CGIER 41 - Buffer systems and Henderson Hasselbalch pH = pKa + log conjugate base/weak acid
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:55 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
1
New cards

composition and action of buffered solutions
**what are buffers**
**what are buffers**
**There are ~ 96,000 km of blood vessels (arteries, veins and**
**capillaries) in your body. This is enough to stretch almost 2.5 times around the equator!**
(when u think buffer think Henderson hasselbalch)
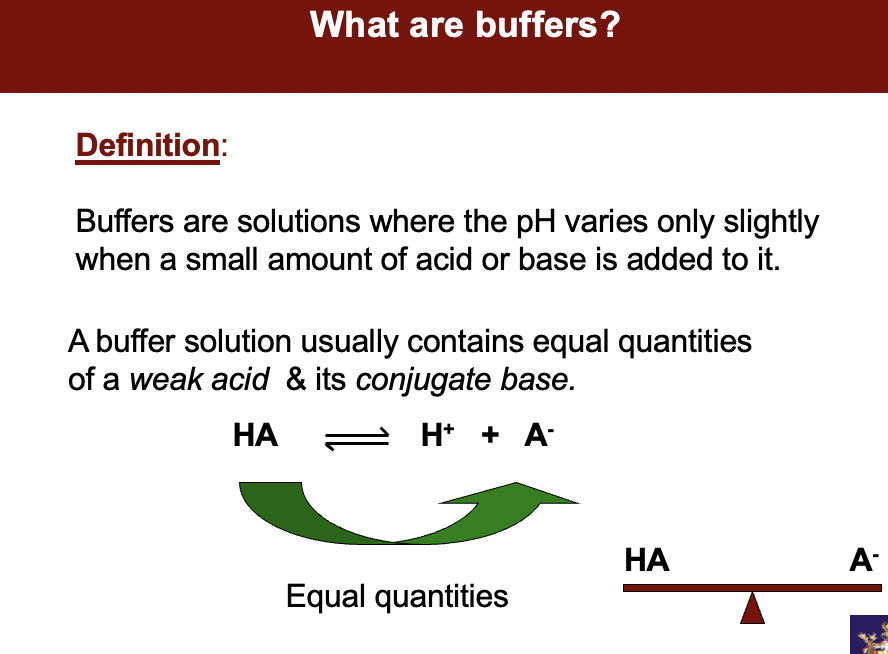
**what are buffers?**
Buffers are **chemical equilibrium systems** /solutions where the pH varies only slightly when a small amount of acid or base is added to it.
A buffer solution usually contains equal quantities of typically a *weak acid* & its *conjugate base.*
\
a lot more bicarbonate anion relative to carbonic acid, this is bc be produce much more side products bc of metabolism. but normally good buffers have same amt of weak acid and conjugate base so that no matter what drops in it it can resolve.
**capillaries) in your body. This is enough to stretch almost 2.5 times around the equator!**
(when u think buffer think Henderson hasselbalch)
