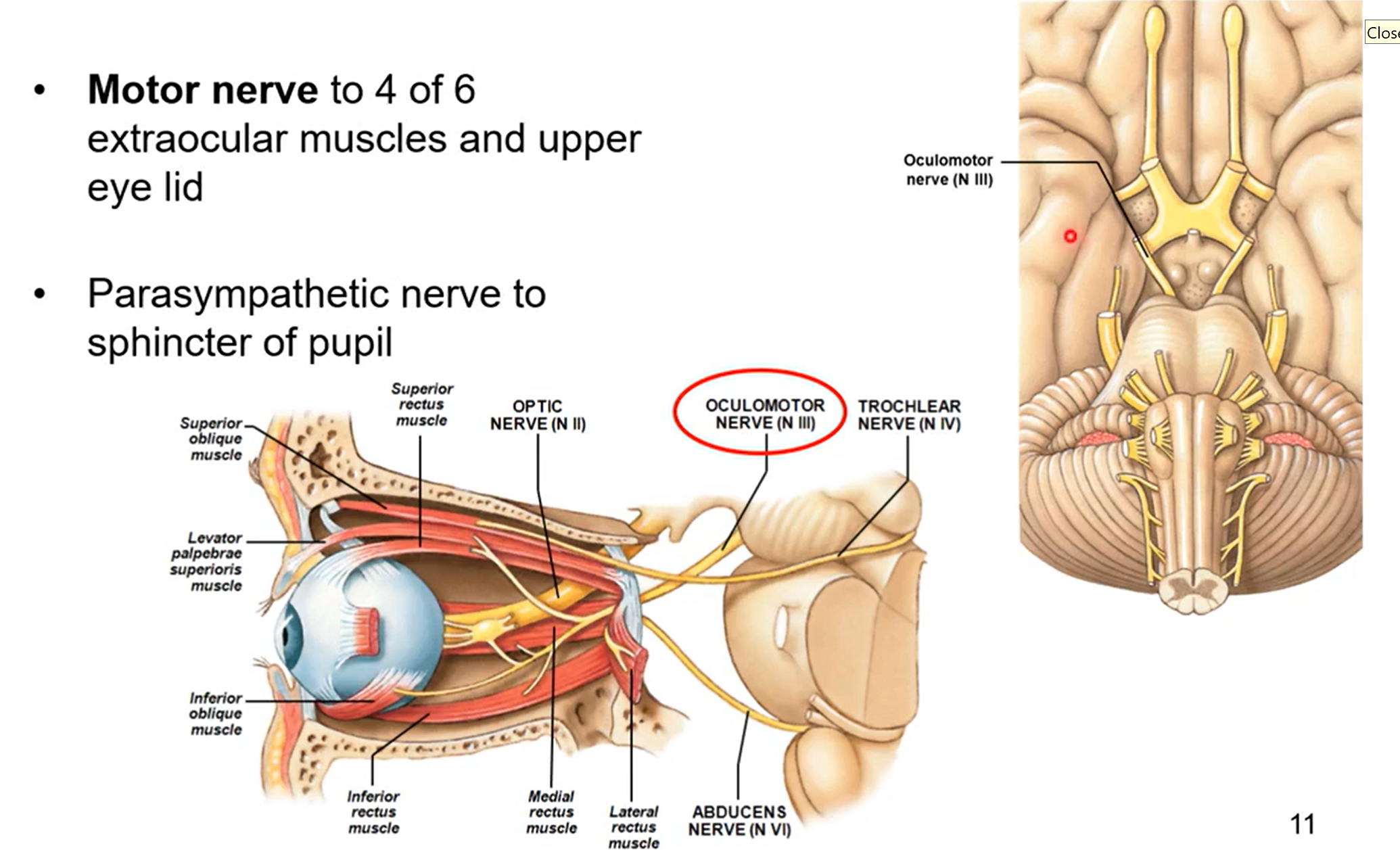
CN III - oculomotor
motor nerve to 4 of 6 extraocular muscles and upper eye lid
parasympathetic nerve to sphincter of pupil
pupil changing sizes due to light
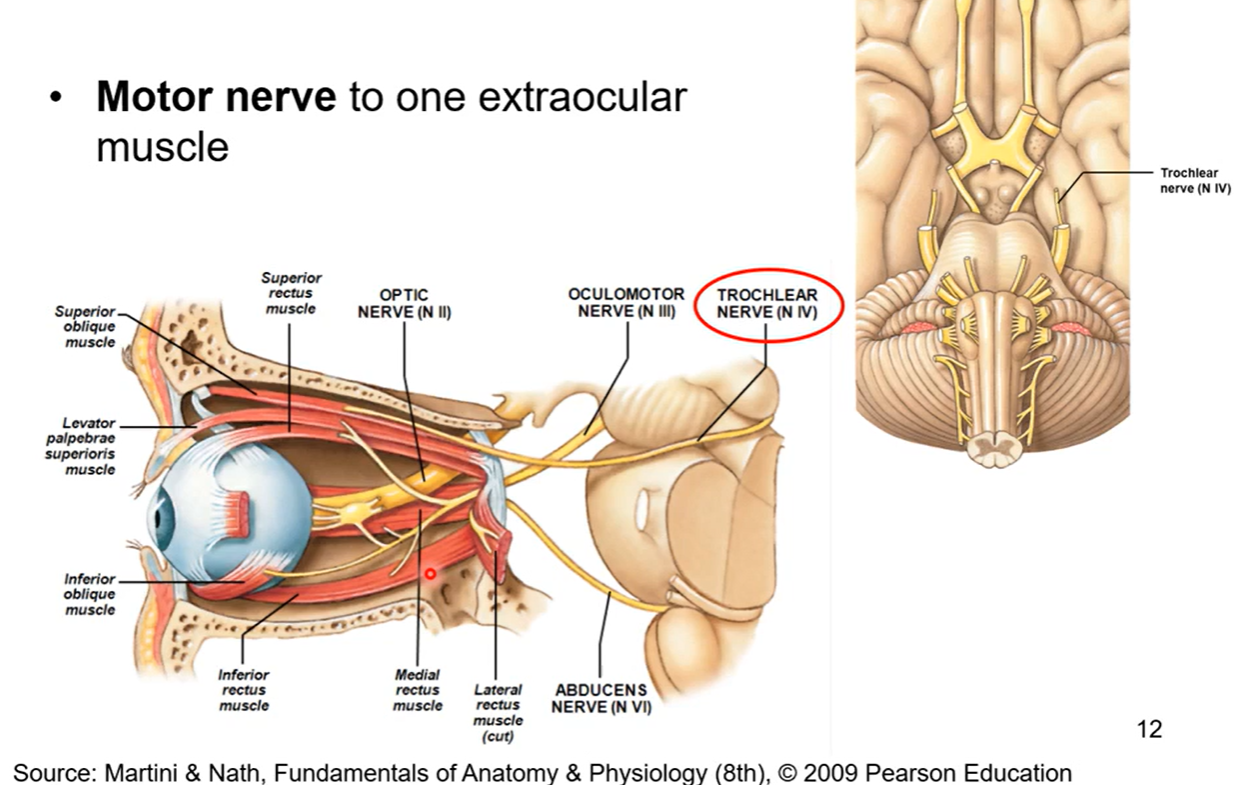
CN IV Trochlear
motor nerve to one extraocular muscle. its the 5th of the 6th extraocular muscle
trochlear= Latin for pulley
trochlear nerve innovates into the superior oblique muscle and has a pulley system. it pulls on posterior side of eyeball. if u want to lower ur eyeball downwards u pull up on pulley and u can look down
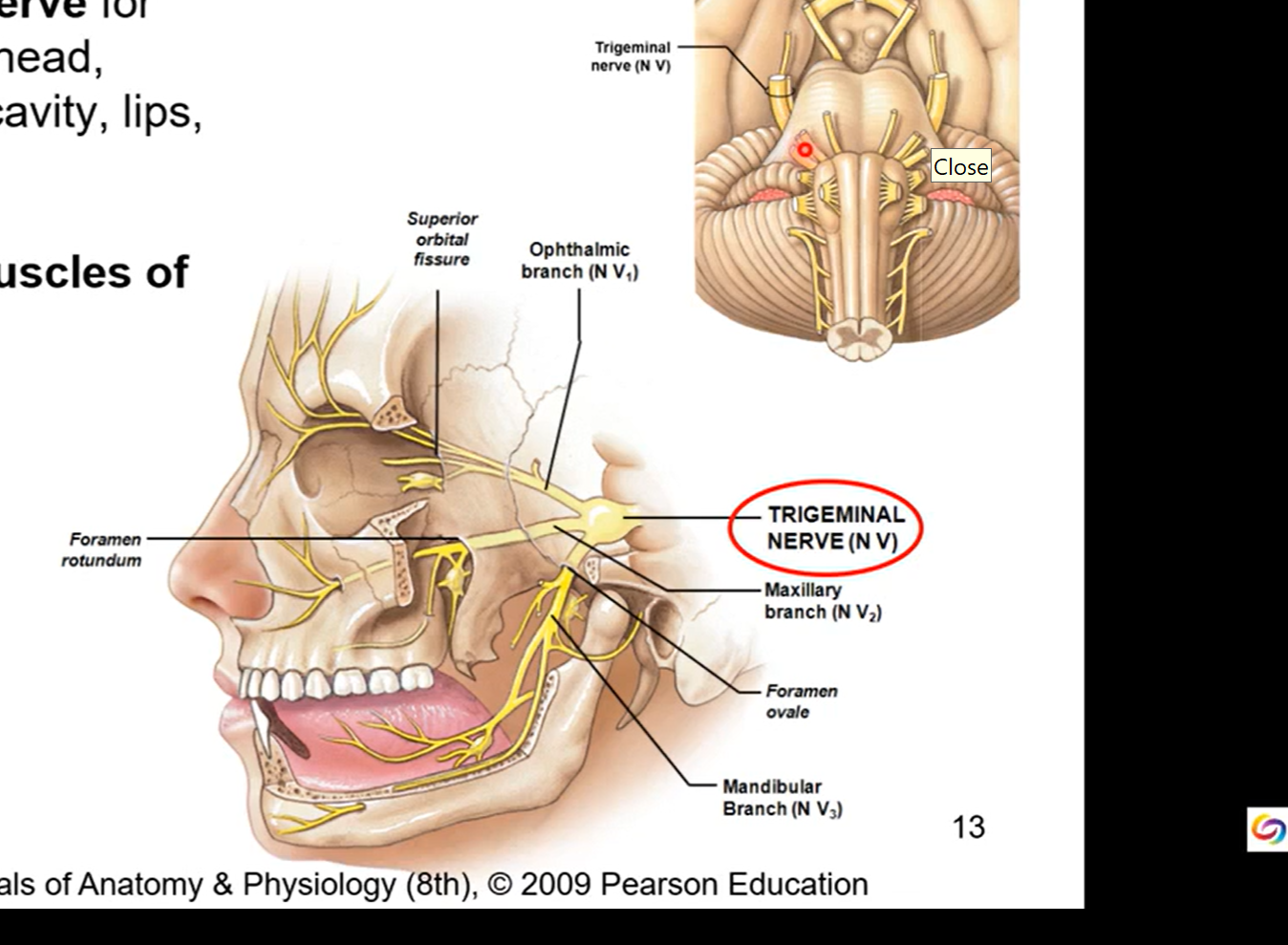
CN V - Trigeminal
sensory and motor nerve
general sensory nerve for cornea, skin of forehead, scalp, nose, nasal cavity, lips, teeth, and tongue
motor nerve for muscles of mastication (chewing)
three branched nerve to 3 diff regions:
ophthalmic- forehead and eye
maxillary - in maxilla region in upper jaw
mandibular - low jaw or mandible
depending on region it goes to it’ll act as either a sensory or motor nerve. all three branches have sensation though.
