L25 Spinal Reflexes (Imported from Quizlet)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
A rapid, involuntary, yet stereotyped and co-ordinated response to a sensory stimulus
What is a reflex?
Muscle contraction
Reflexes usually involved __________ ______________ (but can include glandular responses, e.g. lactation in response to suckling)
Pavlovian, somatic reflexes
Reflexes can be learned (___________) but focus is more on unlearned reflexes, specifically __________ _____________ (i.e. those involving the somatic nervous system)
Spinal reflexes since they involve spinal cord circuitry
What are somatic reflexes also called and why?
Stimulation (i.e. not spontaneous) therefore need sensory input
What do spinal reflexes require and what does this therefore mean?
Few synapses involved
Spinal reflexes are quick, what does this suggest?
Involuntary, automatic, higher centres
Spinal reflexes are _____________ and ____________; you often are aware of them only as they happen and they are difficult to suppress which suggests little input from ________ __________
Occur the same way each time
Spinal reflexes are stereotyped, what does this mean?
Underlying circuitry very simple
Given that spinal reflexes are stereotyped, what does this suggest?
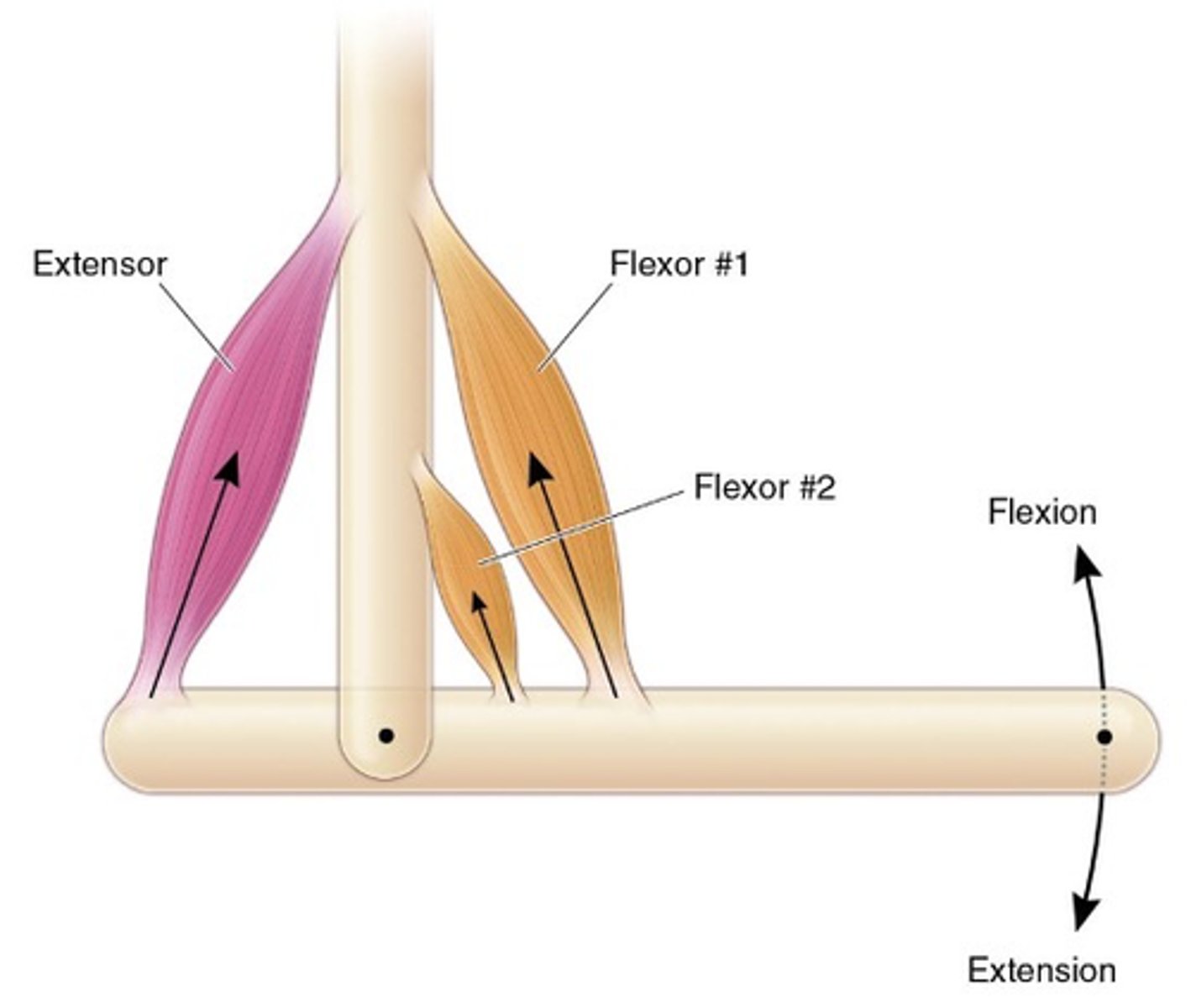
Muscle causing limb to extend
What are extensors?
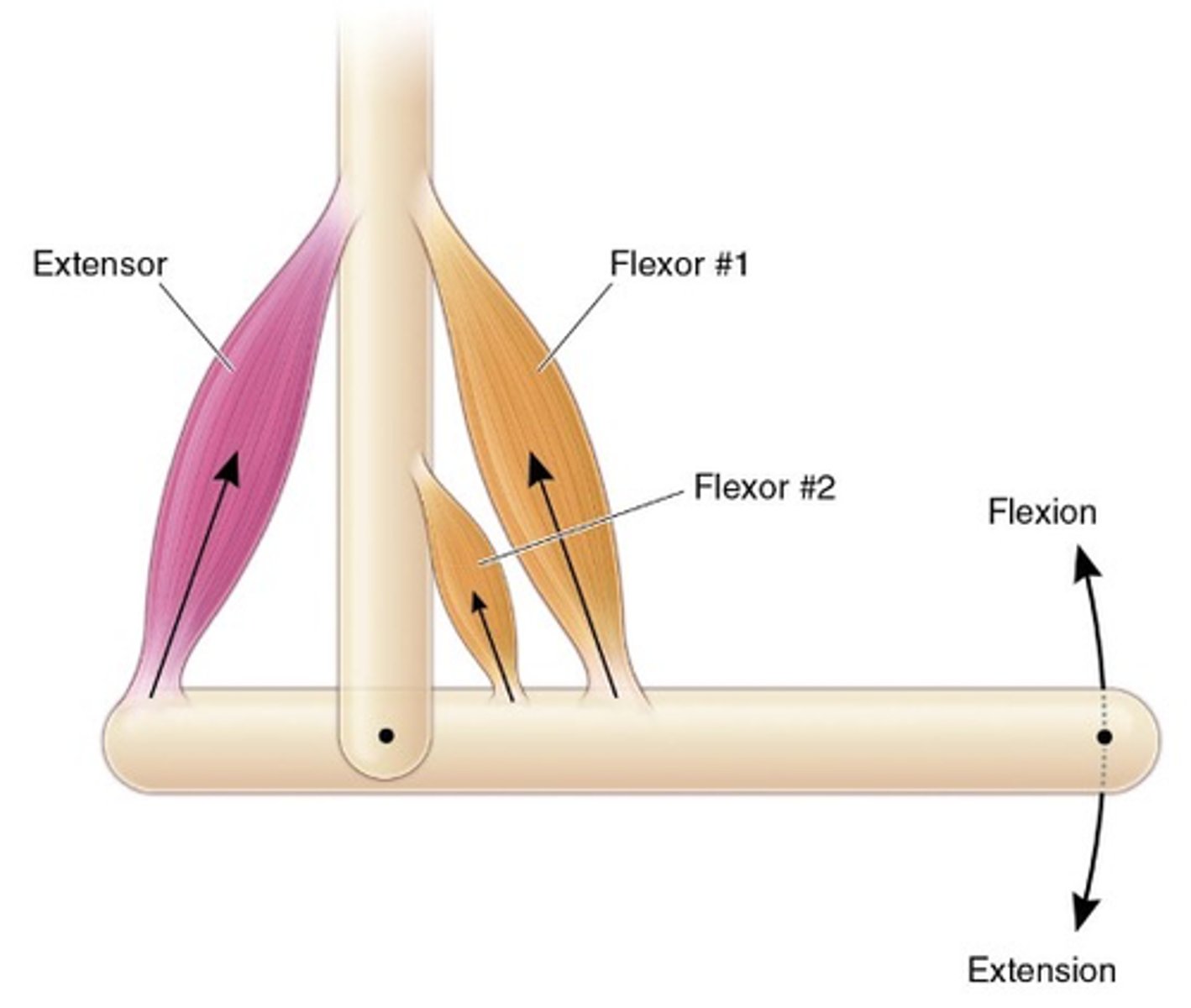
Muscle causing limb to flex (bend)
What are flexors?
Only one synapse involved
What does monosynaptic mean?
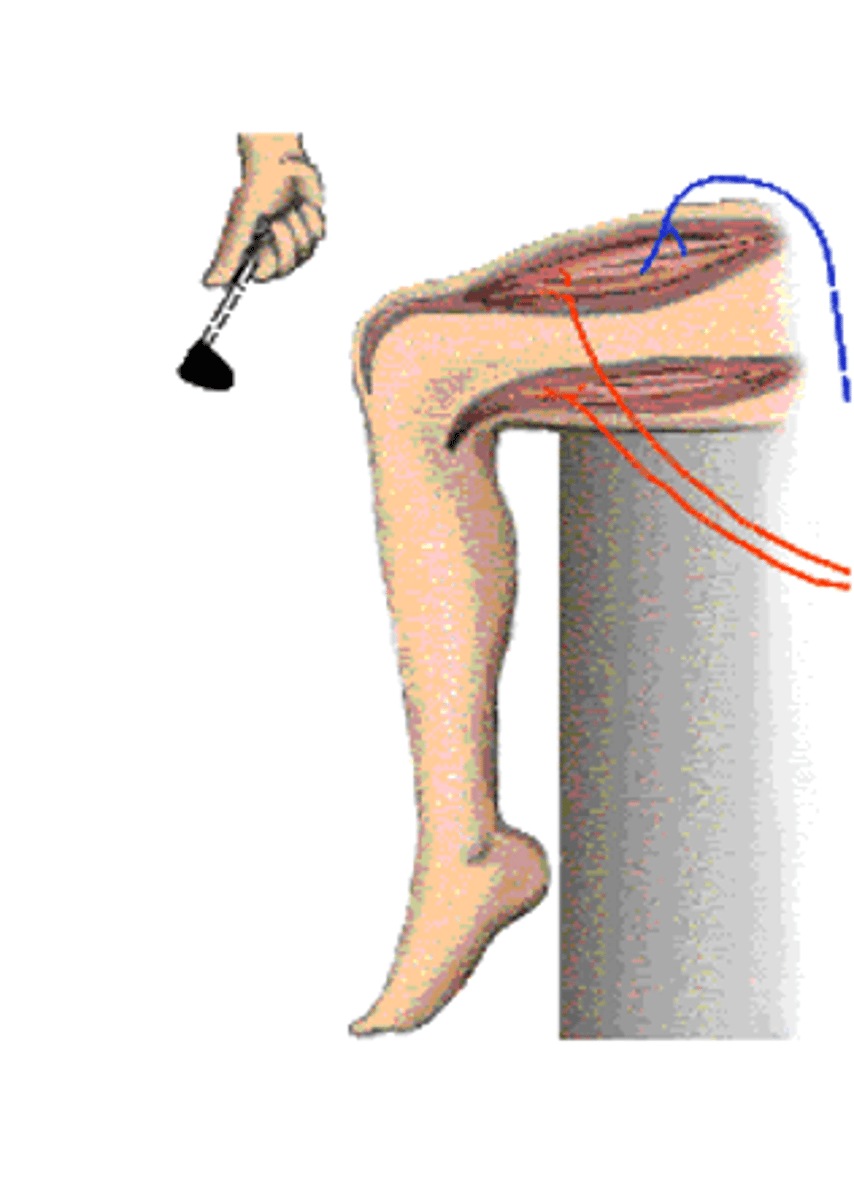
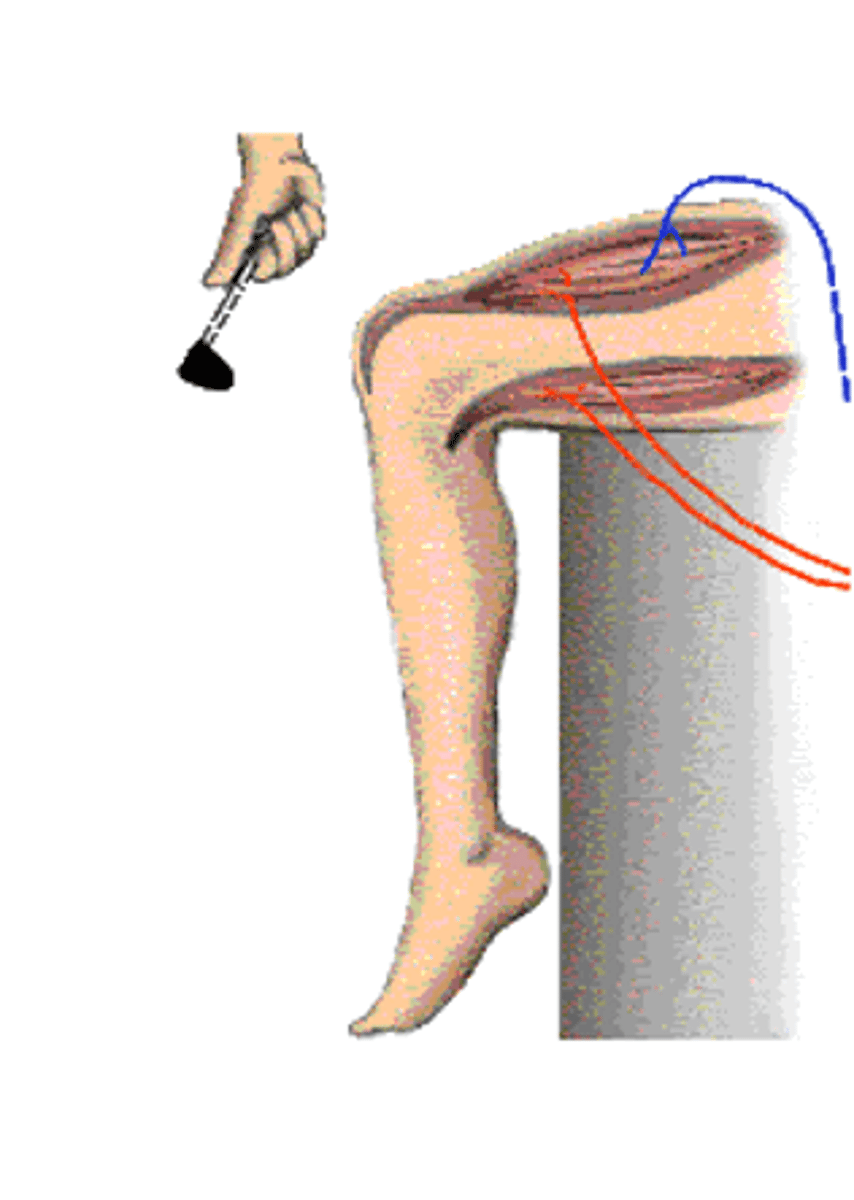
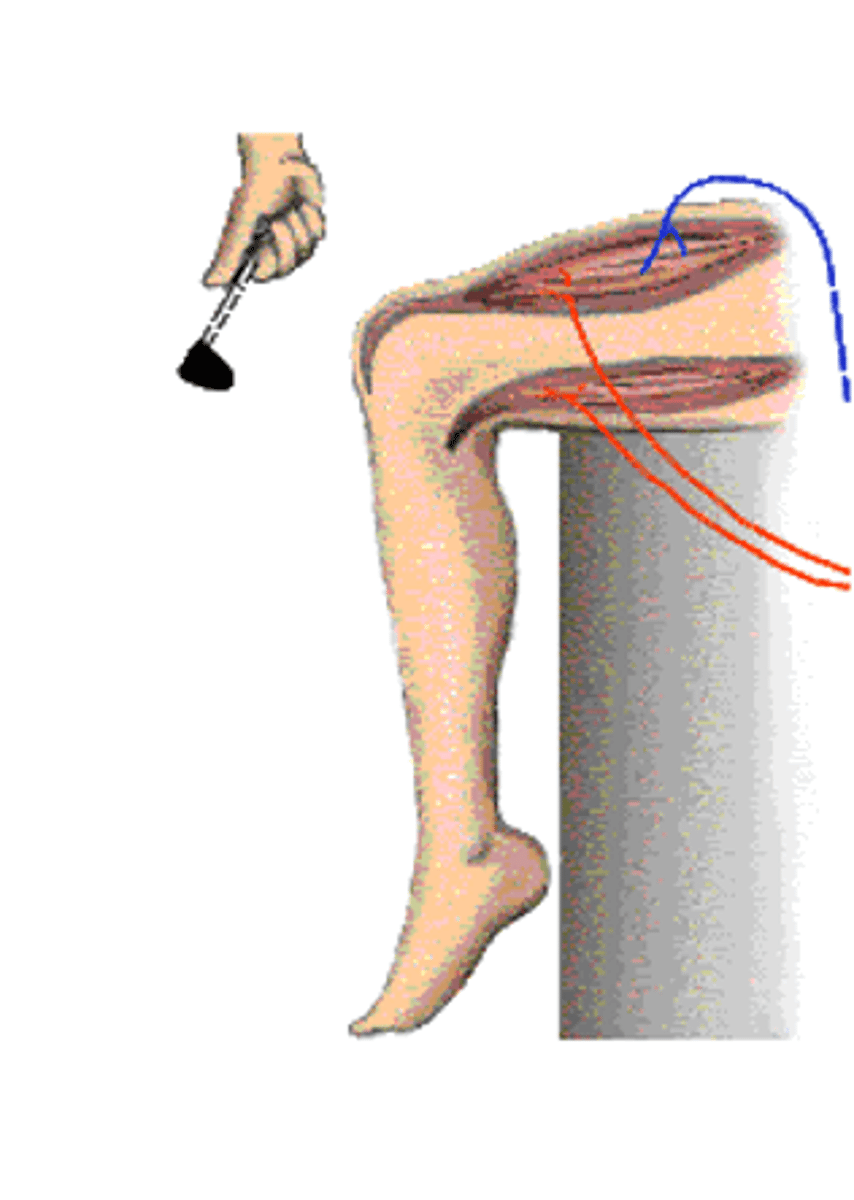
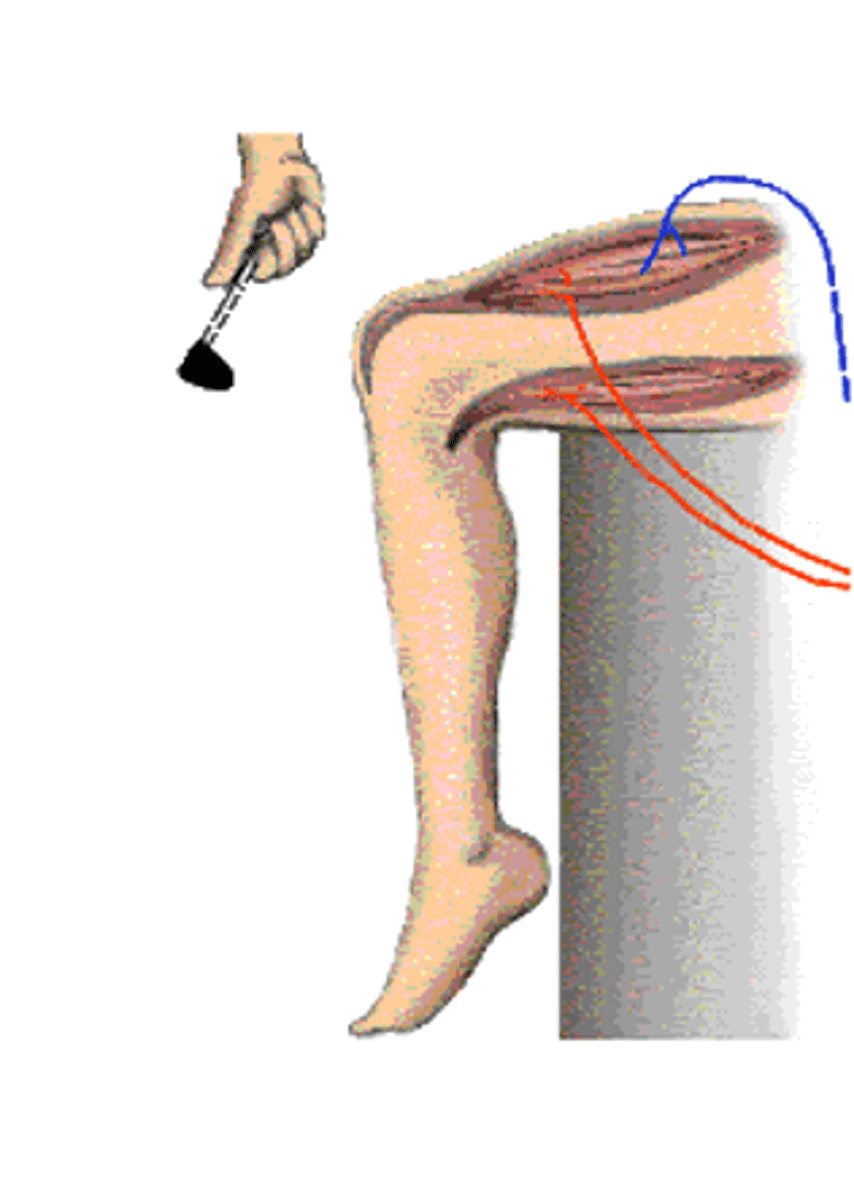
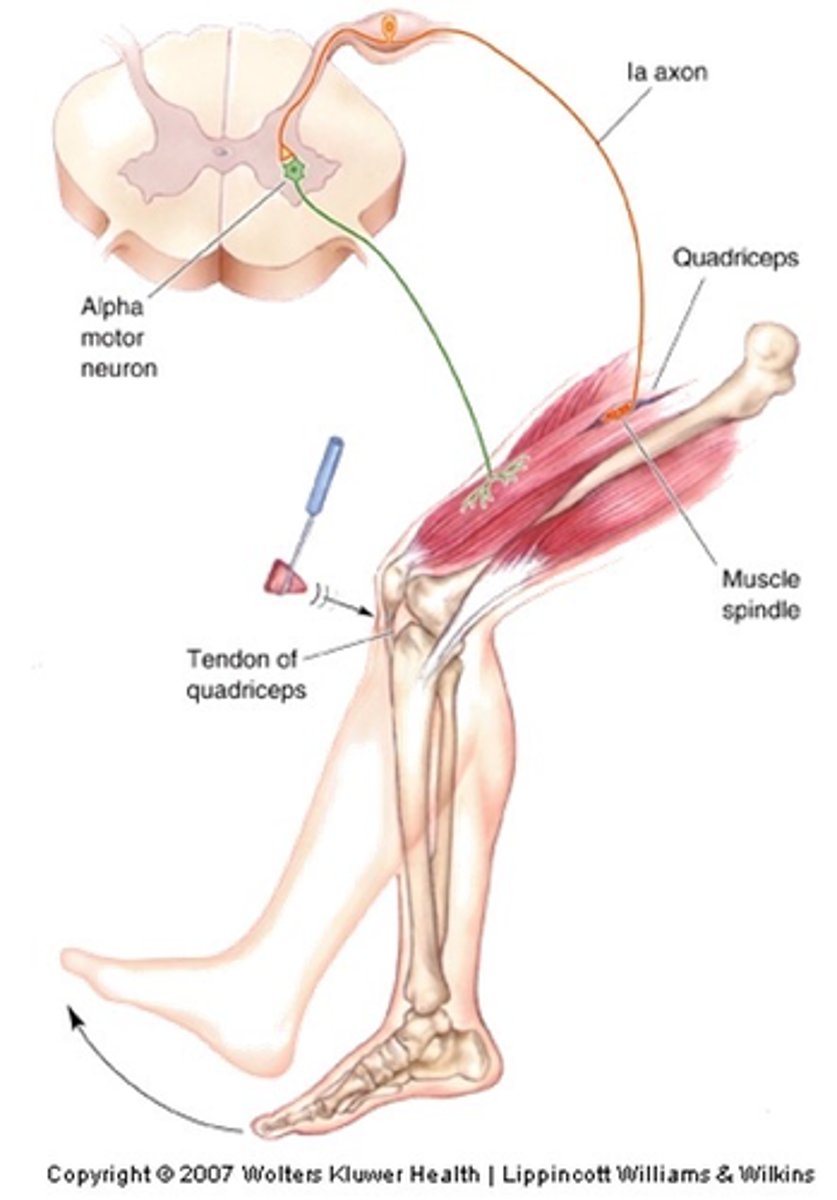
Patellar reflex
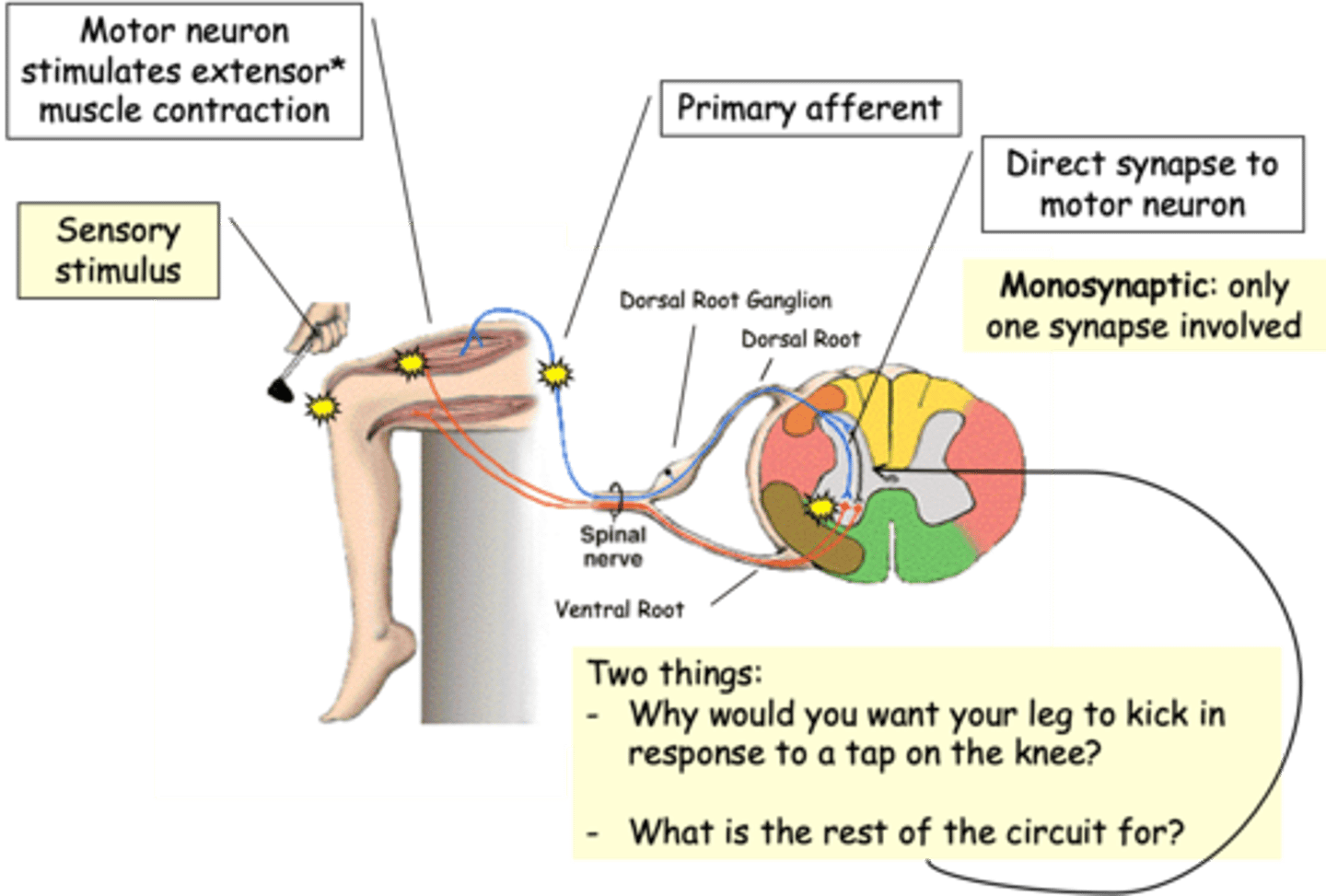
Pain in the knee
The knee jerk is not a response to what?
Thigh extensor muscle, tendon
The tap on the knee stretches the ______ __________ ________ and associated __________ and sets in motion a process to correct the stretching
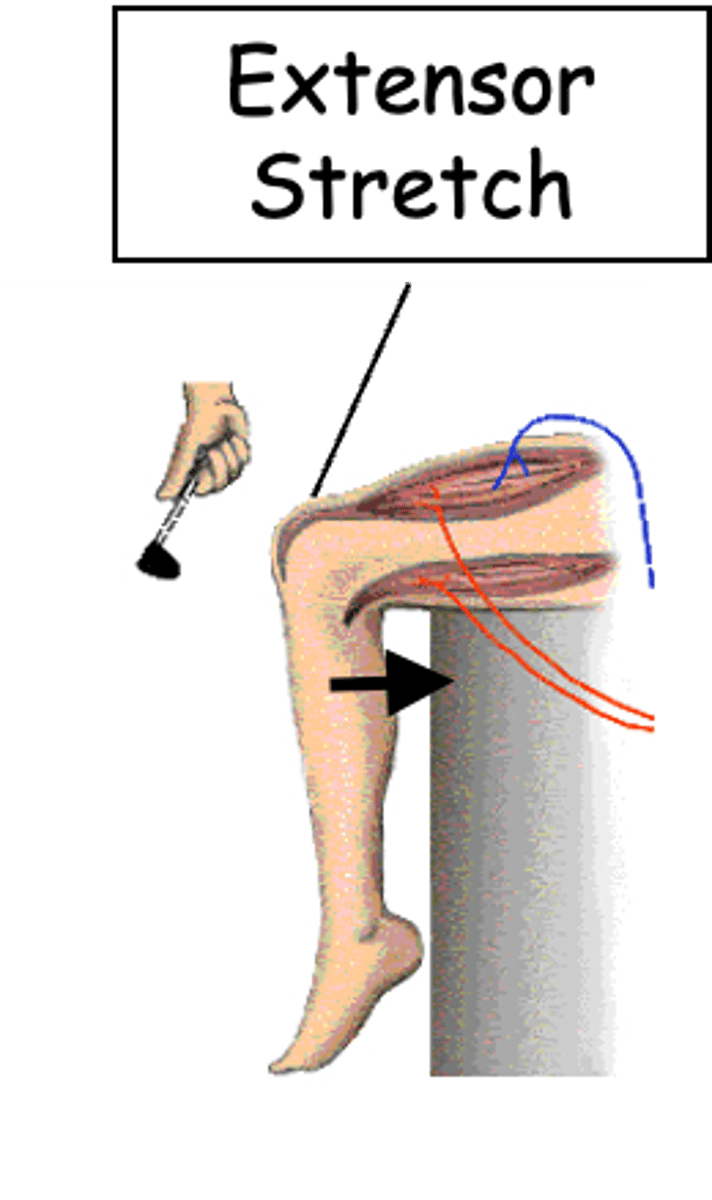
Body posture
What is the stretch (myotactic) reflex important in maintaining?