**what are buffers?**
Buffers are **chemical equilibrium systems** /solutions where the pH varies only slightly when a small amount of acid or base is added to it.
A buffer solution usually contains equal quantities of typically a *weak acid* & its *conjugate base.*
\
a lot more bicarbonate anion relative to carbonic acid, this is bc be produce much more side products bc of metabolism. but normally good buffers have same amt of weak acid and conjugate base so that no matter what drops in it it can resolve.
2
New cards
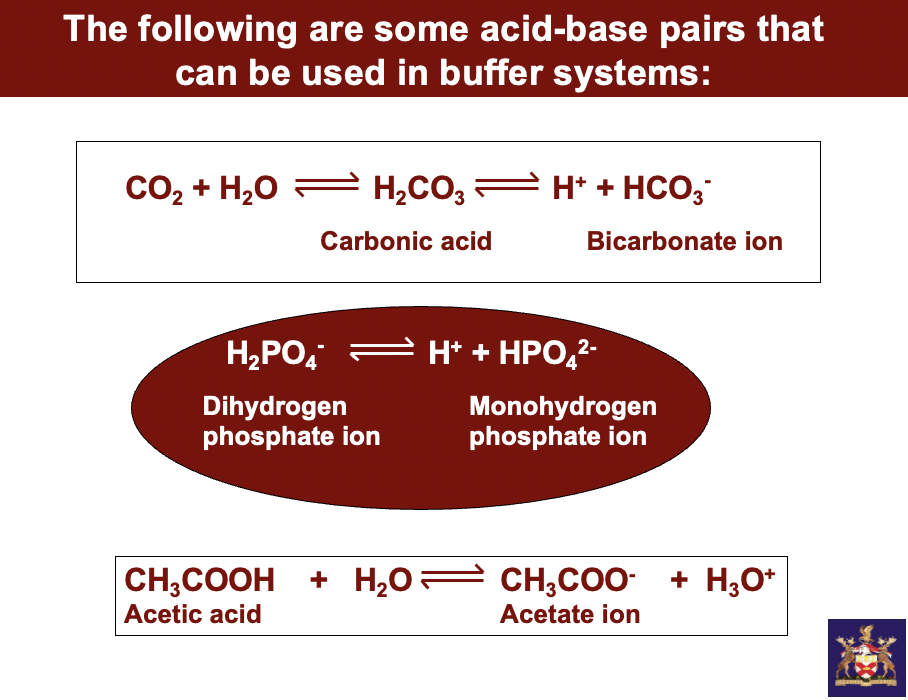
some acid-base pairs that can be used in buffer systems:
carbonic acid
carbonic acid
**carbonic acid
3
New cards
![__**The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation**__ **relates the [buffer mixture] to the pH of the solution**](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4a43a146ca584eb1aa910a86d67676d5.jpeg)
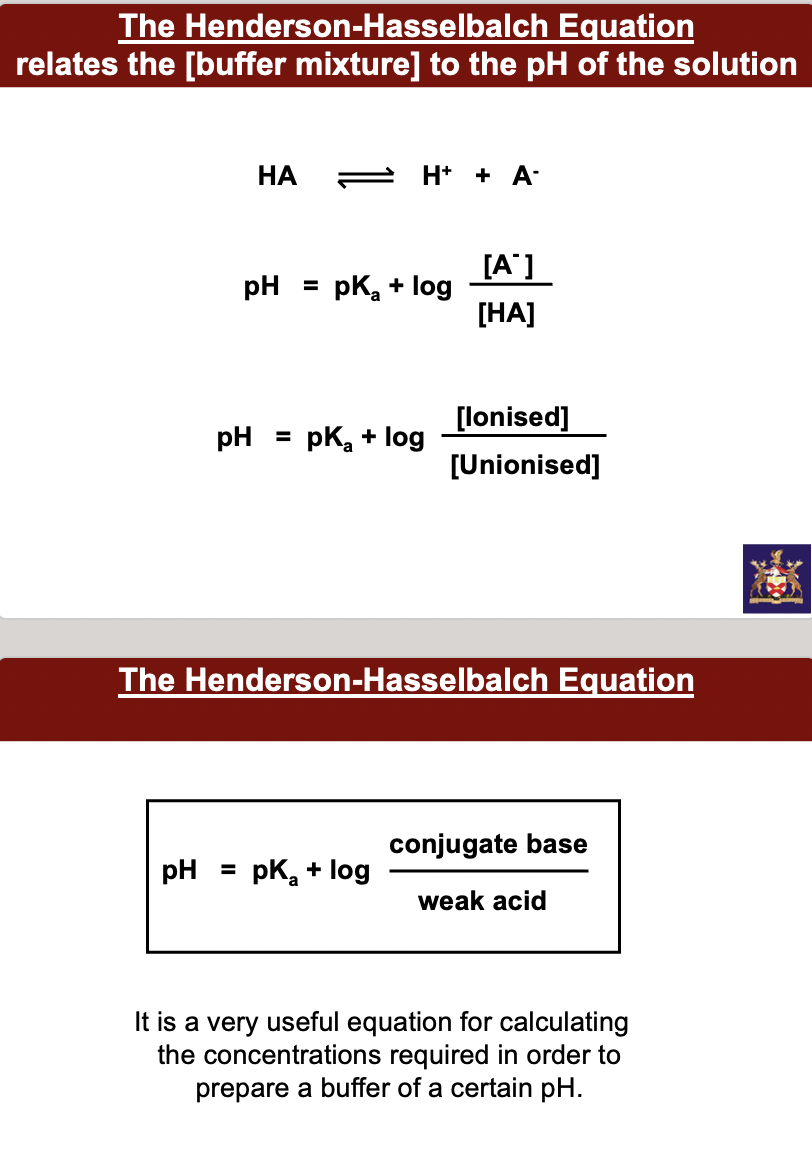
__**The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation**__ **relates the [buffer mixture] to the pH of the solution**
**pH = pKa + log conjugate base/ weak acid**
It is a very useful equation for calculating the concentrations required in order to prepare a buffer of a certain pH.
It is a very useful equation for calculating the concentrations required in order to prepare a buffer of a certain pH.