CN VI abducens
motor nerve to the final or 6th extraocular eye muscle
abducens is going to the muscle that will abduct your eye
if u look to left, right eye will abduct. if u look to right, left eye will abduct. all due to abducens
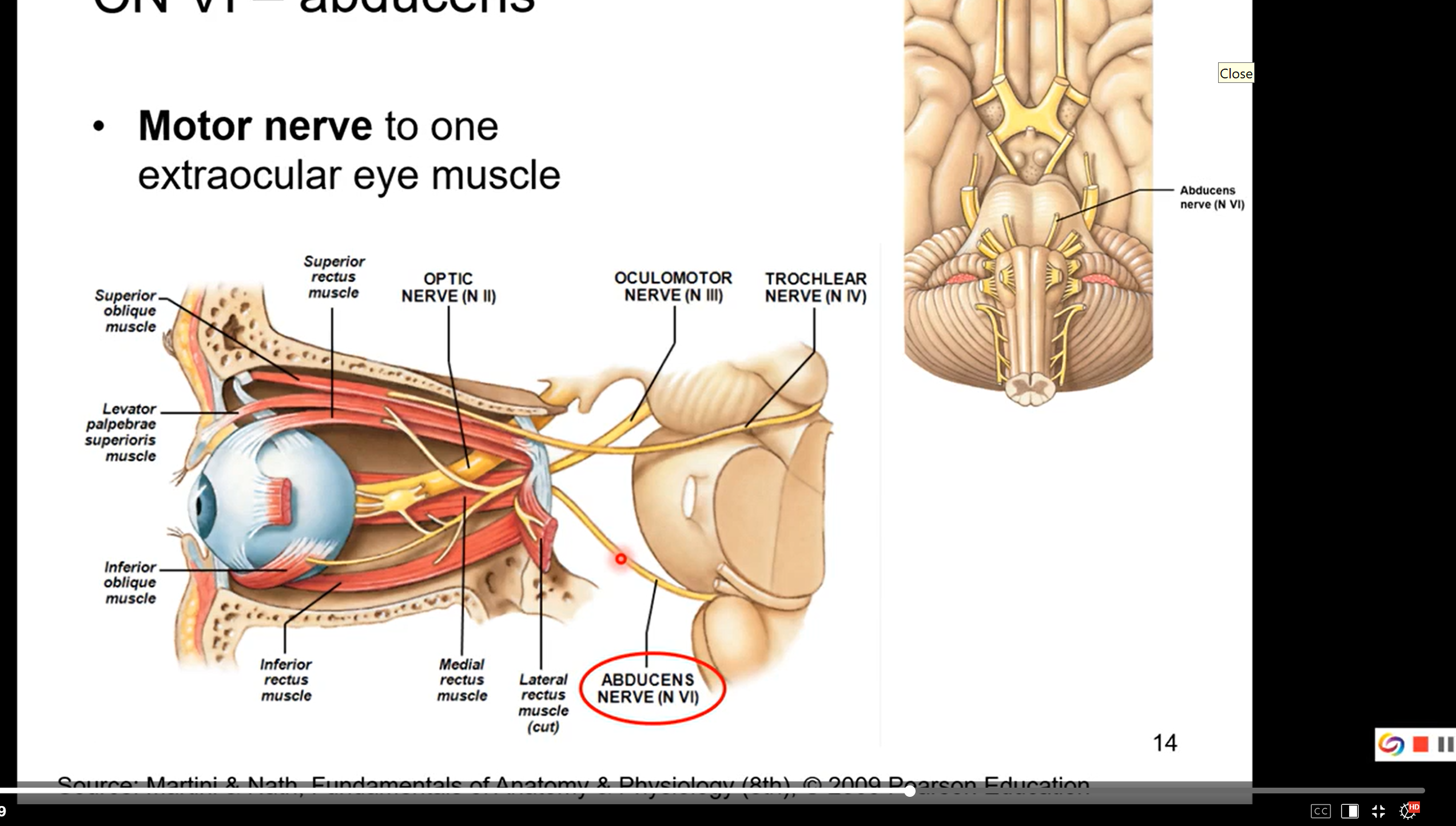
CN VII - facial
motor nerve to facial muscles of expression and to scalp
motor and sensory
motor aspect- allows for facial muscles of expression in the scalp. ex a big smile, frowning, surprise
sensory aspect-
taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue, floor of mouth and palate
sensation from outer ear
parasympathetic innervation to submandibular, sublingual, and lacrimal glands and glands of nose and palate
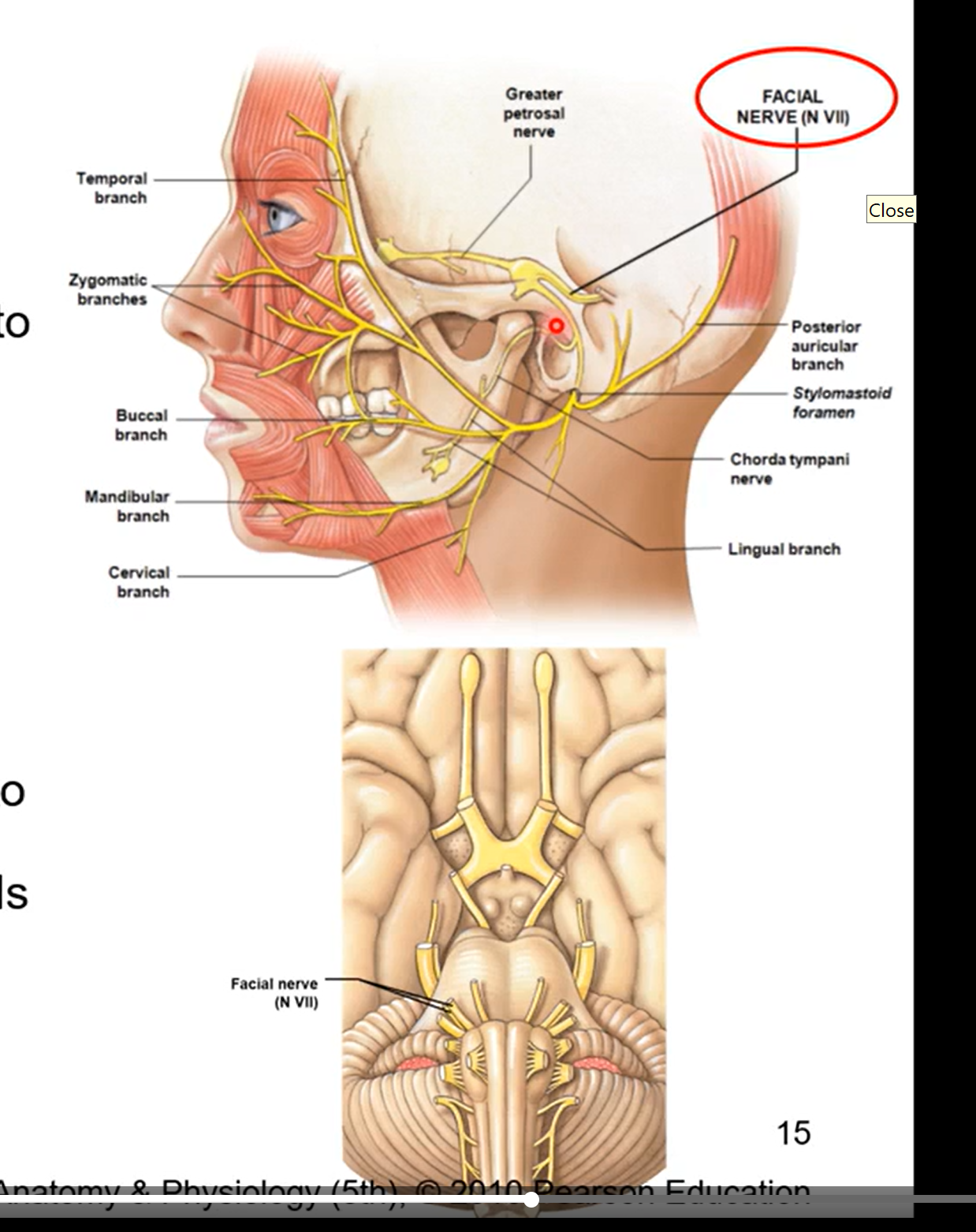
CN VIII - auditory / vestibulocochlear
sensory nerve form inner ear related to position and movement of head
also associated with hearing
balance
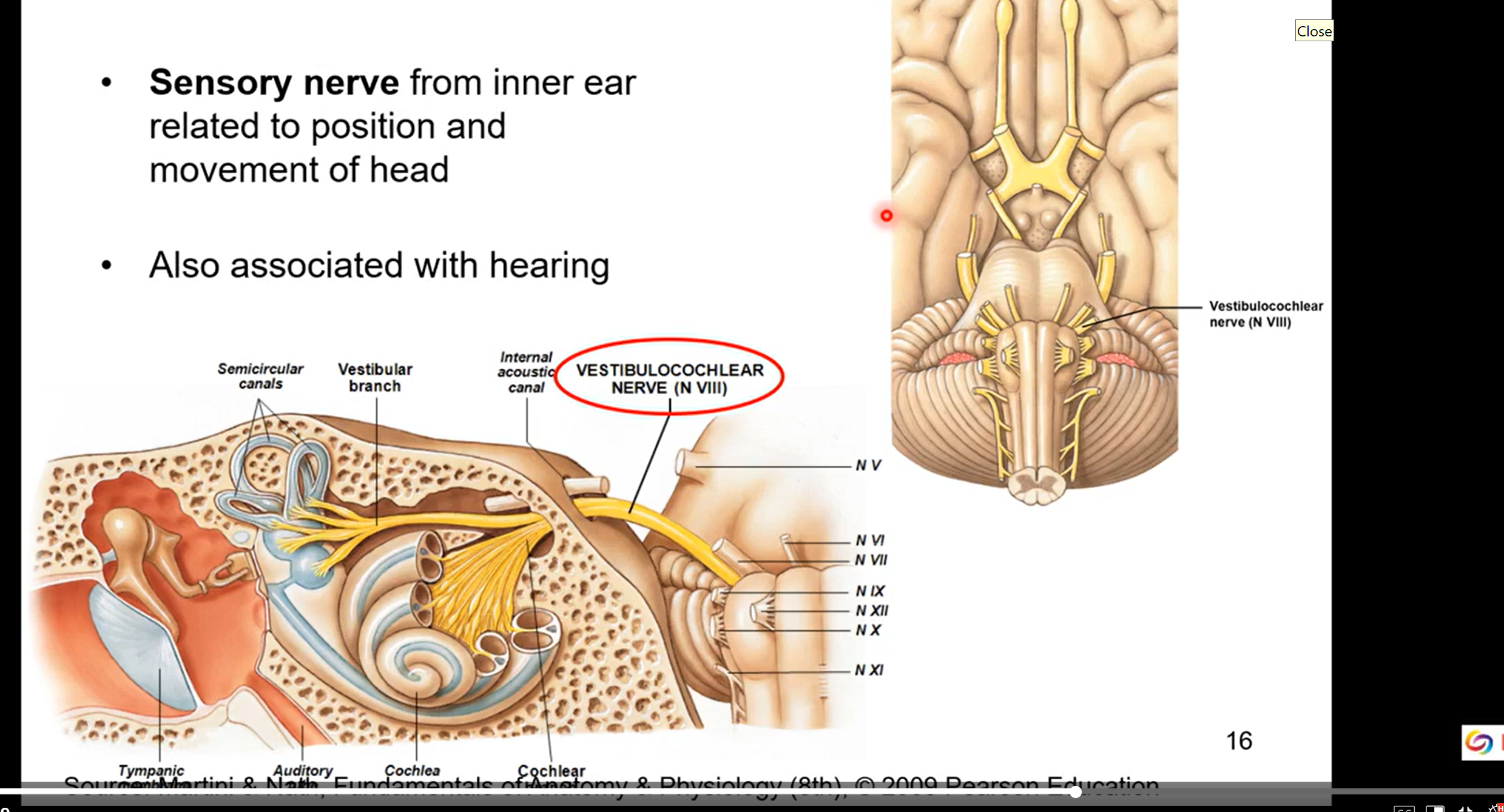
CN IX Glossopharyngeal
motor and sensory
motor nerve for swallowing
parasympathetic nerve to parotid gland ( gland in cheek)
