7-Swallowing, gastric Emptying, intestinal motility
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
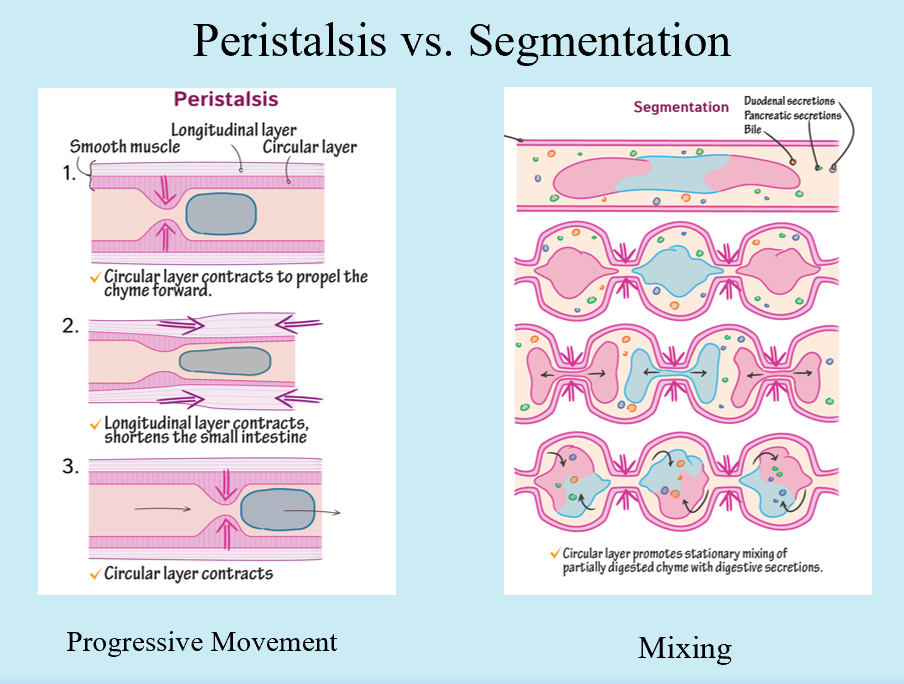
Peristalsis vs. Segmentation
Peristalsis
Progressive movement
Segmentation
Mixing
What detects stretch in the GI system? What NT’s are involved? How do interneurons come into play?
Sensory neurons
CGRP and ACh
Interneurons stimulate enteric motor neurons (ACh here too)
2 types of enteric motor neurons?
Excitatory EMN
ACh or Substance P
Inhibitory EMN
VIP or NO
What do stimulated enteric excitatory motor neurons result in? What about inhibitory?
Excitatory = Smooth muscle contraction (oral side)
Inhibitory = Smooth muscle relaxation (anal side)
What big things are involved in the swallowing reflex?
Touch Receptors (pharynx opening)
Integration center (medulla/pons)
Effectors (pharyngeal/esophageal striated & smooth muscle)
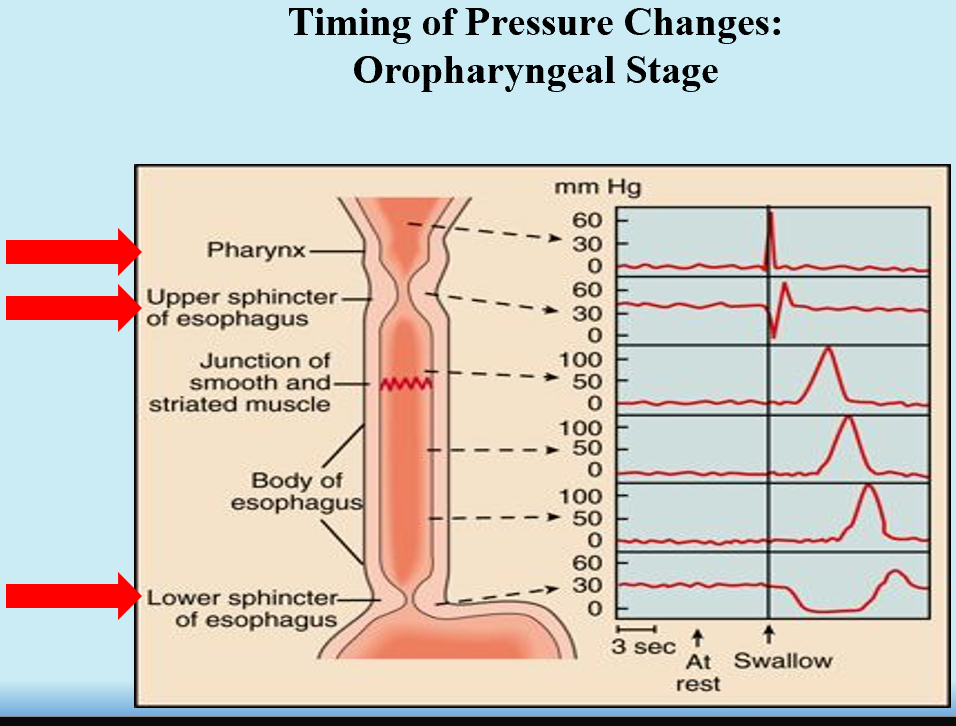
What are the 3 phases of the swallowing reflex?