4
New cards
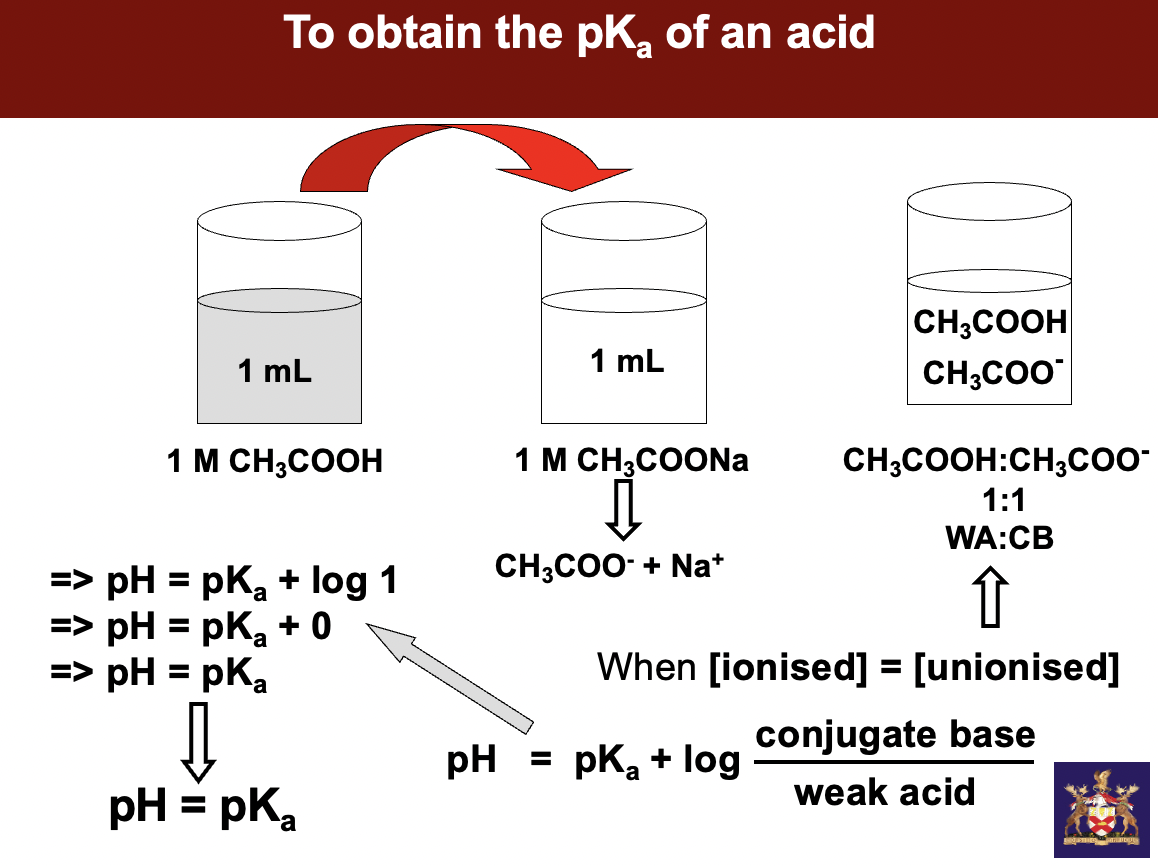
to obtain the pKa of an acid
**if u have a solution containing equal quantities of weak acid and base, if u measure pH of solution it will give u pKa of ur weak acid!! When the pH = pKa then u have equal concentration of ur weak acid and conjugate base**
\
Ka of weak base is so small bc dissociation is small.
\
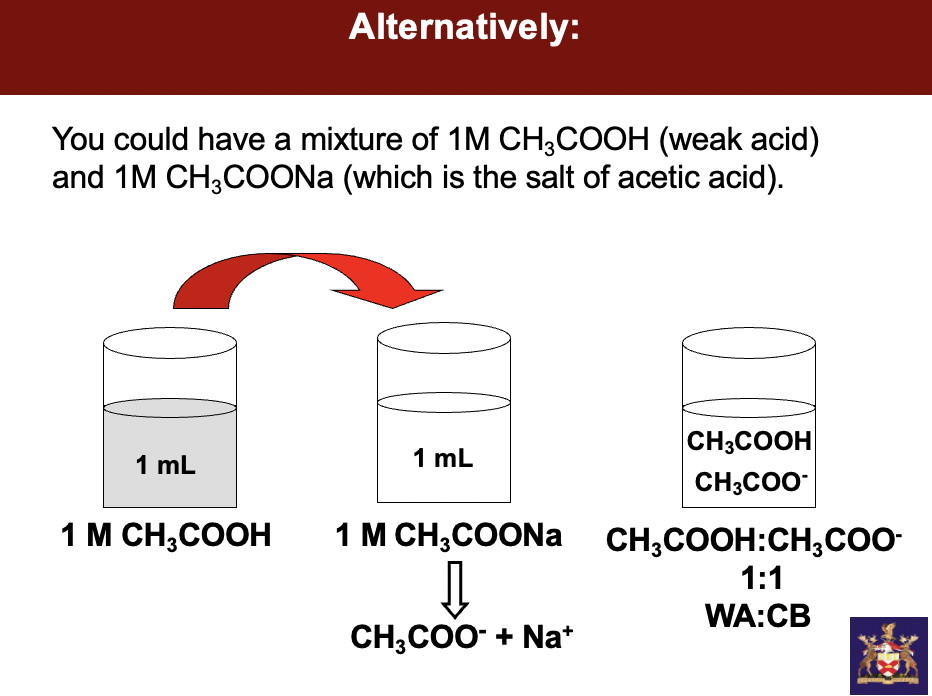
