describe the A&P of the male and female reproductive system
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
reproductive system
Reproduce offspring- produce male sex cells (sperm) and female sex cells (oocytes)
the reproductive system works with
the endocrine system to influence many other parts of the body.
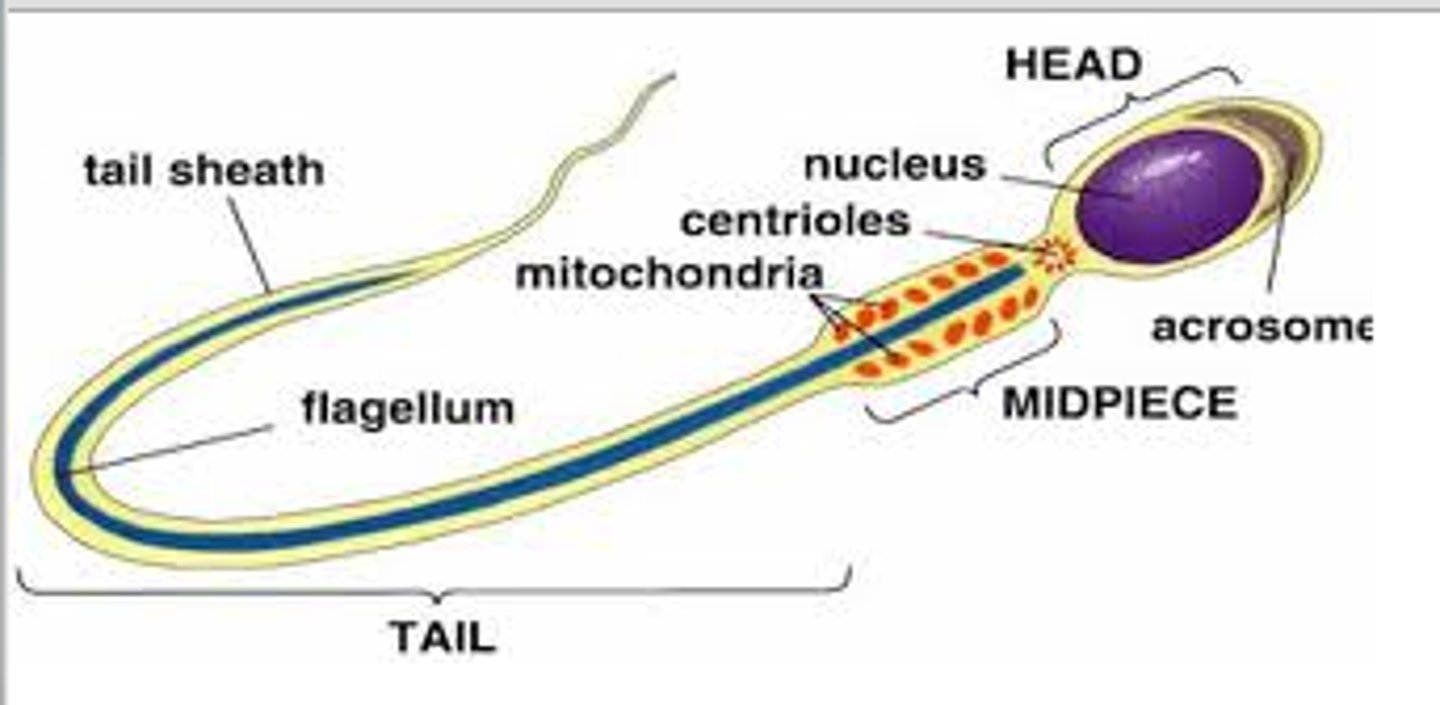
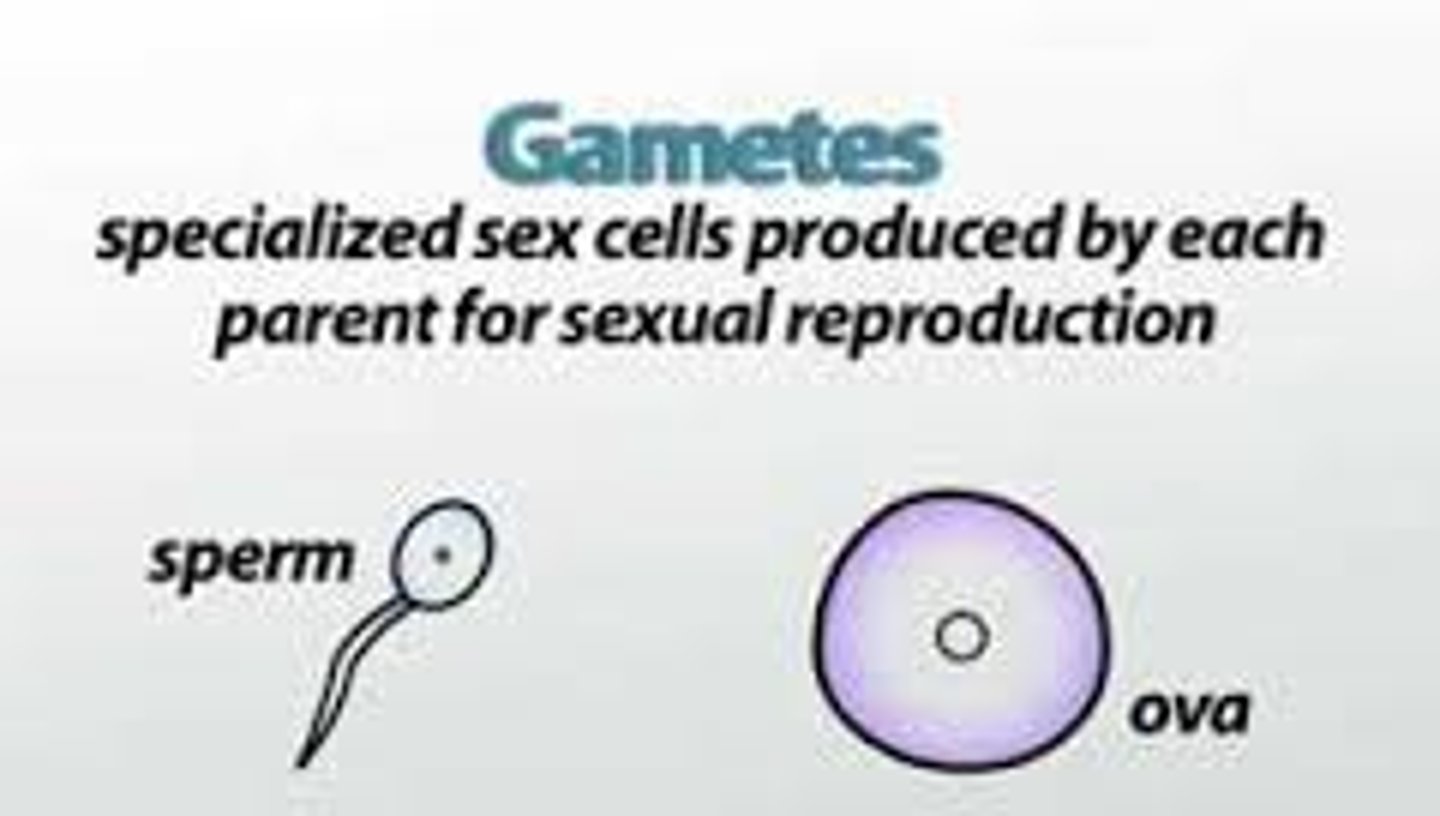
sperm
male gamete
penis
organ for the elimination of urine and sperm from the male body
the male reproductive system is to
generate males (sperm) and deliver them to the female reproductive system.