Oral
Pharyngeal
Esophageal
Oral Phase
Voluntary
Touch receptors of pharynx detect bolus
Reflex initiated!
Pharyngeal Phase
Involuntary
Propels food from pharynx → esophagus
Epiglottis blocks tracheal entry!
UES Relaxes → Peristalsis → UES Constricts (after bolus passes)
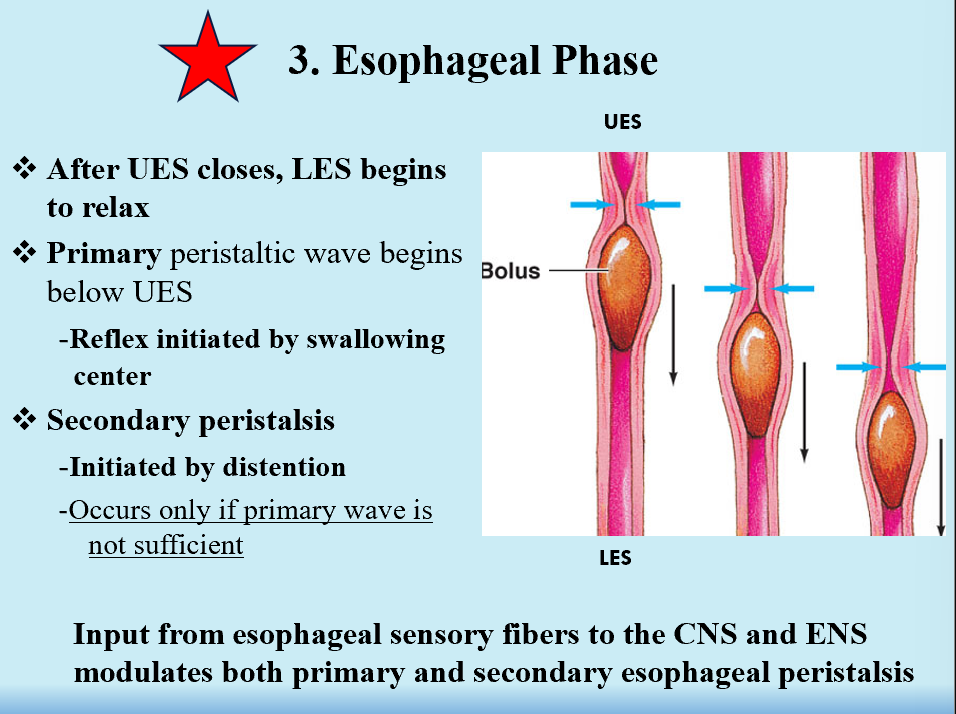
Esophageal Phase
Involuntary
UES closes →LES relaxes (opens)
Primary peristaltic wave below UES → swallowing center initiates reflex → secondary wave (initiated by distention)
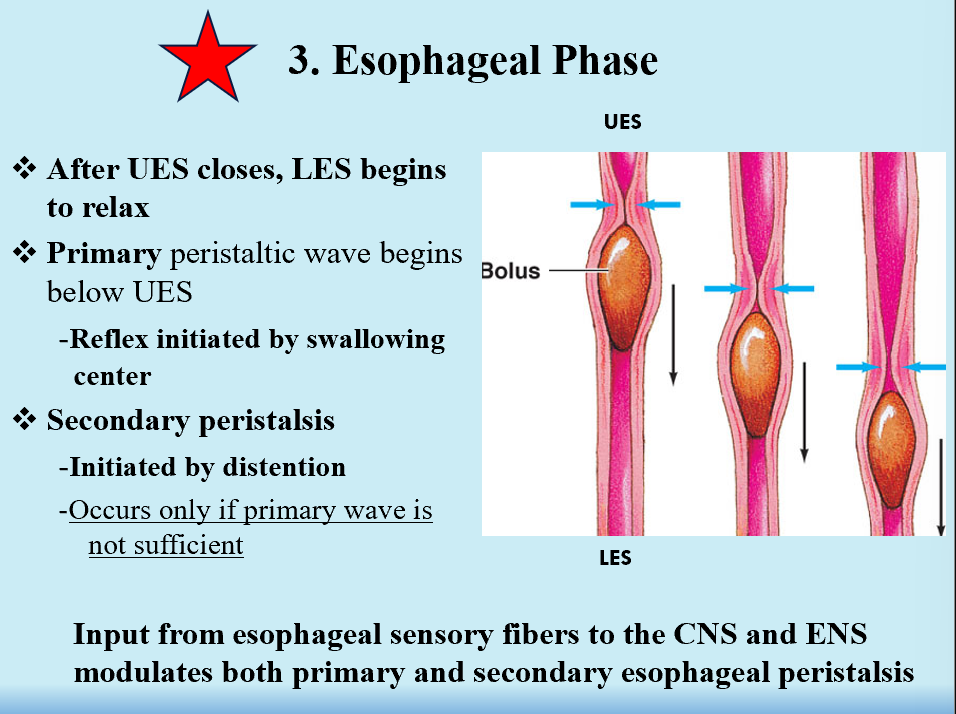
CNS and ENS
Input from esophageal sensory fibers to HERE modulates both primary and secondary peristalsis.
