Core Concepts of Nursing - Exam 1 Blueprint
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What Makes Nursing a Profession?
Regulation (Nurse Practice Act + Standards of Care)
Licensure (NCLEX)
Education (life-long learning process)
Professional Organization (being an active member)
Code of Ethics (from the ANA)
Board of Nursing (BON)
Standards of practice establish a minimal acceptable level of nursing practice in any setting for each level or nursing licensure or advance practice authorization
When was nursing NOT the #1 most respected job?
In 2001, firefighters were the most respected because of 9/11
Ethics
the study of conduct and character; affect judgments about what is right or wrong
ethical principles
Autonomy
Beneficence
Nonmaleficence
Justice
Fidelity
Veracity
DO NOT CHANGE
Autonomy
the right to make one's own personal decisions
Justice
fairness in care delivery and use of resources
Veracity
a commitment to tell the truth
Fidelity
fulfillment of promises
Beneficence
Action that promotes good for others, without any self-interest
Nonmasleficence
a commitment to do no harm
What about ethical principles DOES change?
interpretation and application
ethical dilemma
occurs when ethical principles and their application DIFFER
ethical decision making
involves finding a balance between science, ethics, and personal moral values
morals
a system of beliefs that is taught for deciding good and bad
- what's right or wrong for one's self
values
personal beliefs about ideas that determine standards that shape behavior
- comes from within
- professional and societal standards
self-reflection
first step in developing self-awareness
moral distress
situation where the actions taken are different from what the nurse feels is ethically correct
ANA Code of Ethics
9 provisions that serve as a basic ethical guideline for nursing
Caring
the basis of the nursing profession
- NOT an ethical principle
Kindness
an outward expression of caring
5 Auscultation Sites of the Heart
1. Aortic: 2nd ICS (right)
2. Pulmonic: 2nd ICS (left)
3. Erb's Point: 3rd ICS (left)
4. Tricuspid: 4th ICS (left)
5. Mitral: 5th ICS (left)
Erb's Point
the transition point where "lub" (S1) becomes louder than "dub" (S2)
Mitral
the apex of the heart
- point of max impulse (PMI)
- medial to the midclavicular line
S1
"lub" - first heart sound
- atrioventricular
- closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves (contraction; systole)
S2
"dub" - second heart sound
- semilunar
- closure of aortic and pulmonic valves (relaxation; diastole)
S3
ventricular gallop heard after S2
S4
strong atrial contraction, expected finding in older and athletic adults/children, use bell
murmurs
abnormal heart sounds created by increased blood volume in the heart, or impeded flow
Bruits
abnormal blowing or swishing sound of the heart; decreased blood flow
Where to Hear Bruits
1. carotid arteries
2. abdominal aorta
3. renal arteries
4. iliac arteries
5. femoral arteries
Patient Position for Listening to the Heart
1. sitting, leaning forward
2. lying supine