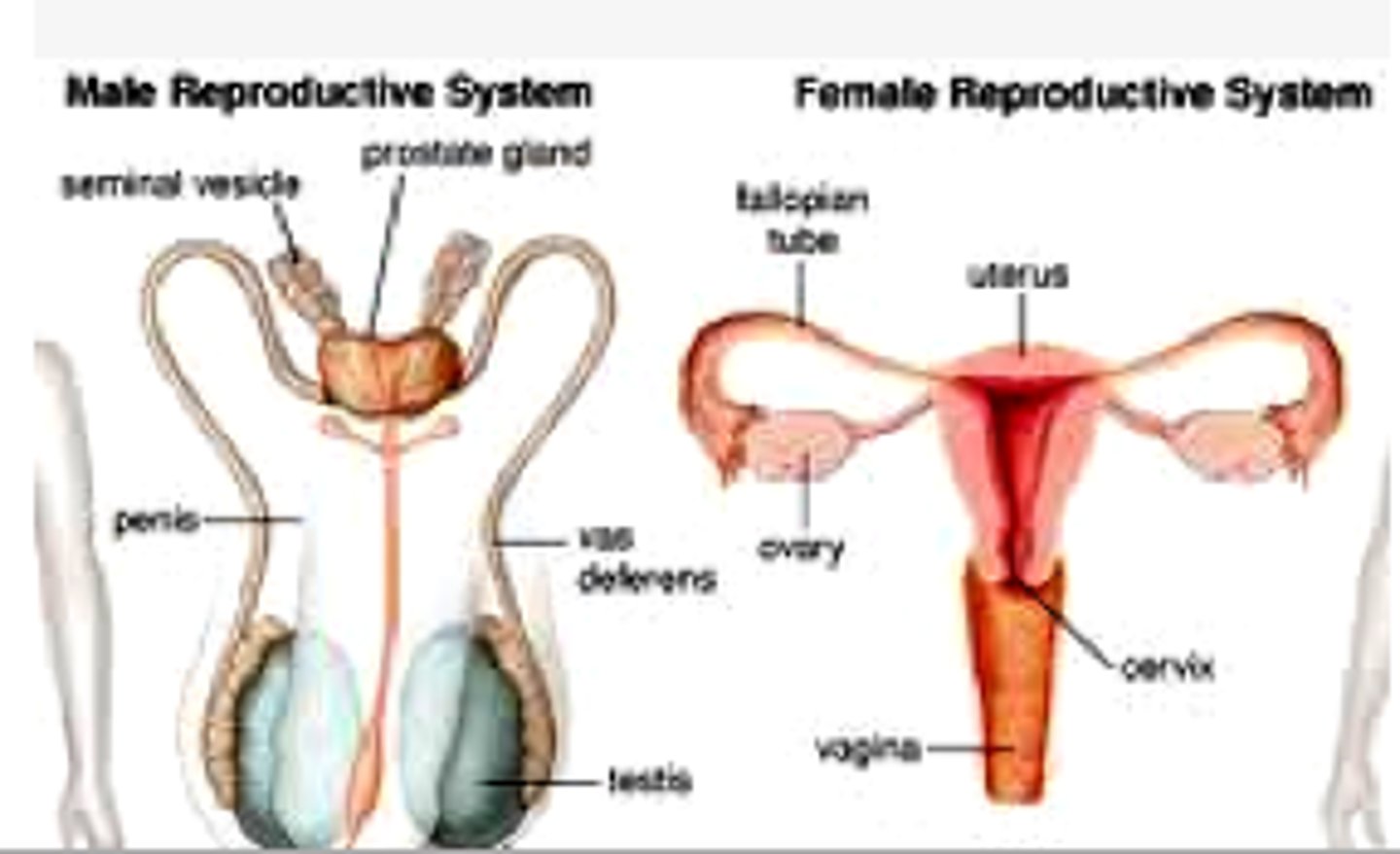
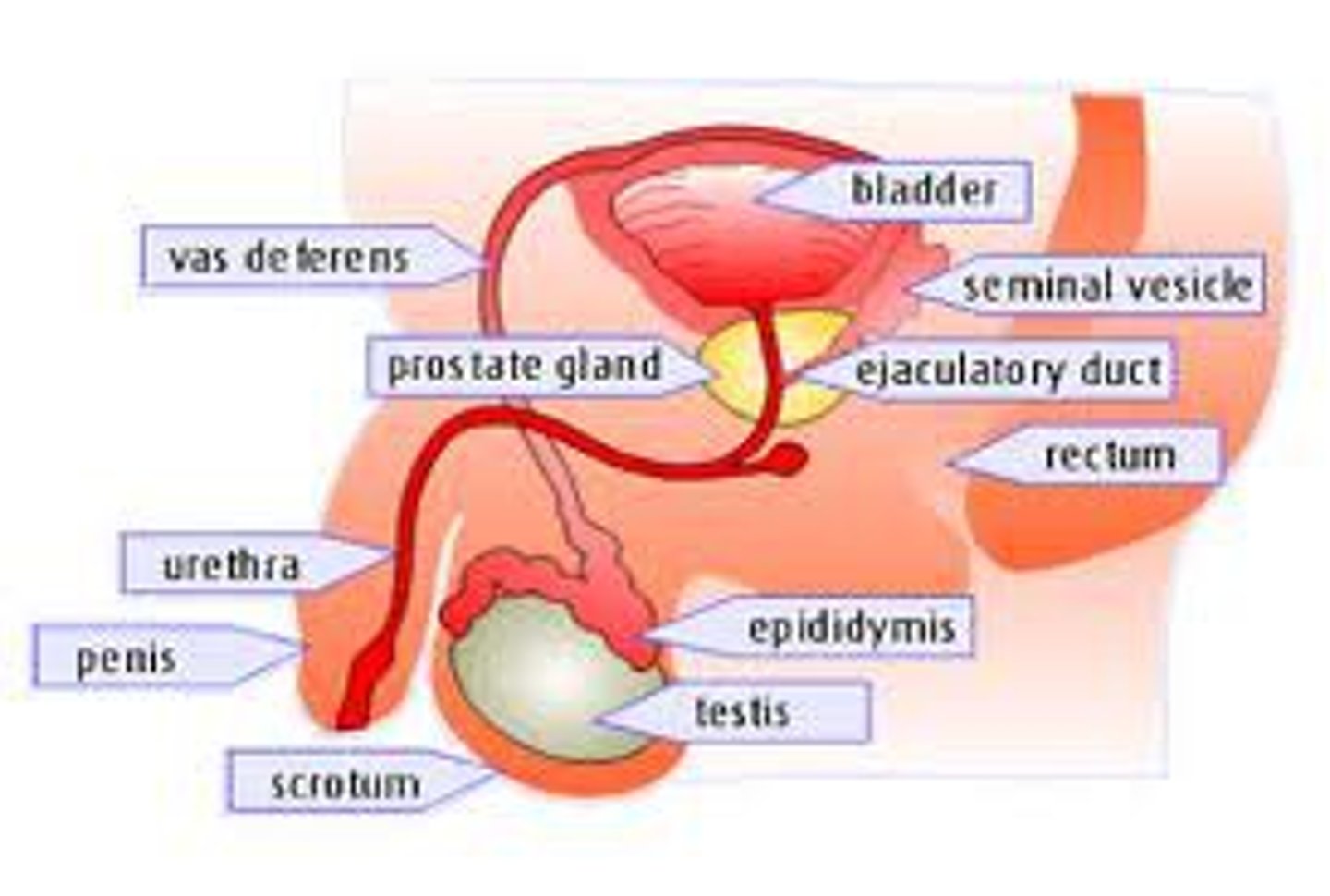
the components of the male system includes
the penis, vas deferens, urethra, prostate, seminal vesicles, testis (testes), and scrotum.
vas deferens
the duct in which sperm moves from a testicle to the urethra