Dysphagia
Trouble swallowing
Can be:
Structural
Anatomy
Functional
Abnormal swallowing reflex
Achalasia
Failure of LES to relax (constantly contracted)
Food is retained in esophagus and in LES
Complete lack of peristalsis within esophagus!
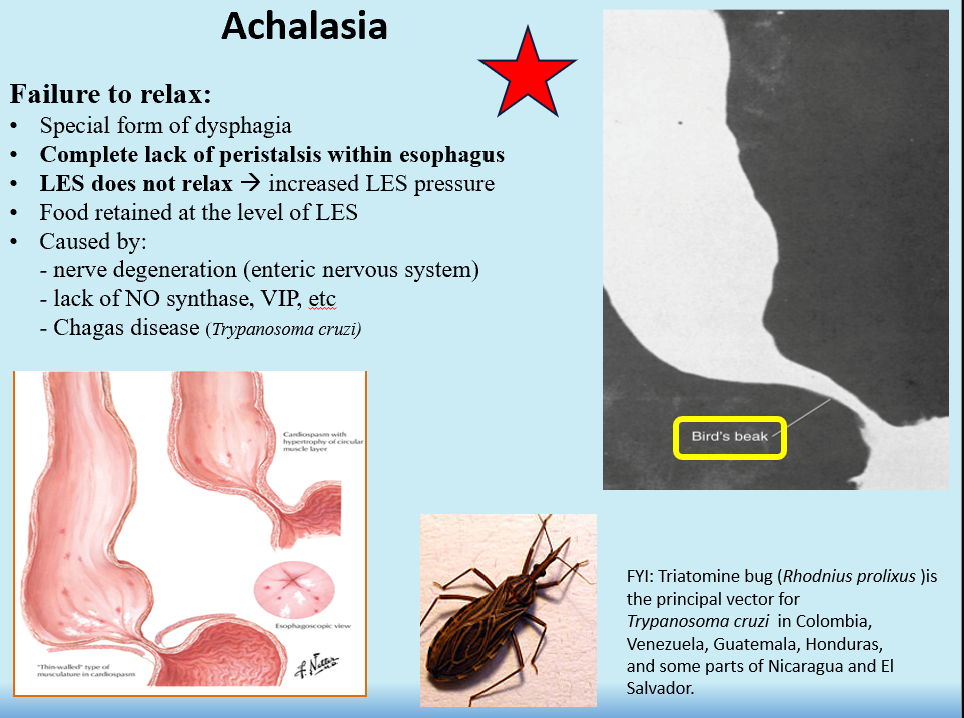
Incompetent LES
Failure of LES to contract (constantly relaxed)
Cause is unknown!
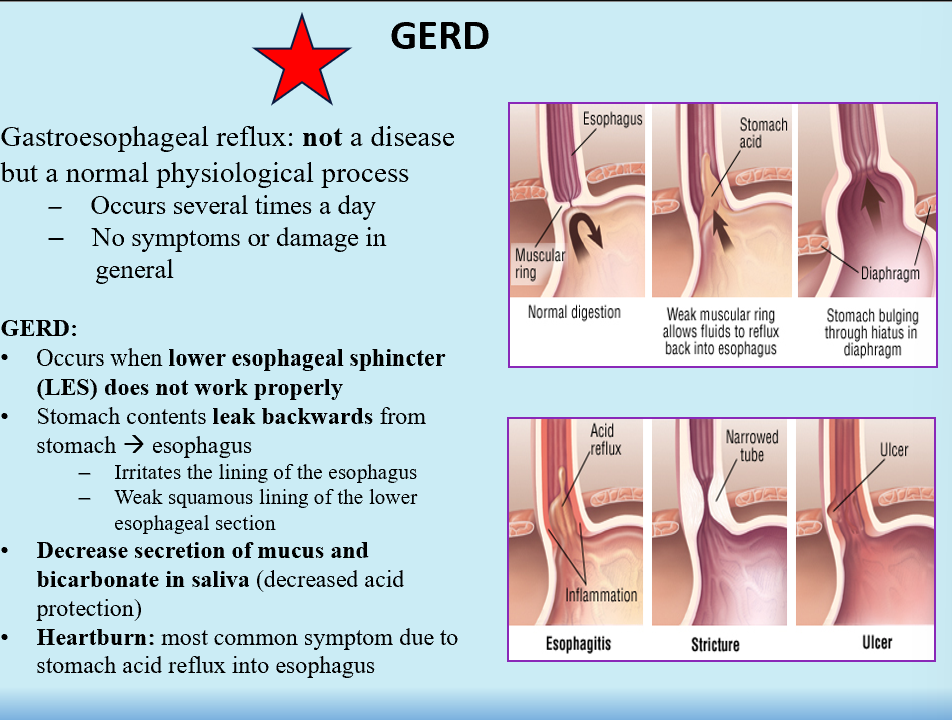
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, common
LES doesn’t work right
Stomach contents leak back into the esophagus
Decreased secretion of mucus and bicarb in saliva (decreased protection against acid)
Heartburn!!
