Biology: The Cell Cycle Test
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What limits a cell's size?
The surface area to volume ratio. Also information crisis and traffic problems.
The larger the ratio, the bigger the cell.
What is a chromosome?
A coiled strand of two sister chromatids (identical DNA)
Parts of chromosomes?
Two sister chromatids
They meet in the middle at the centromere
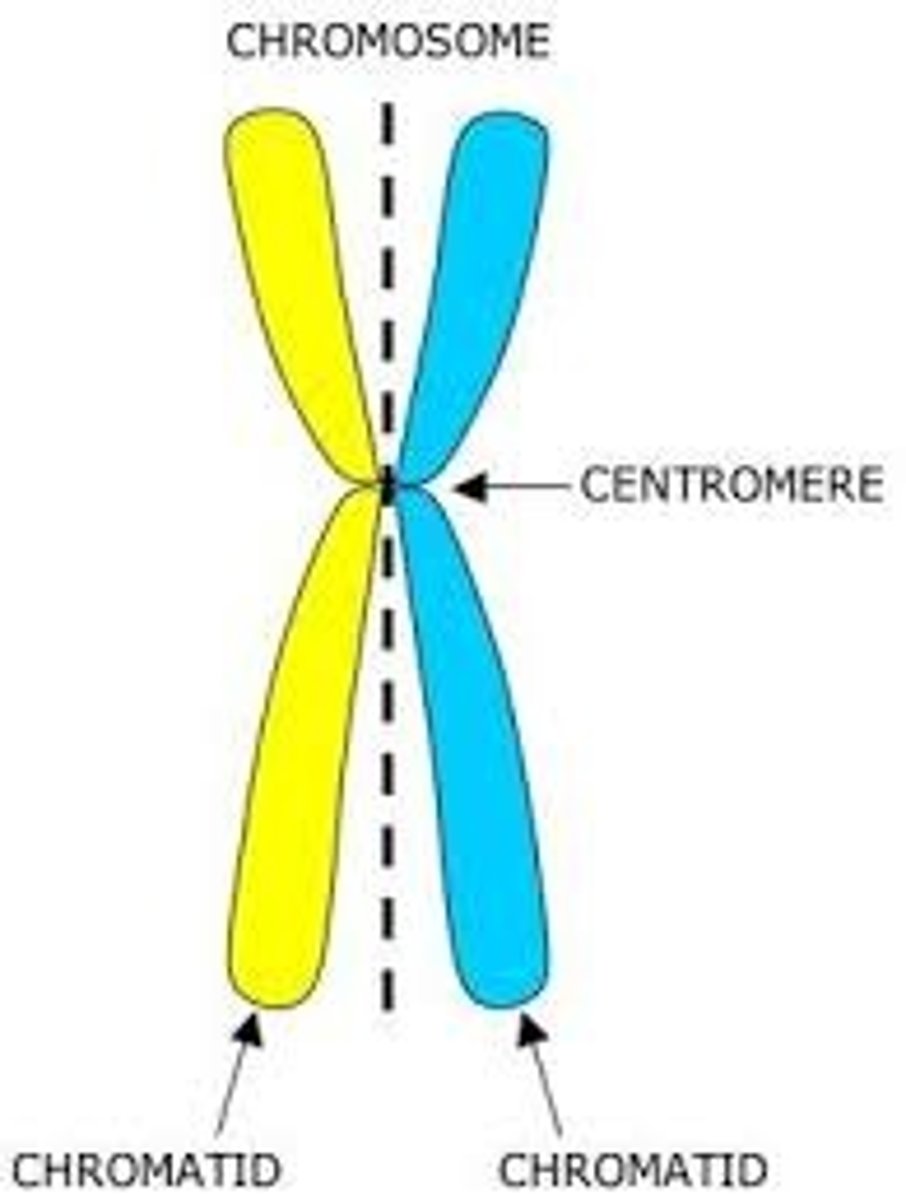
What are chromosomes made of?
DNA and protein
How many chromosomes does a human have in each body cell?
46
What does chromosome start out as and what does it become?
It starts as a big jumble (pasta noodles) of genetic material, called chromatin, but during Prophase it condenses to form chromosomes
Sexual vs. asexual reproduction:
sexual: two cells fuse together to make new (two sets of DNA
asexual: one set of DNA copies itself (one set of DNA)
Order of the cell cycle? What happens in interphase vs M phase?
Interphase
- G1
- G0
- S Phase
- G2 Phase
M Phase
- Mitosis
- Cytokinesis
What happens in G1?