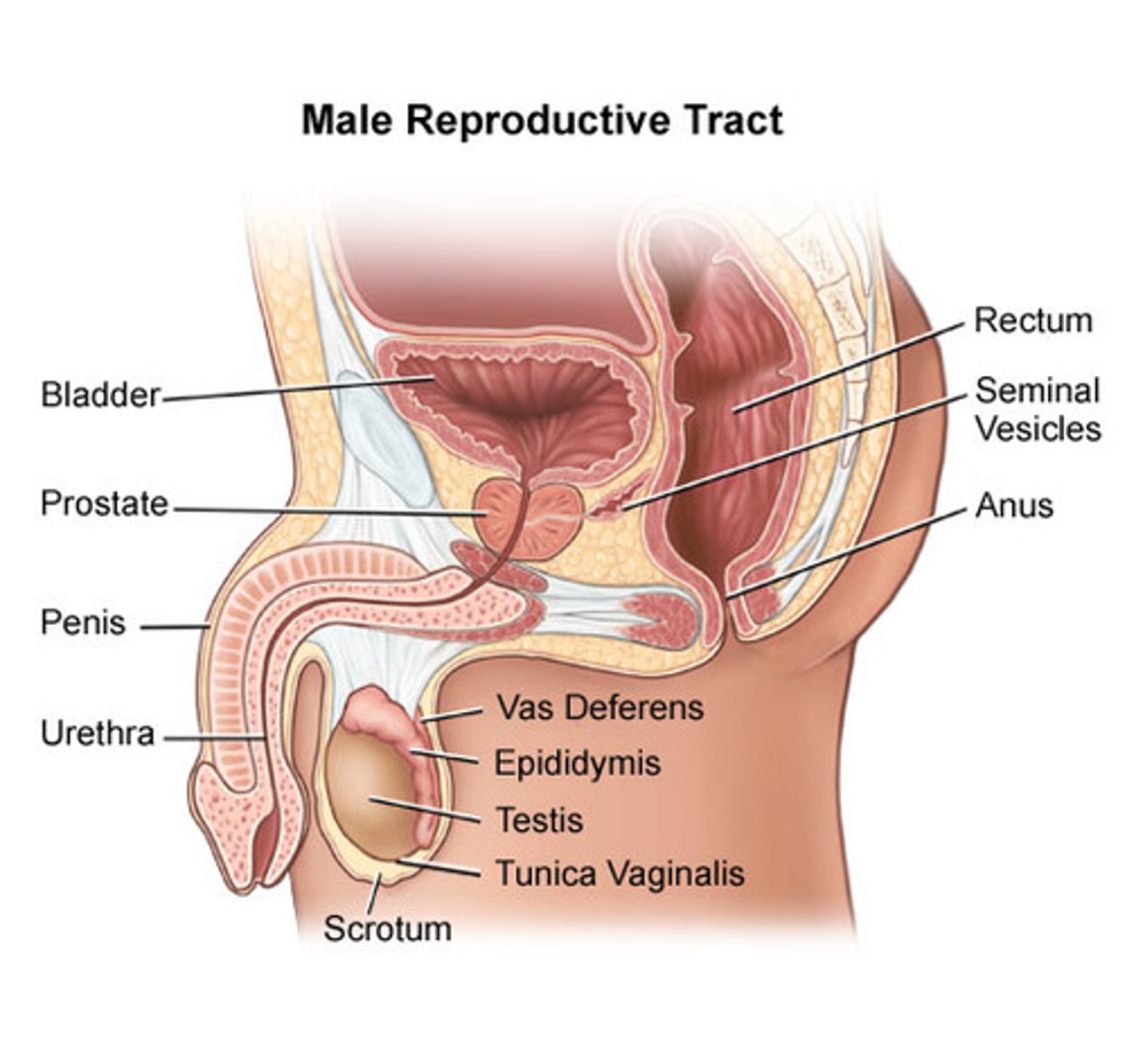
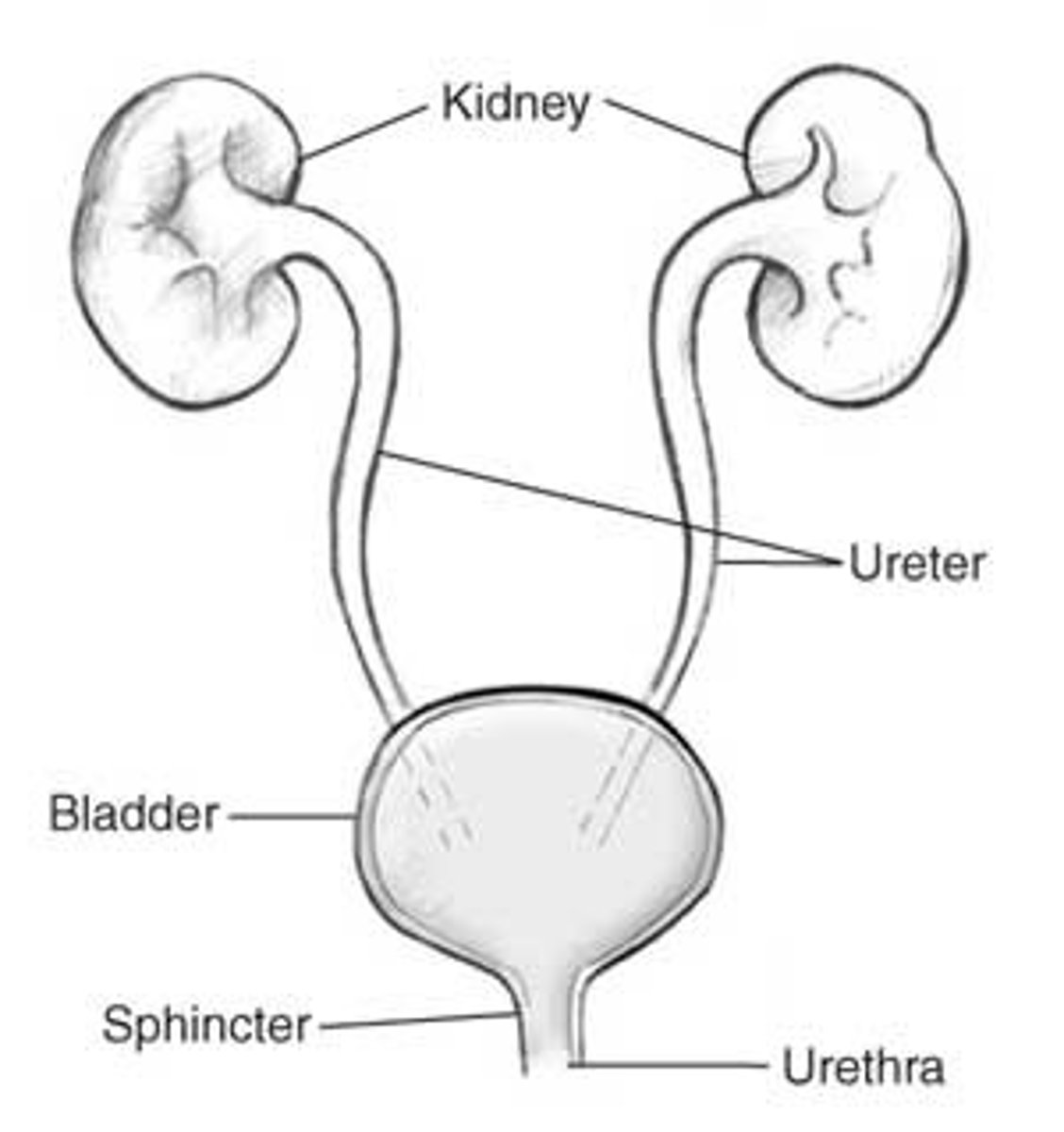
urethra
the duct that delivers urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body
prostate
the gland in males that controls the release of urine and secretes a portion of semen that enhances the motility and fertility of sperm.