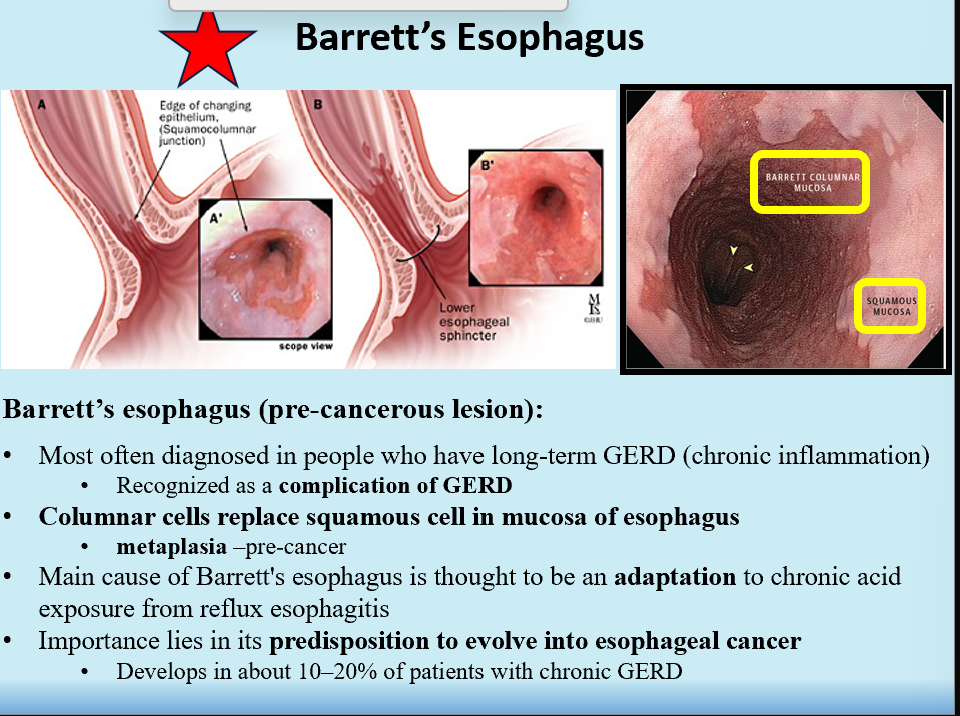
Barrett’s Esophagus
Special type of GERD, a complication of it
An adaptation to chronic acid exposure
AKA pre-cancerous lesion (Metaplasia)
Columnar cells replace squamous cells in mucosa of esophagus
Predisposition to esophageal cancer
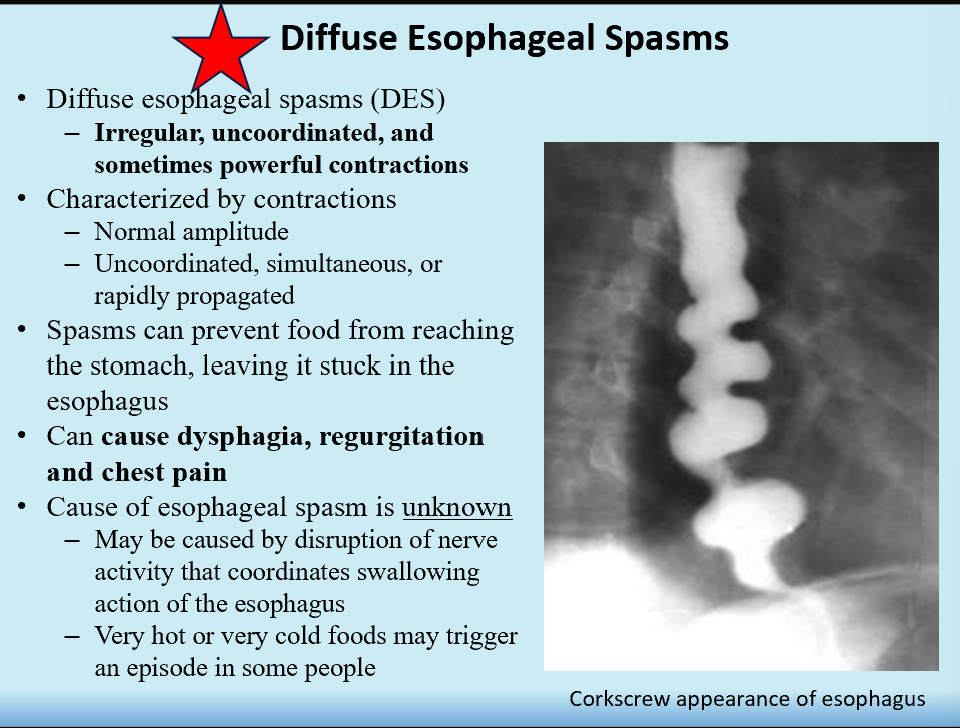
Diffuse Esophageal Spasms
Irregular, uncoordinated esophageal contractions
Contractions can be powerful
Sx:
dysphagia
regurgitation
chest pain
Corkscrew esophagus appearance!