Proprioceptive
What system is the stretch (myotactic) reflex a part of?
Simple proprioceptive feedback pathway
The monosynaptic reflex, first described by Charles Sherrington is a classic example of a ...?
The stretch (myotactic) reflex is easier to understand if imagining a drink being poured
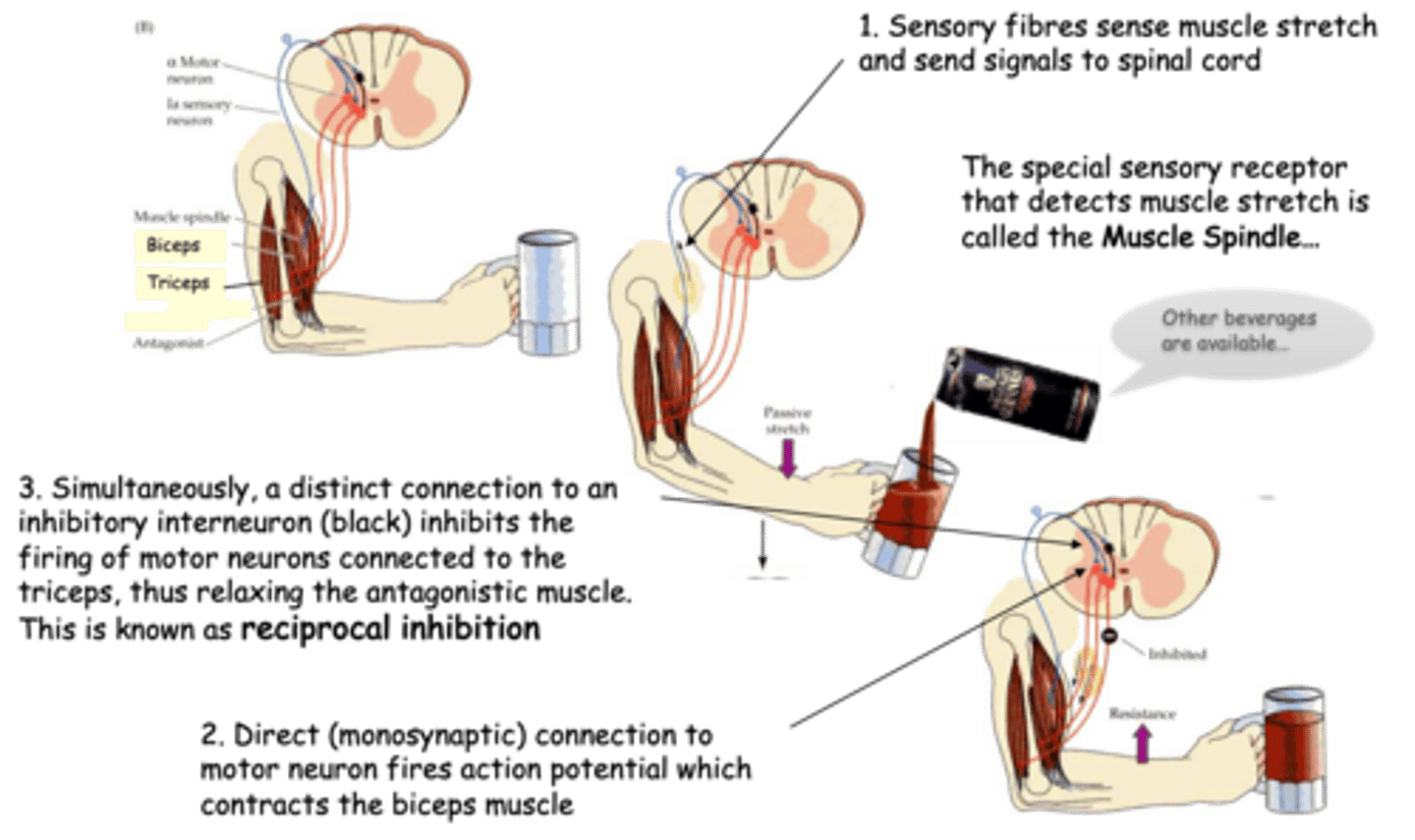
Proprioceptors, position, movement
Muscle spindles are among the body's _____________ - sense organs that monitor the _____________ and _______________ of body parts
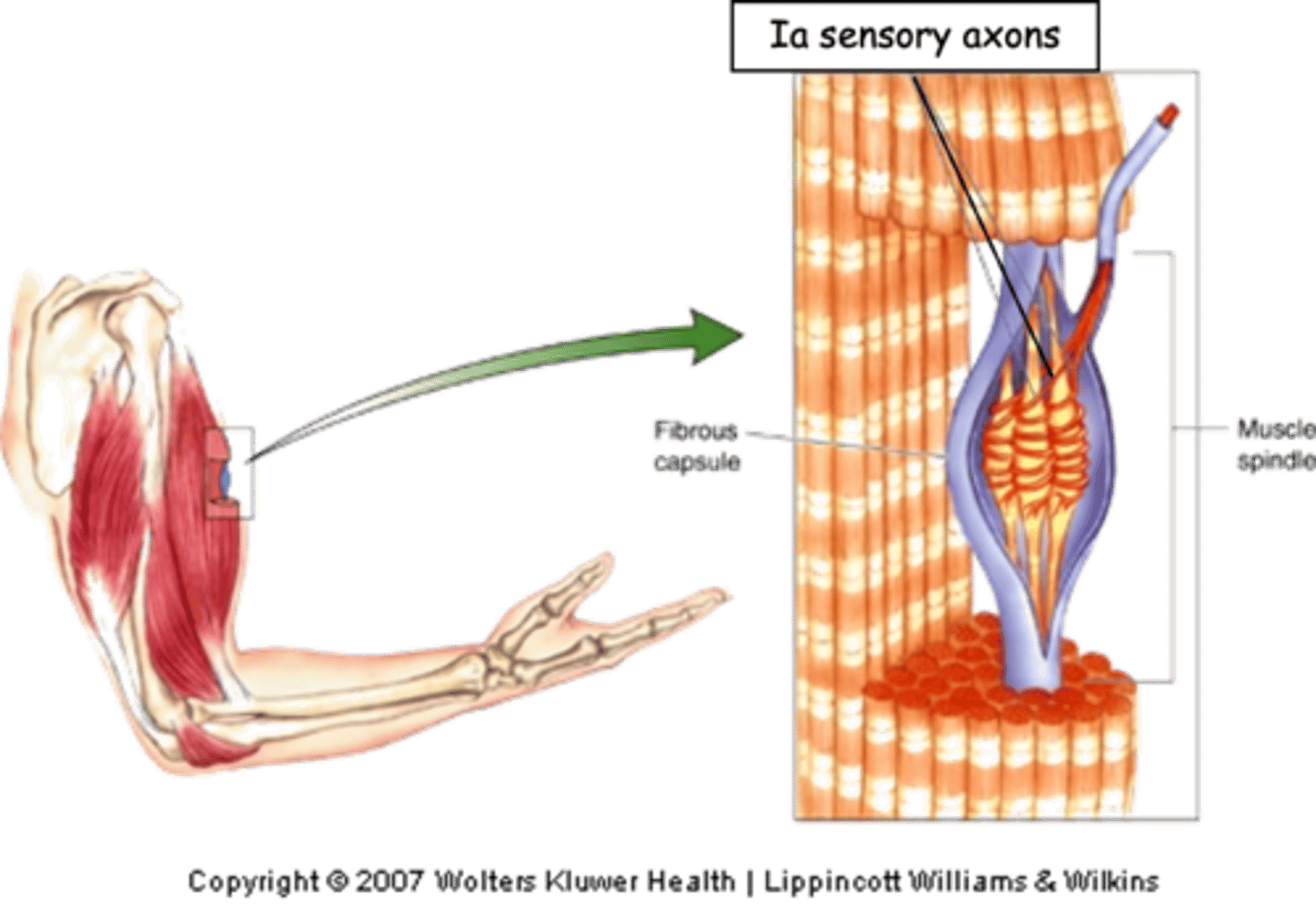
Striated, fine motor control
Muscle spindles are found in most __________ muscle and are particularly abundant in muscles involved in ______ ________ ____________ (e.g. hand)
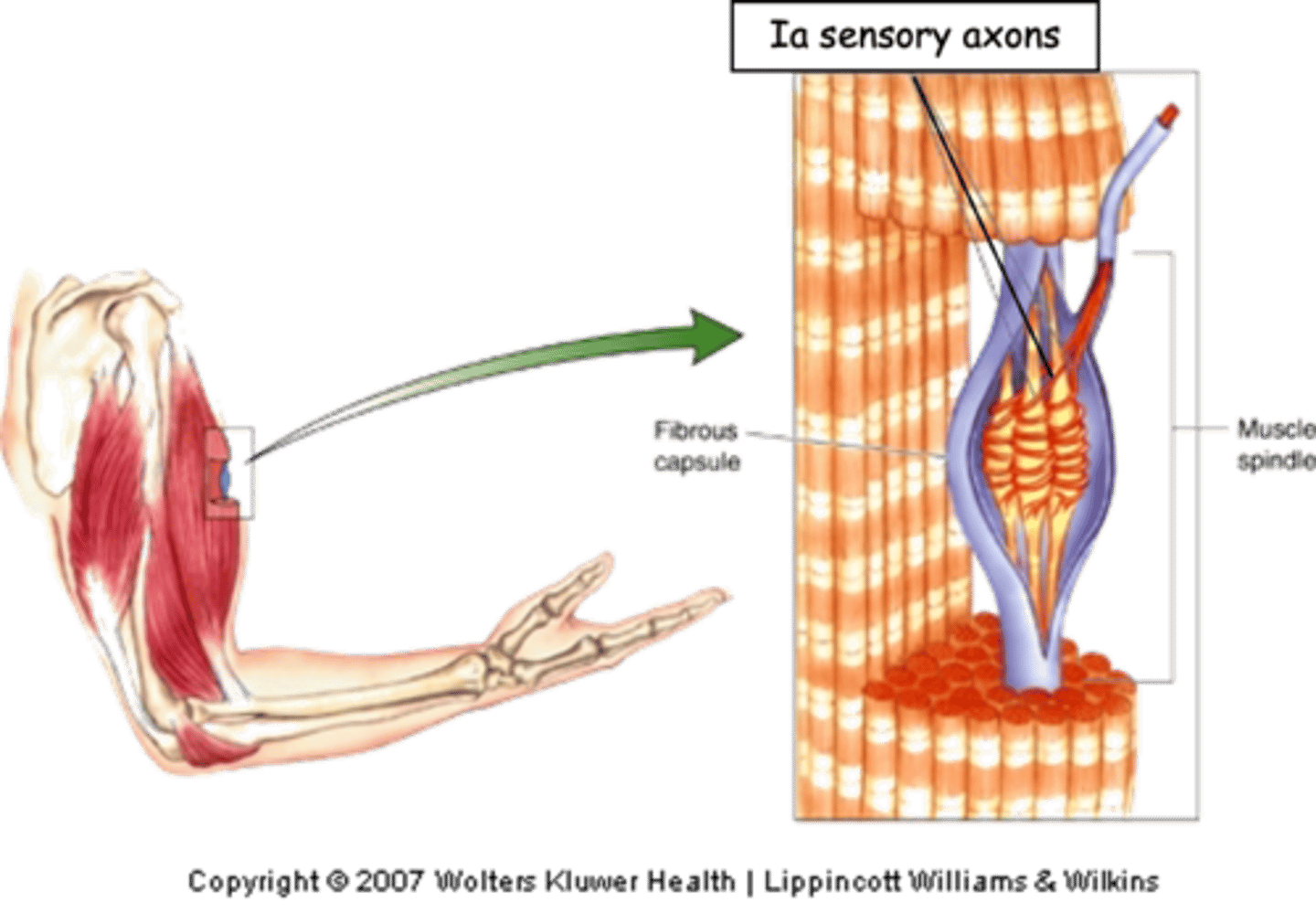
Ia sensory fibres
The muscle spindle are innervated by ...?
Provide feedback to the motor neurons innervating the surrounding muscle (properly called alpha motor neurons) on the amount of muscle stretch that is occurring (as we have seen in the 'knee-jerk' reflex)
What do Ia sensory fibres do?
Because of their conduction velocity
Why are alpha MNs given that name?