visceral (organ) sensation to carotid body and carotid sinus, pharynx and middle ear. give info about blood pressure
sense of taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue
glossal= tongue
pharynx= throat
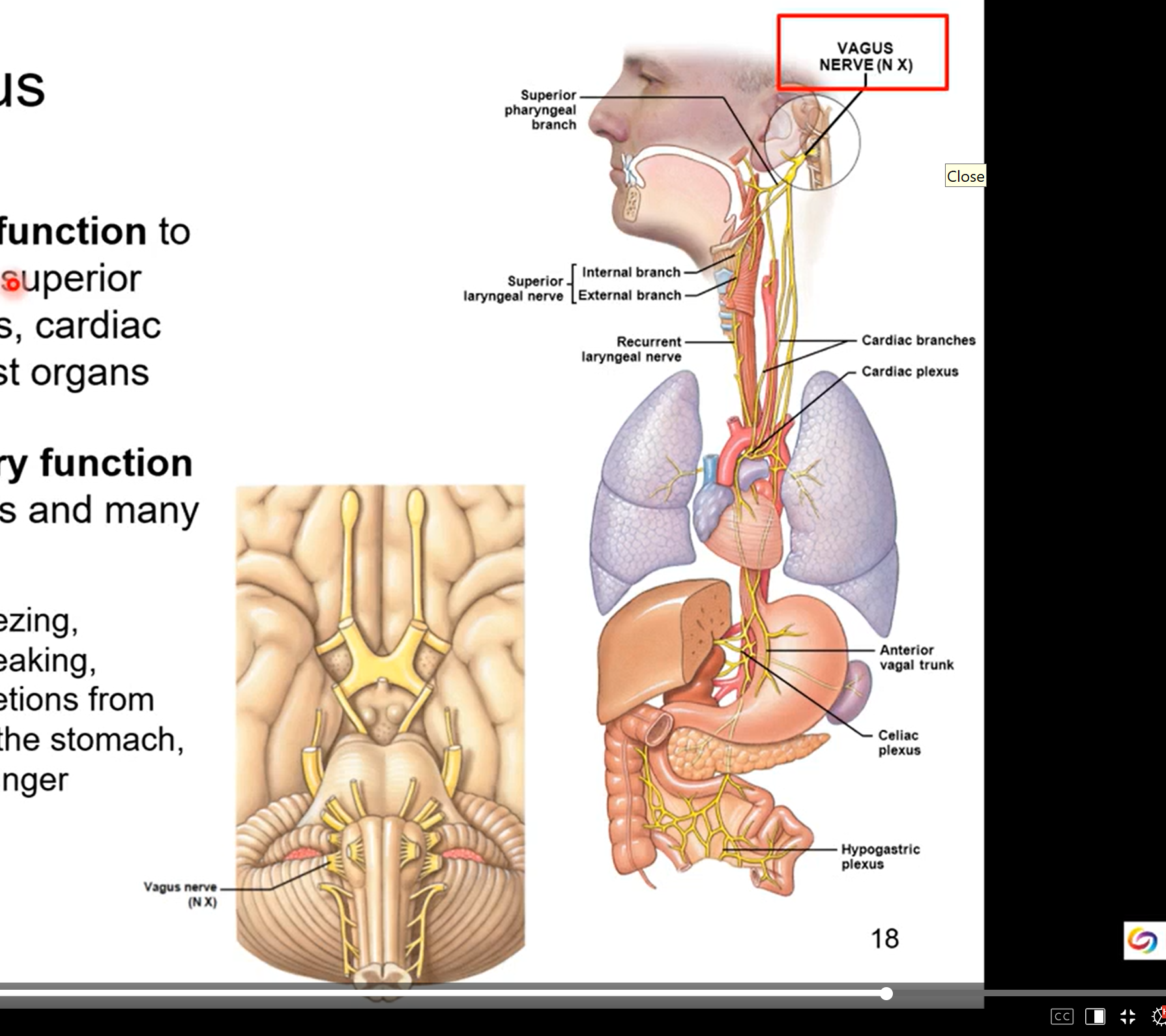
CN X - Vagus
visceral motor function- it will innervate the pharynx, larynx, superior 2/3 esophagus,, cardiac muscle, and most organs
you don’t have control of the organs but it controls them with smooth muscles motor activity
visceral sensory function from most organs and many others
coughing, sneezing, swallowing, speaking, digestion, secretions from the glands of stomach, sensation of hungry
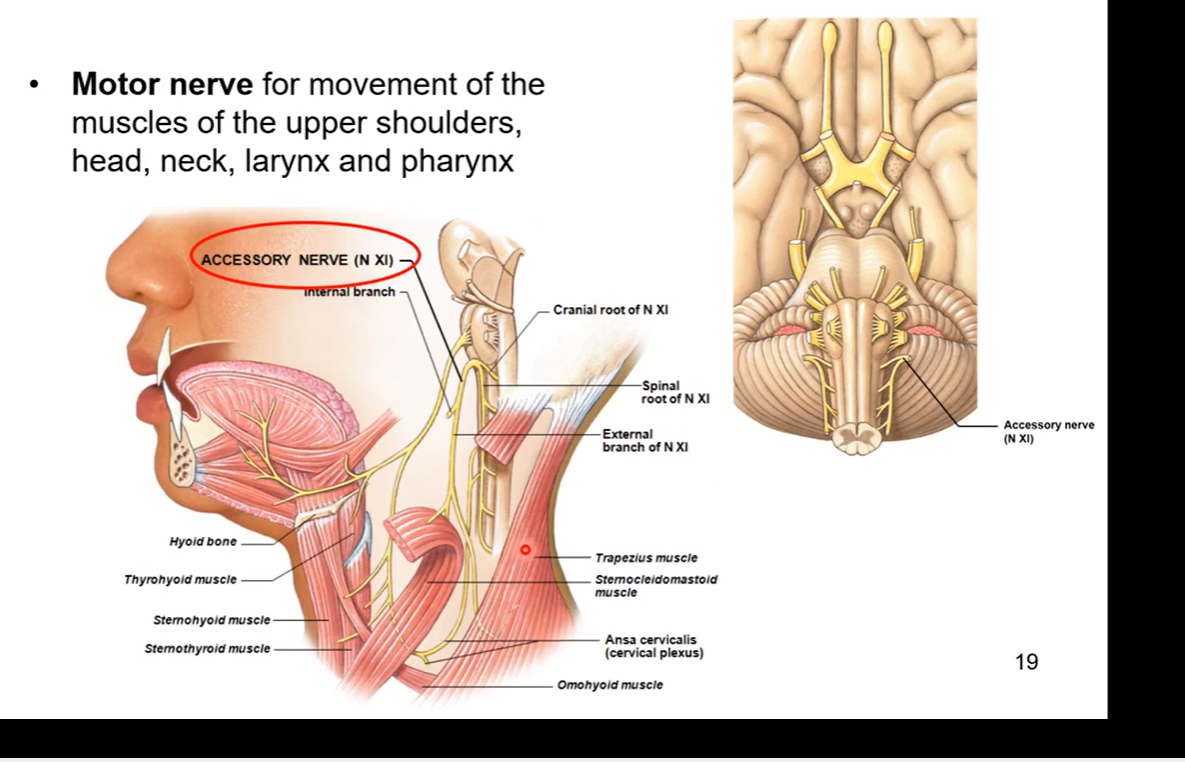
CN XI - Accessory
motor nerve - helps innervates for movement of the muscles of the upper shoulders, head, neck, larynx, and pharynx
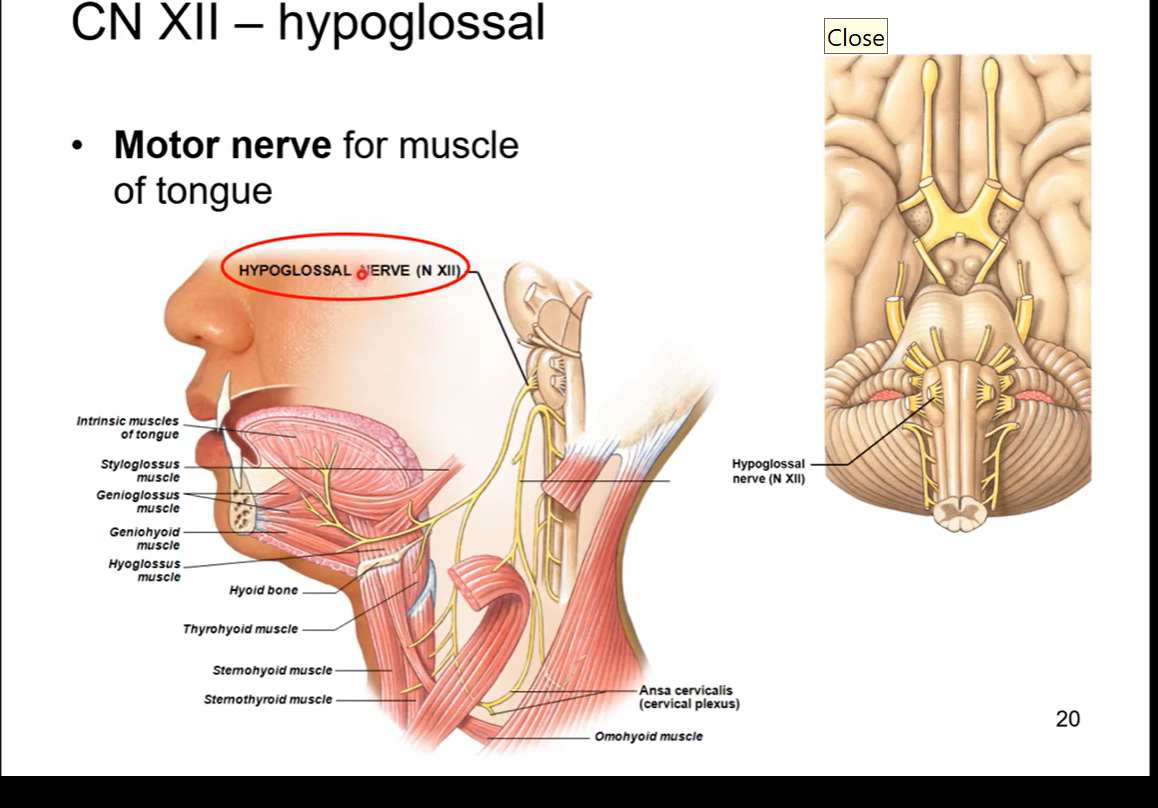
CN XII - Hypoglossal
motor nerve for muscle of tongue. allows for movement of tongue so u can talk, speak, move ur tongue when u eat, etc
hypo=above
glossal= tongue