Disorder of Esophageal Function
Dysphagia
Achalasia
Incompetent LES
GERD
Barrett’s Esophagus
Diffuse Esophageal Spasms
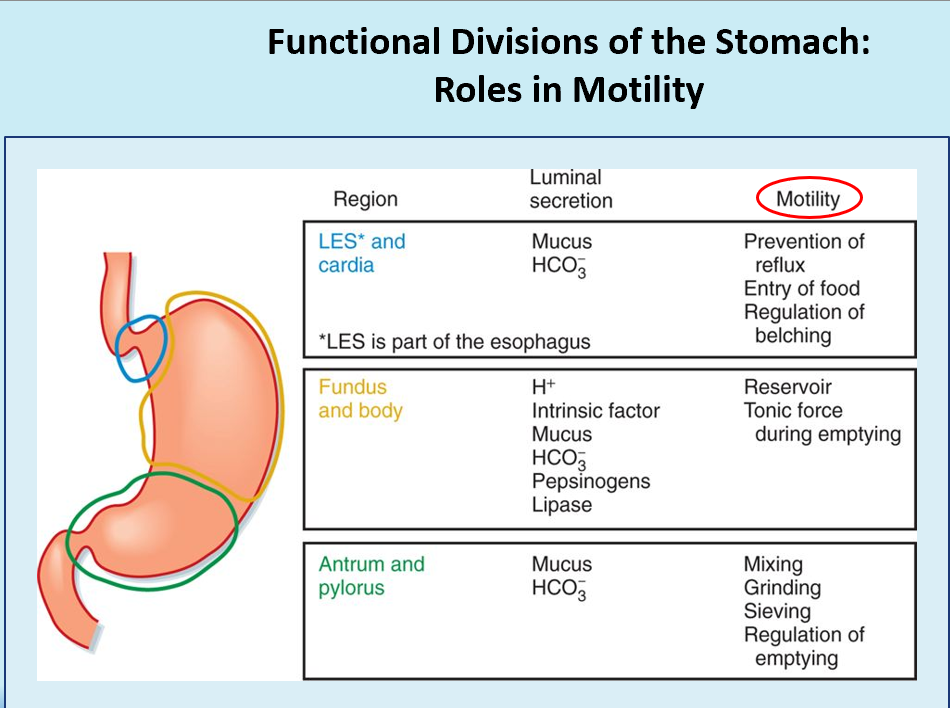
3 types of gastric motility:
Mixing
Peristalsis
Migrating Myoelectric Complex (MMC)
Sweep undigested stuff out during fasting
Orad vs. Caudad Regions of Stomach
Orad = Fundus and proximal body (receives/stores food)
Caudad = Distal body and antrum (mixes/propels)
Receptive Relaxation
Allows for gastric accommodation.
Initiated by swallowing, causes stomach to relax.
Modulated by vagus n.
Gastric Accommodation
LES and stomach relax.
Ensures changes in volume don’t result in increased gastric pressure.
Modulated by vagus n.
A way to temporarily store ingested food before controlled release (gastric emptying) into the intestine occurs.
Antral Pump: Gastric Mixing
Propulsion
Grinding
Retropulsion
Trituration: reducing particle size right after a meal
Emptying
THIS is delayed until solids are mechanically broken down!
Slowed by byproducts of digestion and hypertonic chyme.
Rate of gastric emptying contents:
Liquids > Carbs > Proteins > Fats
Isotonic > Hyper/Hypotonic
Duodenal Contents
Delays gastric emptying.
Enterogastric Reflex
Stimulated by:
Duodenum pH 3-4
Gastric pH 1.5
Gastric motility inhibited
Pyloric Sphincter Hormonal & Neural Regulators
Increased constriction:
CCK, GIP, Secretion, Gastric
Sympathetic
Relaxation:
Parasympathetic
Fasting State
The only time MMC occurs!
Removes remaining ingested (but not digested) contents!
Vomiting (Emesis) (stimuli and steps?)
Stimuli:
Gastric/duodenal distention
Dizziness
Drugs
GU injury
Steps:
Reverse peristalsis (SI → pylorus)
Pyloric sphincter relaxes
Abdominal muscle contraction
Pylorus/Antrum Contract
LES relaxes
Gastric contents move up esophagus
UES relaxes
Glottis closes
Increased saliva
Expulsion
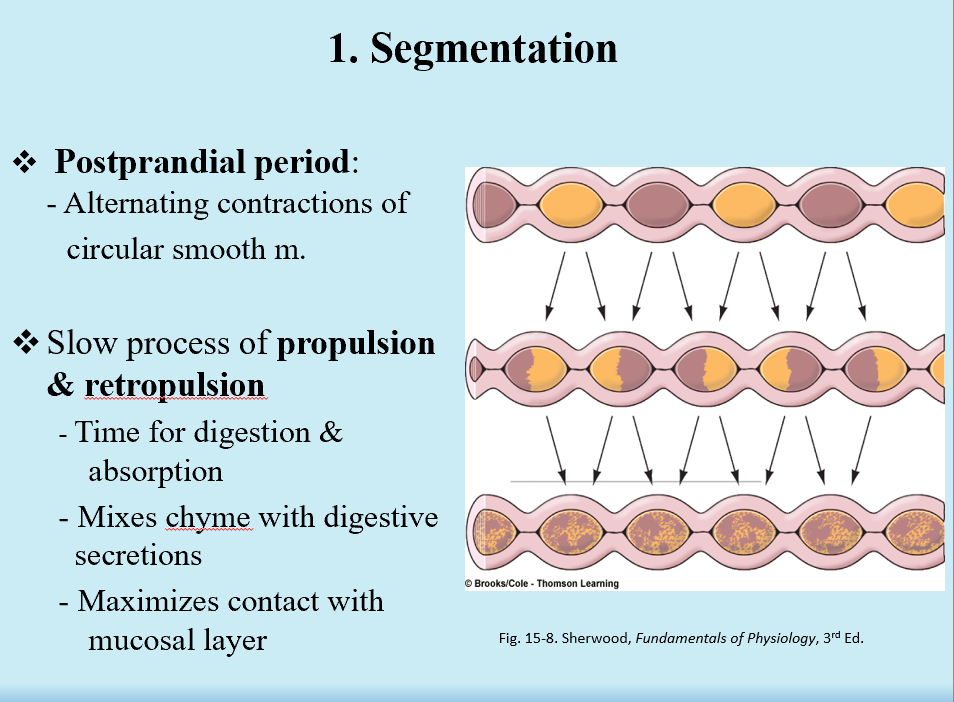
Segmentation
Postprandial period (alternating contractions of smooth m.)
