ECONOMICS- EXCHANGE RATE
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Foreign exchange market- why was it established?
established to allow trade between countries with different currencies
Define exchange rate
price of one countries currency in terms of another currency eg. 1USD= 1.45 AUD

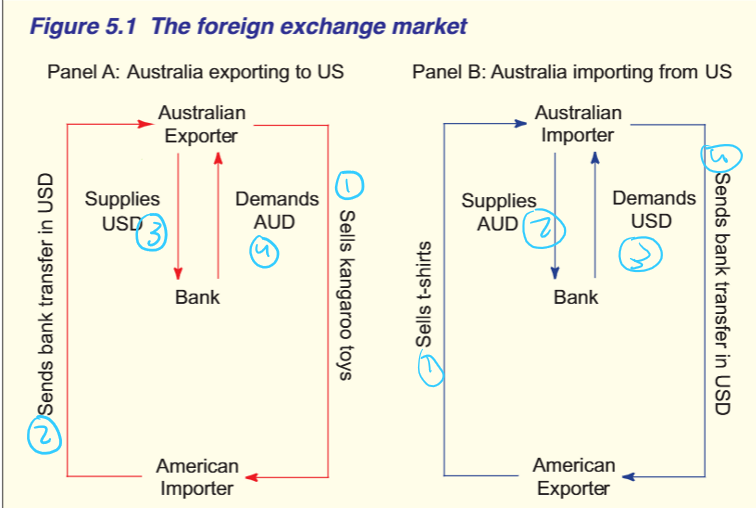
Steps to foreign exchange market- explain
Panel A- Aus exports to US
Aus Exporter sells kangaroo toy to american importer
American importer sends bank transfer in USD to australian exporter
Aus exporter supplies USD to Bank
Aus exporter demands AUD back
Panel B- Aus imports from US
US exporter sells t shirts
Aus importer supplies AUD to bank
Aus importer demands USD back
Aus importer sends bank transfer in USD
Demand for AUD
what relationship is it?
what causes movements and shifts of curve?
negative relo- as price of AUD1 in USD decreases, then Quantity of AUD demanded decreases
movements- caused by reliance on other countries/ exchange rate
shift- caused by no exchange rate factors
2.1 List all the non exchange rate factors
Relative price levels
Real world gdp
Foreign preferences for Aus G&S
Relative interest rates
Commodity prices
Expectation and speculation
2.1.1 non exchange rate factors- relative price levels
If inflation in other countries is greater than aus, ts causing aus g&s will be cheaper= increased demand for AUD and more appealing for foreign importers = shift right

2.1.2 non exchange rate factors- real word gdp
Higher economic growth in world real GDP in australias trading partners= increasing real income of foregn citizens. This increases D for Aus g&s= increase D for AUD= shift right
Eg. Chinas econ growth= increased real income of chinese citizens= increased D for aus iron ore, beef etc-> increased D of AUD and shift right.

2.1.3 non exchange rate factors- foreign preferences
If aus g&s become more popular overseas, then demand for AUD increases= shift right
Eg. If tourism campaign for aus= increased demand for aus tourism= increased D for AUD= shift right.

2.1.4 non exchange rate factors- relative interest rates
define Interest rate differential
explain effect on D
Interest rate differential= the difference between australian interest rate and foreign interest rate
Interest rates reflect the return on financial assets. So when australias interest rate is higher than the US then IRD increases= increased demand for Aus assets= increased demand for AUD= shift right.

2.1.5 non exchange rate factors- commodity prices
Commodity prices determined by demand in world market.
If iron ore prices increase due to increased demand by china= increased value of exports= increased demand for AUD= shift right
2.1.6 non exchange rate factors- expectations and speculations
Foreign currency traders expect movements in currency.
If AUD is believed to appreciate in future- they will purchase now to take advantage of lower prices = increased demand for AUD= shift right.
Supply of AUD
define
law
where aus wants to sell aud to buy foreign currency to purchase g and s from overseas
pos- as ER increased, quantity of AUD supplied increases
3.2 causes of shift/ movement in supply curve
shift= non exchange rate factors
movement- change in ER
3.3 List the factors that cause shift in supply cirve
Relative price levels
AUS real GDP
Aus preference for foreign goods and services
Relative interest rates
Expectations and speculation
3.3.1 Relative price levels
If inflation is lower in other countries relative to aus, then foreign g&s will be more attractibe to aus importers= increased D for foreign g&s = increased Supply of AUD= shift right
3.3.2 Aus real gdp
If econ growth in aus increases= increased domestic income = increased imports from overseas = increased D for imported g and s = increased S of AUD= shift right.
3.3.3 Aus preferences for foreign g and s