Gamma (γ) motor neurons
Muscle spindles are also innervated by axons from ________ (_) ________ _________
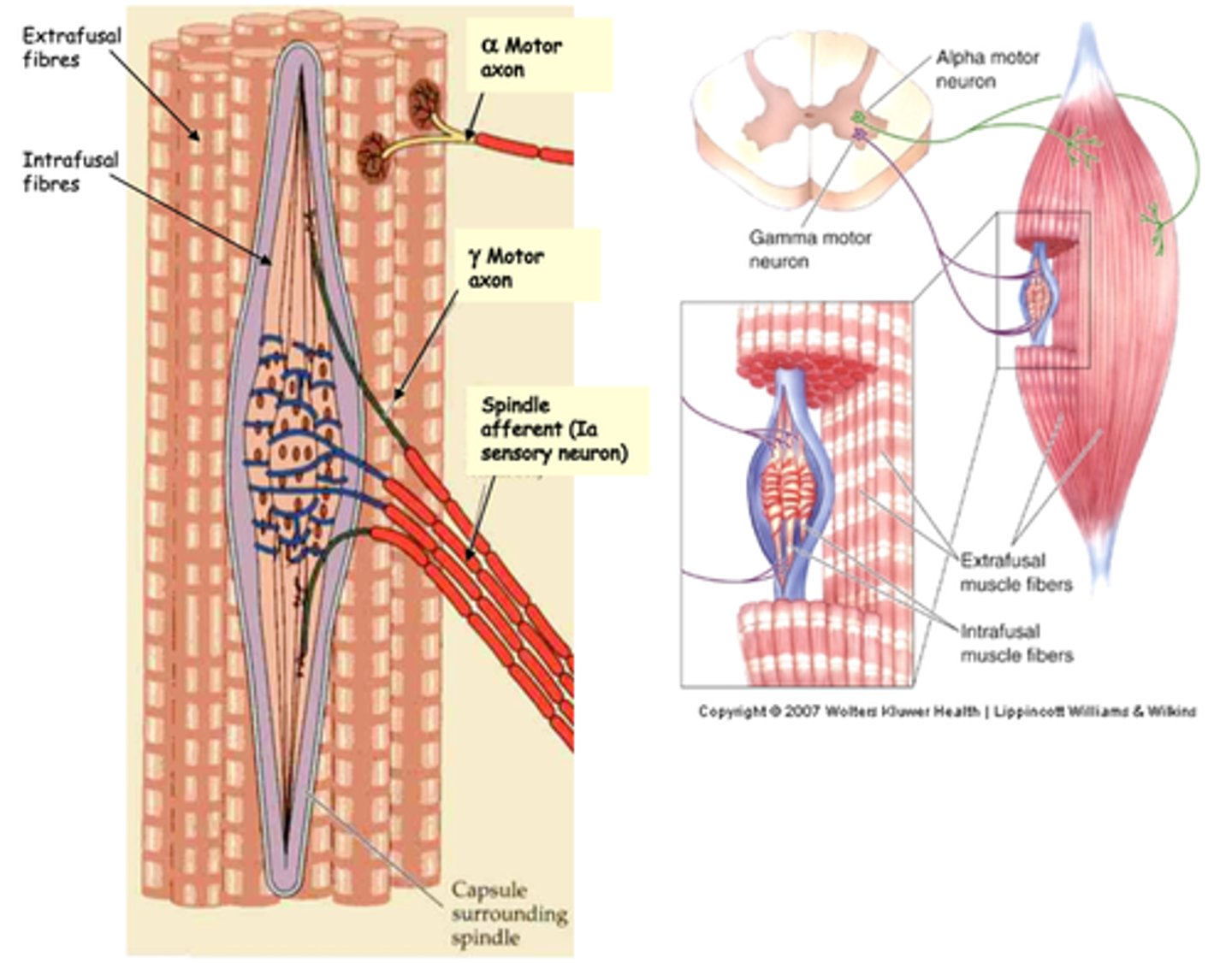
Stimulate the intrafusal (muscle) fibres to adjust the tension in the spindle as the surrounding muscle contract (so that the muscle spindle is never slack)
What do the gamma (γ) motor neurons do?
Co-ordinate any kind of movement unconsciously and was effectively bed bound, unable to get up
In 1972, a viral infection destroyed all of the nerves that provided Ian Waterman's sense of touch and all of the nerves attached to muscles and tendons that provide a sense of joint and limb position, what did he lose the ability to do?
His proprioception, the sense of the position of parts of the body relative to other neighbouring parts of the body
What did Ian Waterman lose?
How to move again by consciously controlling and visually monitoring every action
What did Ian Waterman achieve over 3 years of trail and error?
He would crumple to the floor, unable to budge until they come back on
If the lights were to go off unannounced, what would happen to Ian Waterman?
Kinaesthesia
Along with proprioception goes a sense of your body moving in space, what is this called?
Golgi Tendon Organ
What does GTO stand for?
Proprioceptor
The GTO is another kind of _______________
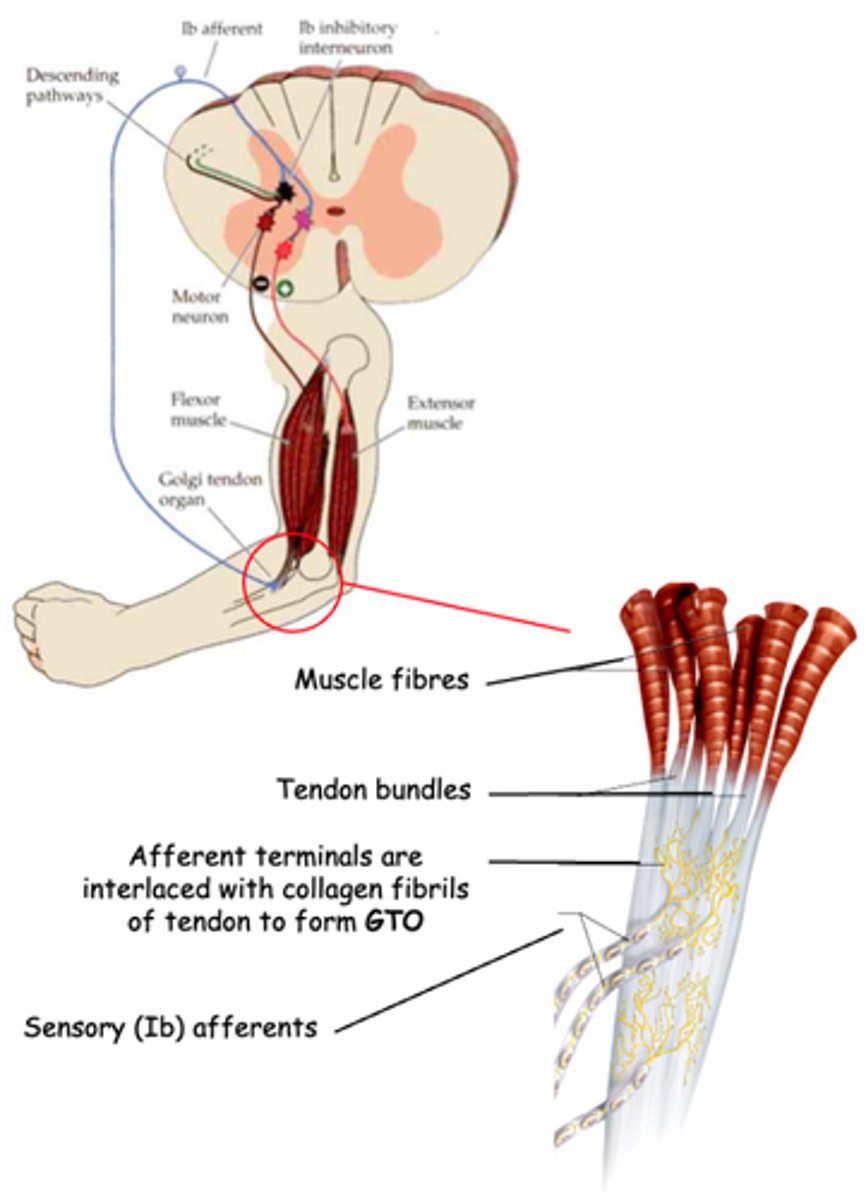
Muscle tension due to muscle contraction, not muscle stretch (which is detected by muscle spindles)
What do GTOs detect?
Activation of inhibitory interneurons which, in turn, inhibit α motor neurons that innervate the same muscle
What does activation of GTO sensory (Ib) afferents lead to?
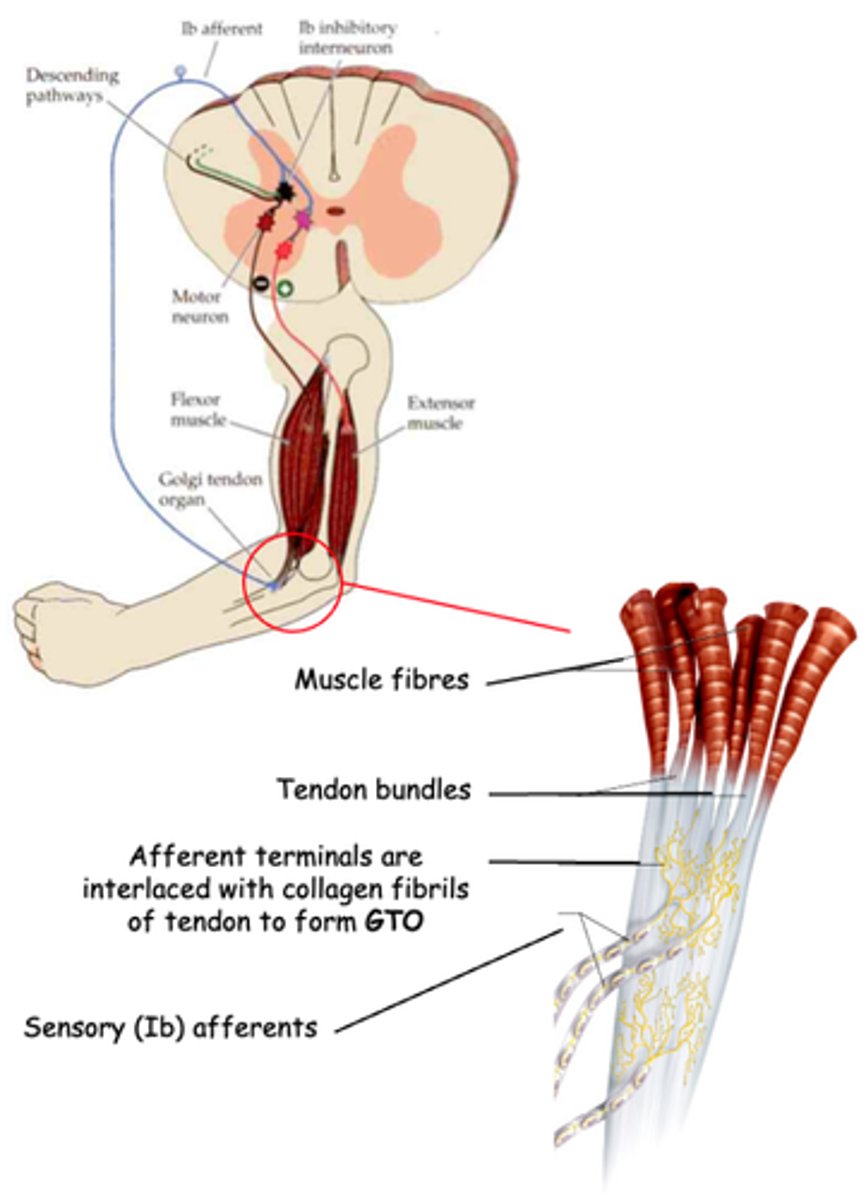
Negative, tension, damage
The Golgi Tendon Reflex is a __________ feedback circuit that regulates muscle _________ and protects the muscle (and tendon) from __________ when large forces are generated
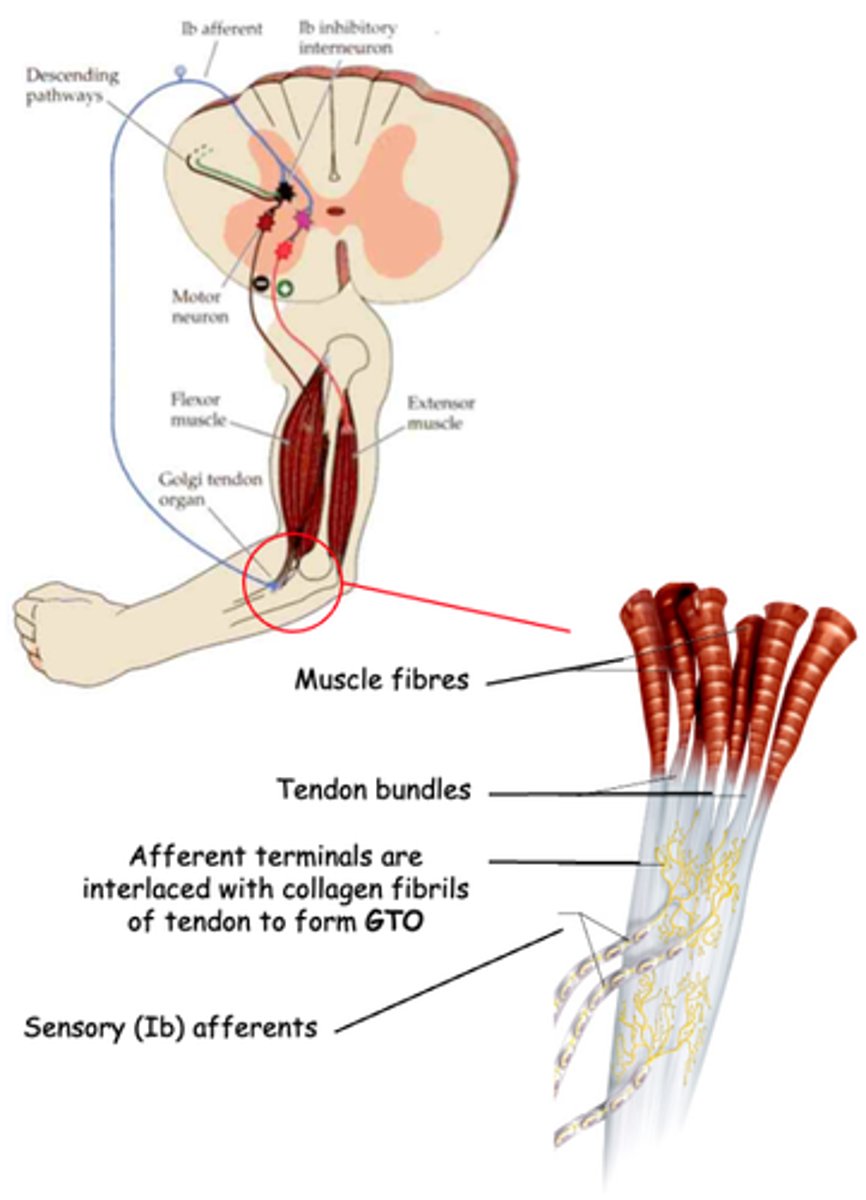
Contraction, prevents, too much
Like the muscle spindle, the GTO also regulates muscle _________________ to maintain muscle length, but in this case it ____________ the muscle contracting ______ _________
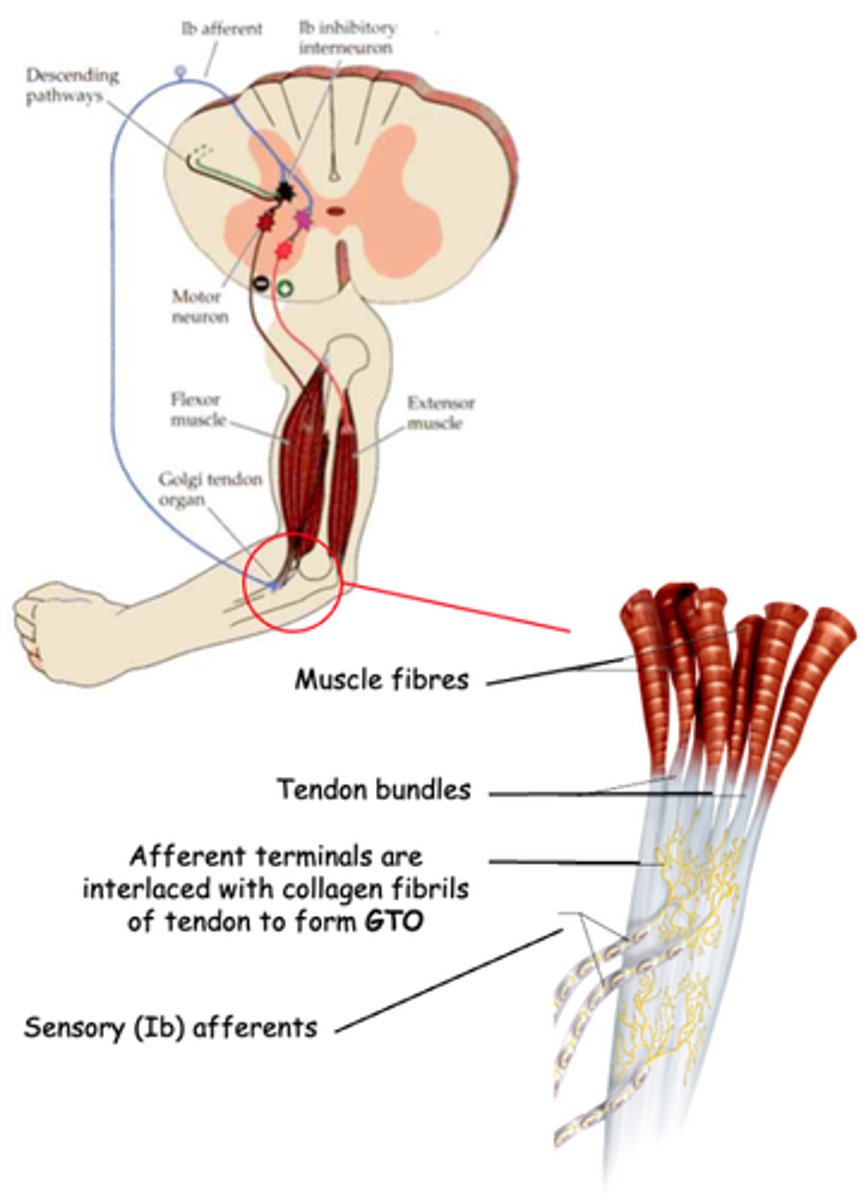
Higher centres
Both the Golgi tendon reflex and stretch reflex are under control of ...?