EXTREMITY NERVES BELOW
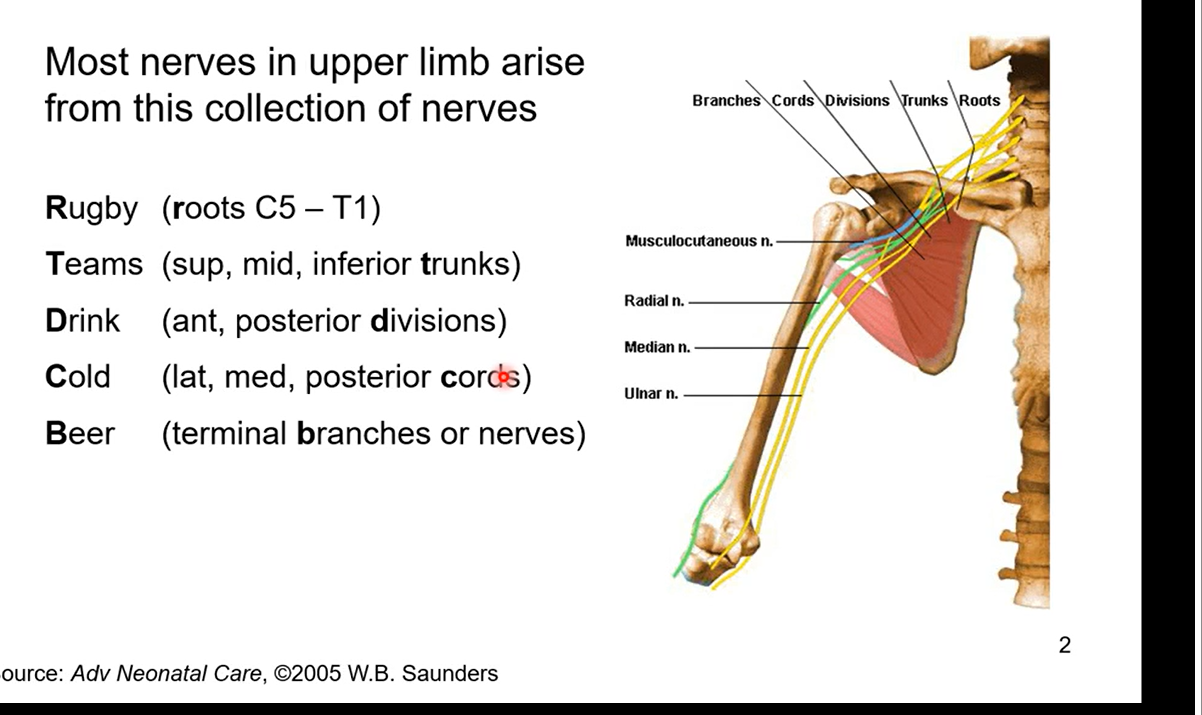
Brachial Plexus
most nerves in upper limb arise from this collection of nerves
R - roots C5-T1
cervical nerve 5 to thoracic nerve 1
T - sup, mid, inferior trunks
Trunks then branch off into divisions
D - ant, posterior divisions
C - lat, med, posterior cords
anterior divisions are lat and med cords and posterior division is posterior cord. the posterior cord is an extension of the divison
B - terminal branches or nerves
innervate muscles in upper extremities
brachial is made of 5 sections RTDCB above
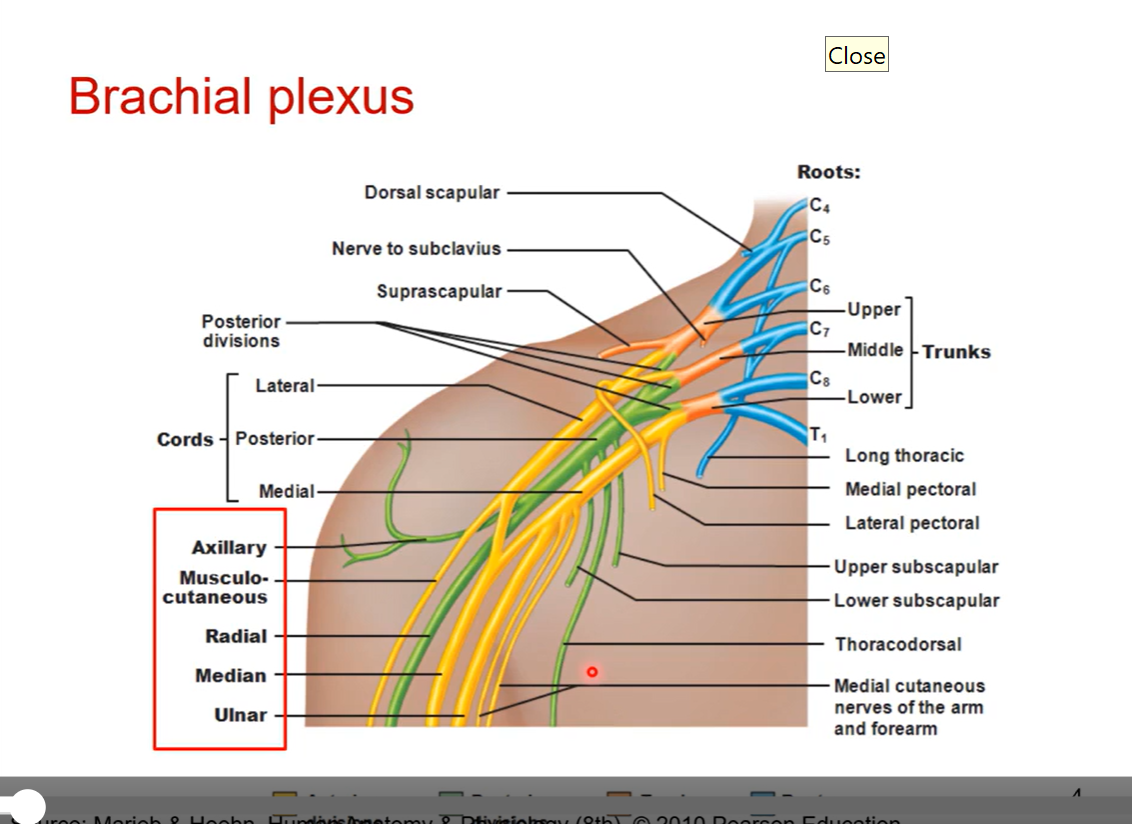
Finding brachial plexus
Find elusive “M” and then work backwards
musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar n.
all arise form anterior division and from either lateral or medical cords
posterior division (cord) is axillary n. and radial n.
posterior division has an elusive “Y”
pic is brachial plexus
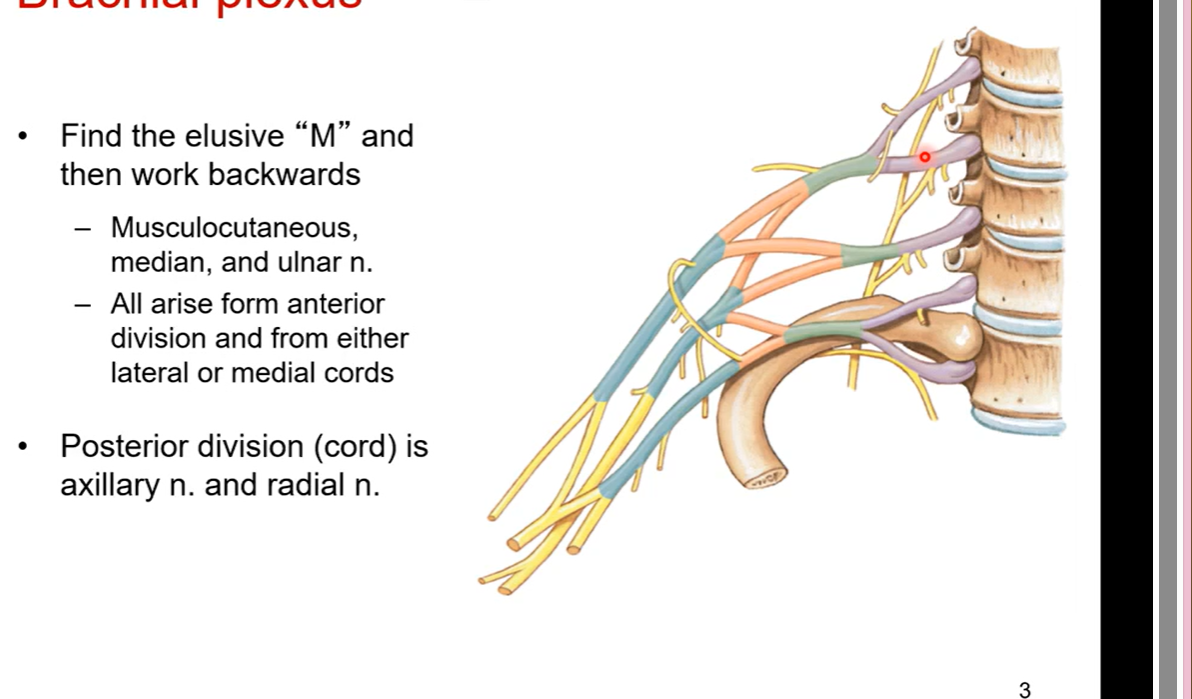
Notes in brachial plexus:
there are 7 cervical vertebrae and 8 cervical nerves why?
