Electrolysis
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Electrolysis-
breaking down of a substance using electricity
during electrolysis (what happens) don’t PANIC
electric current is passed though an electrolyte . the ions move towards the electrodes where they react and the compound decompresses.
+ions to cathode -ions to anode
Why are electrodes made of Graphite?
Graphite can conduct electricity because it is mad eof carbon and each atom in carbon is bonded to 3 others. each atom also contains one unbonded electron which becomes delocalised so it can carry the charge.
at the electrode ions are turned back to
atoms
Why do the electrodes/anode need replacing?
they are made of graphite and the carbon atoms in graphite react with oxygen gas being produced and produces carbon dioxide so the electrode slowly burns away.
Why can aluminium not be extracted with carbon?
ORE NAME?
Aluminium is more reactive than carbon so it cant be reduced by it.
Bauxite - cleaned then electrolysis
What si the problem with electrolysis?
very expensive because lots of energy required to melt core and produce the required current
Aluminium oxide has a high melting temperature so
it is mixed with cryolite to lower the melting temperature so using less energy (saving money)
Aluminium oxide is solid/liquid/gas/molten because
molten so the ions are free to move and conduct electricity
learn Aluminium oxide full equation 2 half eqeastions
2Al3+ + 3e– → Al
2O2– → O2 + 4e–
2Al2O3(s)→4Al(l)+3O2(g)
In aqueous solutions there will be
h+ and OH- ions
aqueous solutions At the cathode if
the metal ion formed a metal more reactive than hydrogen hydrogen gas will be produced if less reactive layer of pure metal produced
aqueous solutions at the anode if ..
OH- ions and halide ions group 7 are present molecules of the g7 are produced(chlorine, bromine)
No halides then OH- ions are discharged AND OXYGEN FORMS AND WATER
learn 4OH- →
4OH- →O2+2H20+4E-
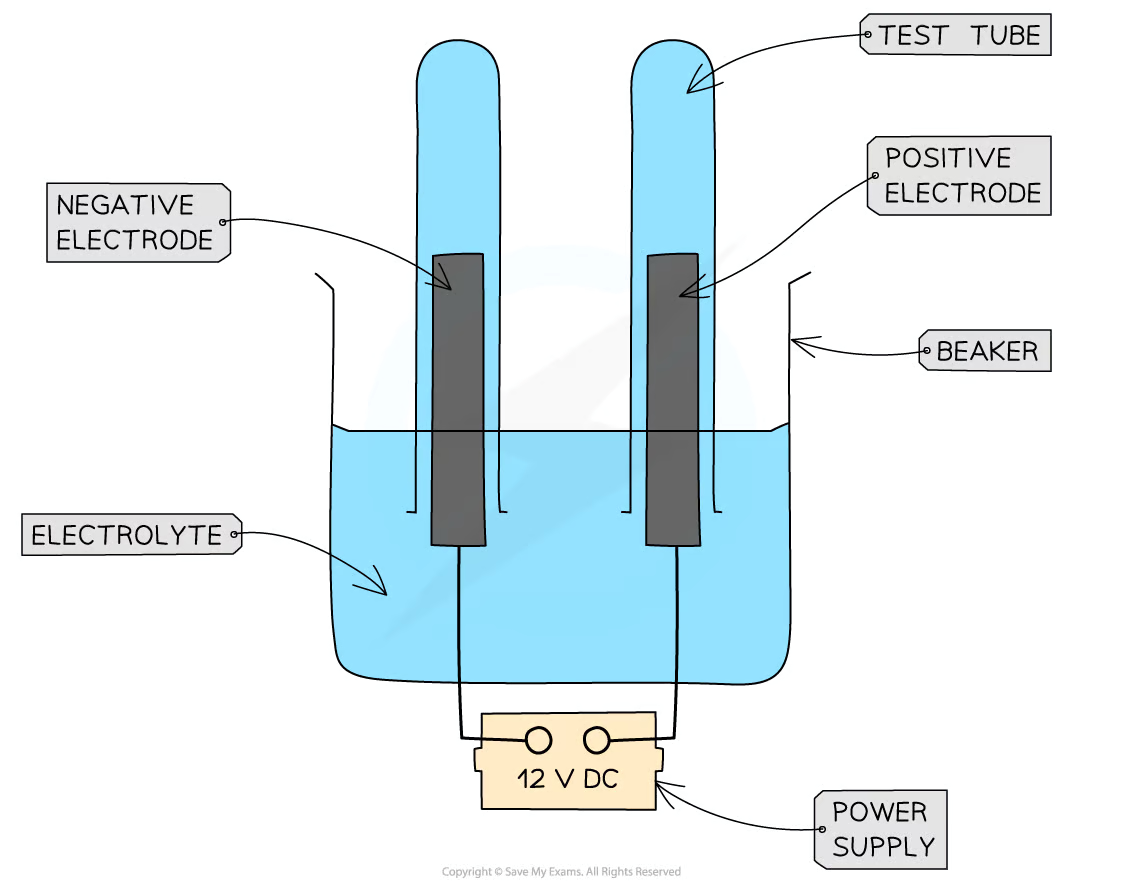
Required Practical
1)set up apparatus -_____ electrode connected to ____ ______ of ___ ________ _____ electrode connected to ______ ________.
2) Add ______ solution to beaker
3)Add ___ _____ rods as the electrodes and connect to a _____ ____.
4)Turn on ___ ___ and allow ____ to take place
5)______ the ______ and _____ for another solution, checking the _____ in-between
6)The _____ produced can be collected in the ____ ____.
positive positive terminal DC power bank negative negative terminal aqueous graphite power bank power bank electrolysis record results repeat electrodes gasses test tubes
How to test for
Hydrogen Oxygen Chlorine
lighted spill goes out squeaky pop sound glowing spill relights damp blue litmus paper turns red and then bleached white