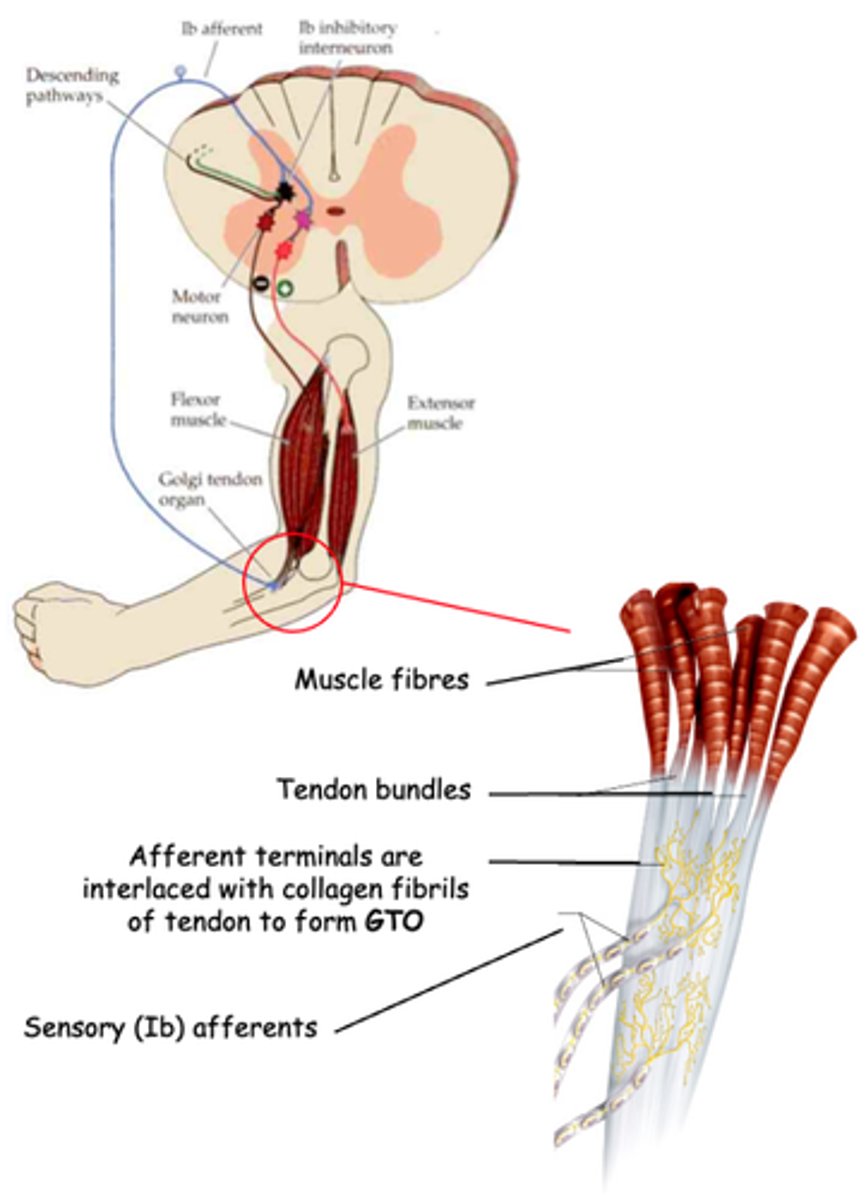
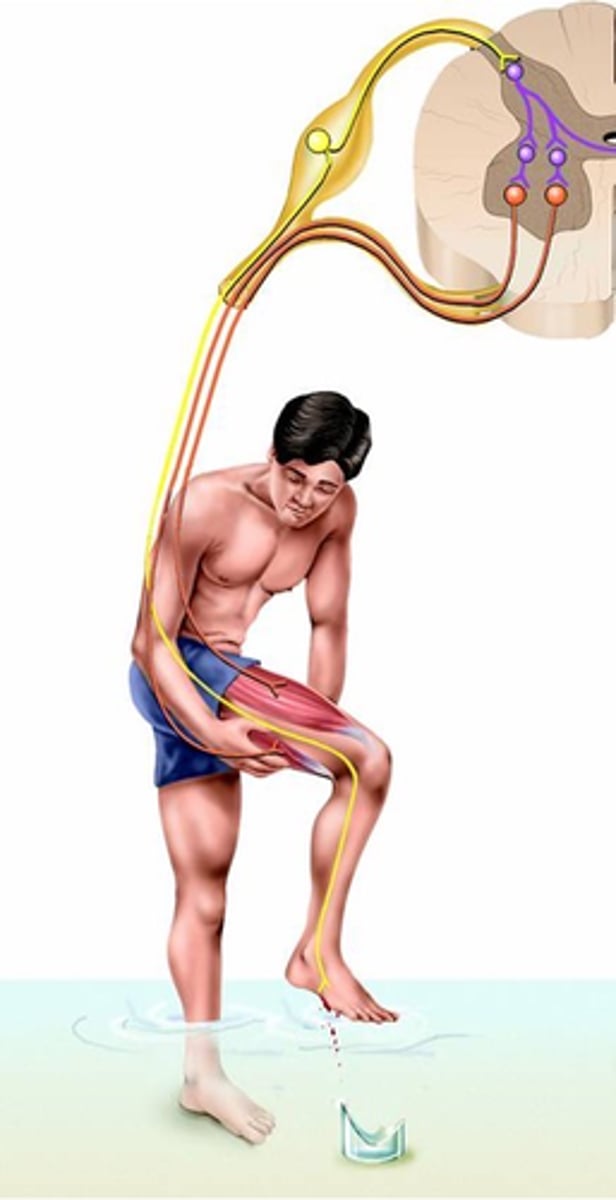
A quick contraction of flexor muscles to withdraw a limb from a injurious stimulus (e.g. heat or cut)
What is a flexor reflex?
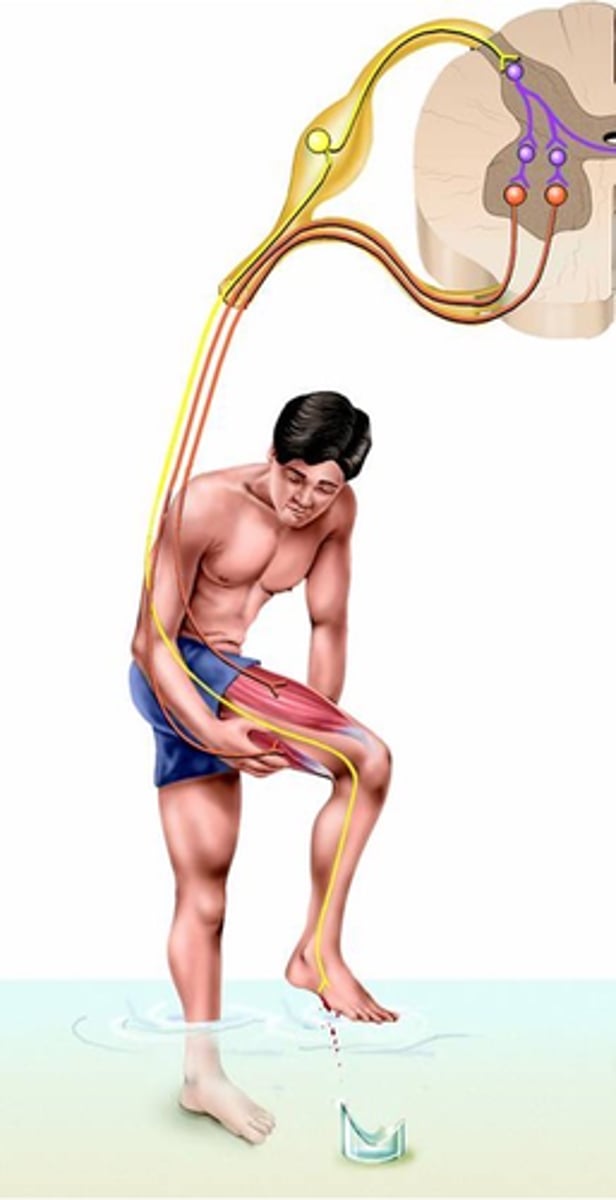
Activation of nociceptive sensory receptors (noci = hurt, e.g. noxious) or nociceptors
Where does the flexor reflex result from?
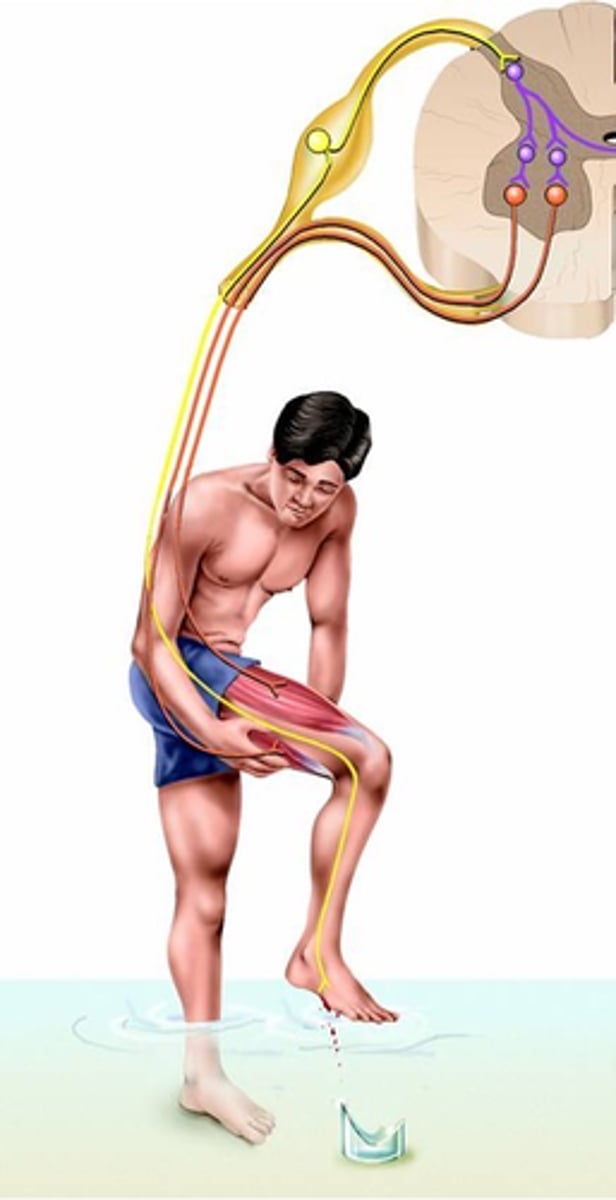
Polysynaptic, sustains
Despite speed of response, the flexor reflex is a _______________ reflex:
-> Activation of multiple excitatory interneurons __________ the response:
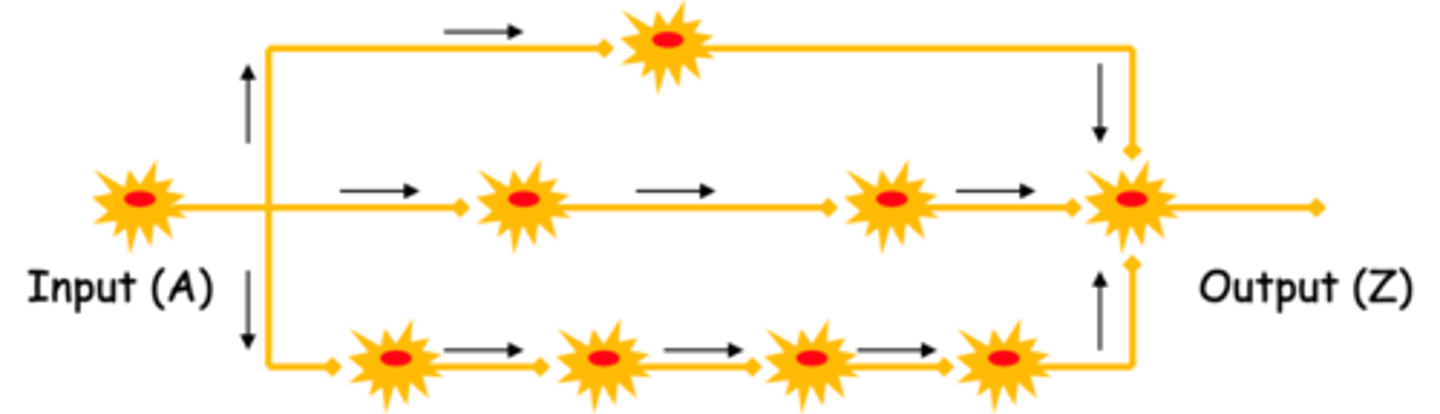
- 'Parallel after-discharge circuit'
Different times, sustained
Assume time taken to cross each synapse is the same, therefore, stimulus initiated by A will take ______________ _______ to reach output neuron Z and the result is that initial signal is __________ over extended period
Relax extensor muscles
As in the stretch reflex, inhibitory interneurons are also activated to ________ ___________ __________ (reciprocal inhibition again)
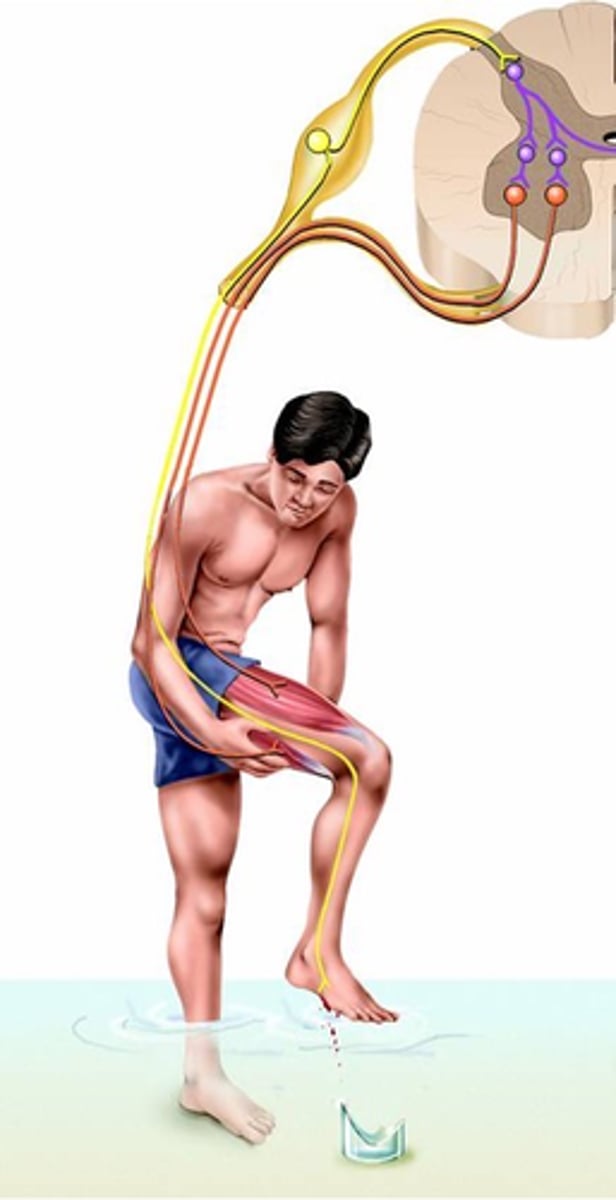
A contralateral element
Because rapid withdrawal of limb (esp. leg) may lead to imbalance, what do flexor reflexes often include?