there is a cervical nerve one 1 sitting on top of the atlas and cervical nerve 2 under the atlas. there is an extra nerve on top of the atlas essentially
lumbar nerves, thoracic all do not have a mismatch with nerve and bone
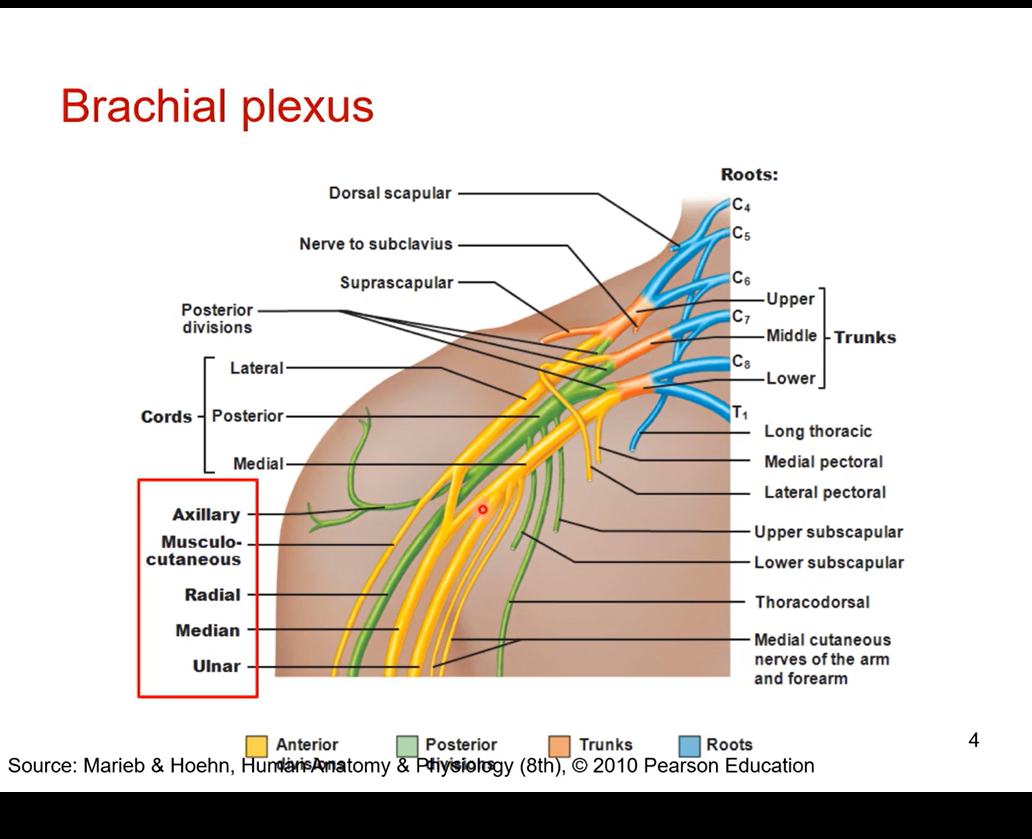
Describe the boxed red
median nerve- cuz running midline of the 3 nerve bundle
musculocutaneous- towards upper arm muscles
ulnar nerve- running down ulnar side so most medial of the 3 nerves in the anterior division and it is coming of the medical cord
in posterior division it branches off into the auxiliary nerve- right into the armpit and into shoulder
radial nerve- running down posterior side of the arm and the forearm
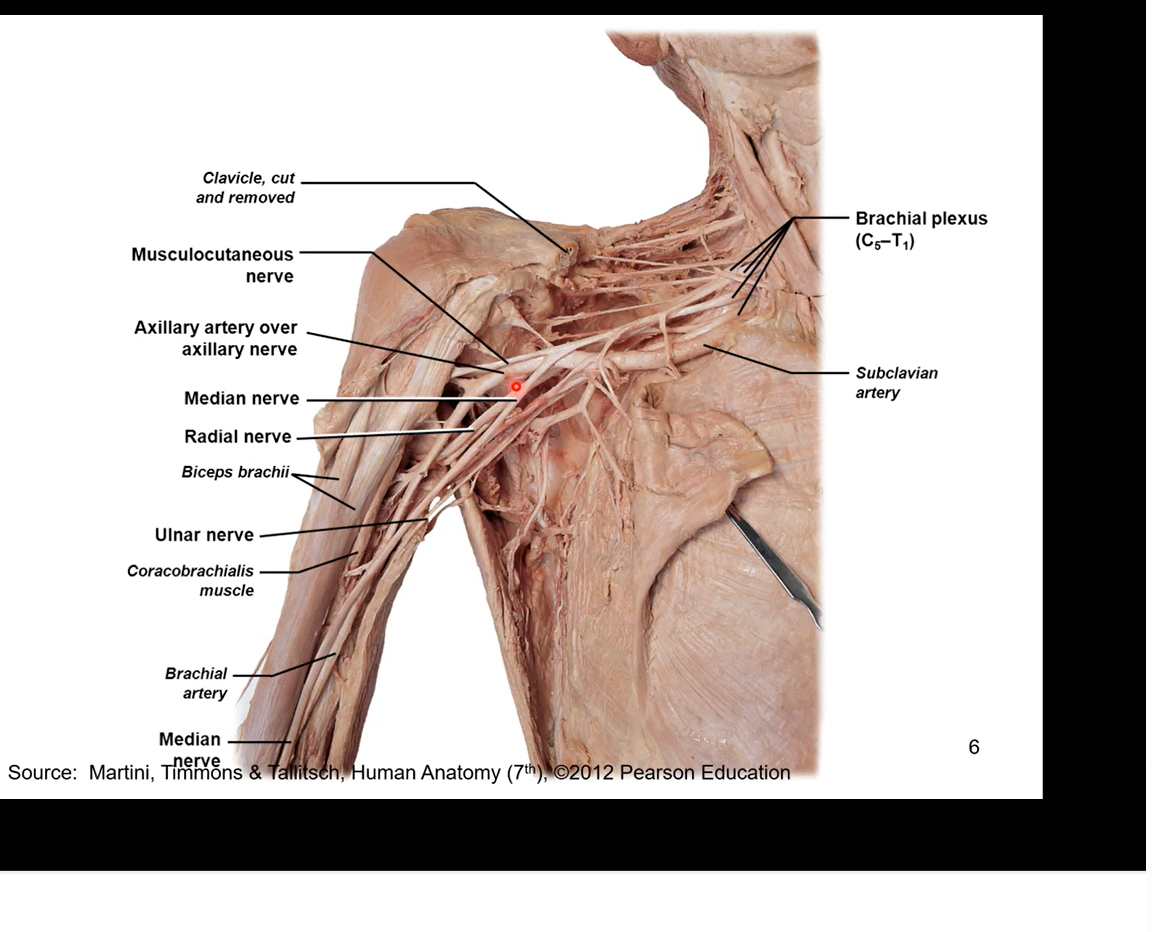
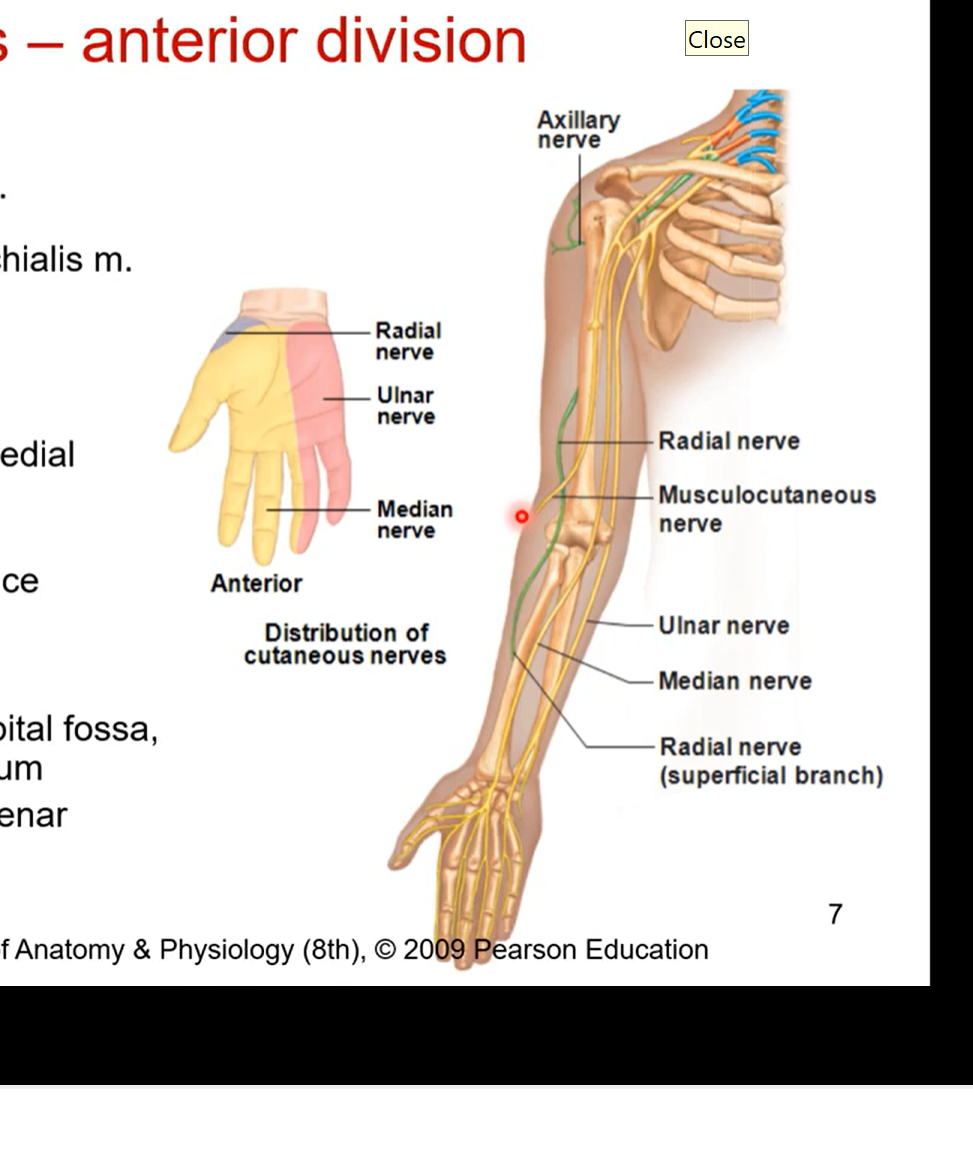
Brachial Plexus - anterior division in detail
musculocutaneous nerve
pierces coracobrachialis muscle
innervates all muscles on anterior brachium ( responsible for elbow function)
most lateral nerve
ulnar nerve- most medial nerve or the branch
medial humerus, medial epicondyle
innervates 1 ½ forearm flexors then goes hypothenar eminence. innervates 5th digit and half of 4th.