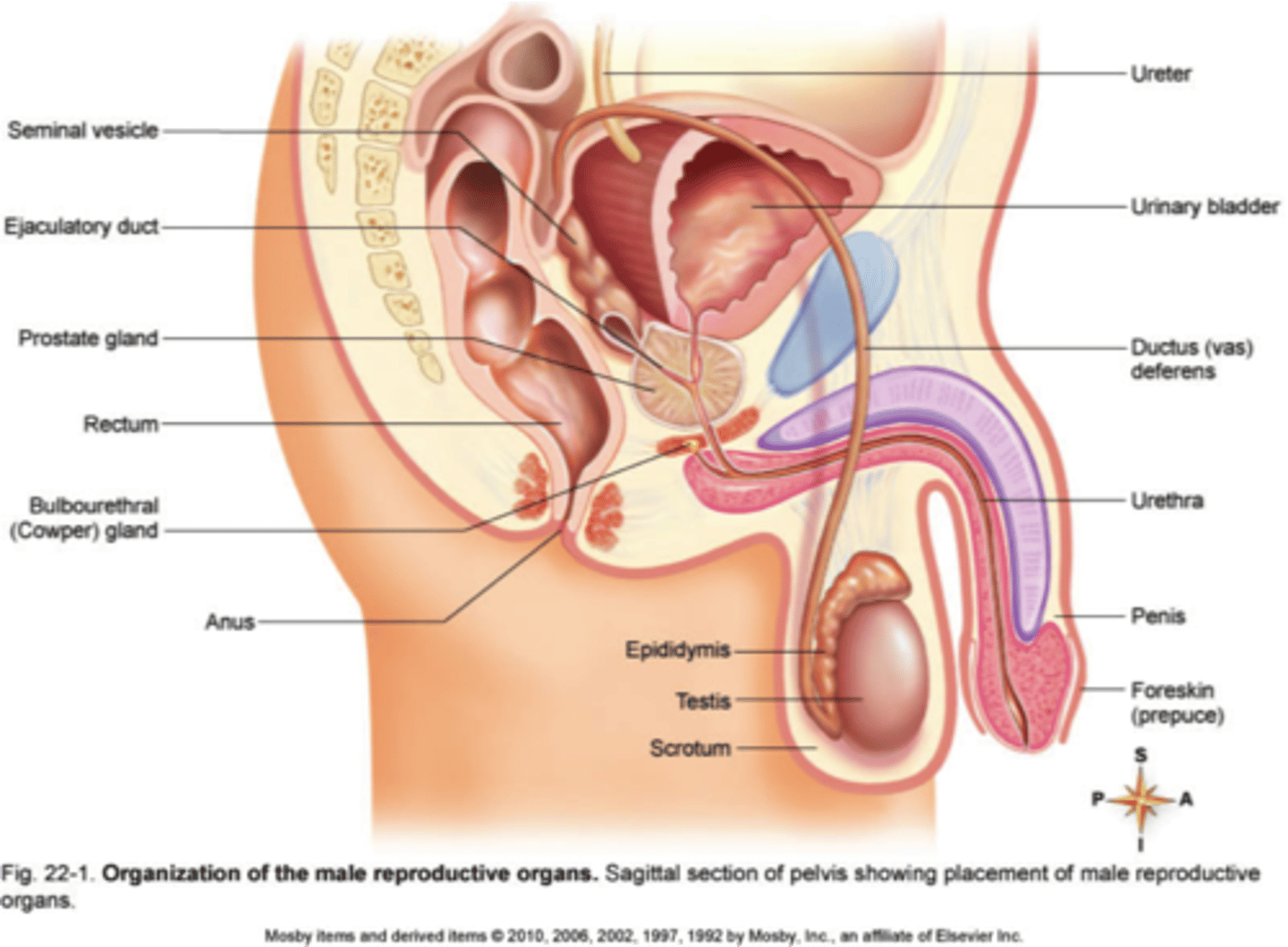
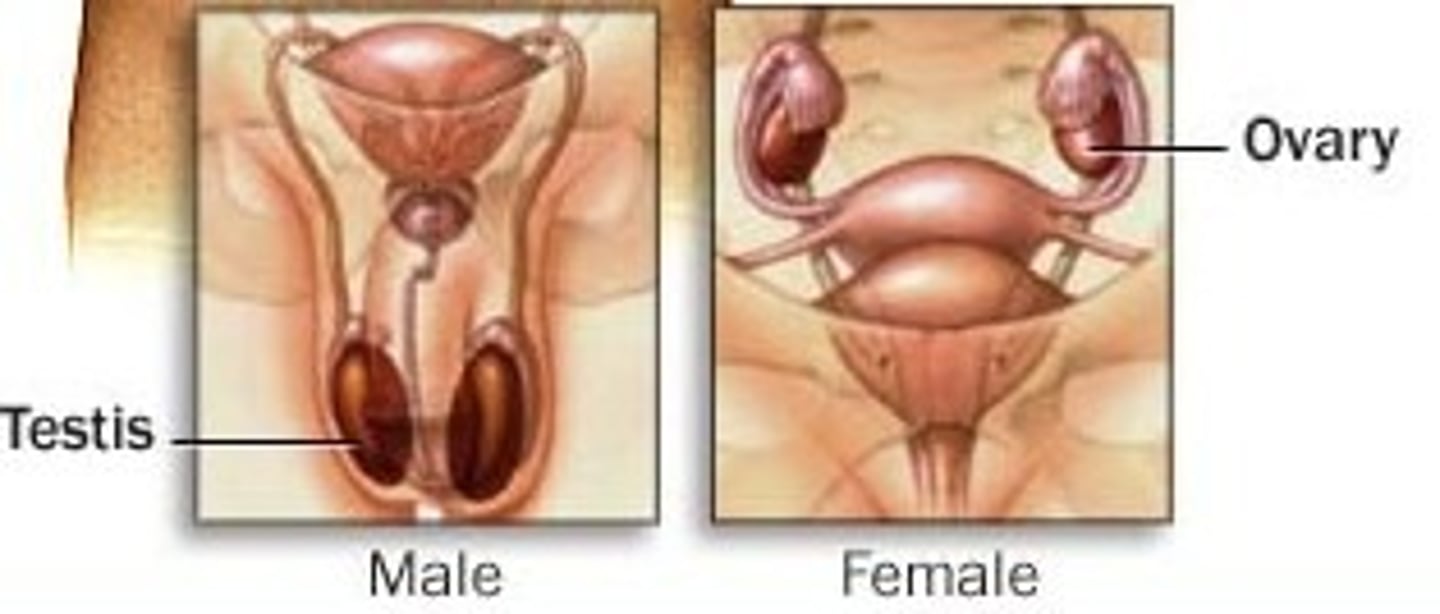
testes (testicles)
the male gonads. the organs that produce sperm
Scrotum
The pouch of skin that contains the testicles
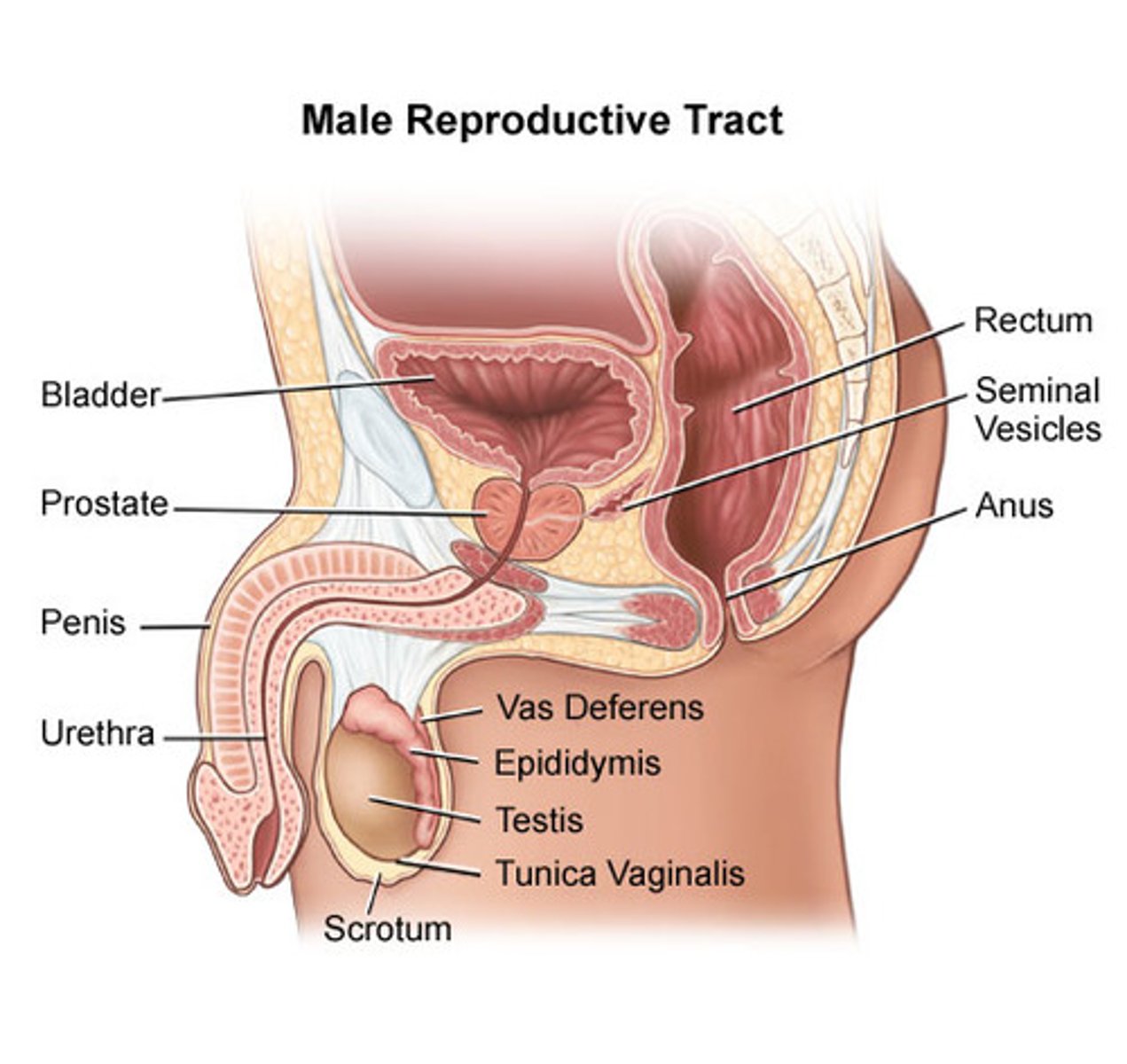
seminal vesicles
two small glands that secrete a fluid rich in sugar that nourishes and helps sperm move
the primary male reproductive organ is
testes
within the testes, there are tubules in which sperm are produced called
seminiferous tubules
what sac houses the testes away from the body to lower temperature during sperm production?
scrotum
what's the appropriate temperature environment for sperm to mature?
lower temperatures
what happens if sperm grows in body temperature or warmer?
the sperm do not mature properly
what produces the fluids necessary for lubricating and nourishing the sperm?
