Dielectrics !
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Dielectric does not contain _______ electrons ?
free
In conductor each atom contain atleast ____ free electron
one
In Dielectric all the electrons are tightly bound to ____ of the atom
nucleus
In Conductors all the electrons are _____ bounded with nucleus
loosely
In dielectric the conduction bands are _______
empty
In conductor the conduction bands contain _______
electrons
In dielectric : The charge given to this is _______
localized
In conductor : The charge given to this reside on the _______
surface
In dielectric : The electron takes to and fro motion and just be around ________
nucleus
In conductor : The electron takes translatory motion and can leave the _____
atom
Dielectrics do not conduct _________
electricity
Conductors conduct _________
Electricity
In _________ there is no question of lossing the character and break down strength
Conductor
The higher the breakdown strength, the better the material is at keeping __________
Electricity
What are the examples of Dielectrics ?
Mica
Glass
Plastic
What are the examples of conductor ?
All metals !
What are the uses of dielectrics ?
Capacitors ( between the plates of capacitors )
Microwave Ovens ( Dielectric heating )
Dielectric Mirrors ( to enhance the reflectivity of mirrors )
Transformer Oil ( Dielectric oils used for cooling )
Types of dielectrics ?
Non-Polar dielectrics
Polar dielectrics
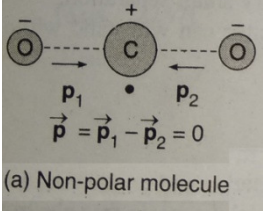
What is non-polar dielectric ?
A non-polar dielectric is an insulating material that does not have a separation of positive and negative charges.
What is polar dielectric ?
A material that has a permanent electric dipole moment due to the presence of polar molecules. This property allows it to interact with electric fields and store electrical energy. Examples include water and certain ceramics.
what is polarization ?
The separation of positive and negative charges within a molecule or object
if the applied field is increased then sepration ?
increase ><
what is permanent dipole moment
Permanent dipole moment is the measure of the overall polarity of a molecule due to the presence of polar bonds. It occurs when the molecule has an uneven distribution of charge
A —————— is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges within a system
dipole moment
The dipole moment is ______ quantity
vector
The formula of dipole moment ?
μ =q⋅d
q is the magnitude of the charge
d is the separation between the charge
what is polarization
the alignment of charges in an material is polarization
formula of polarization ?
P=p/ΔV
P is the polarization vector,
p is the dipole moment,
ΔV is the volume.
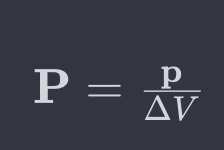
the dielectric constant is also known as
relative permittivity
the dielectric constant is nothing but ——-
how well material can store electrical energy
the ________ is defined as ratio of electric displacement field (D) to the electric field (E)
dielectric constant
the formula of dielectric constant
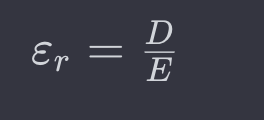
the dielectric constant is related to polarization through the formula of ?
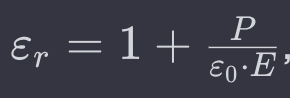
What is E , P & D ?
E - electric Field
P - Polarisation
D - Electric displacement field
What is electric field ?
force experience by positive charge divided by magnitude of the test charge
Formula of electric field ?
E = F/q
The polarisation formula ?
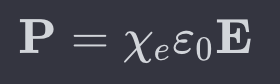
The ________ is related to both the free charge and polarization
electric displacement field
the formula of electric displacement field ?

the relation between that all E , D , P ?
∇⋅D=ρfree where:
∇⋅D is the divergence of the electric displacement field,
ρfree is the free charge density.
The ___________ is a phenomenon where certain materials generate an electric charge in response to mechanical stress or pressure.
piezoelectric
what are two interaction ?
Mechanical behaviours
Electrical behaviours
What are the types of piezoelectric effect ?
Direct Piezoelectric Effect
Converse Piezoelectric Effect
The ————————- refers to the generation of an electric charge in response to mechanical stress or deformation applied to a piezoelectric material
direct piezoelectric effect
The _______________ refers to the mechanical deformation or displacement experienced by a piezoelectric material when an electric field is applied to it.
converse piezoelectric effect