Cell growth
What happens in S Phase?
DNA replicates
What happens in G2?
Cell preps for mitosis
What happens in G0 Phase?
It's a branch off of G1 where cells with problems go and divison is paused dividing. This can be permanent or temporary
What type of cells stay in G0 phase?
Nerve cells. Neurons. Cells that no longer need to divide
What happens in mitosis?
PMAT
What happens in Prophase? 3
Nucleus disappears, chromosomes condense and are visible, spindle fibers form
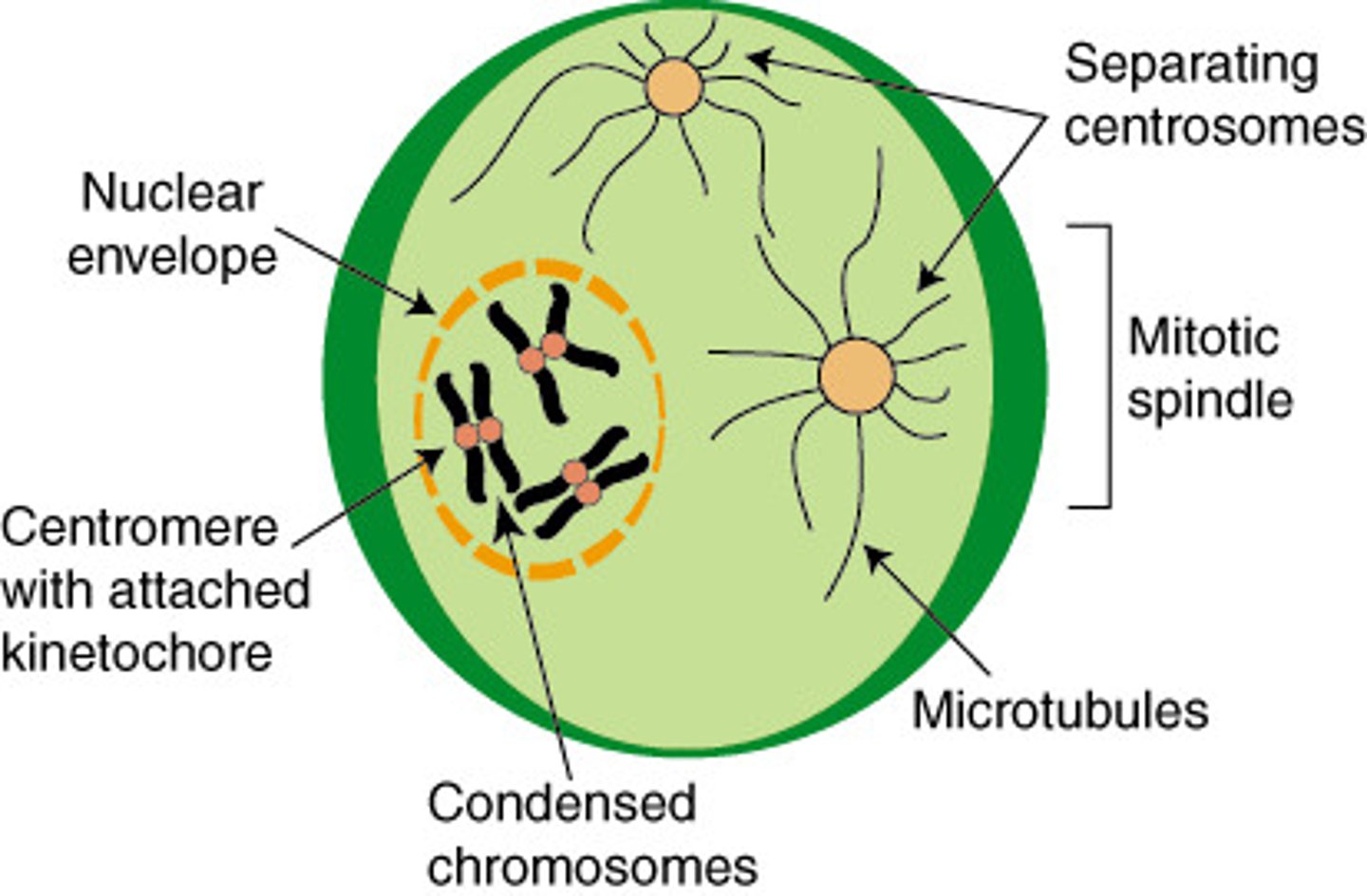
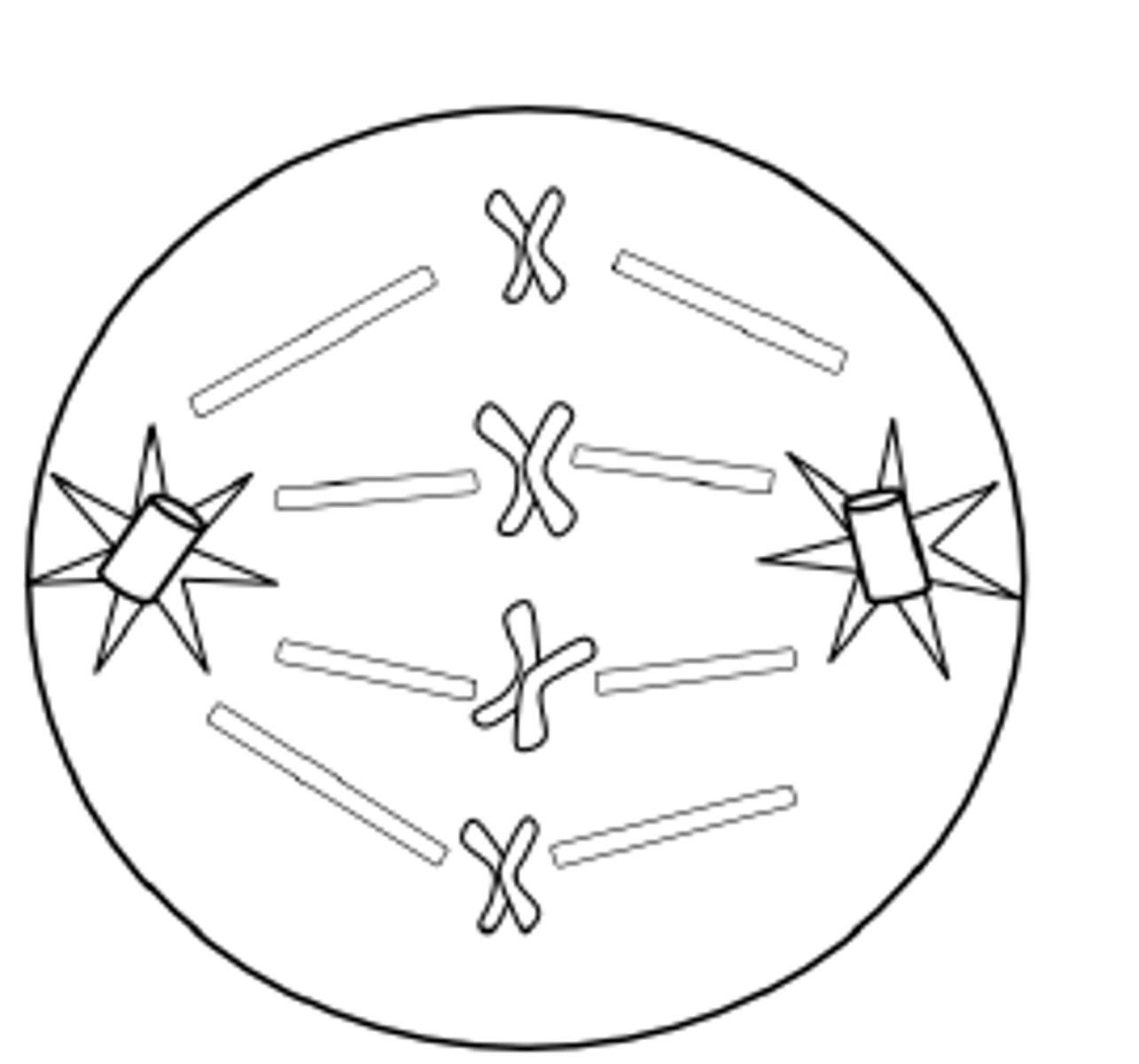
What happens in Metaphase? M for? 2
Middle.