funny bone cause very exposed
median nerve
deep humerus, cubital fossa, anterior antebrachium (forearm)
innervates most of forearm flexors, thenar eminence (around the thumb). innervates digits 1, 2,3 and half of the 4th
runs down middle of ulnar and musculocutaneous nerve
doesn’t touch muscles of anterior brachium just like ulnar nerve
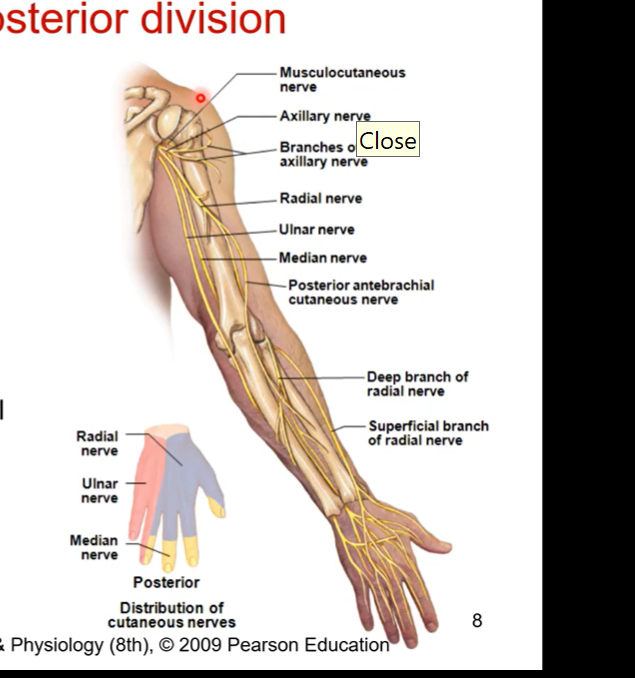
Brachial Plexus - posterior division in detail
axillary nerve
1st branch of posterior division
wraps around humeral head
innervates deltoid (any shoulder muscle movement including extension, abduction, adduction, etc.)
radial nerve
posterior humerus, lateral epicondyle, posterior antebrachium
triceps brachii, forearm extensors
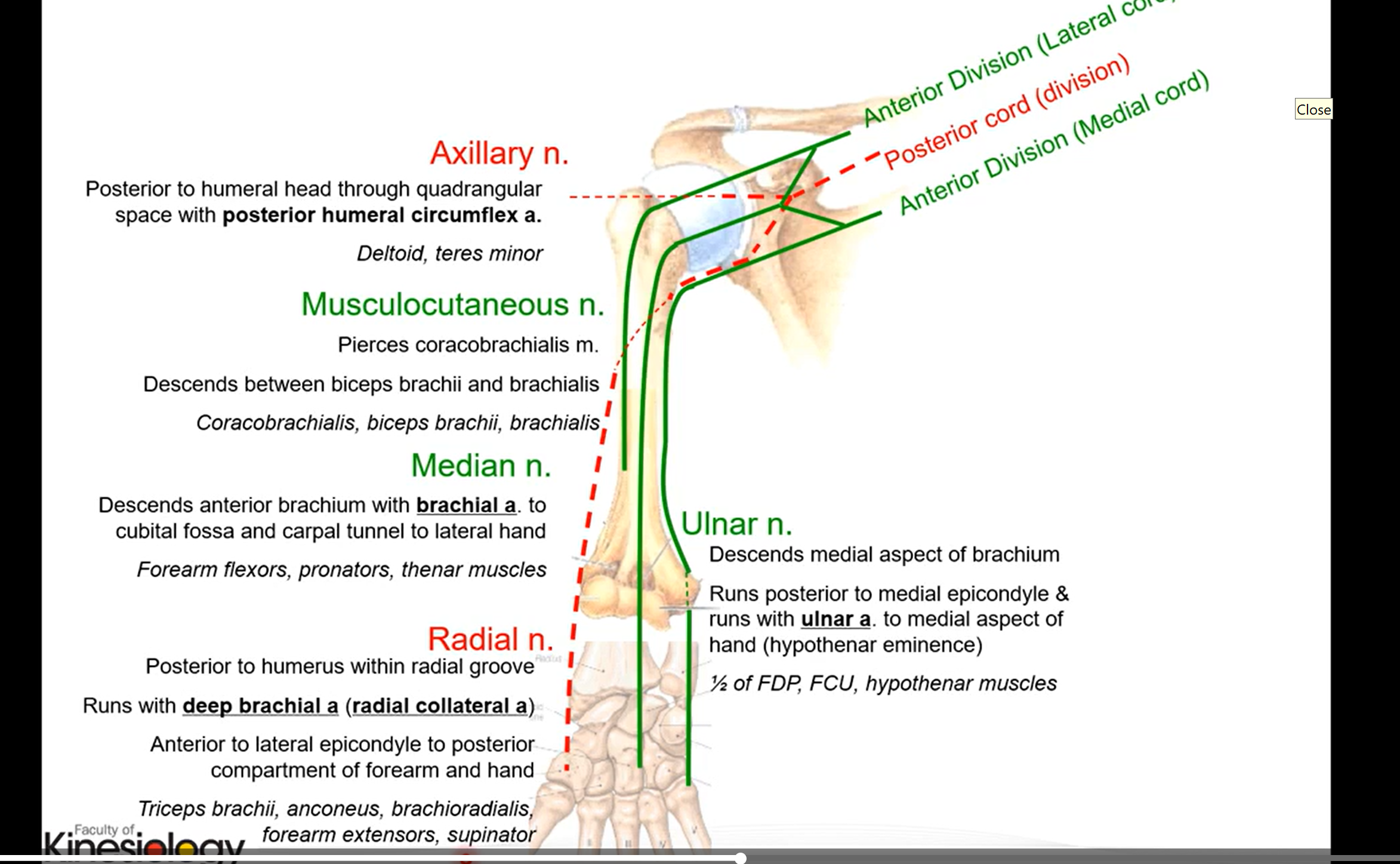
Anatomy of upper extremities summarized
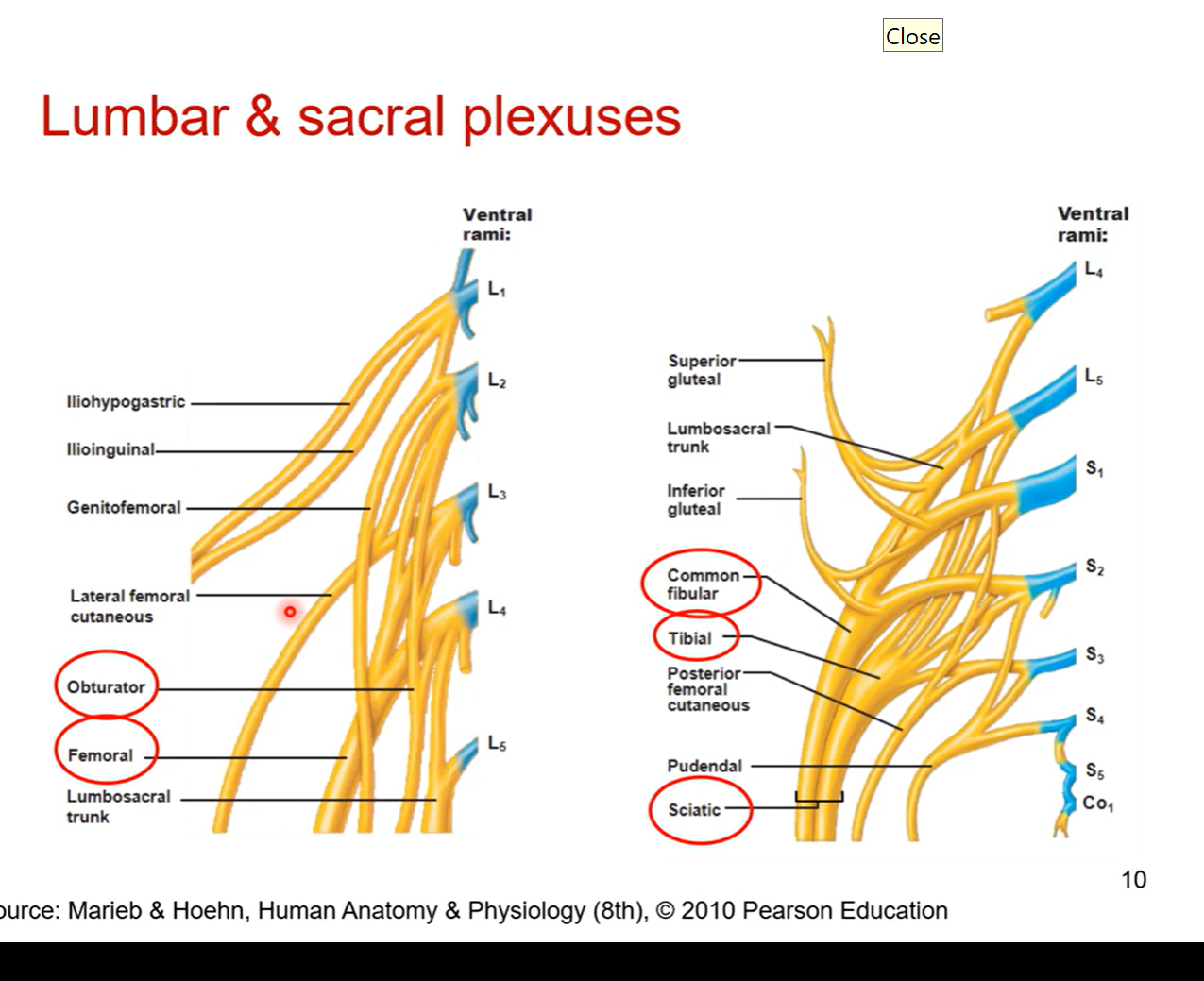
Lower extremities- Lumbar and sacral plexuses
start from lumbar and sacral vertebrae and branch off into diff parts of the lower extremity.