prostate and seminal vesicles
what forms the conduit through which sperm is ejaculated?
vas deferens, urethra, and penis;
the vas deferens leads to the urethra, which leads the sperm outside the body.
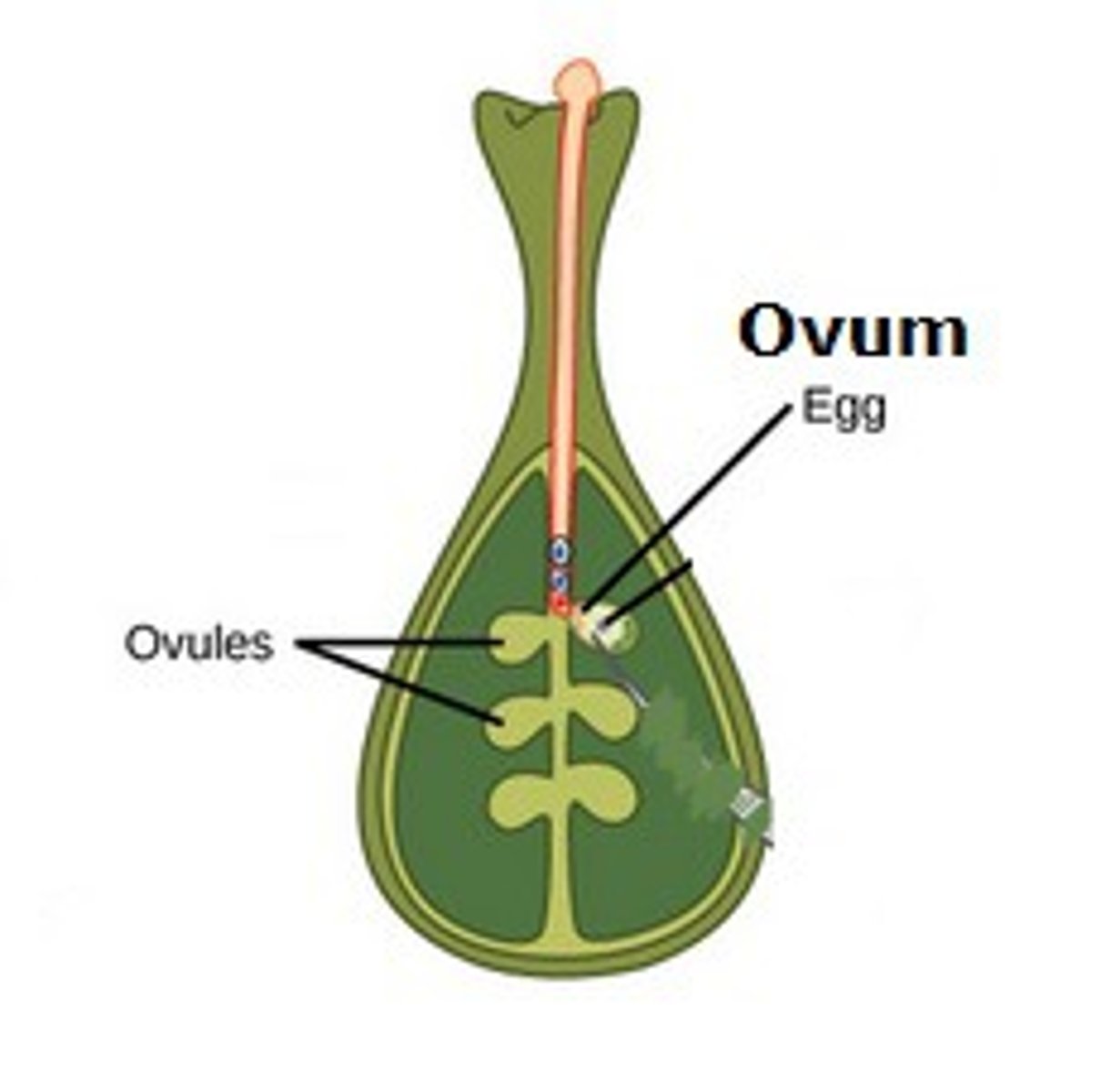
ova
female gametes
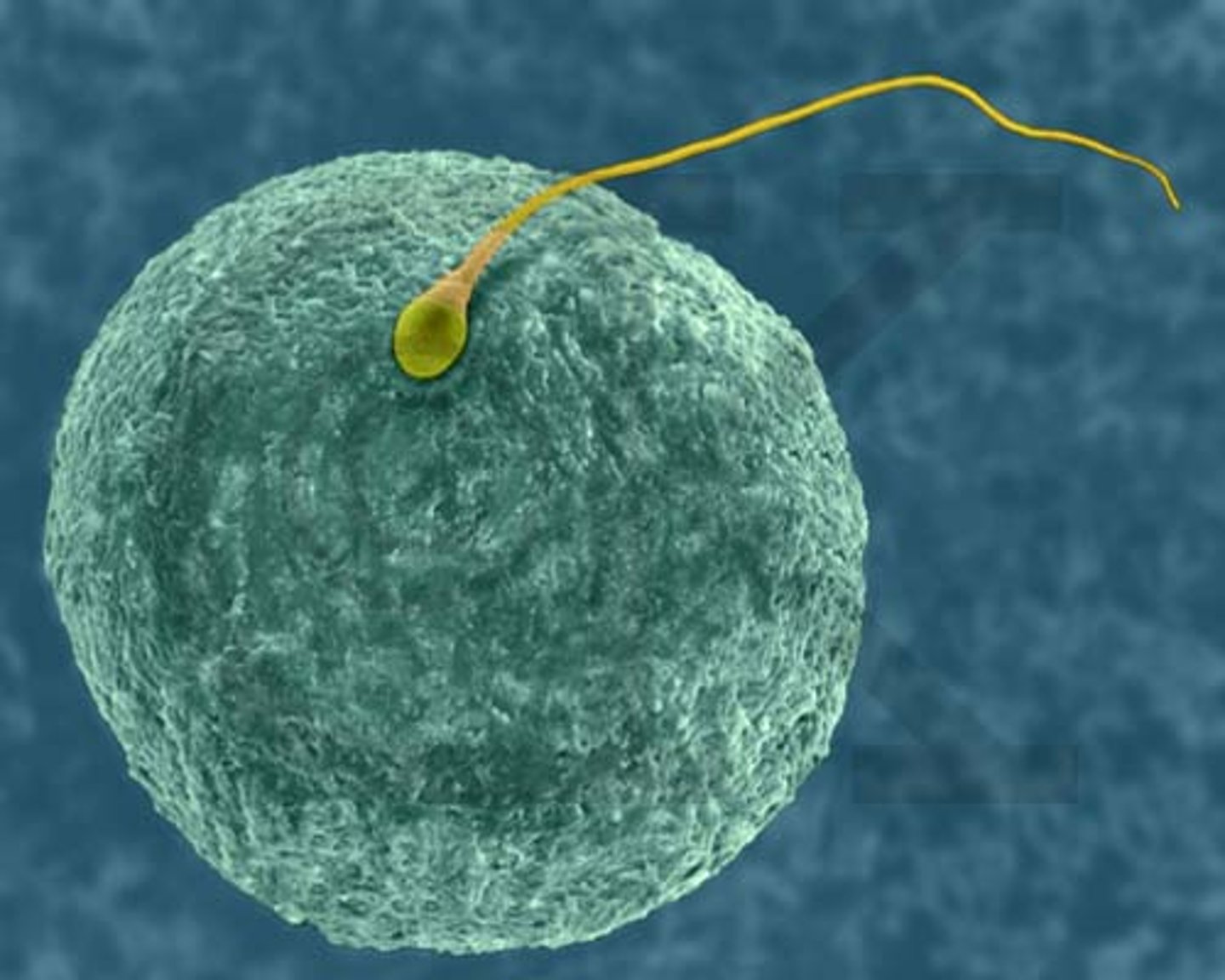
fertilization (or conception)
the fusion of the egg and sperm
ovaries
the female gonads. organs in which eggs are produced for reproduction
Gonads
sex glands
Gametes
reproductive sex cells
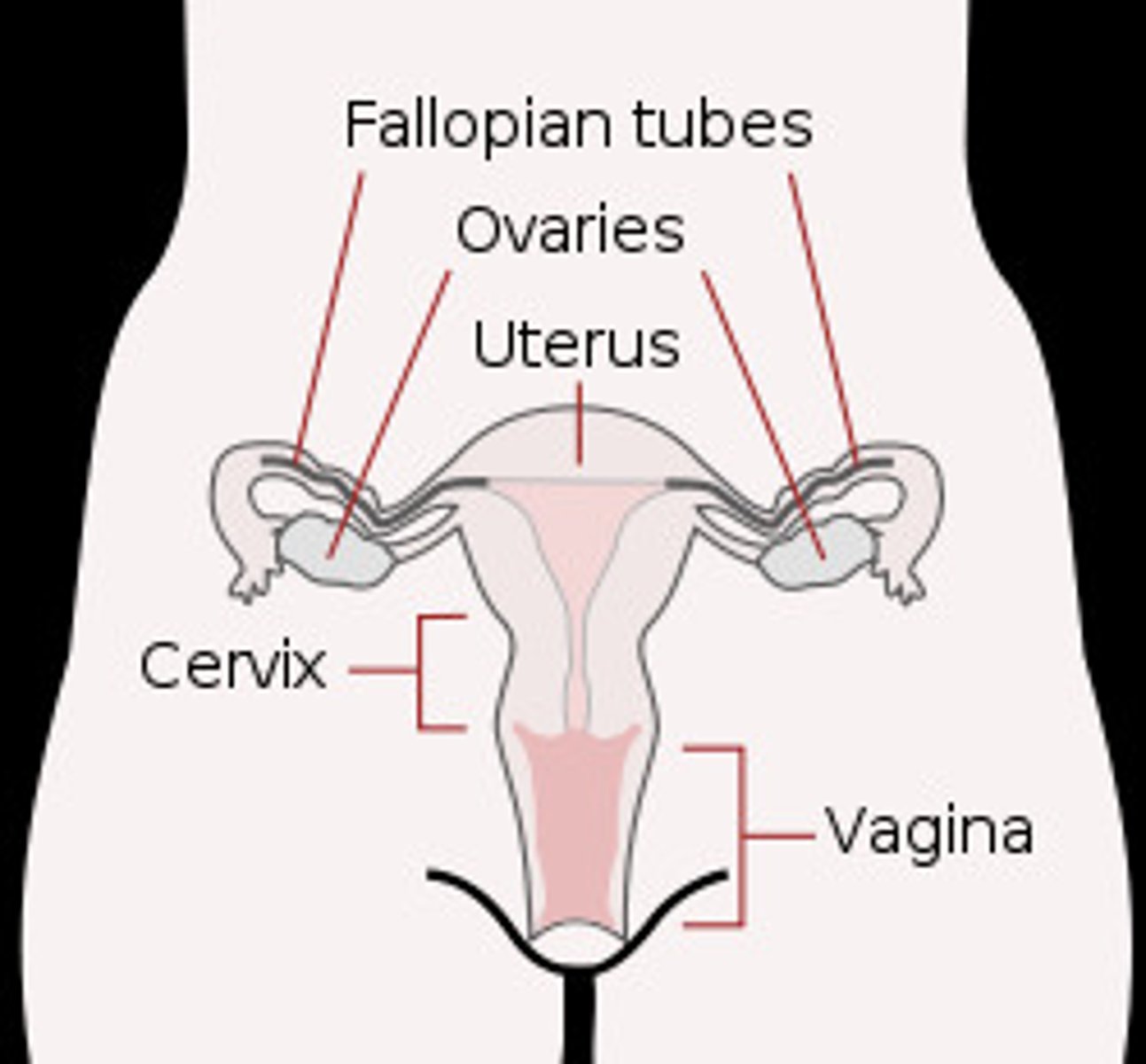
fallopian tubes
tubes that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus
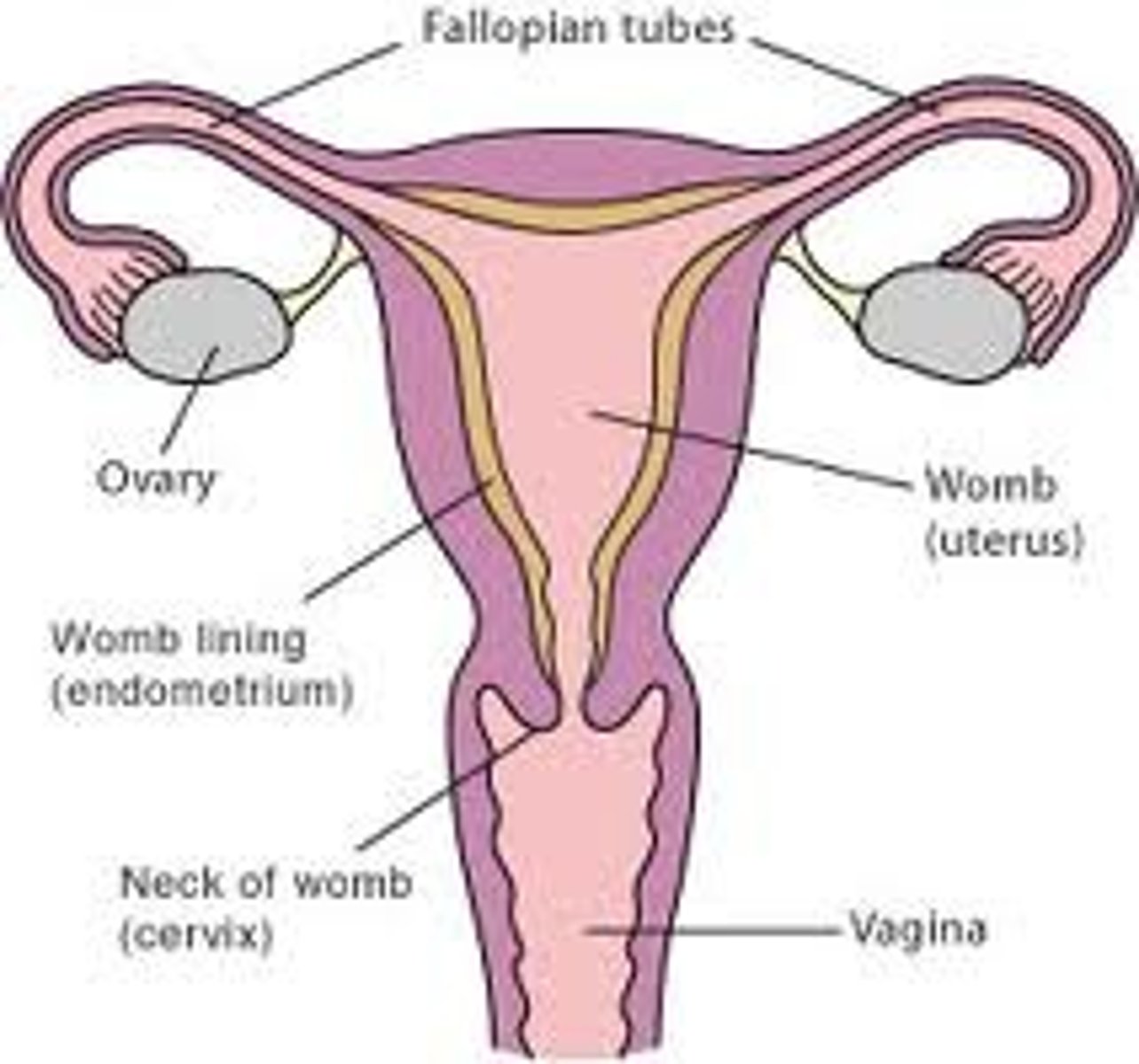
uterus
womb
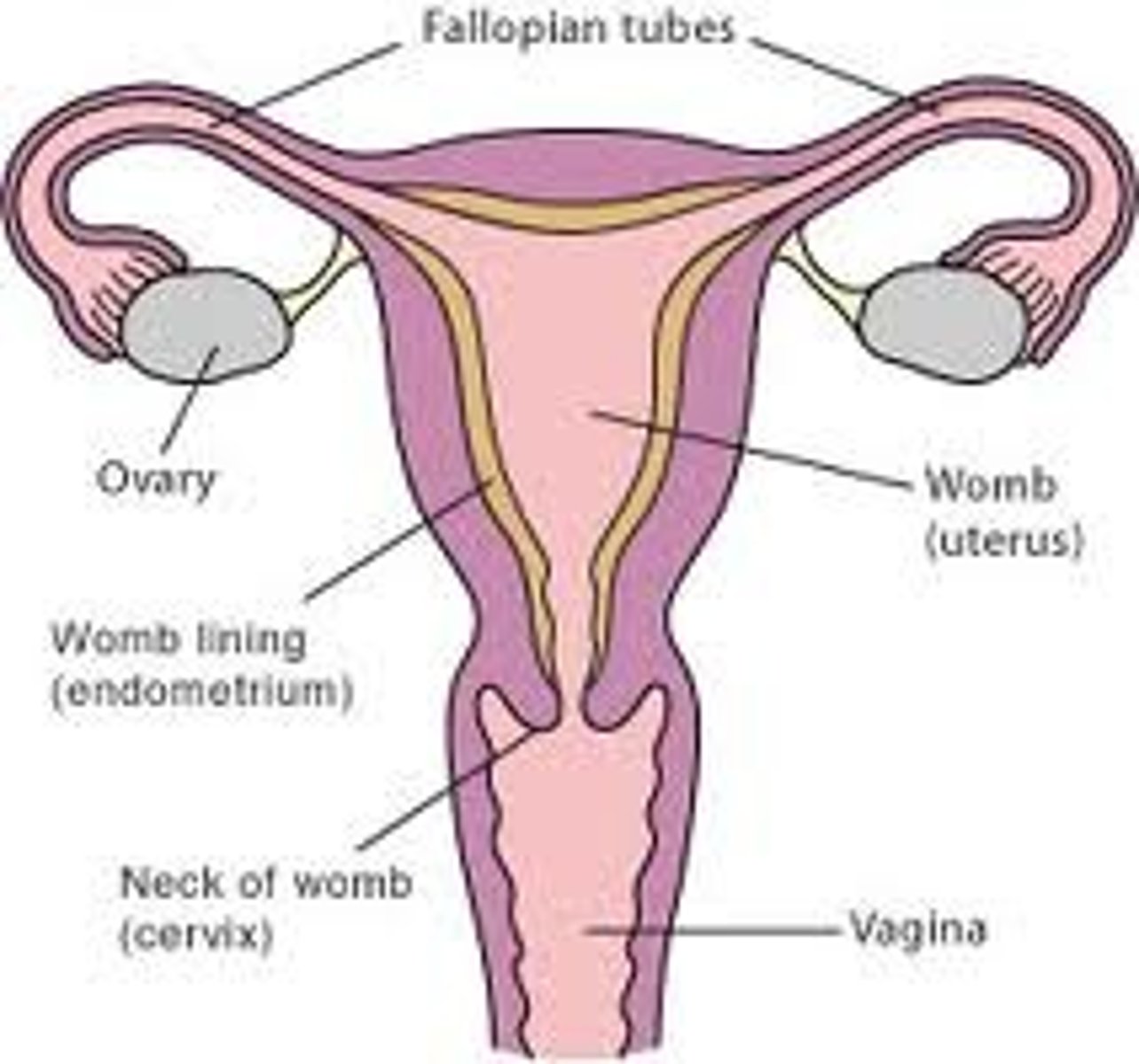
vagina
the canal that connects the external genitals to the cervix in the female
hormone