If foreign g and s are more attractive- if US released ad for tourism then increased D for foreign g and s= increased S of AUD= shift right

3.3.4 Relative interest rates

If foreign IRD increases, then demand for foreign assets increases= increased S of AUD= shift right

3.3.5 Expectations and speculation

By foreign investors or trackers
If USD is likely to appreciate in future, then australians may sell more AUD to purchase USD now before becomes more expensive = Increased S of AUD = shift right.
4. Floats-
define
2 types
countries use a float/ market determined exchange rate as it is influenced by market forces of SnD.

4.1 Clean float

When a currency is allowed to float free from interference of central bank (RBA)

4.2 Dirty/ managed floats

When interfference of foreign exchange rate by central bank
Act as buyer or seller, influencing exchange rate
Eg. When RBA would buy AUD in market to prevent AUD from falling too low
5. EQ ER
when does EQ occur?
what would happen if ER was higher than EQ
what would happen if ER was lower than EQ
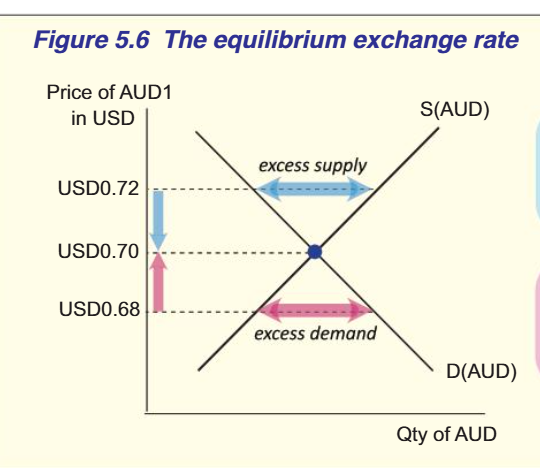
occurs when QD=QS
QS>QD= excess supply causing price to decrease
QS<QD= excess demand causing price to increase
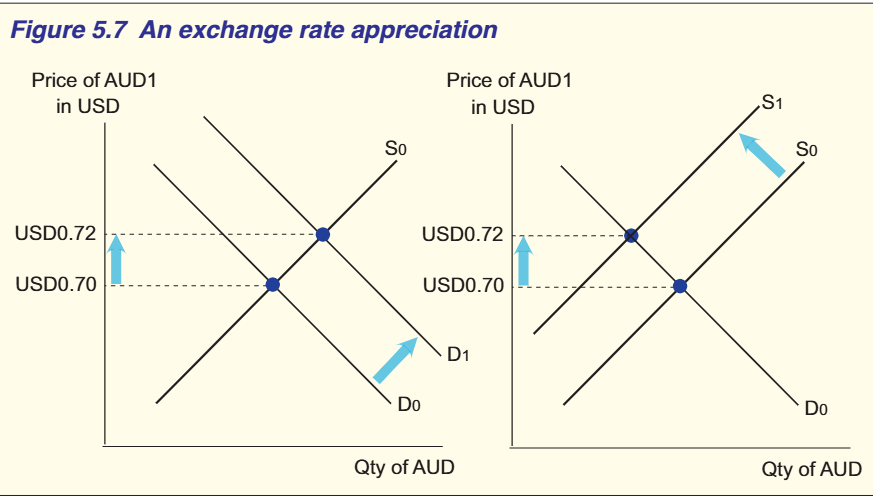
What 2 factors cause appreciation?
Demand of AUD increases= shift right
Supply of AUD decreases= shift left
6.1 Demand of AUD increases= shift right is caused by…

Increased demand for aus exports
Increased commodity prices
Aus IRD increases= increased foreign investment into aus