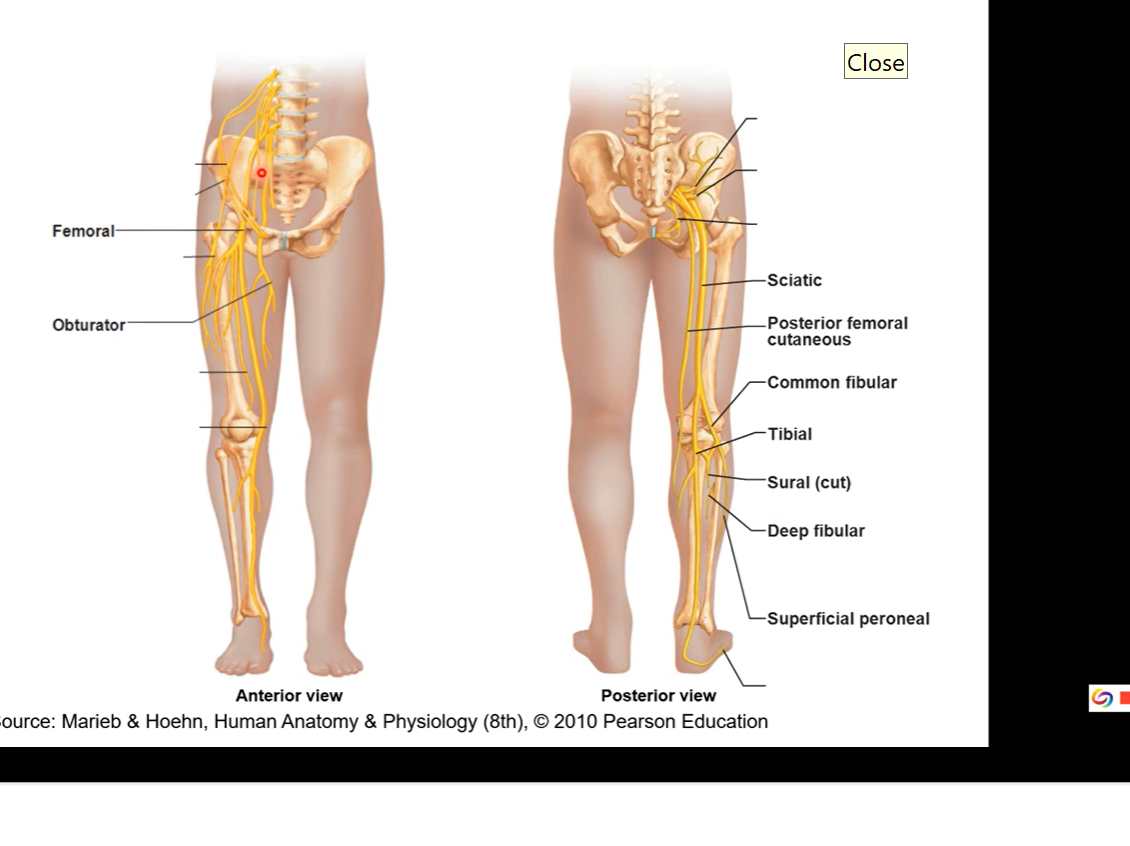
Full view of lower extremity
femoral and obturator come out of lumbar and sacral plexuses
responsible for anterior thigh and medial thigh
obturator nerve travels through framing and then innervates into medial thigh specifically
posterior side coming from sacral plexus is sciatic
sciatic= bundle of 2 fibres. common fibular/ common peroneal nerve or tibial nerves
fibular nerve also runs on posterior side of calf
superficial peroneal innervates superficial part of the leg
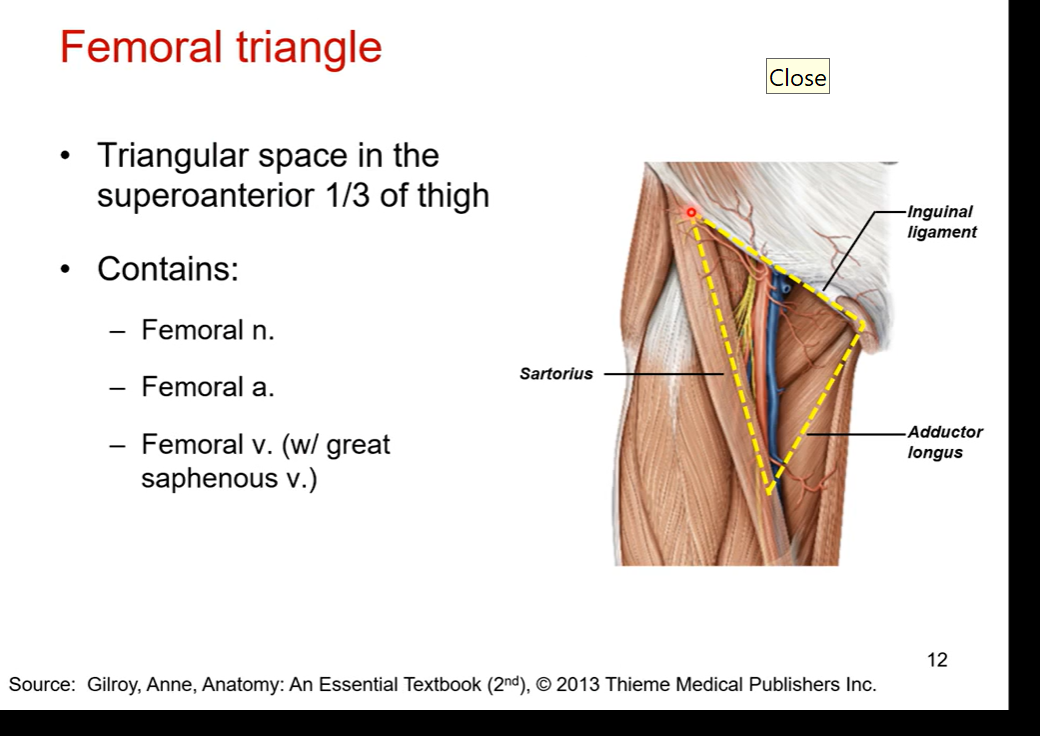
anterior side of nerves for the femoral nerves, look for femoral triangle
triangular space in the superoanterior top 1/3 of thigh.
space borders inguinal ligament ( most superior border), sartorius muscle ( lateral border), and adductor longus (medial border) at the border
contains:
femoral nerve
femoral artery
femoral vein ( with great saphenous vein)
blue in pic is femoral vein ( most medial). femoral nerve in yellow (most lateral). red artery
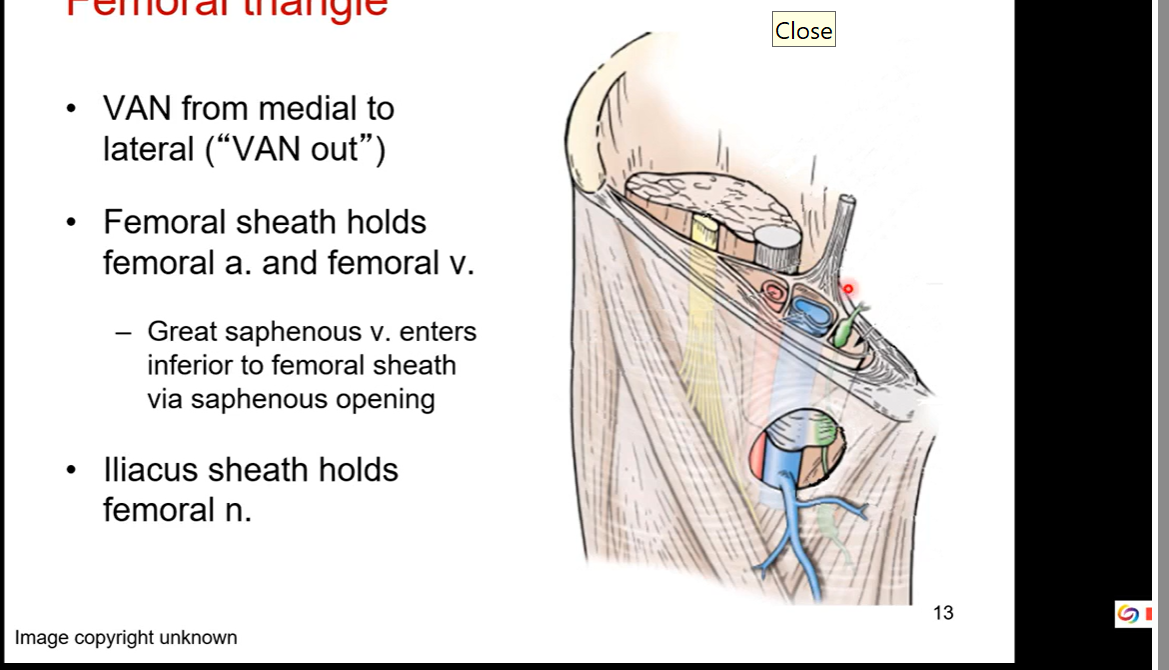
Trick to find femoral triangle
VAN from medial to lateral ( VAN out; VAN outwards from medial to lateral)
femoral sheath holds femoral artert and femoral veins together
greater saphenous veins enters inferior to femoral sheath via saphenous opening
Iliacus sheath holds femoral nerve
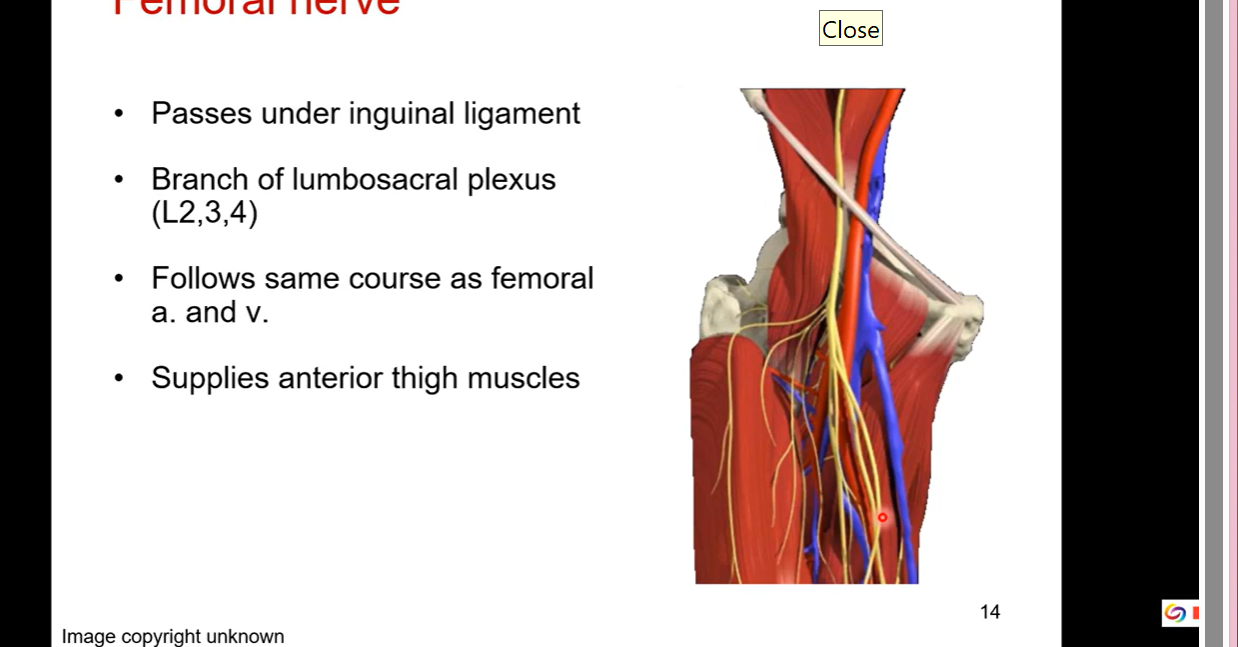
Femoral nerve
passes under inguinal ligament
starts from branch of lumbosacral plexus (L2,3,4)
Follows same course as femoral artery and veins
supplies anterior thigh muscles
Posterior side - Sciatic nerve
branch coming from lumbosacral plexus (L4-S3)
posterior thigh
largest nerve in the body
through greater and less sciatic nerve
supplies no structures in gluteal region but most of lower extremity
tibial and common peroneal portions loosely bound together
obturator nerve also formed from this plexus (L2,3,4). goes to medial thigh