Chromosomes line up single file down middle of cell. Spindles attach to the centrioles of the chromosones
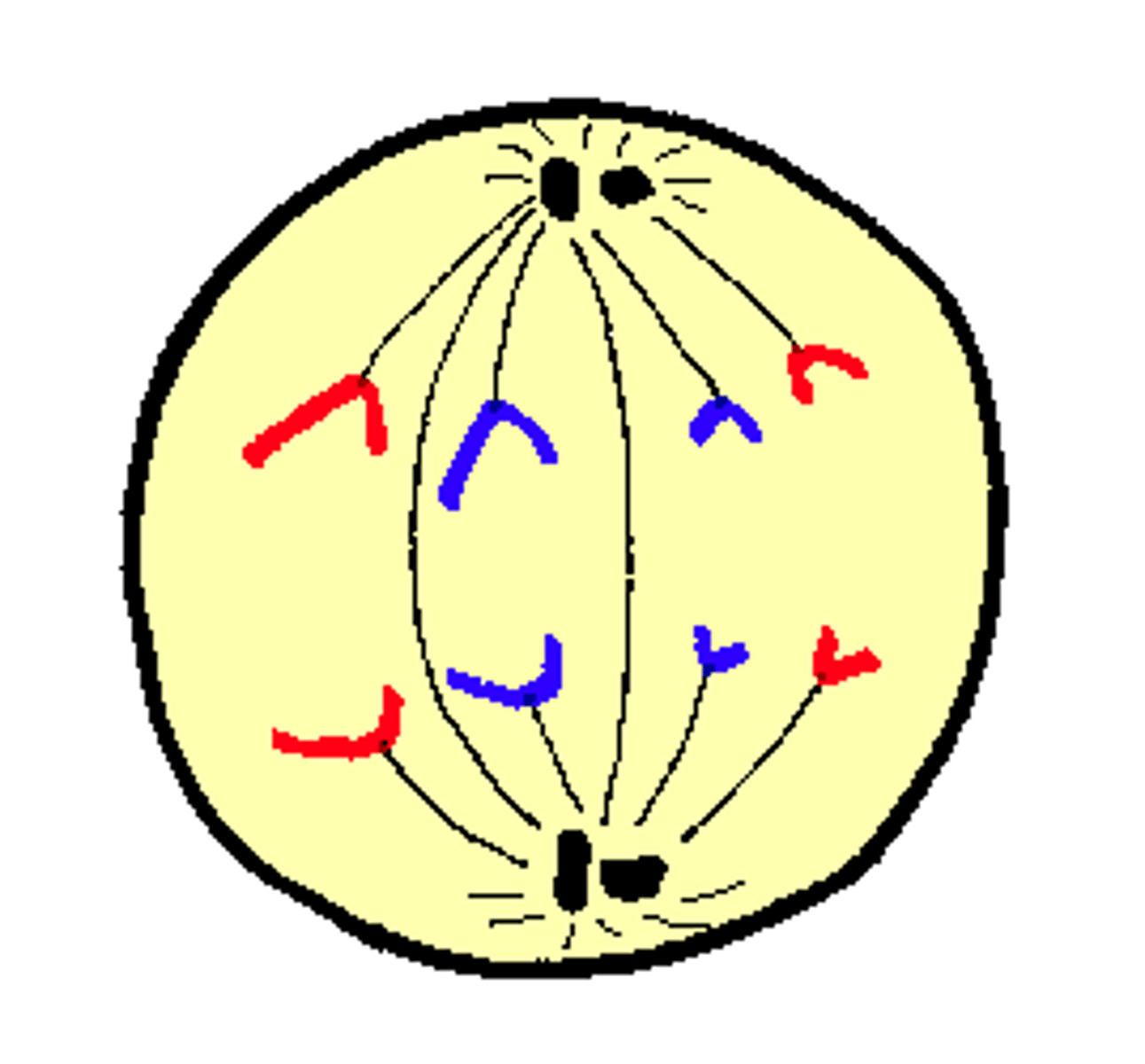
What happens in Anaphase? A for? 1
Away.
Sister chromatids get pulled apart and moved to the opposite sides of cells by the spindles
What happens in telephase? T for? 3
Two.