6.2 Supply of AUD decreases= shift left by

Decreased D for imports
increases in IRD= decrease in aus investment overseas

what 2 factors causes depreciation
decreased demand for AUD= shift left
increased supply for AUD = shift right
7.1 decreased demand for AUD= shift left is caused by…
decreased demand for aus exports
decreased commodity prices
decreased IRD= decreased foreign invest into aus
7.2 increased supply for AUD = shift right is caused by…
increased demand for imports
incrrased inflation in aus
decrease in aus IRD= decreased AUD invest into overseas
summary of determinant of demand and supply
demand is impacted via
supply is impacted via
Demand
exports of g and s
incomr from overseas
capital inflow
Supply
imports of g and s
payment of income to overseas
capital outflow
Effects of movements in the ER impacts…
macroecon
trade balance
consumers and business
8.1 Macroeconomy
how does depreciation impact?
exports
tourism
domestic producers
how does appreciation impact?
DEPRECIATION= EXPANSION IN MACROECON
Increases export advantages because overseas countries can purchase more at lower price, but decreases domestic imports as price decreases
Tourism in aus econ increases
Domestic producers that do not sell imported goods increase competitiveness
APPRECIATION= CONTRACTION
Decreases exports as more expensive
Decreases tourism from overseas, but aus to overseas benefit
Domestic producers lose


8.2 trade balance
depreciation causes-
1. impact on ecports
2. impacts of imports
3. what effect?
Increased quantity of aus exports but no impact on price= increases value
Decreases quantity of aus imports but increases price = increase or decrease value depending on demand
Causes J curve effect- where TB will decrease at first b due to increased import value but then increases due to volume = increased TB

8.3 CONSUMERS AND BUSINESS

what does depreciation cause
DEPRECIATION
Consumers harmed as they pay more for imports or overseas travel
Domestic producers that sell imported goods eg. Petrol will decrease profit due to increases price of imported goods
Firms that export gain as overseas demand increases
Domestic producers that done sell imported goods gain as increased demand for dometic produced goods.
BOP and ER
linked via 2 factors
appreciation and depreciation
protection of econ from external shocks
9.1 Appreciation and depreciation
what causes appreciation
what causes depreciation
Appreciation occurs when-> increased trade balance or increase in capital inflow= demand for AUD increases
Depreciation occurs when-> increased imports or increased capital outflow = increased supply of AUD

9.2 protection from external shocks

explain using examples of positive shock and negative shock
Eg. Positive shock- when china econ growth= increased D for aus g and s/ exports= increased global price= increasd AUS XPI and gdp but can cause inflation. Stronger AUD slowed down the econ and decreased effects of inflation
Eg. Negative shock- global financial crisis= aud depreciated but increased exports and expantion of aus econ= ER prevented recession because depreciated AUD= decreased price of aus g and s and increased competition

10 Recent trends in AUD ER via TWI

define TWI
TWI- weighted average of a basket of currencies that reflect importance of aus trade by country
Most important - chinese yuan, jap yen, euro and USD
10.1 why is AUD 2x as volatile against USD in TWI?
Single currency always flunctuates more than average ER
USD AND TWI ARE DIRECTLY CORRELATED AS USD IS KNOWN AS GLOBAL PRICE AND IS BIGGEST ECON

Key drivers of AUD
list 2 factors
commodity prices
IRD
11.1 Commodity prices

why is aus aka commodity currency?
what do changes in commod prices influence
relationship between the 2
Aus = commodity currency bc over 70% of aus exports are primary commdityes
Changes in com prices infleunce aus gdp and income
AUD and commodity prices are positive relo as increased com prices = appreciation in AUD

11.2 IRD
how is it measured
if AUS IRD with US decreases then…
vise versa
why?
Measured via difference in 3 year bond rates between 2 countries
If AUS IRD with US decreased then AUD depreciates because IRD affects the flow of foreign investment between 2 countries
Investors seek to receive highest returns for their funds- so less FI will flow into aus, decreasing demand for aud and increase supply of AUD as aus investors shift funds into US
If aus IRD increases, then AUD would appreciate as increased D for AUD and decrease supply of AUD