Largest nerve in body cuz its technically made up of two nerves ( sciatic nerve made up of common fibular and tibial)
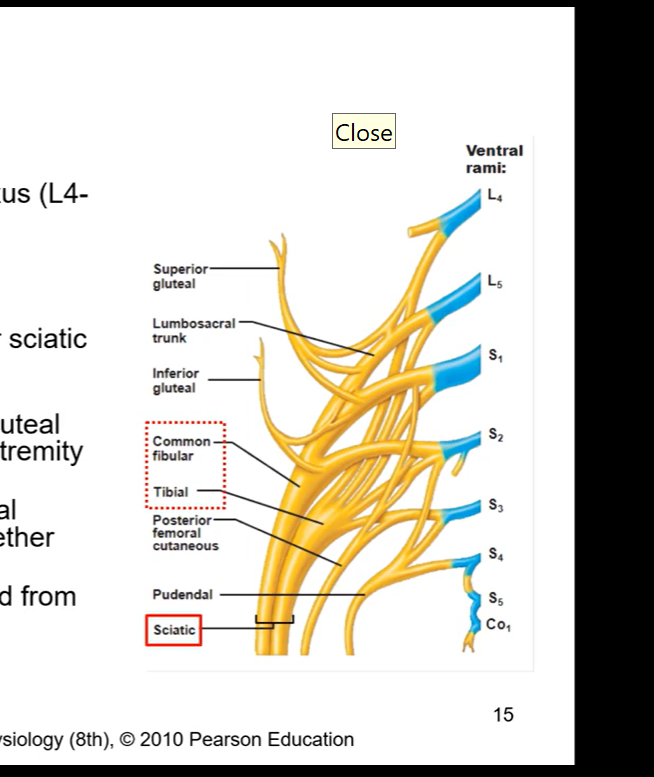
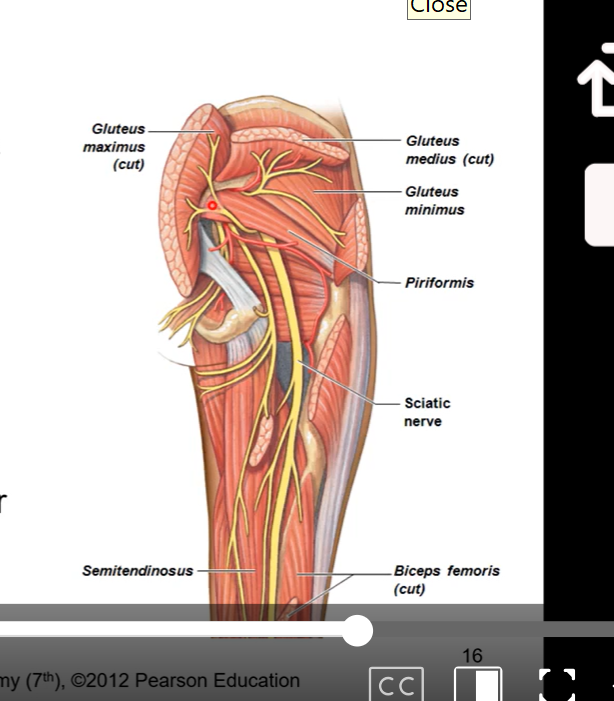
Sciatic nerve
coming from the lumbosacral plexus, meeting at the notches, it is going to pass through posterior side of thigh and exit inferior to piriformis
anterior to gluteus maximus
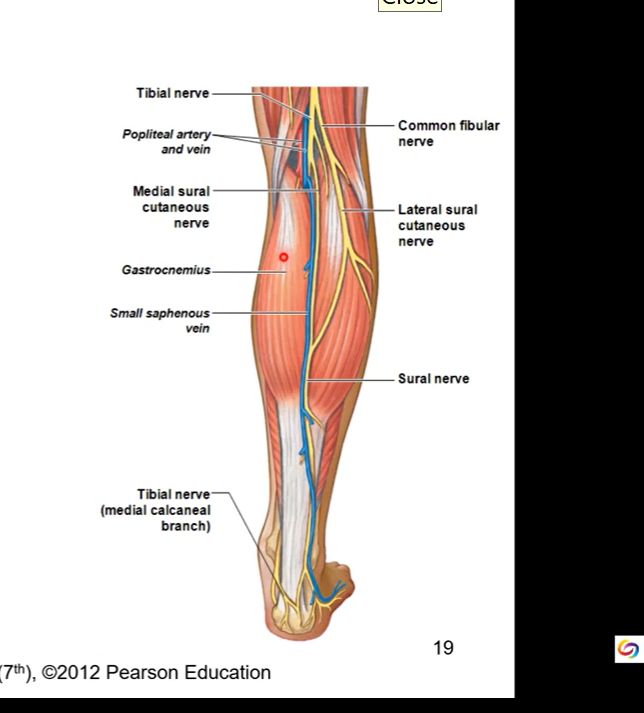
tibial branch supplies flexor muscles of lower leg
common peroneal branch supplies extensor muscles of lower leg
damage to sciatic nerve causes a lot of pain since it innervates so much of leg and foot
tibial nerve runs in deep posterior compartment with posterior tibial artery
innervates posterior side of leg/shank
common peroneal nerve divides into superficial and deep peroneal nerves
superficial runs laterally and hits/innervates all peroneal/fibular muscles on posterior side
deep runs run through trough fossa btw fibular and tibialar. fossa = opening for deep peroneal/ fibular nerve to run through and go to anterior side of lower leg
superficial peroneal nerve runs in lateral compartment
deep peroneal nerve runs in anterior compartment with anterior tibial artery and vein
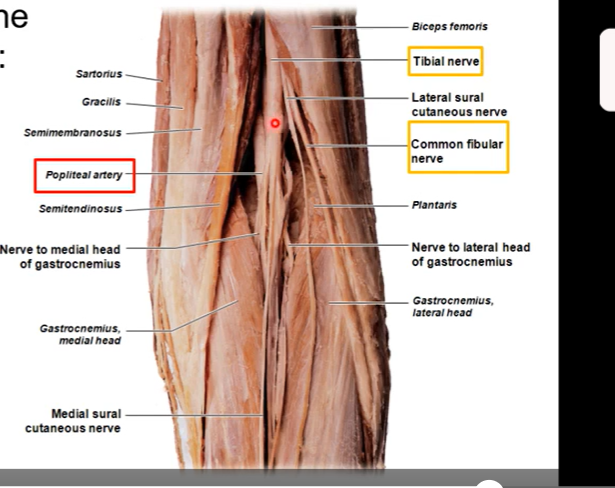
Popliteal fossa ( back of knee)
diamond shaped depression on posterior aspect of thigh
borders consist of the two heads (medial and lateral head ) of gastrocnemius and hamstrings
floor is popliteus muscle
roof is skin
top part of diamond is hamstring muscles. bottom half is gastrocnemius
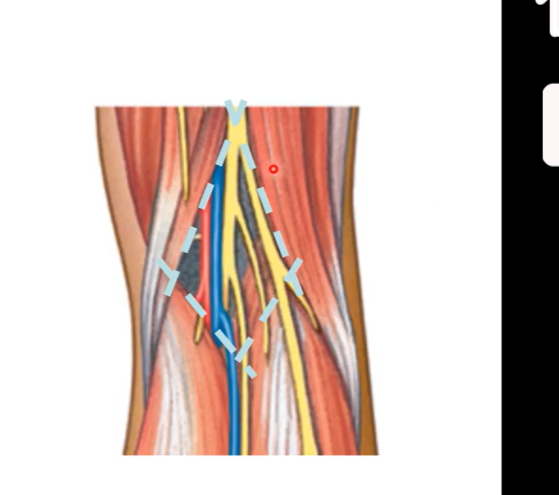
Popliteal fossa
from medial to lateral the popliteal fossa contains:
popliteal arteries
popliteal veins
tibial nerves
common peroneal nerves/ common fibular nerve (runs laterally)
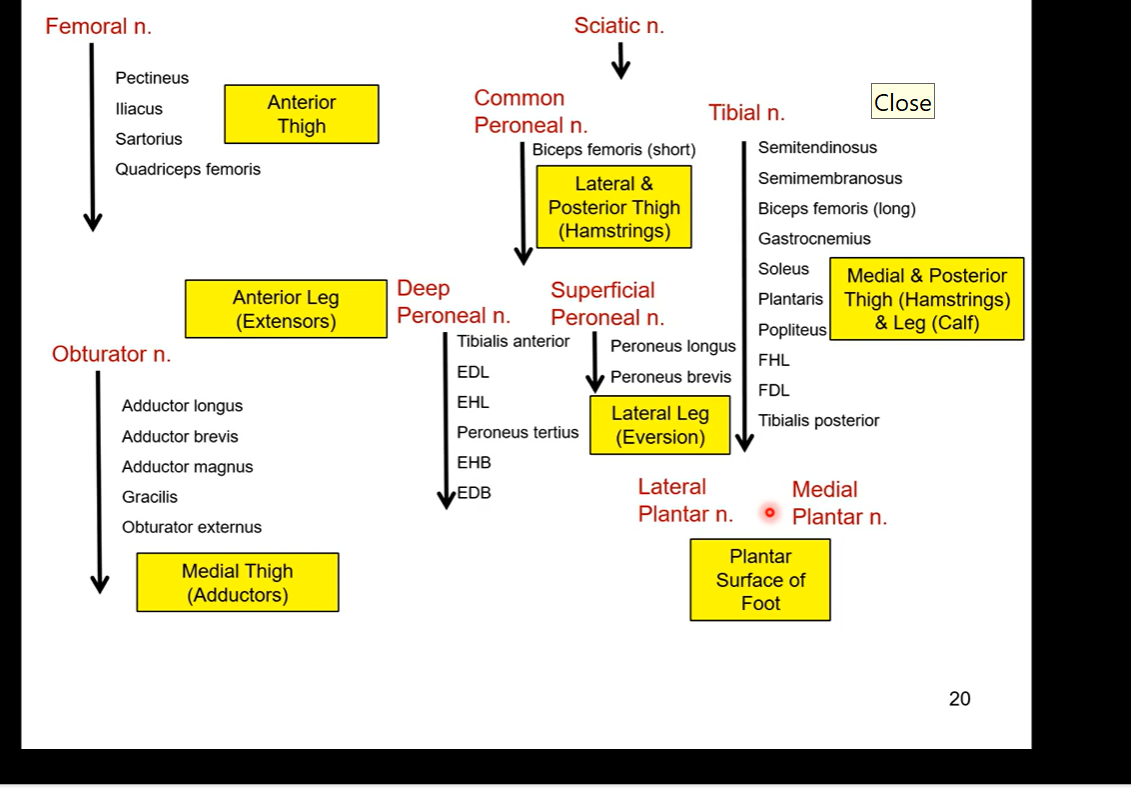
SUMMARY OF WHAT EVERYTHING INNERVATES