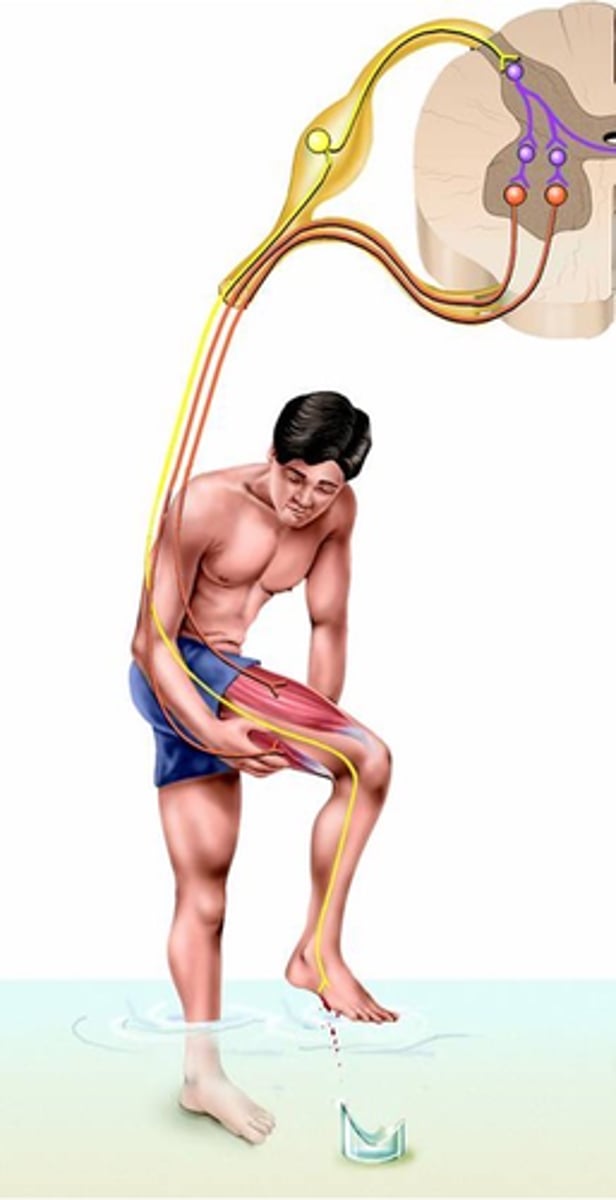
Postural support during limb withdrawal
What does this crossed extensor reflex provide?
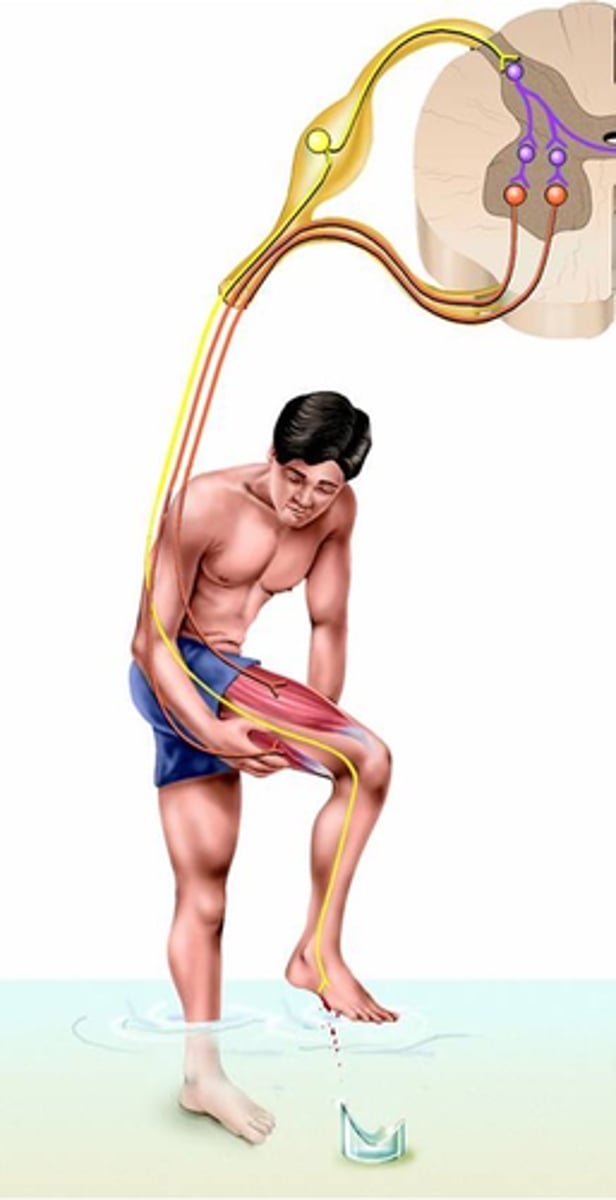
Crossed extensor reflex
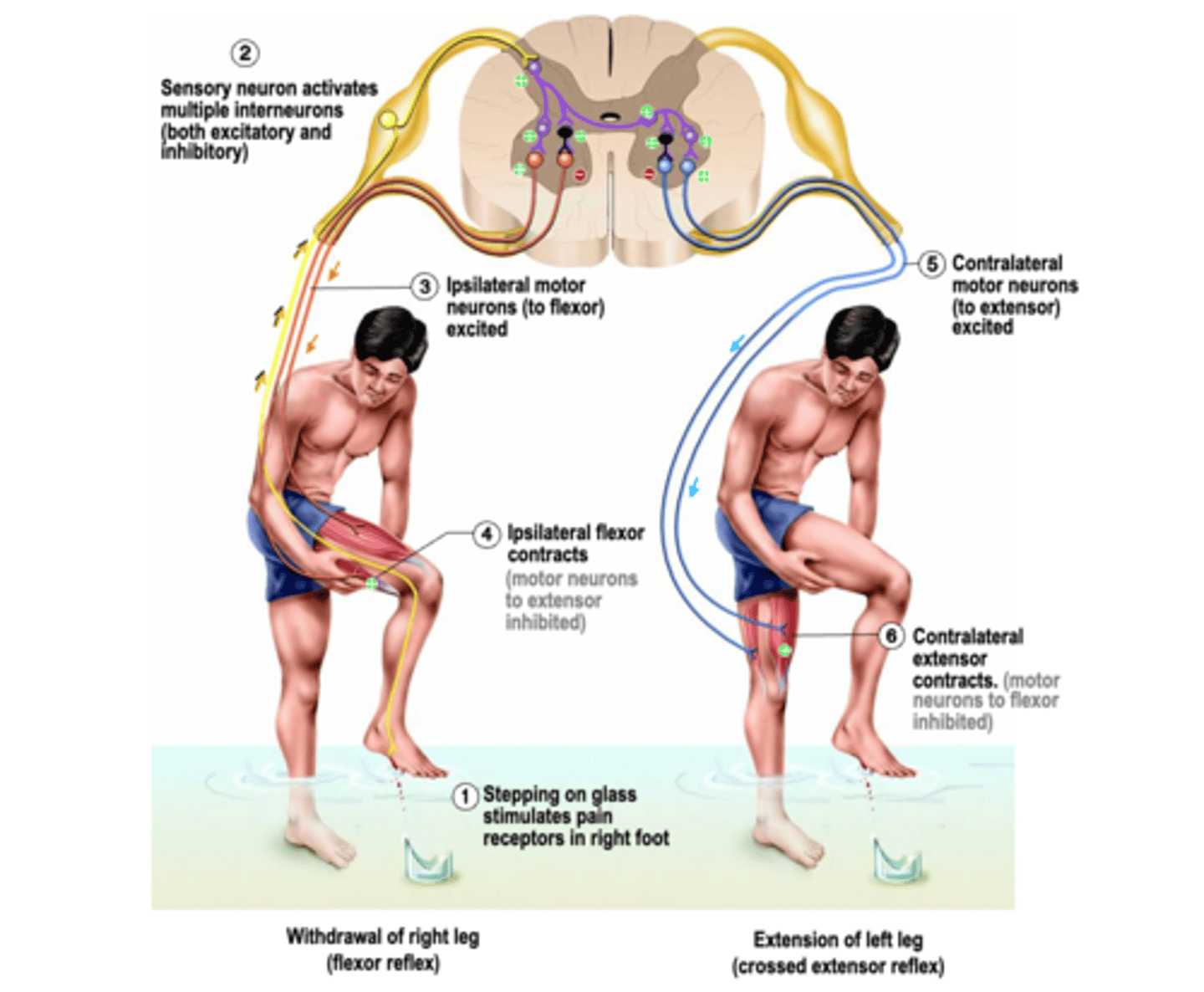
Active, inhibited
In individual limbs, extensors and flexors are alternately _________ or ___________ as animal walks
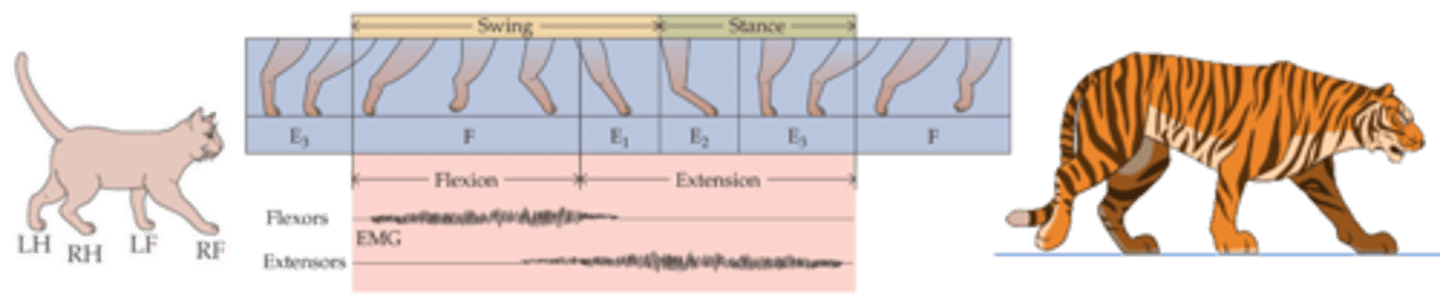
Between, alternate
Activity of these muscles in different limbs is also co-ordinated ____________ the limbs so that legs ___________
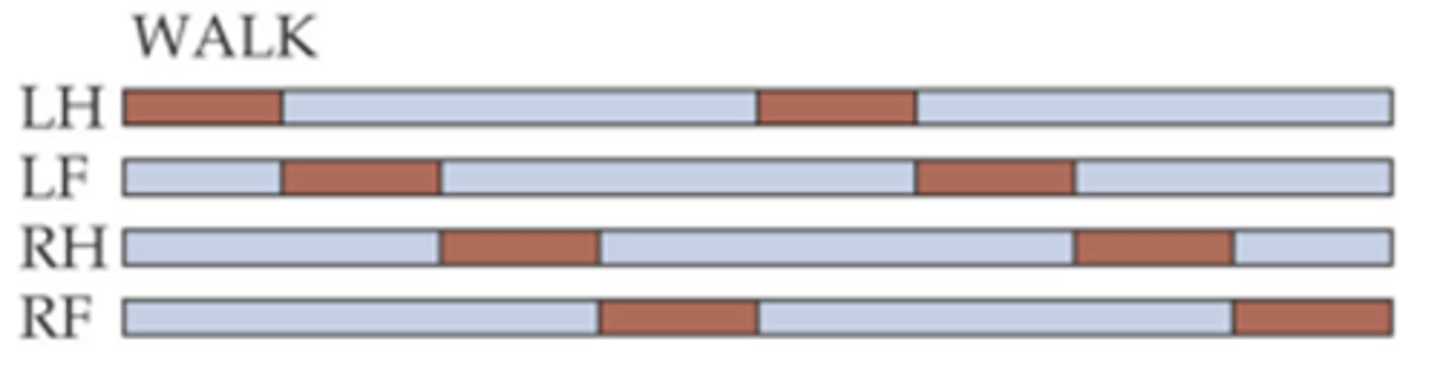
The basic alternation of activity and the co-ordination between legs
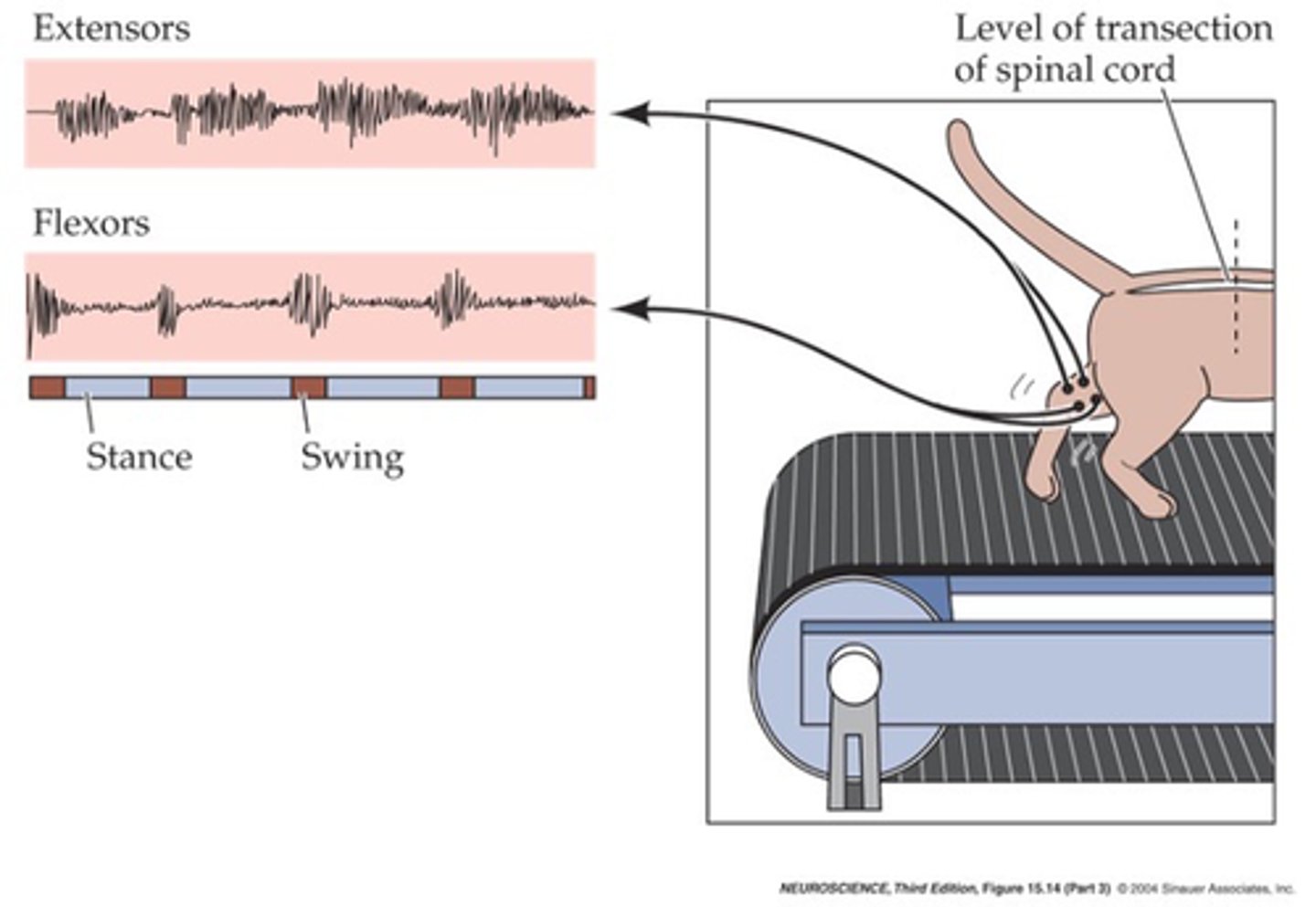
What continues even if the spinal cord connection to the brain is severed?