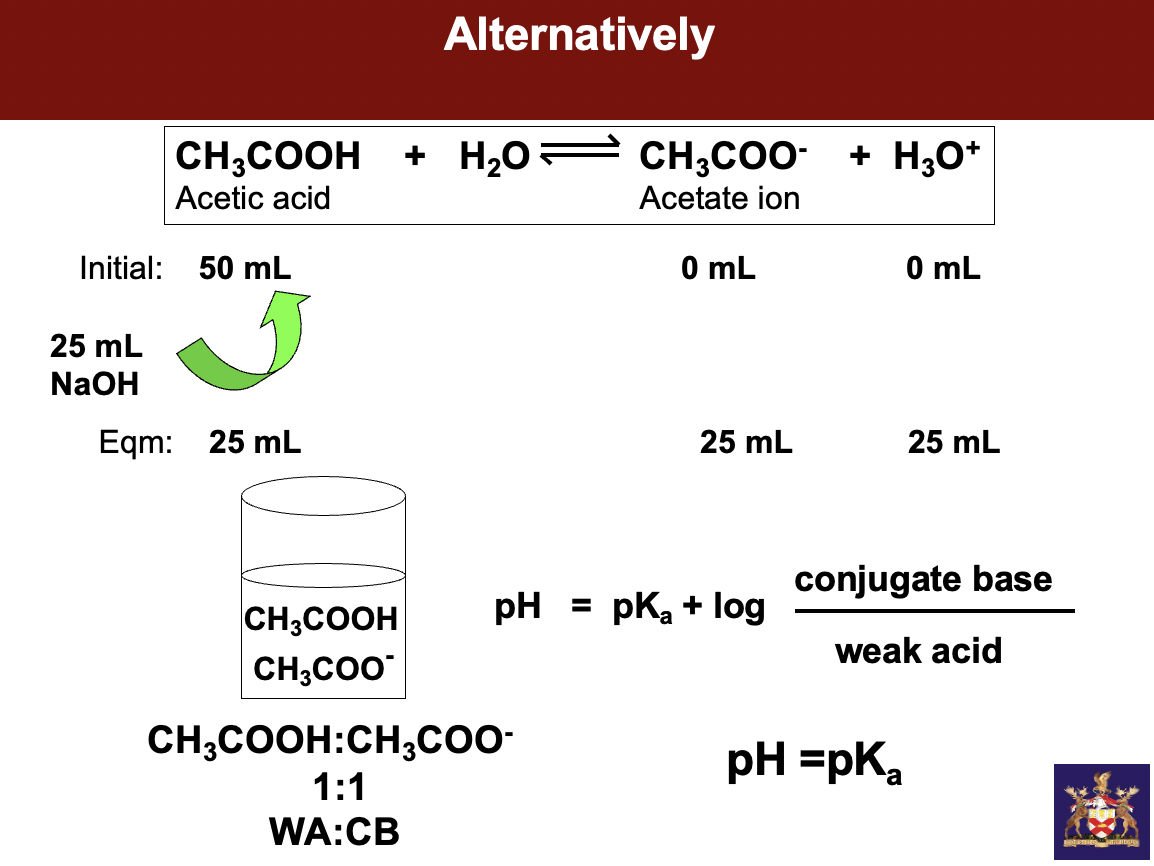
instead of giving us 2 separate beakers w sodium salt and CH3COOH, we get ONE beaker and a strong base - sodium hydroxide. understand how much sodium hydroxide should I force onto any weak acid to half neutralize it
start w 100mls of weak acid add 50mls of strong base to get equal parts weak acid to **conjugate base**
\
Ka of weak base is so small bc dissociation is small.