3. turned towards the left side (best for extra sounds)
Diaphragm of stethoscope
High-pitched sounds (lung, bowel, heart); place firmly against skin
Bell of stethoscope
low pitched sounds (extra heart sounds, murmurs); place lightly against skin
Normal BP Range
90-120 systolic
60-80 diastolic
Prehypertension BP Range
120-139 systolic
80-89 diastolic
Components of a Health Assessment
- systematic (talking precedes touching)
- critical thinking (using the data to make critical decisions
- patient's current and ongoing health status (70% of the diagnosis comes form the health history)
- risk factors (modifiable or non-modifiable)
- identify health-promoting activities
Problems Presented by the Patient
- Physical (pain, SOB, weight gain, rashes, etc)
- Social (anxiety, stress, sexual history, etc)
- Emotional (recent life-altering events, depression, mental health, etc)
- Cultural
-Environmental (occupation, home life, etc)
Four Types of Assessments
1. Initial (baseline): performed after admission to establish a baseline (K levels, vital signs, etc)
2. Problem-focused: determines the status of a specific problem; ongoing process (specific vascular checks, cranial nerve assessments, etc)
3. Emergency: during a crisis to identify life-threatening problems (ABC method for respiratory distress)
4. Ongoing Reassessment: comparison of the patient's current statue to the previous baseline data (head-to-toe, looking at trends)
Sources of Data
Primary = the CLIENT
Secondary = all other sources which does NOT COME FROM THE client (family, friends, patient record, literature, other healthcare providers)
Subjective data
anything reported by the patient
- typically SAID; presents in quotations
EX: pain, symptoms verbally expressed, family history, social history, etc
Objective data
anything that can be measured by the healthcare professional
EX: heart rate, urine output, lab reports, weight, vital signs, etc
Methods of Data Collection
1) Observation
2) Interviews
3) Examination
Observation Method of Data Collection
Using the senses to observe patient data
Vision: skin color, body language, weight gain/loss, etc
Hearing: cough, speech, wheezing, etc
Smelling: body odor, infection, melena, etc
Touch: edema, temperature, equal pulses, etc
Interviewing Method of Data Collection
A sit down conversation with the patient in an appropriate setting with an adequate amount of time
- Techniques: Standardized formats or Therapeutic techniques
- have privacy, consider having an interpreter, pull up a chair and face the patient
General Examining Sequence
1. Inspection
2. Palpate
3. Percussion
4. Auscultation
Abdomen Examining Sequence
1. Inspection
2. Auscultation
3. Percussion
4. Palpate
- Auscultation comes prior to steps 3 & 4 to ensure that the bowel sounds do not become obstructed
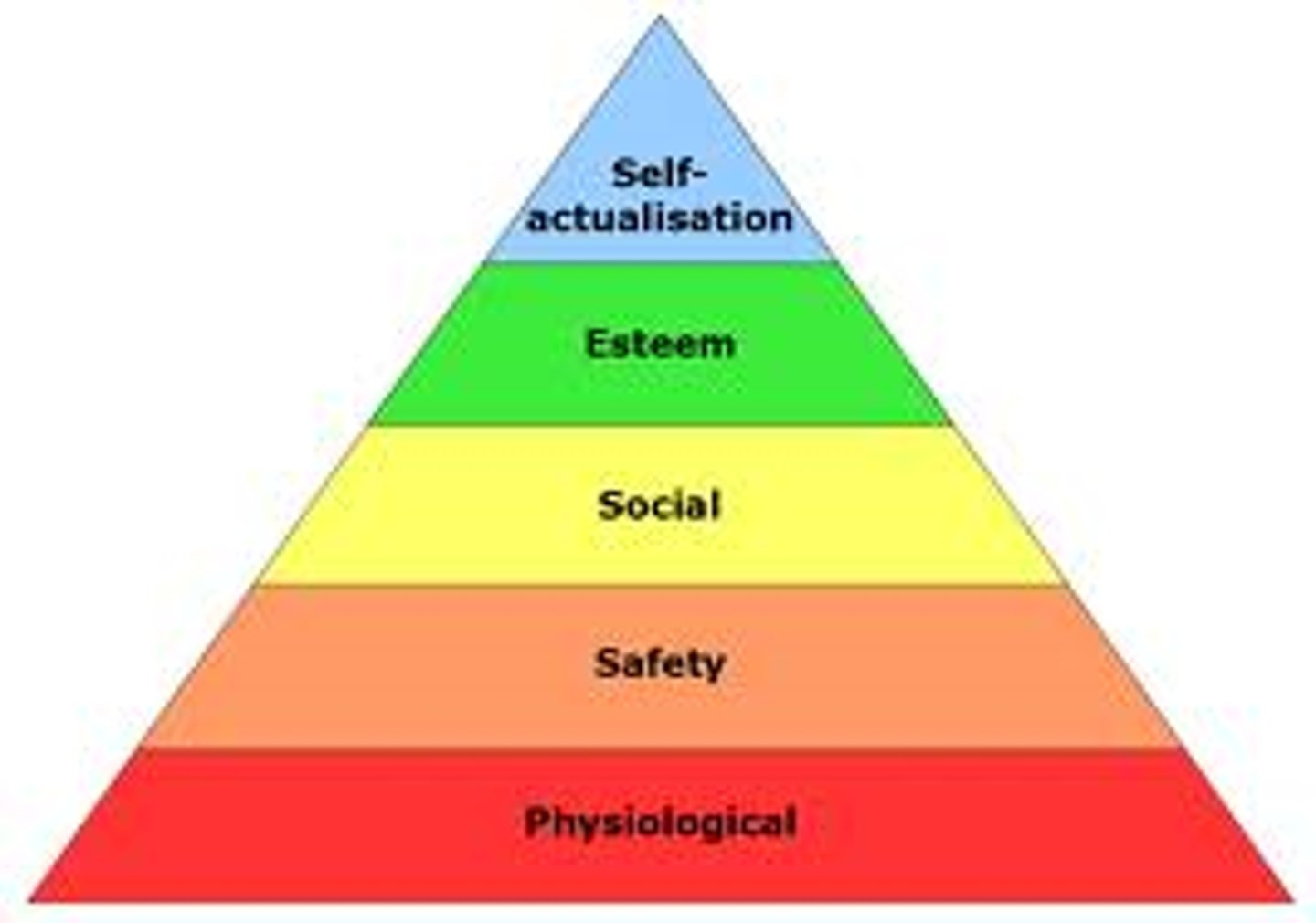
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
1. Physiological Needs: the priority concern to address first (respiratory status, cardiovascular health, GI needs such as food, fluids, and nutritional intake as well as elimination, etc.)