Slow propulsion/retropulsion
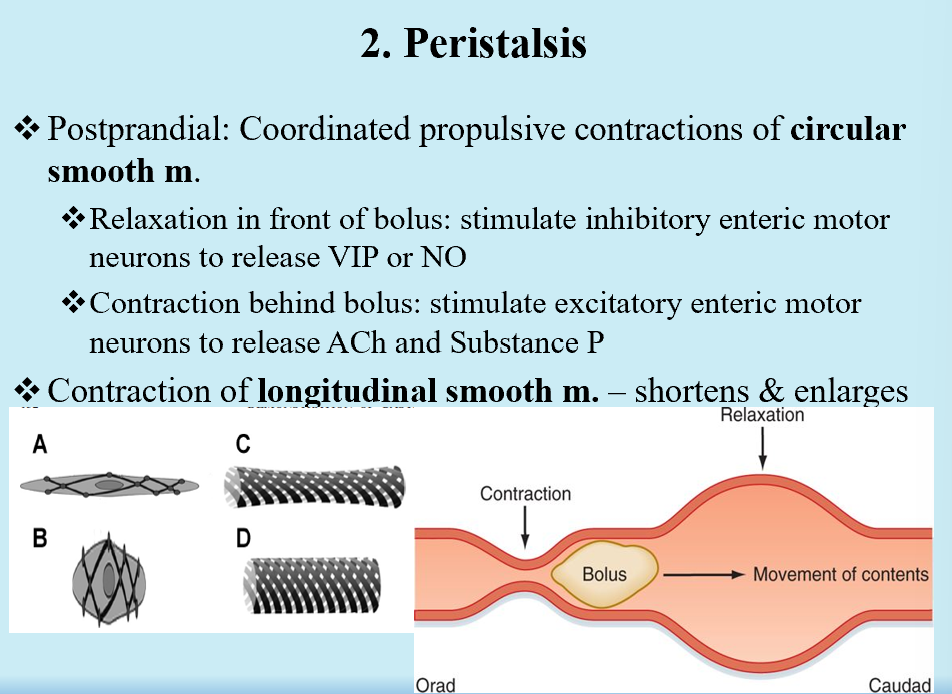
Peristalsis
Coordinated propulsions of circular smooth m.
Contraction of longitudinal smooth m.
Intestinointestinal Reflex
Distention in one segment, relaxation in the rest of the small intestine
MMC (migrating myoelectric complex)
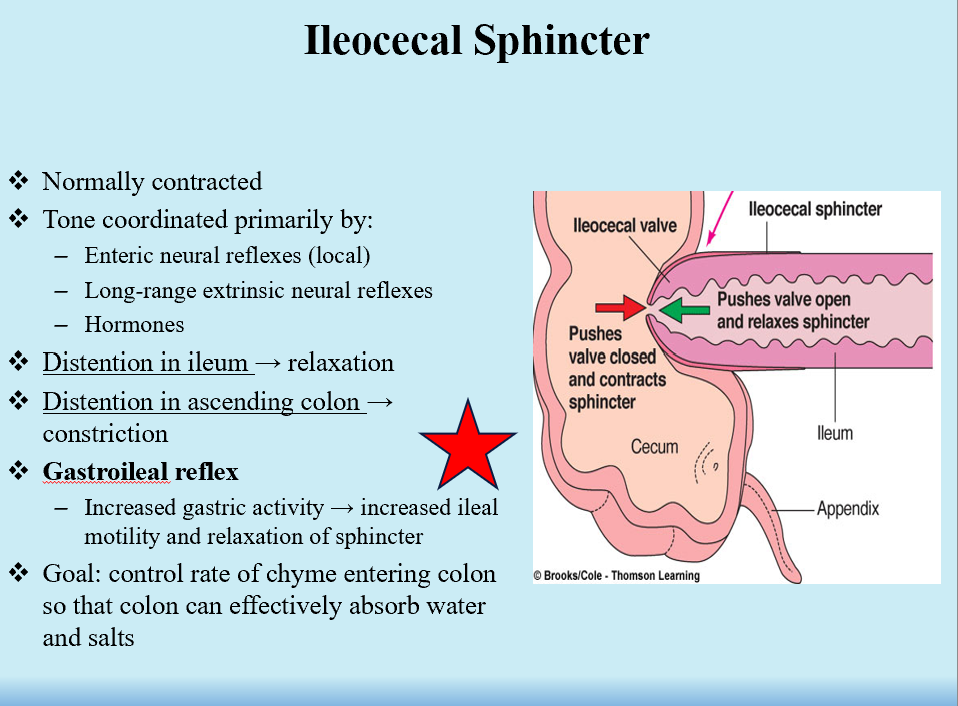
Ileocecal sphincter is relaxed
Correlated with high levels of motilin (SI hormone)
Prevents backflow of bacteria from colon → ileum
Gastroileal Reflex
Increased gastric activity → increased ileal motility and relaxation of sphincter
Controls rate of chyme entering the colon so colon can effectively absorb everything!