\
instead of giving us 2 separate beakers w sodium salt and CH3COOH, we get ONE beaker and a strong base - sodium hydroxide. understand how much sodium hydroxide should I force onto any weak acid to half neutralize it
start w 100mls of weak acid add 50mls of strong base to get equal parts weak acid to **conjugate base**
5
New cards
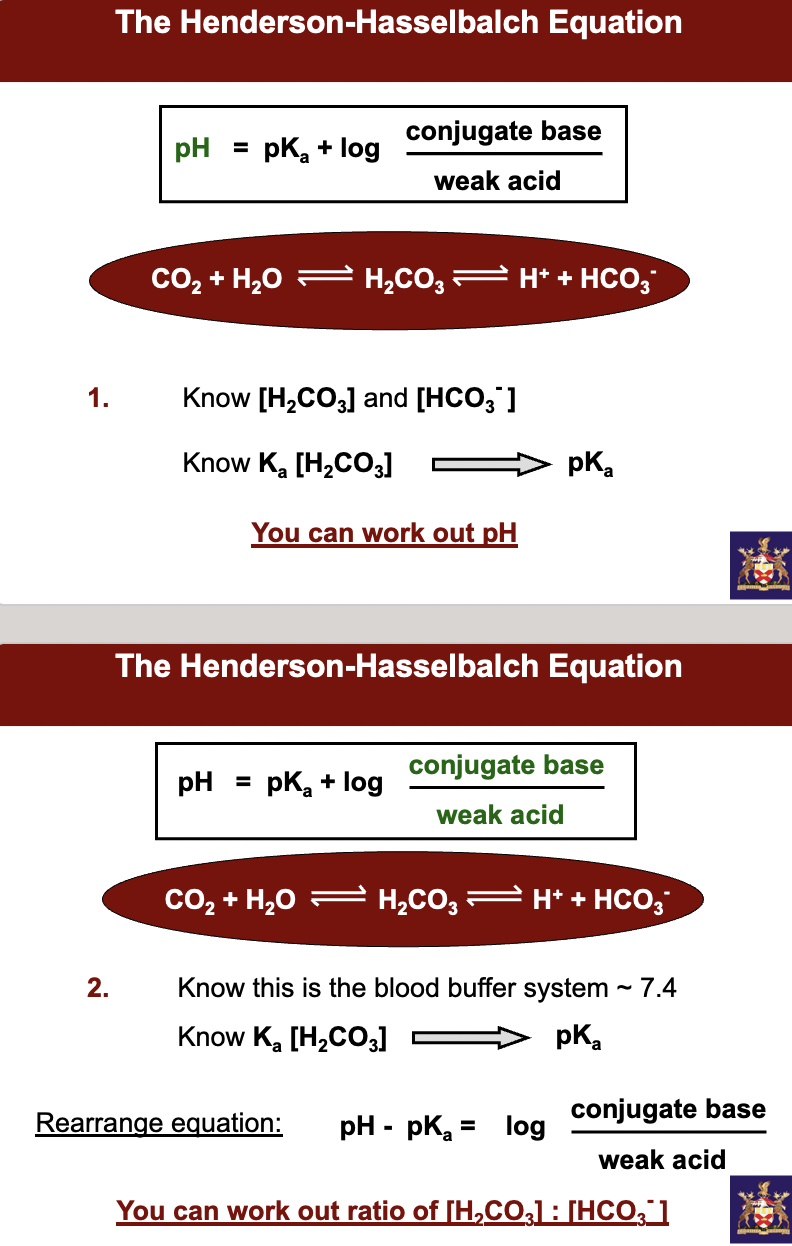
what are some situations using Henderson hasselbalch
will only ever be given a question w only one missing variable
will only ever be given a question w only one missing variable
1. **Know [H2CO3] and [HCO3-]**
Know Ka \[H2CO3\] →pKa
you can work out pH
pH = pKa + log conjugate base/weak acid
CO2 + H2O
![1. **Know [H2CO3] and [HCO3-]**
Know Ka \[H2CO3\] →pKa
you can work out pH
pH = pKa + log conjugate base/weak acid
CO2 + H2O <=> H2CO3 <=> H+ + HCO3-
\
2. **Know this is the blood buffer system ~7.4**
Know Ka \[H2CO3\] → pKa
Rearrange equation: pH - pKa = log conjugate base/ weak acid
you can work out ratio of \[H2CO3\] : \[HCO3-\]
pH = pKa + log conjugate base/weak acid
CO2 + H2O <=> H2CO3 <=> H+ + HCO3-
\
3. **You want the buffer system to have a certain pH**
Given a \[H2CO3\] and \[HCO3-\]
Know Ka \[H2CO3\] → pKa
You can work out ratio of \[H2CO3\]: \[HCO3-\] required](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ed0485575ee24558802f23b682410760.jpeg)
6
New cards
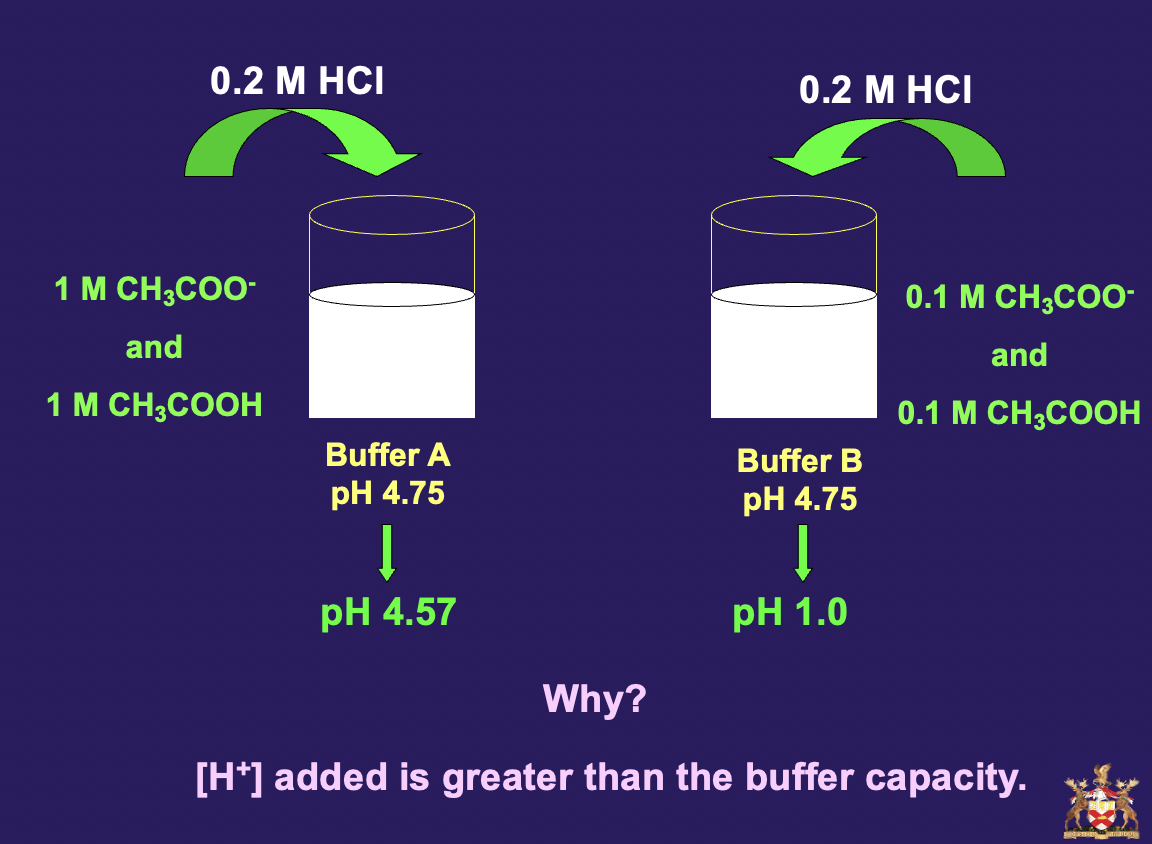