a chemical messenger produced by a gland and transported by the bloodstream that regulates specific processes in the body

follicle
saclike structure that contains and allows for maturation of the female ovum (egg) within the ovary
zygote
fertilized egg with full set of genetic material resulting from merging of egg and sperm
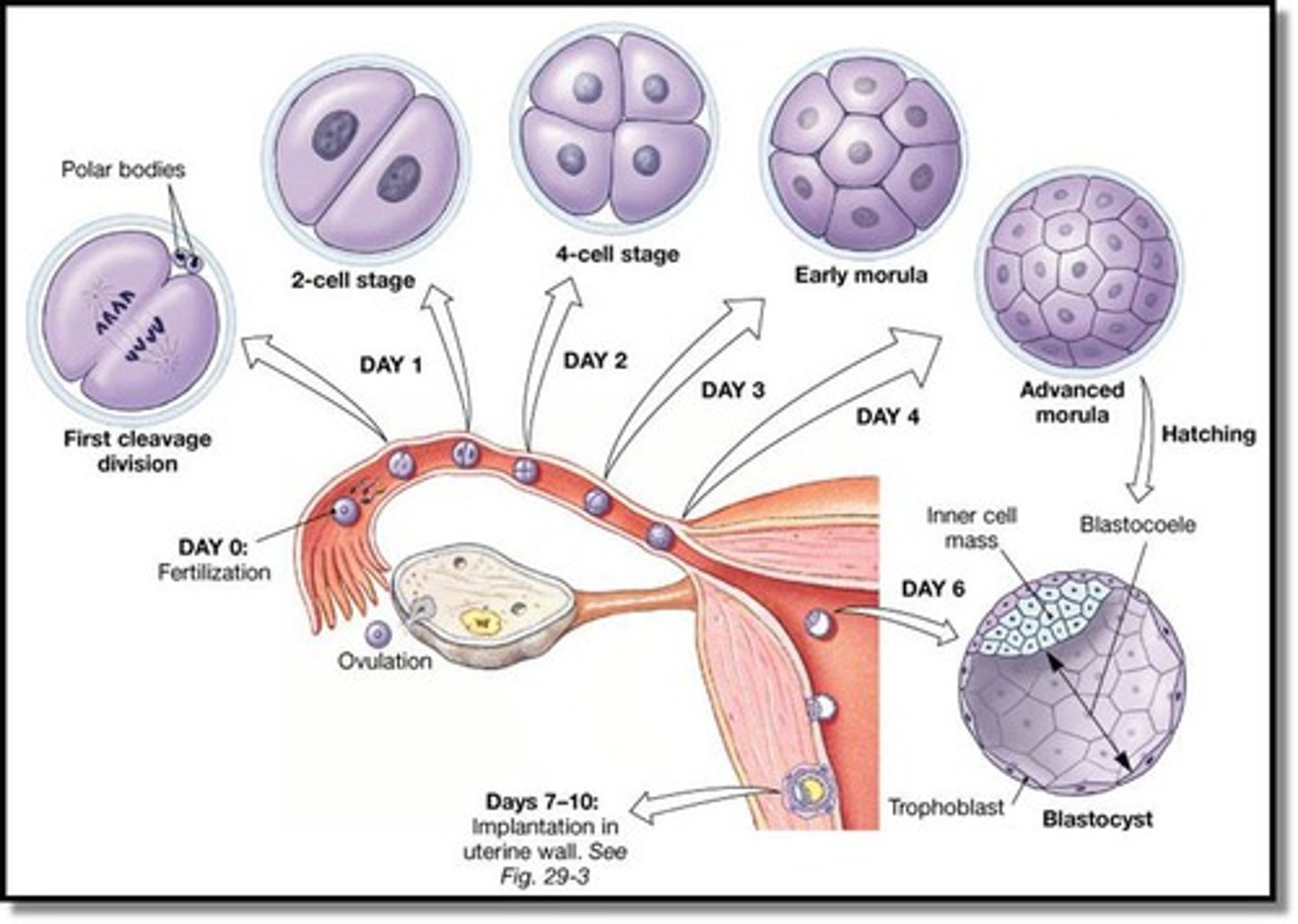
the female reproductive system's primary roles include:
-generating female gametes (eggs)
-fertilization
-implantation (start of pregnancy)
-gestation (pregnancy)
-parturition (birth)
the components of the female reproductive system includes:
-ovaries
-fallopian tubes
-uterus
-cervix
-vagina
-labia minora
-labia majora
-clitoris
the labia majora and minora opens into:
the vagina
in response to hormones levels,
a follicle in the ovary matures and releases an egg that then travels down the fallopian tubes to the uterus.