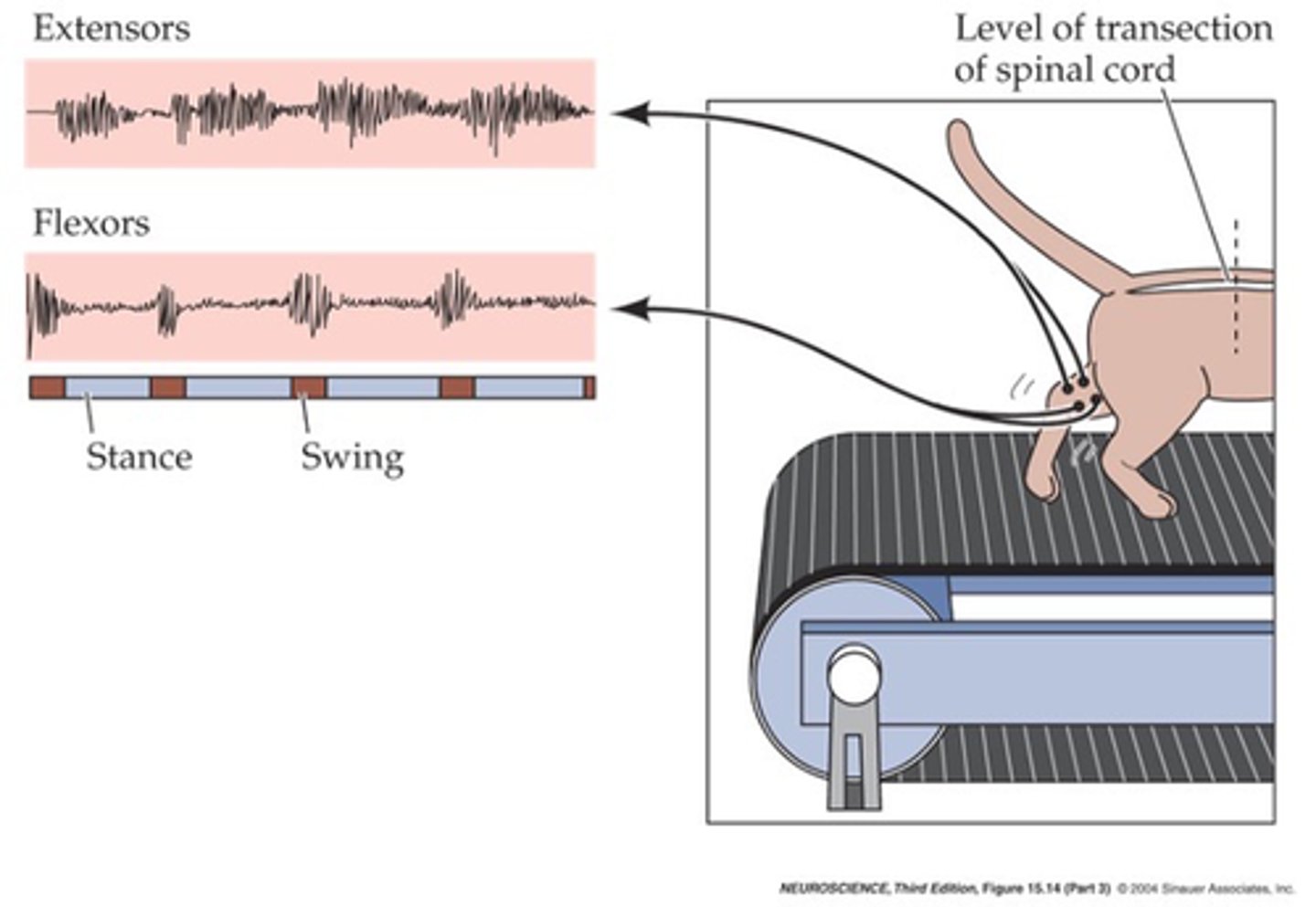
The presence of local circuits that can generate the pattern of alternating flexion and extension - these are known as central pattern generators
What does the alternation of activity and co-ordination between legs even if spinal cord connection to the brain is severed imply?
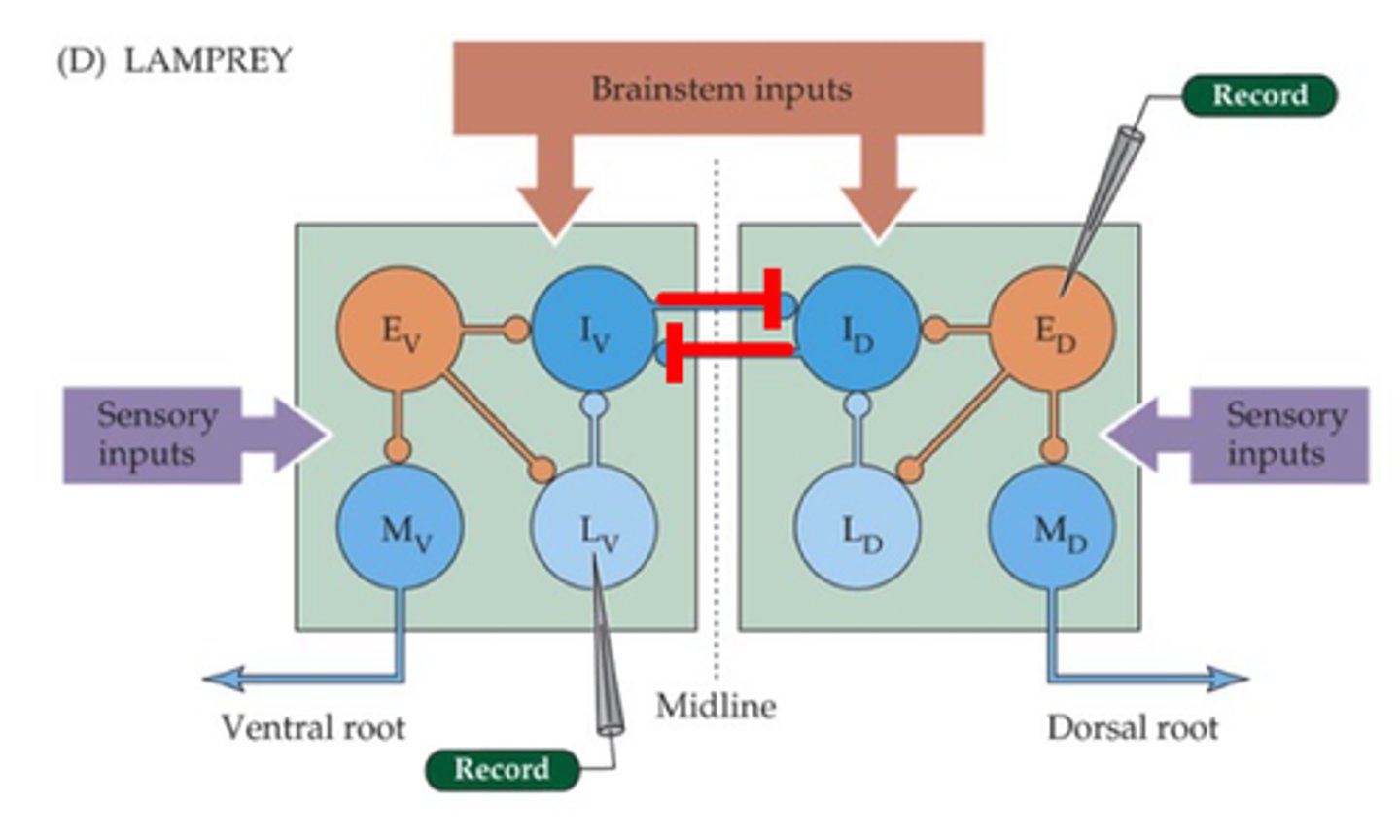
Lampreys
The cellular basis of pattern generators has been worked out in simple organisms, give an example of one
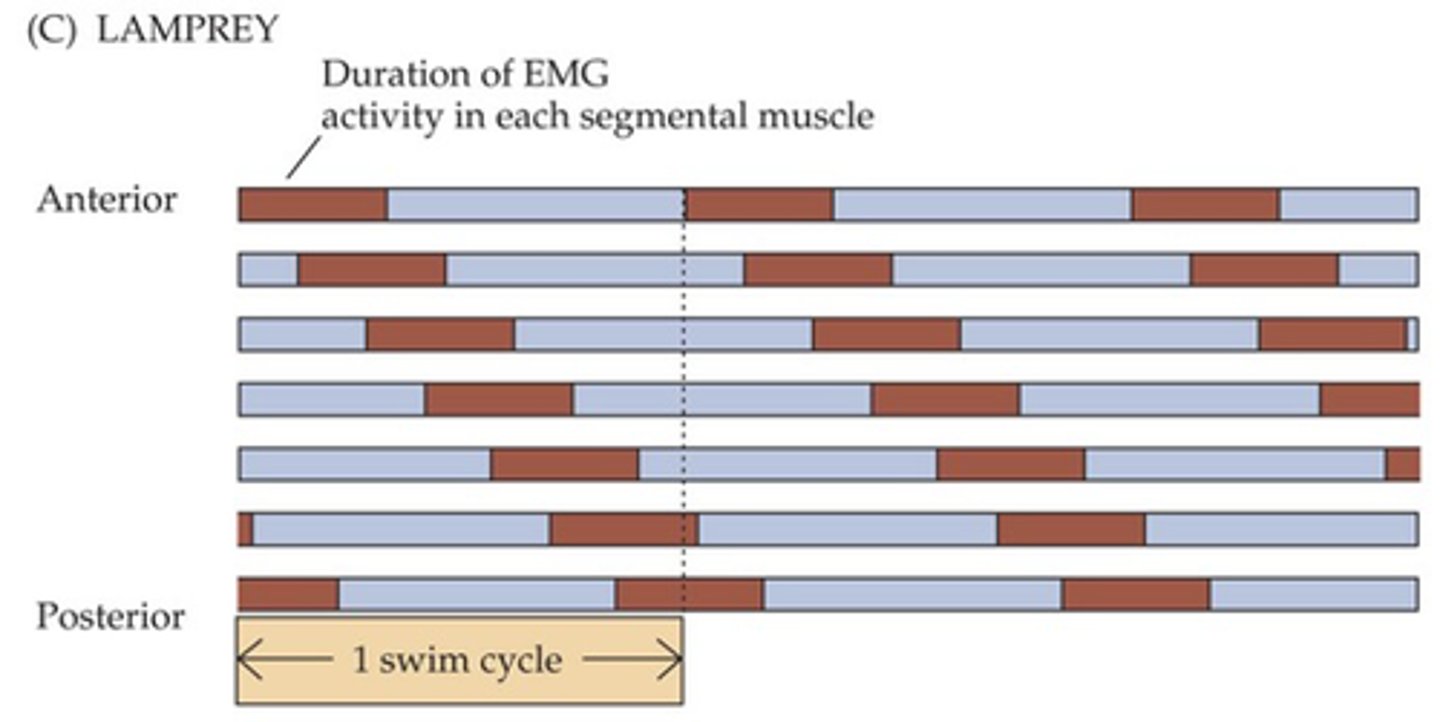
Rhythmic firing
Different neurons exhibit distinct patterns of __________ __________
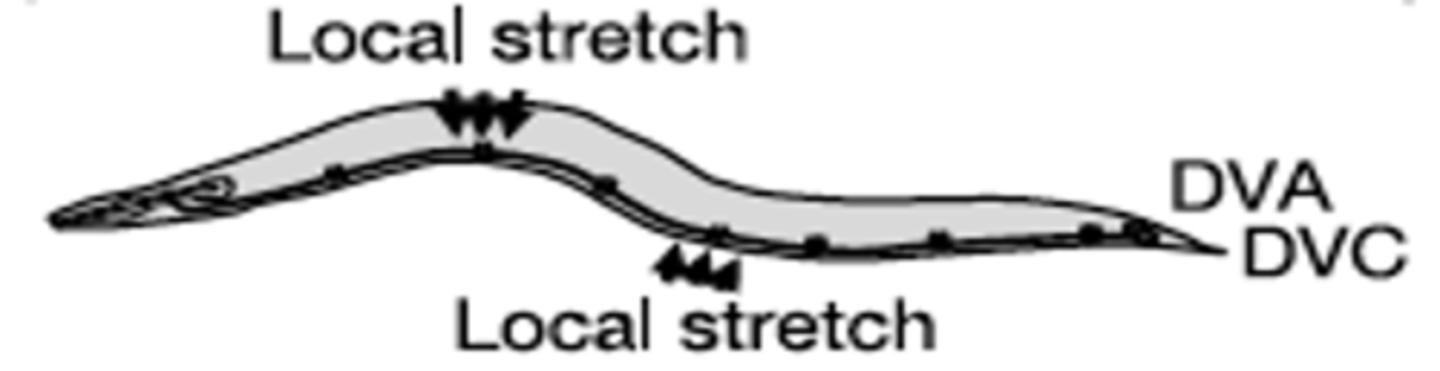
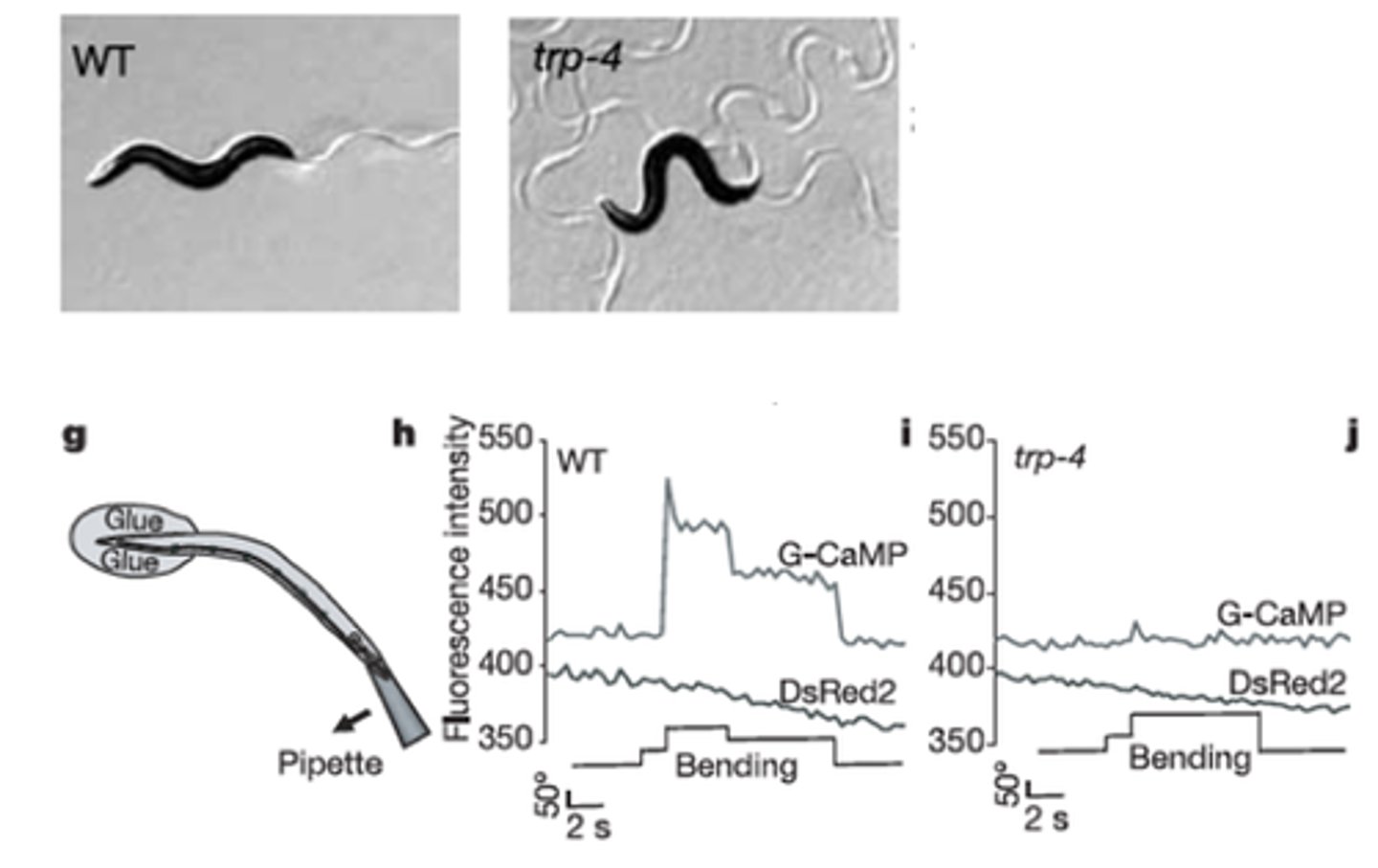
Nematode worm - C. elegans
What was used to dissect proprioception at the molecular level?