Nucleus reforms, spindles fibers disapear, chromosomes start to no longer be visible
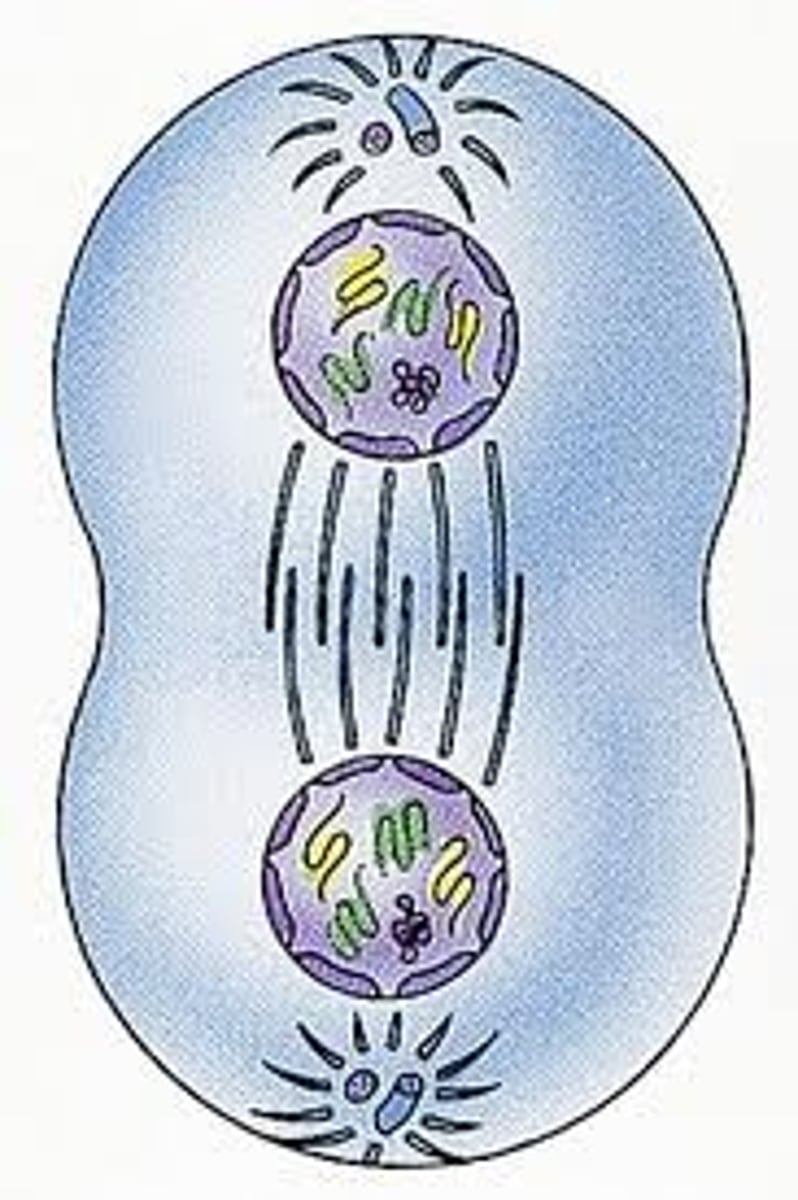
What happens in Cytokynesis?
Cytoplasm divides to create to identical daughter cells. Cell membrane pinches and causes clevage until fully apart and now 2 cells
What happens in a plant cell division?
Can't pinch due to cell wall, cell plate forms down middle and will turn into new cell wall for 2 new cells?
Why do cells divide?
To help repair the body and for general maintenance of body tissue. To make new cells to repair damaged ones.
What is a cyclin? When does it show?
A protein that helps regulate the cell cycle. Only when needed at checkpoints
Why would a normal healthy cell stop dividing?
it is touching another cell
What is a cancer cell?
A cell that doesn't respond to regulatory growth signals.
It divides uncontrollably and very frequently.
What causes a cancer cell to occur?
When control over the cell cycle has been lost
How can you tell a cancer cell is present?
When they produce a tumor and begin to displace other cells.
If you cannot catch their is damage, not listening to other cell next to it and keeps growing and pushing
What are the signs of cancer?
Cells dividing too quickly, not listening to checkpoints
What does cancer do?