Works with gastrocolic reflex to stimulate urge to defecate.
3 types of colonic motlity:
Haustrations
Long-duration contractions
Mass movements (propulsion)
Gastrocolic Reflex
Stomach distention results in generalized increase in colonic motility
Can lead to ‘urge’ to defecate
Stimulates mass movements
Regulators of colonic motility:
Parasymp:
increased motility via excitatory EMN
Excessive = diarrhea
Symp:
Inhibits motility via inhibitory EMN
Excessive = constipation
Internal Anal Sphincter
Smooth muscle, involuntary, most tone
External Anal Sphincter
Striated muscle, involuntary and voluntary!
Rectosphincteric Reflex
For defecation
Relaxes IAS (urge):
VIP and NO
Defecation Steps
Voluntary relaxation of EAS
Contract abdominal muscles
Relax pelvic muscles
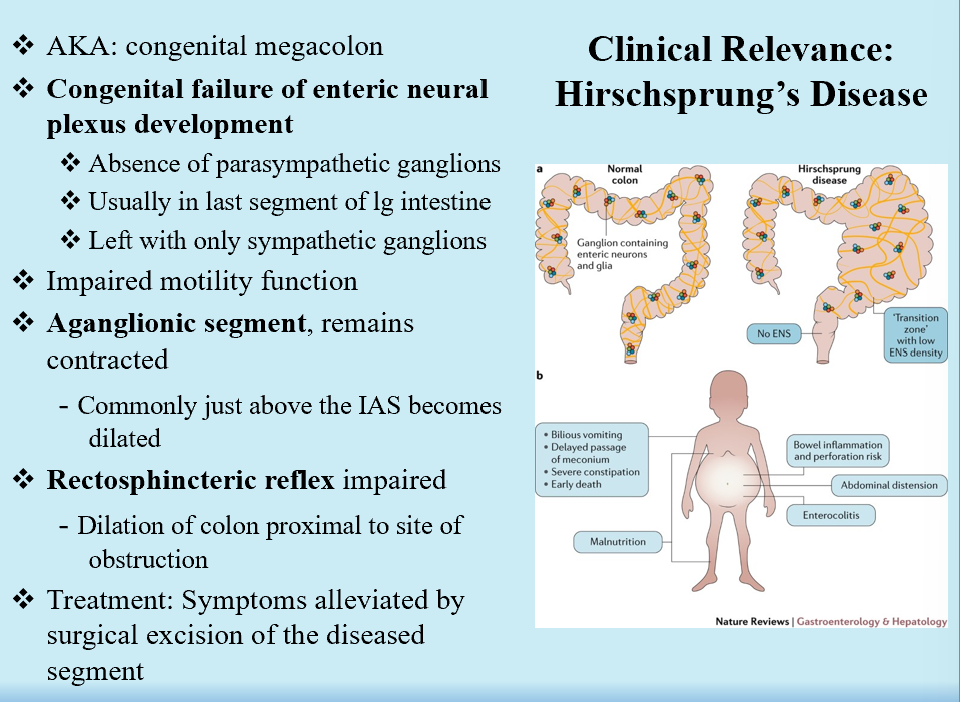
Hirschsprung’s Disease
Congenital megacolon
Congenital failure of ENS development
No PNS ganglion
Aganglionic segment stays contracted
Rectosphincteric reflex is non-functional
Colon proximal to obstruction is inflated!
