Biology - Digestive System
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Purpose of Digestion
To break down large molecules of food into smaller molecules, in order to obtain essential nutrients
Large molecules are chemically inert, must be broken down and reassembled into usable products
Large molecules typically insoluble, smaller subunits are and can be absorbed into cells
Mouth
Begins mechanical digestion (chewing)!
Begins chemical digestion (salivary glands secrete saliva that moistens food into soft bolus)!
Esophagus
enters here after bolus swallowed
is lined with epithelial tissue that pushes food down by peristalsis!
glands in lining produce mucus so tube is moist and moves through easily!
Epiglottis at top of trachea (next to epiglottis), closes to ensure bolus doesn’t enter
Stomach
chemical digestion!
gastric juice secreted: kills harmful substances and denatures proteins
Mucus: protects stomach from acid
Pepsin: breaks down protein
food digested here for hours, then turned to chyme (creamy paste)
Small Intestine
chemical digestion and absorption
digestive enzymes secreted
nutrients diffuse through intestinal wall into bloodstream for transportation
has villi
has 3 parts
Large Intestine
reabsorbs fluid + electrolytes, sends 90% of water back to blood
assimilation + starts elimination
contains cecum (blind pouch at upper end),
colon (longest part), rectum and anus
Rectum
stores feces
Anus
opening where waste is egested
elimination
Pancreas
secretes 2 hormones: insulin and glucagon to control blood sugar levels
when acidic food enters small intestine, secretes bicarbonate to neutralize it
secretes pancreatic juice (contains enzymes) into upper small intestine via pancreatic duct
Bile: what? where produced and stored?
a substance that breaks down fats into smaller globules
produced and synthesized in the liver
stored in the gallbladder
Purpose of digestive Enzymes
Secreted into system to break down food further into smaller molecules (chemical digestion)
How do strcuture of villi aid function
They increase surface area in the small intestine, which aids in absorption
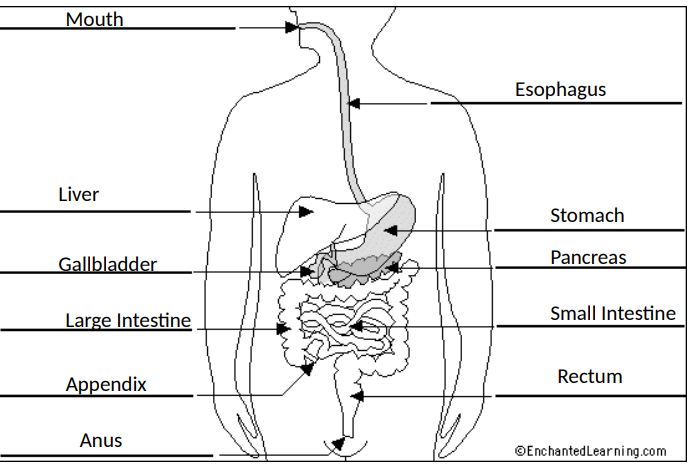
Diagram
(11)
Digestion VS Absorption VS Assimilation
Digestion - breaks larger molecules down into smaller molecules (physically and chemically)
Absorption - uptakes molecules into bloodstream (where they’re transported to tissues and their cells)
Assimilation -Molecules are taken in to be used. Converted into the fluid and solid parts of a cell/tissue