Core Practical 6: Investigate the chlorination of 2-methylpropan-2-ol
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Overview:

Procedure:

Procedure:
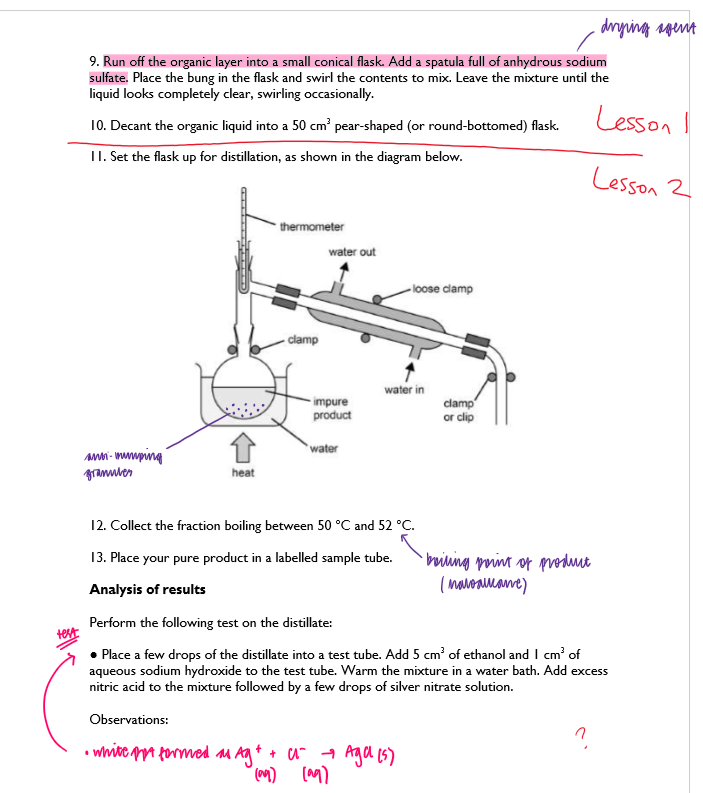
Learning Tips;
the hydroxyl group in an alcohol can be replaced by a halogen
PCl5 can be used as an alternative reagent to HCl to make a chloroalkane
50% concentrated sulphuric acid and potassium bromine (which makes HBr in situ) can be used to make a bromoalkane (+heat)
red phosphorus with iodine can be used to make an iodoalkane (+heat)
the purity of a liquid can be checked by measuring its boiling temperature
Write an equation for the reaction of 2-methylpropan-2-ol with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
CH3C(OH)(CH3)CH3 + HCl → CH3CCl(CH3)CH3 + H2O
What is removed from the crude product when it is shaken with sodium hydrogencarbonate solution? Write an equation for any reaction that occurs.
HCl is removed.
HCl + NaHCO3 → NaCl + CO2 + H2O
2-methylpropan-2-ol has a boiling temperature of 82 degrees C and is soluble in water. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane has a boiling temperature of 51 degrees C and is insoluble in water. Explain these differences.
both 2-methylpropan-2-ol and 2-chloro-2-methylpropane have london forces and permanent dipole - permanent dipole forces.
however 2-methylpropan-2-ol also contains hydrogen bonding due to the hydroxyl group
this means that the 2-methylpropan-2-ol can hydrogen bond with water molecules
these hydrogen bonds are similar in strength to those between water molecules
so it is soluble in water
hydrogen bonds are relatively much stronger than pd-pd interactions and london forces therefore it takes much more energy to overcome them and so 2-methylpropan-2-ol has a higher boiling point than 2-chloro2-methylpropane