the fallopian tubes connect the
ovaries to the uterus
fertilization occurs in the
fallopian tubes
if a released egg is fertilized by a sperm, it is then called:
zygote
blastocyst
stage of early development in mammals that consists of a hollow ball of cells
blastocyst develops into an:
embryo
the placenta nourishes the embryo as it grows into a
fetus and removes wastes
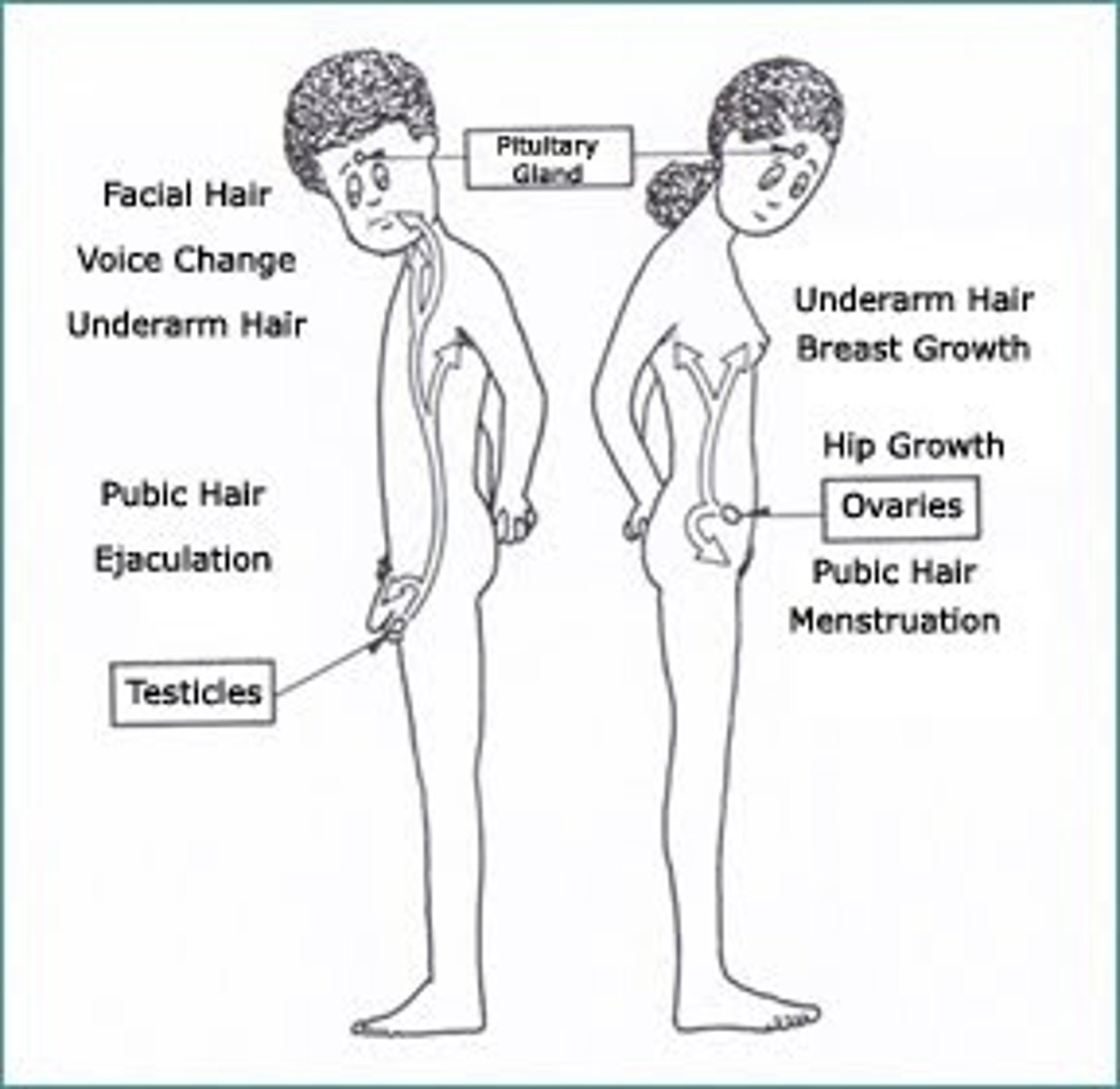
puberty
a physiological period in which changes in hormone levels cause a general "growth spurt" and development of secondary sex characteristics
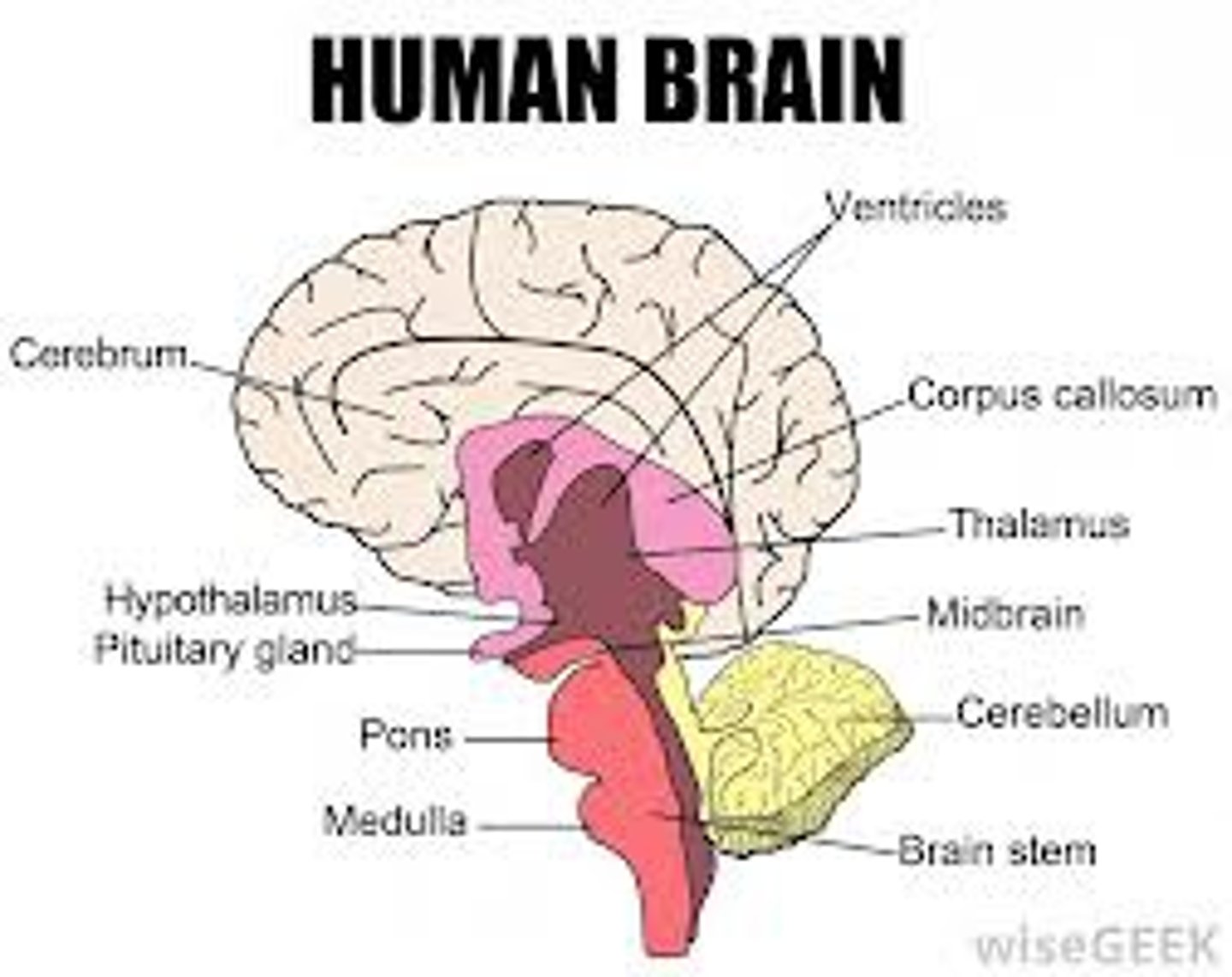
hypothalamus
a location in the brain that integrates the endocrine and nervous system.
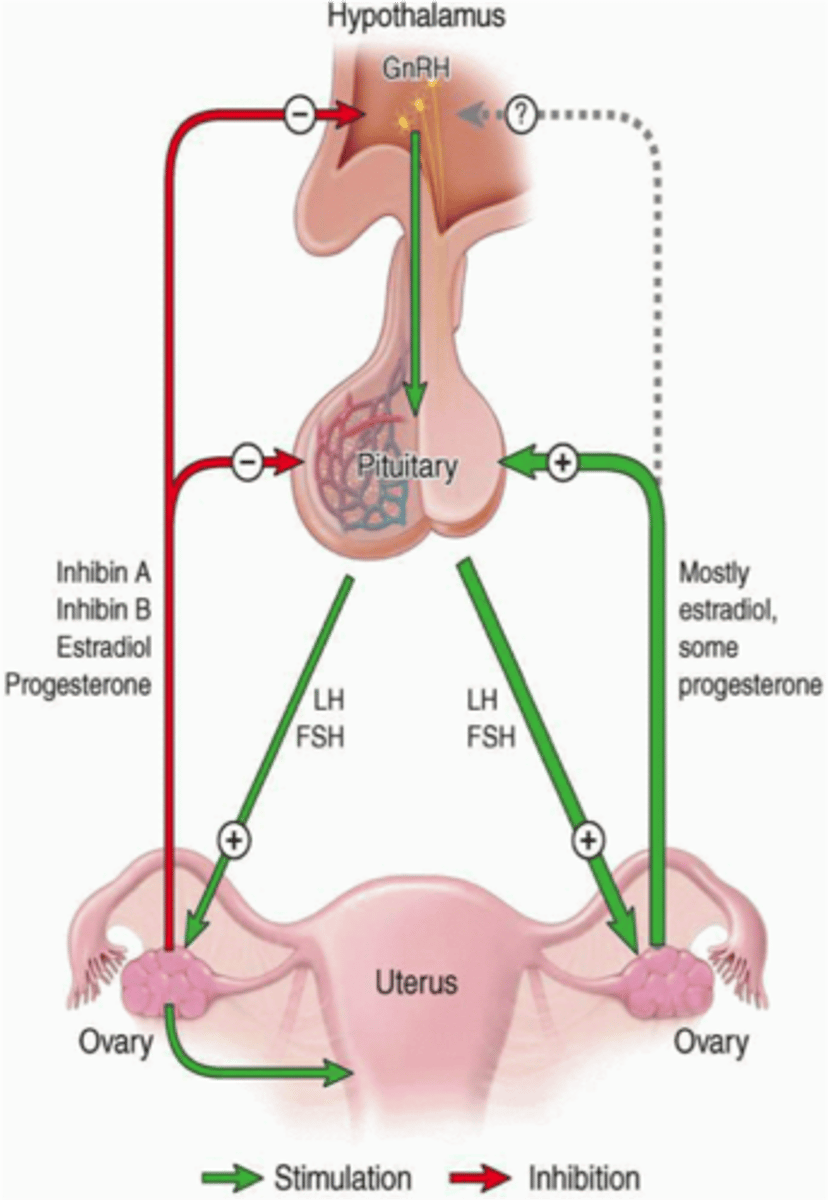
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the development of eggs in the ovaries and sperm in the testes
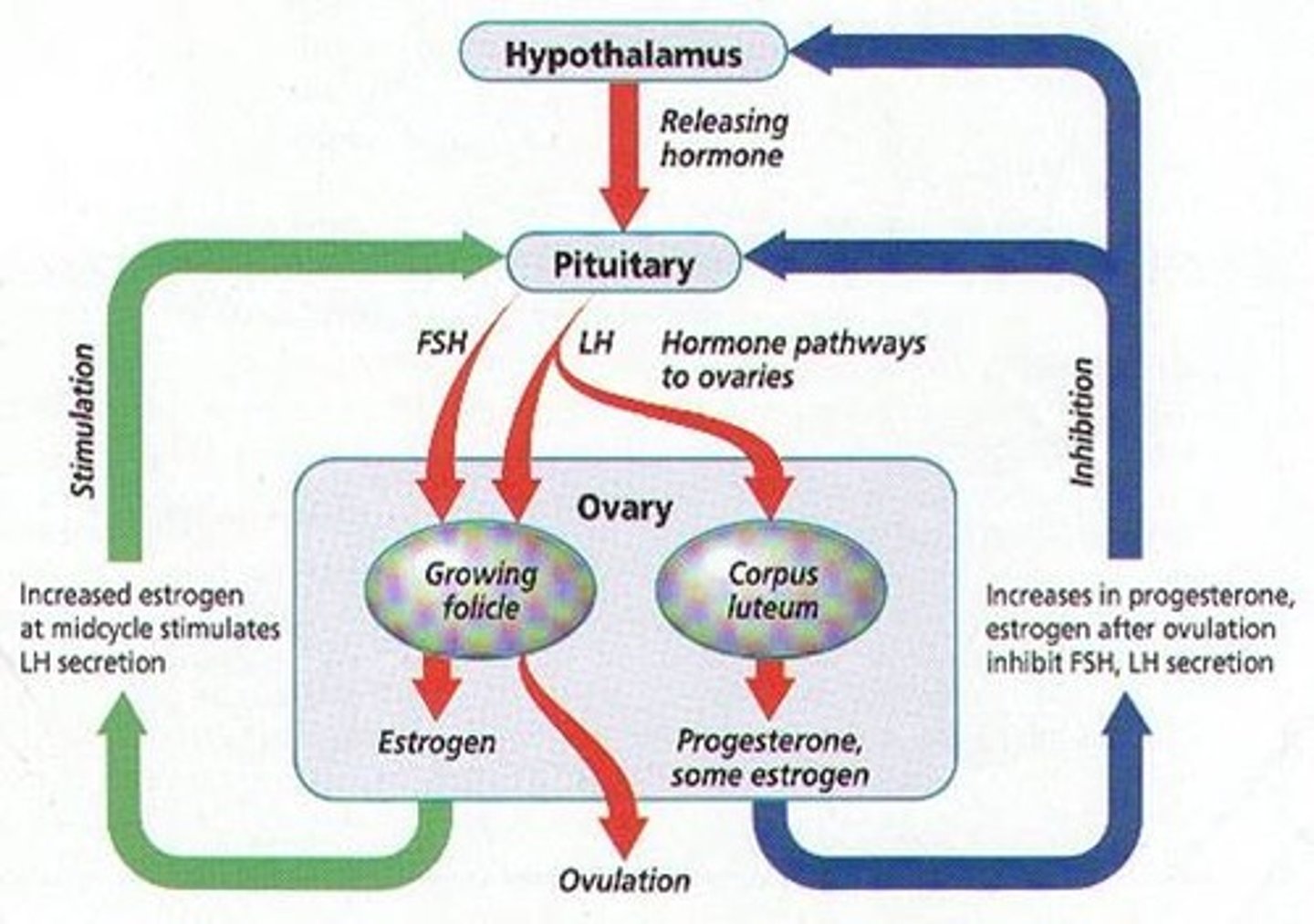