2. Safety and Security (preventing injuries or illnesses from occurring, establishing security and safety, building trust, etc)
3. Love and Belonging (ensure adequate support systems are maintained)
4. Self-Esteem (promoting a sense of worthiness and acceptance, etc)
5. Self-Actualization: lowest priority
Erickson's Stages of Development
- Infancy (birth to 18 months) Trust vs. Mistrust
- Early Childhood (2 to 3 years) Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
- Preschool (3 to 5 years) Initiative vs. Guilt
- School Age (6 to 11 years) Industry vs. Inferiority
- Adolescence (12 to 18 years) Identity vs. Role Confusion
- Young Adulthood (19 to 40 years) Intimacy vs. Isolation
- Middle Adulthood (40 to 65 years) Generativity vs. Stagnation
- Late Adulthood (65 to death) Ego Integrity vs. Despair
Validating Data Collection
checking allergies, clarifying vague statements, checking extreme abnormal findings a second time or manually
Interpreting Data Collection
using the information to determine nursing care
- includes nursing autonomy
Documentation
a part of communication; if it was not documented, it was not done
- objective
- use SBAR during handoffs
General Survey Components
information gathered upon the first encounter with the patient
- AIDET
- physical appearance, body structure, mobility, behavior, and vital signs
- always check patient ID (name, DOB, etc)
AIDET
Acknowledge
Introduce
Duration
Explain
Thank
PQRST
Provoked (what causes the pain?)
Quality (what does the pain feel like?)
Region (where is the pain?)
Severity (0-10 scale)
Timing (when did it start? is the pain consistent?)
What is the nursing action for a patient with an irregular pulse?
Count the pulses for the entire minute instead of 30 seconds
If there are no bowel sounds heard, what action should the nurse take?
Listen to each quadrant for 5 minutes
Regular Respiration Rate
12-20 breaths per minute
Regular Pulse Rate
60-100 beats per minute
- measure using radial pulse
Normal Blood Pressure Range
90-119 systolic
60-79 diastolic
Tympanic Temperature
measuring the body temp from the heat of the eardrum; range: 96.2 to 100
- for older patients, pull the ear back and up
- for children, pull the ear back and down
Temporal Temperature
measuring the body temp using the forehead; range: 98.7 to 100.5
Oral Temperature
measuring the body temp sublingually; range: 96.8 to 100.4
- wait 10-30 mins if the client has been eating, drinking, etc
- instruct patient to breathe out their nose
What temperature is considered a fever?
100.4 F
When measuring the Blood Pressure...
...ensure the cuff is the correct size, and place the cuff about 2 inches above where you palpated the brachial pulse; use the diaphragm of the stethoscope on the brachial artery
- if the cuff is too big: BP reading will be a false LOW
- if the cuff is too small: BP reading will be a false HIGH
Pulse Oximeter
attaches to the earlobe or fingertip to measure the oxygen saturation of arterial blood
- results may be skewed with nail polish or excessive movement
Before beginning any personal care delivery, what task should be completed?
an evaluation of the client's ability to participate in personal hygiene; encourage them to participate as much as they can
Types of Baths
complete baths, partial baths, and therapeutic baths
- bathe systematically from the upper extremities to the lower extremities
- long firm strokes form distal to proximal
Changing Bed Linens
- do unoccupied linen change as often as possible
- smooth wrinkles
- keep soiled linens AWAY from you
- DO NOT SHAKE linens because it spreads micro-organisms through the air
- mitered corners
Nail, Hand, and Foot Care
- Inspect the feet daily, do not apply lotion between the toes or fingers, cut nails straight across (check the facility's policy prior to cutting)
- Check nails for cracking, clubbing, and fungus
Nail and Foot Care for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- do not soak the feet due to the risk of infection
- do not cut the nails; file nails using a nail file
- do not apply lotions between the fingers and toes
-a qualified professional may be needed
Oral Hygiene for Unconscious Patients
- have suction set up at bedside
- use a soft-bristled brush
- use a syringe with a small amount (10mL) of water
- place patient on one side with the head turned toward you or in semi-Fowler's position
- DO NOT put your fingers in their mouth
- perform oral care every 2 hours
Denture Care
BE HELLA CAREFUL
- remove/insert the top dentures first (down and out)
- remove/insert the bottom dentures second (up and out)
- place a towel in the bottom of the sink
- use tepid water
- place the dentures in a cup with water to keep them moist
Perineal Care
always use fresh water and a new area of the washcloth to perform perineal care; cleanse from front to back
- Males: cleanse penis in a circular motion; retract foreskin to wash the tip (meatus outward) then replace the foreskin
- PAT dry
Hair Care
brush or comb hair daily with soft-bristled brush or wide-toothed comb
- use dry shampoo or no-rinse shampoo (heat activated) and shampoo cap
For Shaving:
- if patient is prone to bleeding, is on anticoagulants, or has a low platelet count, use an electric razor
- shave in the direction of the skin
- large strokes for large areas, short strokes for the chin and lips
What's the priority action to prevent falls?