Not listen to checkpoints, grow uncontrollably
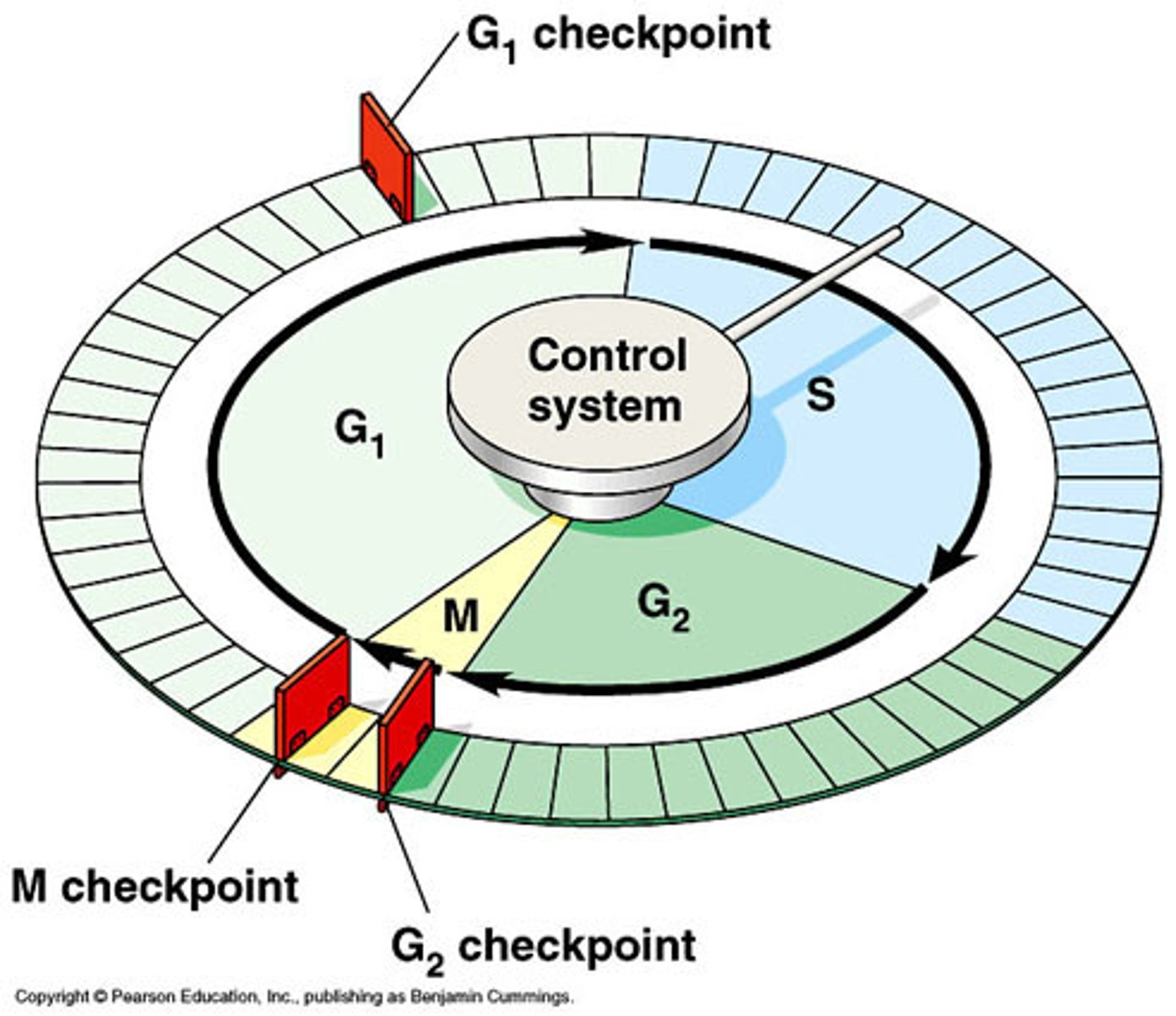
What happens in the G1 Checkpoint? 3
It checks for:
- enough room around for cell division
- Cell has grown enough for enough energy and material for cell function
- no damage to DNA
What happens in the G2 Checkpoint? 3
It checks for:
- checks that DNA is fully replicated
- check for no DNA damage
- have all materials ready for M Phase
What happens in the M Checkpoint? When does it take place?2
Checks for:
- All chromosomes have spindles correctly attached
Metaphase
cell cycle checkpoints
are where the said phase takes place
What is a proto-oncogene? Simple word for it?
Normal genes that play a role in regulating the cell cycle
Green light
What is an example of a proto-oncogene?
Cyclin, go signal for cycle
What is CDK?
Enzyme that is always present but only works when cyclin needed is present. Regulates cell cycle
What do CDK and cyclin do together?
Manage checkpoints
What is a stem cell?
Stem cells are the unspecialized cells from which differentiated cells develop.
What is a Totipotent stem cell?
can develop into any type of cell in the body
(including the cells that make up the extraembryonic membranes and placenta)
What is a Pluripotent stem cell?
cells that are capable of developing into most, but not all, of the body's cell types
What is a Multipotent stem cell?
Can become one cell. limited potential to develop into many different types of differentiated cells
eview how cells differentiate from stem cells into the specialized cells of the body
stem cells start out basic and not specialized and once developed or needed it will become a specialized cell for particular job in the body