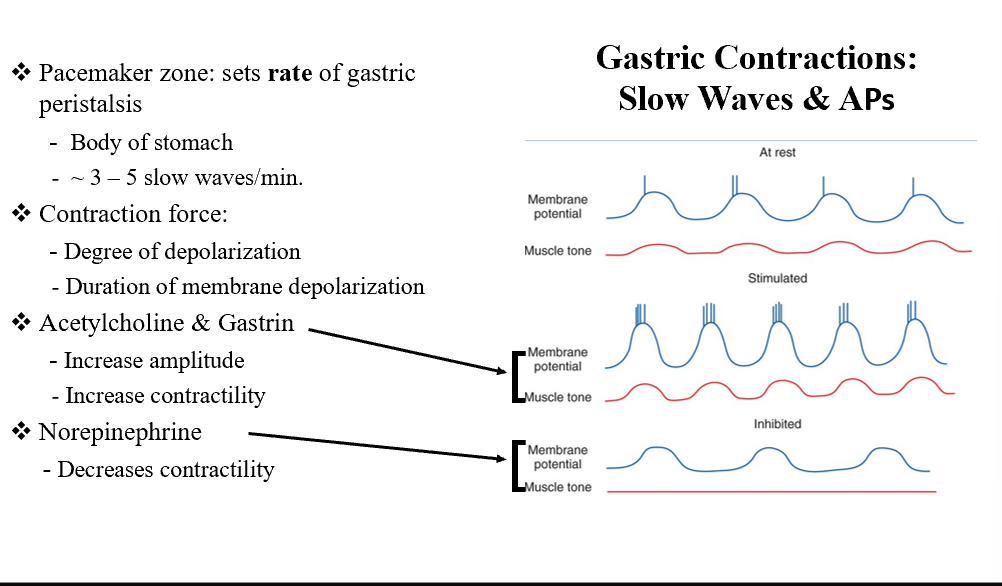
Pacemaker Zone
Sets the rate of gastric peristalsis (body of the stomach)!
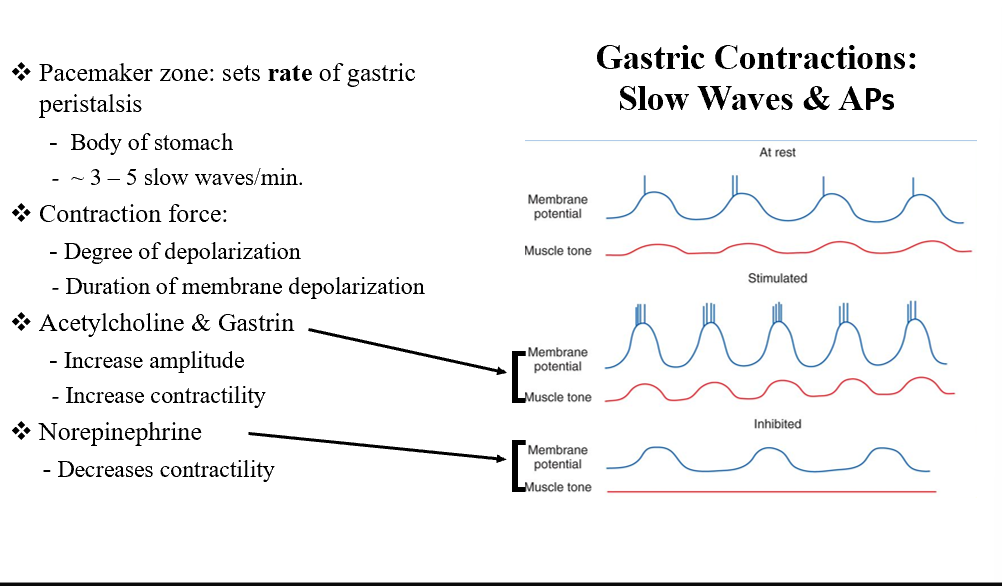
ACh and Gastrin
Increases amplitude
Increases contractility
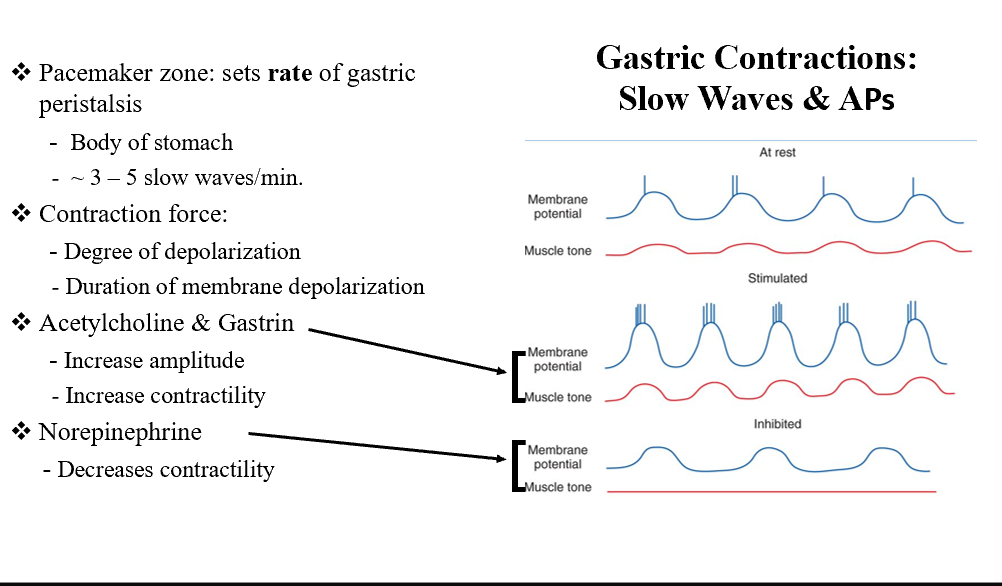
NE
Decreases contractility
Variables influencing gastric emptying
Volume of chyme
Degree of fluidity
Presence of fat, acid, hypertonicity, or distension
Emotion
Intense pain