complete a fall-risk assessment for each client upon admission and at regular intervals
- use the Morse Fall Scale or the Hendrich II Fall Risk Model
Other Priority Actions for Fall Prevention
1. Bed Locked
2. Bed Low
3. Call light within reach
4. Bedside table w/in reach
5. Correct number of side rails up
Which organization sets the National Patient Safety Goals?
The Joint Commission (TJC) in 2002
- developed and revised by a panel of healthcare experts
- maximum impact and usefulness for the minimum cost
QSEN 6 Core Competencies
1. Patient-centered care
2. Informatics and Technology
3. Evidence-based practice
4. Quality improvement
5. Safety
6. Teamwork and collaboration
- ensures that nurses have knowledge, skills, and attitude (KSA)
Fire Safety
All staff must know the location of exits, alarms, fire extinguishers, and oxygen shut-off valves; know the evacuation plan
- change smoke detector batteries twice a year
- use cotton material to prevent fire
- have "No Smoking" signs
RACE
fire response acronym
R = rescue and protect clients
A = activate the facility's alarm system
C = contain/confine the fire by closing doors and windows & turning off oxygen
E = extinguish the fire
PASS
acronym for fire extinguisher use
P = pull the pin
A = aim at the base of the fire
S = squeeze the handle
S = sweep the extinguisher from side to side
Why is Carbon Monoxide so dangerous?
It binds to hemoglobin and reduces oxygen; it cannot be seen, smelled, or tasted; can cause death
Food Poisoning
- most caused by bacteria
- most occurs due to unsanitary food practices
ABCDE principles
Airway: open airway?
Breathing: chest rise and fall, RR
Circulation: heartbeat, pulse, cap refill, BP, stop any bleeding
Disability: level of conciousness
Exposure: prevent hypothermia; warm blankets, fluids
CPR
sustains oxygenation and circulation to vital organs
- involves "CAB"
CAB
components of CPR
C = chest compressions
A = airway
B = breathing
What should be the temperature of the water heater in someone's home?
below 120 degrees
Standard Precautions
- proper hand hygiene
- PPE
- effective management of potentially contaminated surfaces
Restraints
protective devices used to limit physical activity of the client or a part of the body
- used to protect the patient from self-harm and to protect other patients and staff
Physical Restraints
any manual method, material, or device attached to the patient's body to limit or restrict free movement
- limb restraints
- belts
- mitts
- wheelchairs with stationary lap trays
- bed rails
Chemical Restraints
pharmacological agents administered for the purpose of controlling behavior
- sedatives (EX: Benedryl)
Unethical uses of Restraints
- convenience of staff
- punishment for the patient
- patients who are extremely physically or mentally unstable
Policies and Procedures for Using Restraints
- MUST BE PRESCRIBED AFTER A F2F ASSESSMENT
- can be applied in emergencies, but a prescription must be obtained from the provider within 1 hour
- max 24 hours
- Length of application: Adults = 4 hours; Ages 9-17 = 2 hours; under 9 = 1 hour
- Assess skin every 2 hours
- always offer food, fluids, and bathroom breaks
- pad bony prominences
- use a QUICK-RELEASE KNOT
- do not secure restraints to the bed rails
Homeopathic medicine and herbal remedies are...
...not FDA approved
Non-pharmacological Nursing Interventions
Guided Imagery, healing intention, breath work, humor, meditation, simple touch, music or art therapy, therapeutic communication, and relaxation techniques
Pain
an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage
THE #1 PRIORITY
- based on duration and origin
pain threshold
the point at which a person feels pain
Pain tolerance
the amount of pain a patient can endure
Acute Pain
pain that lasts less than 6 months
- has a direct cause, sudden onset, and is temporary
- causes changes in physiological responses (vital signs)
- deal with the source!!!
- can lead to chronic pain if not handled
EX: breakthrough pain