A mutant with 'loopy' swimming
What did mutagenesis identify?
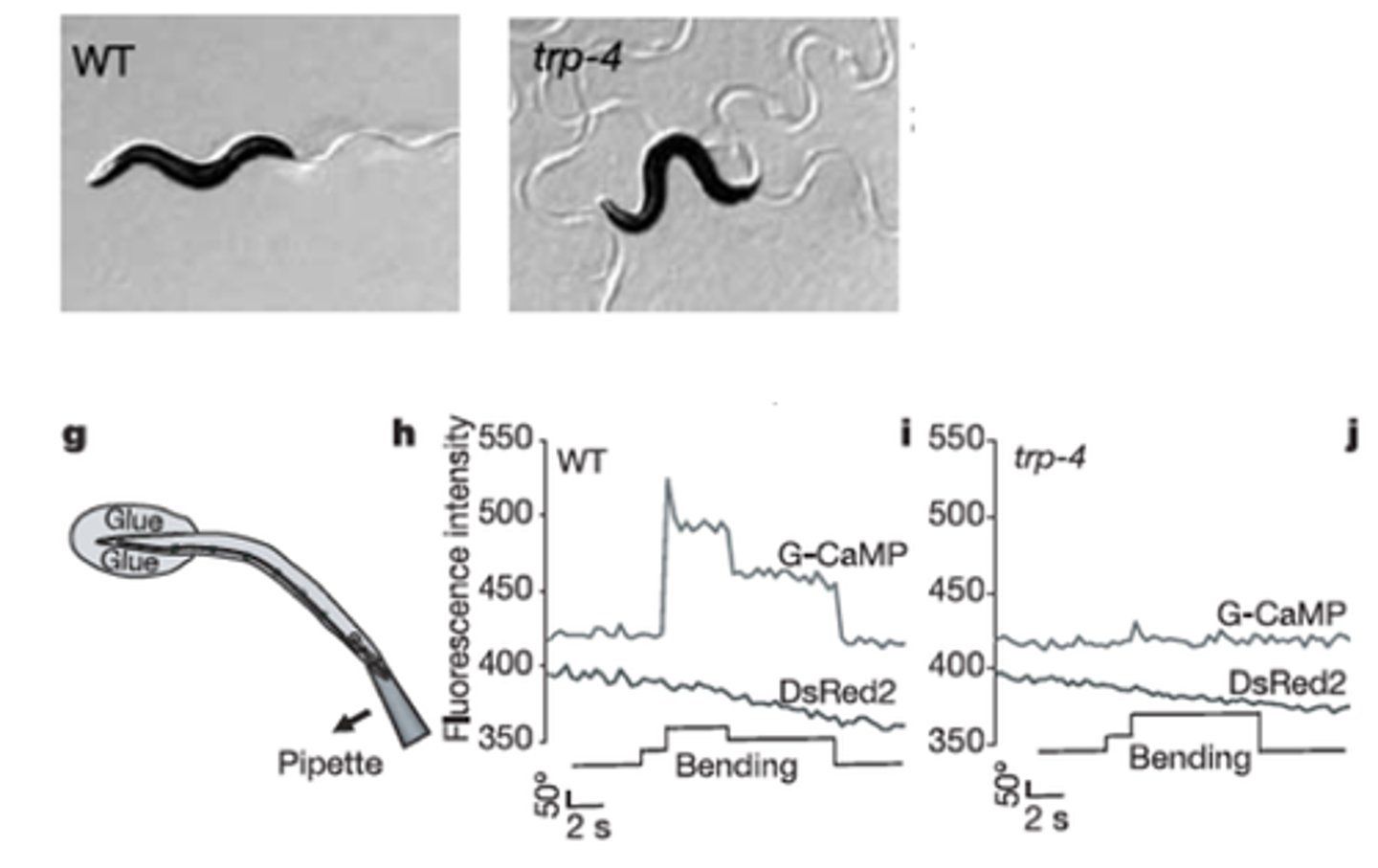
Due to loss of TRP-4 'stretch' receptor in DVA neuron (Homolog of TRPN cation channel (mechanosensitive) in humans)
Why did this mutant have 'loopy' swimming?
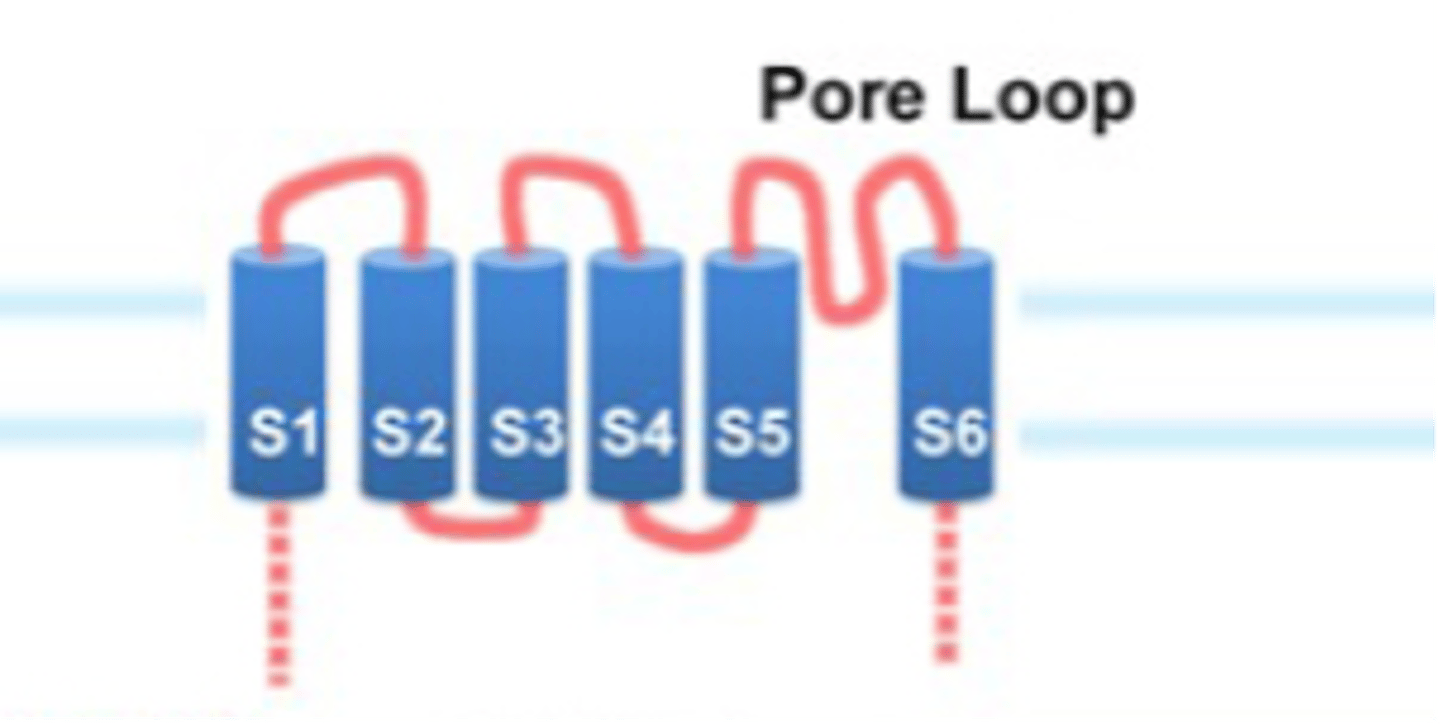
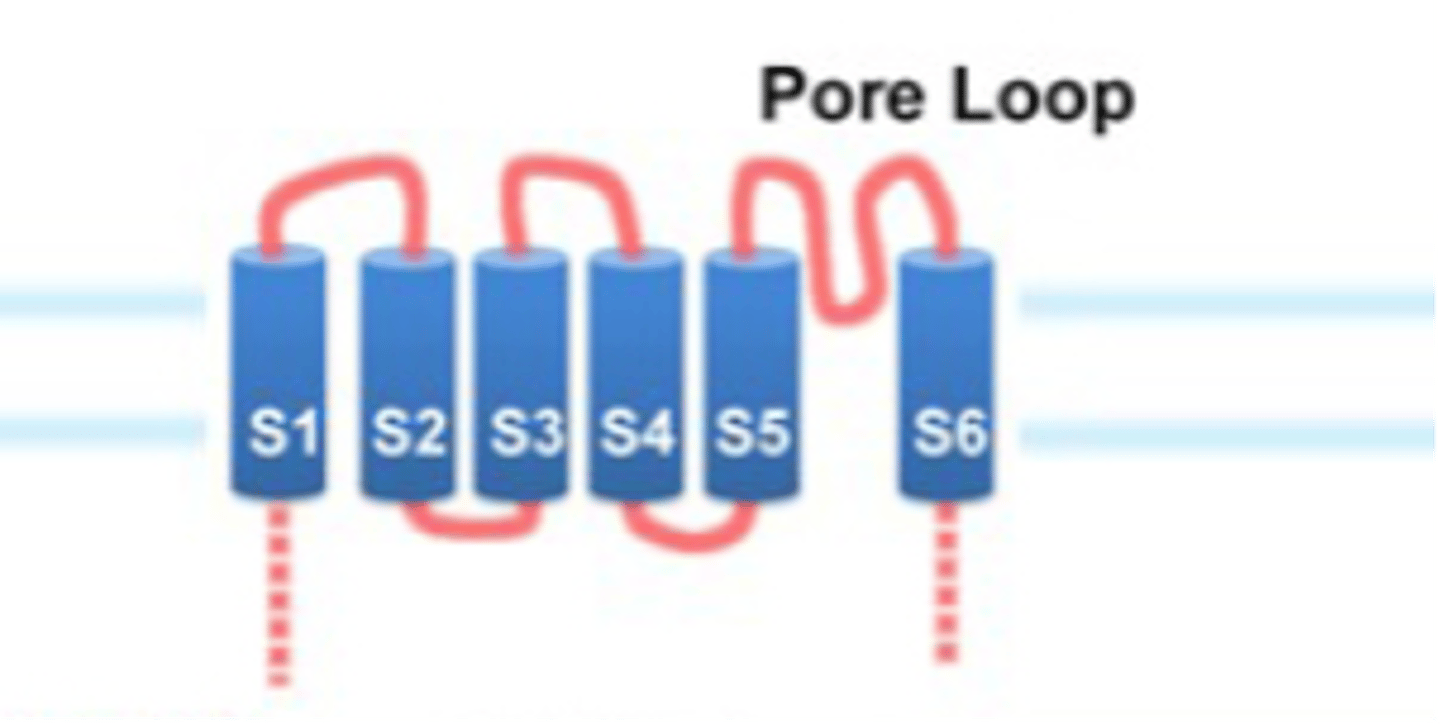
Transient Receptor Potential proteins
What does TRP stand for?
Body bending directly using the TRP-4 mechanosensor
What do DVA neurons detect?
Motor neurons
DVA appears to inhibit ________ ___________, allowing alternating muscle contraction
Simple, local, sensory, motor
Reflexes are ________, _______ circuits in the spinal cord usually involving _________ input and ________ output
Monosynaptic, polysynaptic
Reflexes may involve a single synapse between sensory and motor neuron (i.e. ______________ e.g. stretch reflex) or may involve interneurons (i.e. ______________; e.g. flexor reflex)
Posture, proprioceptors, somatic sensory system
Reflexes are important in maintaining body ___________, allowing the brain to monitor the position and movement of body parts - sensory receptors involved in this are called ___________________ and are an essential component of the ___________ ___________ __________
Pain, nociceptors
Reflexes are also important in responses to noxious (harmful stimuli) and help the organism avoid ______ - such reflexes involve ________________ (e.g. flexor withdrawal)
Circuits, locomotion
Reflex ________ are also likely to be essential components of simple (and repetitive) behaviours such as ____________
Influence, spinal motor output
Higher motor centres in the brain exert considerable _____________ on ________ _________ _________