is there a perfect buffer system? there kind of is isn’t there. obvi the higher the concentration the greater its capacity but it is good
Buffer capacity and pH
Buffer capacity and pH
the best buffering occurs when the \[acid\] = \[conjugate base\]
HA
HA
![the best buffering occurs when the \[acid\] = \[conjugate base\]
HA <=> H+ + A-
Equal quantities pH = pKa of the weak acid
useful buffer range is pKa +/- 1
\-
The buffering capacity is the amount of acid or base a buffer can accept without the pH changing appreciably. The greater the amounts of the conjugate acid-base pair, the more resistant they are to change in pH.
$$Buffer A$$ - 1 M CH3COO- and 1 M CH3COOH - pH = 4.75
$$Buffer B$$ - 0.1 M CH3COO- and 0.1 M CH3COOH - pH = 4.75
**remember** **pH = pKa + [COO3COO-]/[CH3COOH]**
Buffer A has 10 times the concentration of CH3COOH/CH3COO- compared with Buffer B. Therefore, the buffer capacity of Buffer A is 10 times that of Buffer B.
\
if we now added 0.2 M HCL to buffer A the pH wouldn’t change too dramatically but if we added this to Buffer B wev completely acidified it bc wev put in twice as much base as fecking buffer, uv poisoned it.](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f1060a3d15364e8285b48fdd31849591.jpeg)
7
New cards
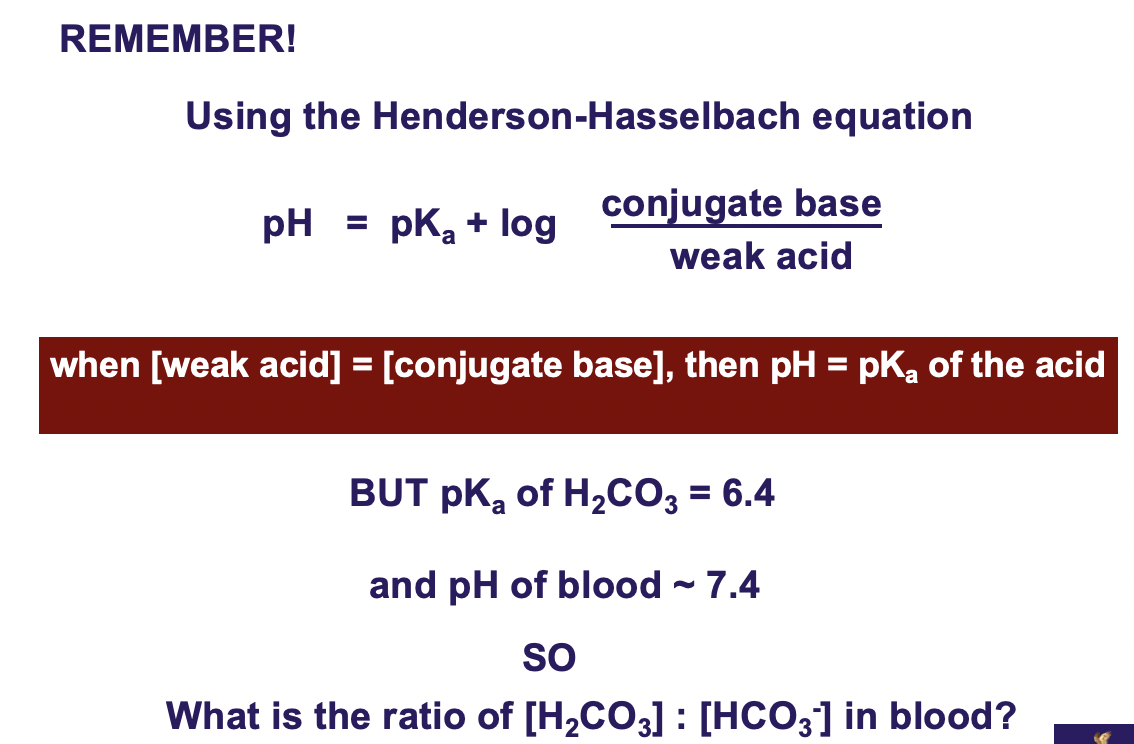
Major buffer systems in the human body - bicarbonate buffer
how do buffer systems control the pH of blood?