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that is responsible for triggering ovulation in ovaries and the production of testosterone by the testes
pituitary gland
the endocrine gland at the base of the brain that controls growth and development
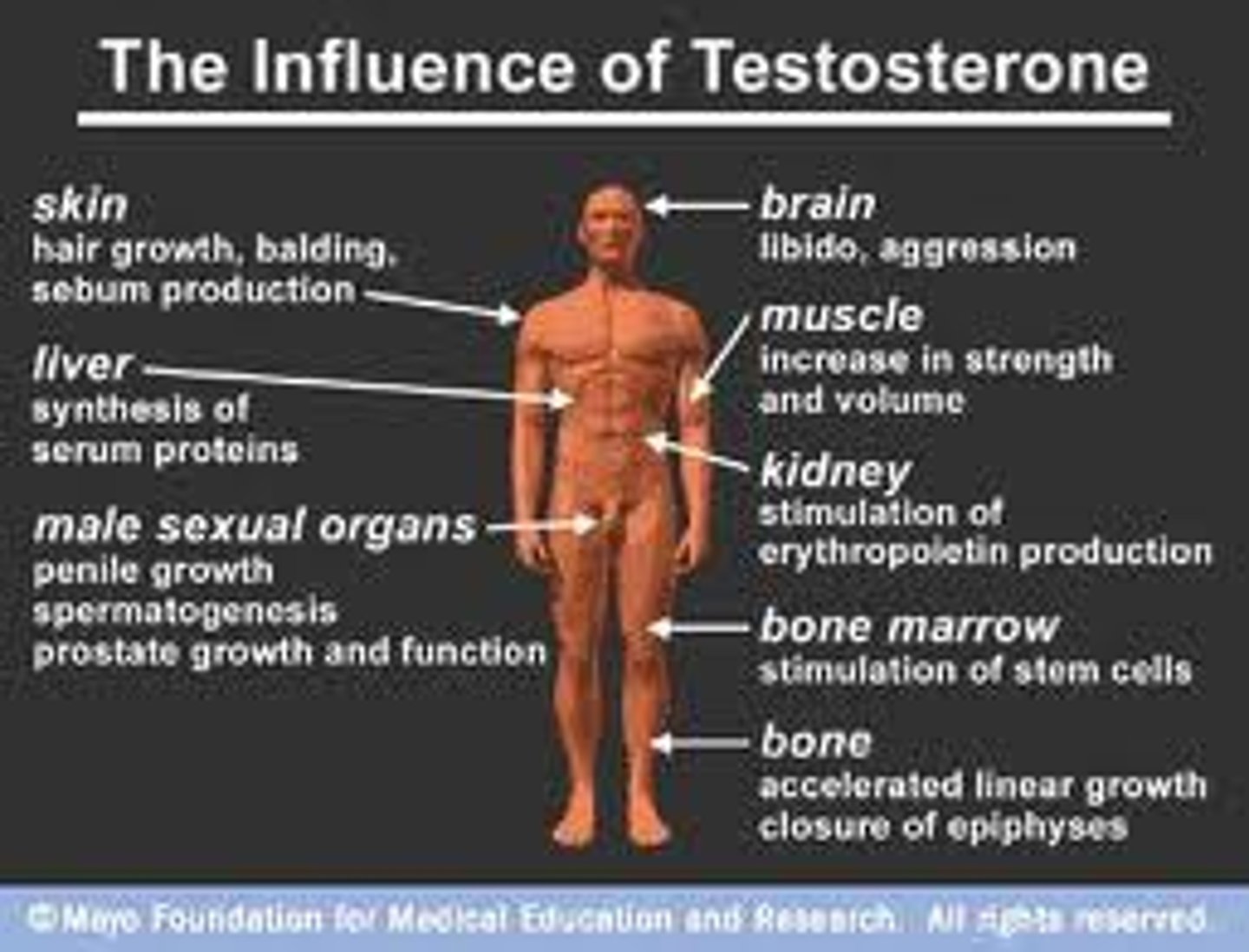
Testosterone
The hormone that stimulates male secondary sexual characteristics
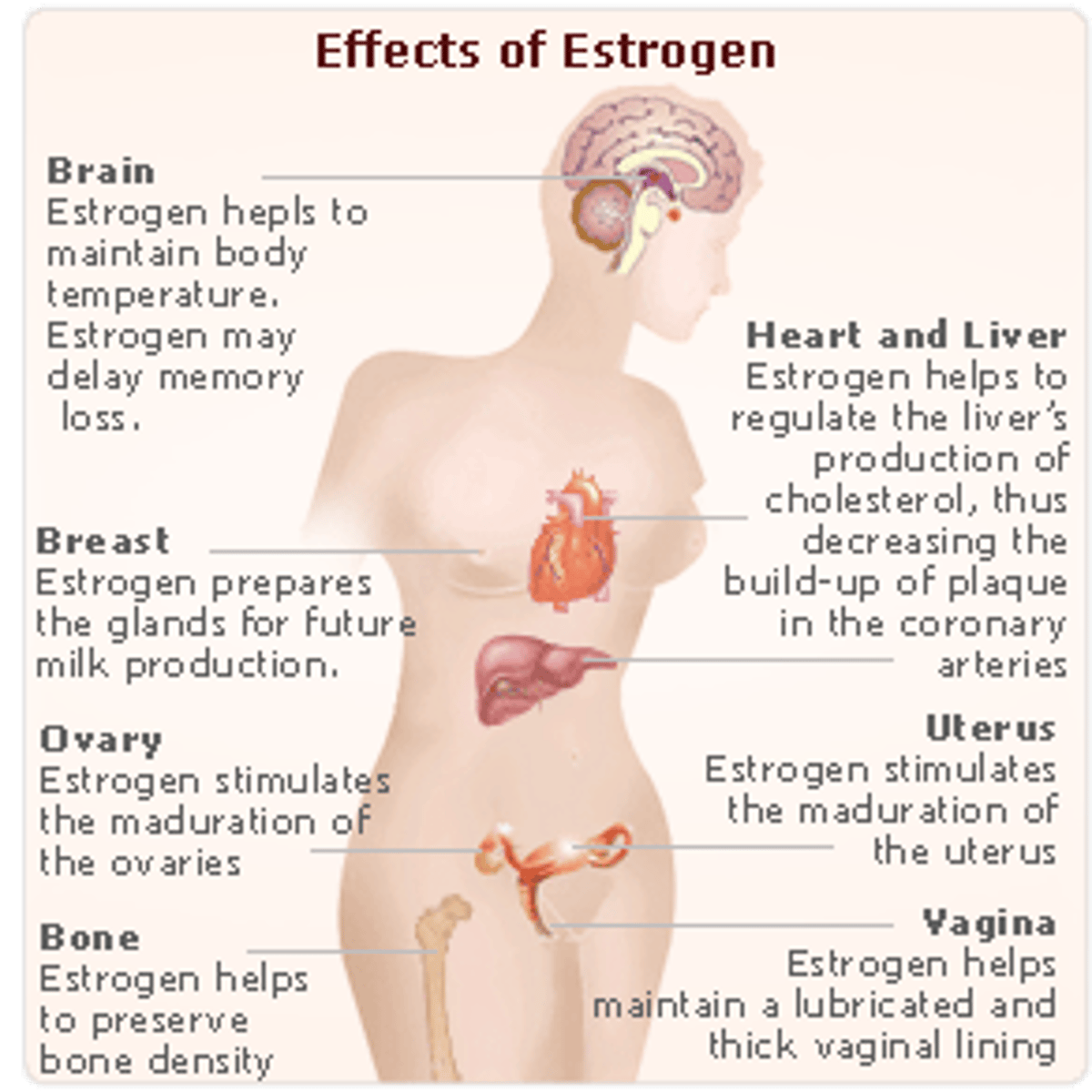
Estrogen
a female sex hormone released by the ovaries
Hormones are part of what system?
endocrine system
Puberty is initiated by the production of
gonadotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus, which triggers the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland
in males LH is
released and signals the testes to produce testosterone.
testosterone and FSH
stimulate the production of sperm cells
in females, FHS signals
the ovaries to produce more estrogen.