how do buffer systems control the pH of blood?
**Blood must be maintained at pH ~7.4 The pH of the** __**blood**__ **is controlled by the bicarbonate buffer system**
CO2 + H2O
CO2 + H2O
![**Blood must be maintained at pH ~7.4 The pH of the** __**blood**__ **is controlled by the bicarbonate buffer system**
CO2 + H2O <=> H2CO3 <=> H+ + HCO3-
\
__**Adding a strong acid to the carbonic acid -bicarbonate buffer system**__
**will increase [H+],**
**• driving the reaction to the left and forming more carbonic acid.**
**• carbonic acid is unstable and will decompose rapidly to form**
**carbon dioxide and water.**
**The carbon dioxide so formed can be removed from the blood**
**and exhaled by the lungs.**
__**Adding a strong base to the system**__
**• Base will react with the H+ ions present to produce water,**
**• thus decreasing the [H+] in the system.**
**• This will drive the above reaction to the right.**
**[H+] ion restored and blood pH restored**
**when [weak acid] = [conjugate base], then pH = pKa of the acid**
**BUT pKa of H2CO3 = 6.4 and pH of blood ~ 7.4 SO what is the ratio of [H2CO3]:[HCO3-] in blood?**
\
\](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff076b9f1b7e497a9acee6494259982e.jpeg)
8
New cards
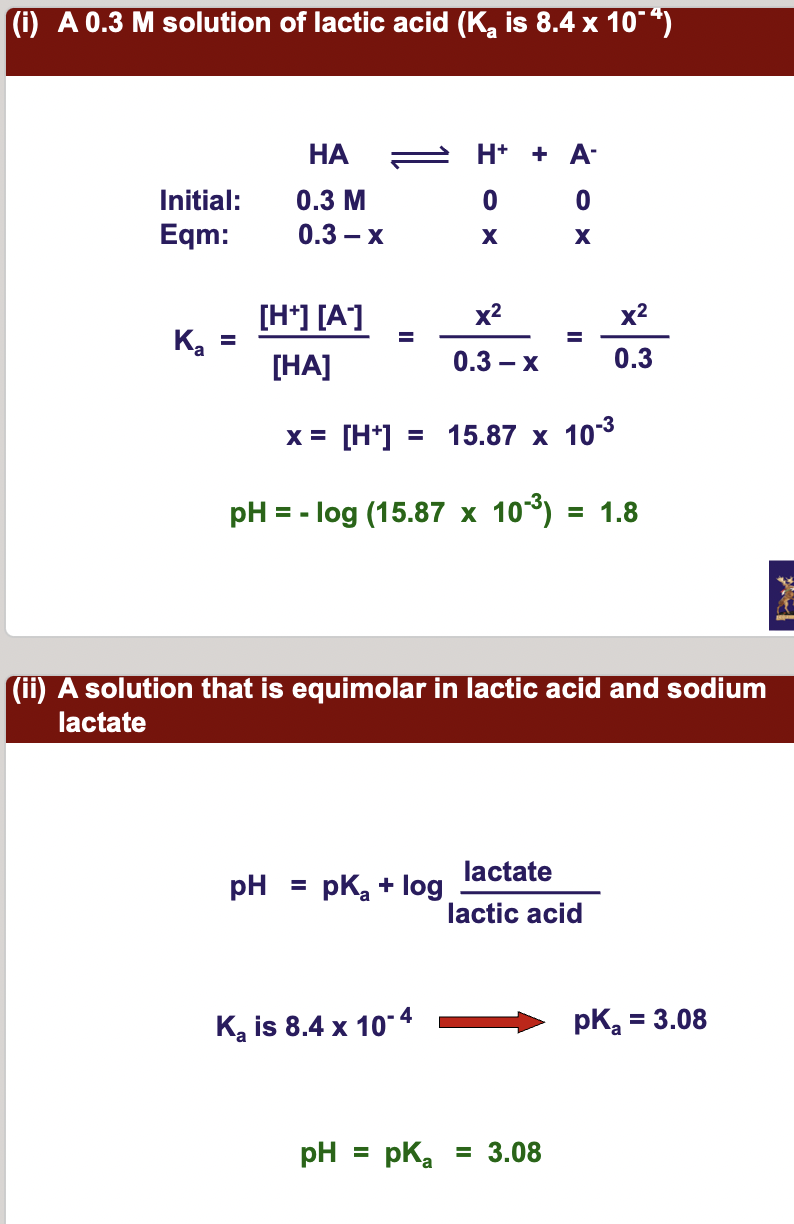
**May 2001**
**Calculate the pH of the following solutions:**
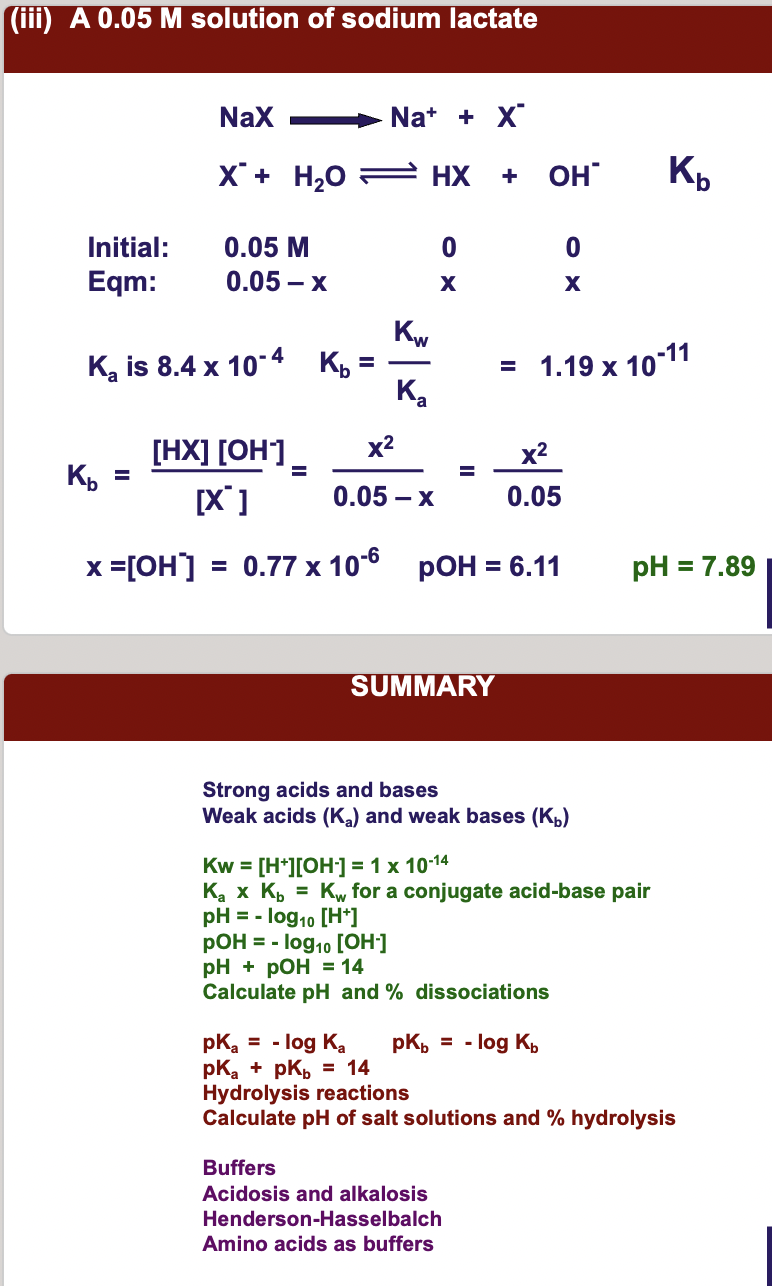
(i) **A 0.3 M solution of lactic acid (Ka is 8.4 x 10- 4)**
(ii) **A solution that is equimolar in lactic acid and** \n **sodium lactate**
(iii) **A 0.05 M solution of sodium lactate.**
**Calculate the pH of the following solutions:**
(i) **A 0.3 M solution of lactic acid (Ka is 8.4 x 10- 4)**
(ii) **A solution that is equimolar in lactic acid and** \n **sodium lactate**
(iii) **A 0.05 M solution of sodium lactate.**