Fluid Mechanics Conceptual Questions 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Write an equation that relates absolute pressure to gage pressure
Pabs = Pgage + Patm
(absolute pressure = gage pressure + atmospheric pressure)
Write down Pascal's Law.
P=F/A
Pressure is the same in all directions in a fluid. It equals force divided by area.
Define an inviscid fluid.
A fluid with no viscosity (no internal friction).
How does density change with temperature for liquids?
As temperature increases, density decreases.
In solids, shear stress is proportional to ...
shear strain
In fluids, shear stress is proportional to ...
the rate of shear strain
What fundamental law is the basis of the energy equation?
The First Law of Thermodynamics (Conservation of Energy)
What fundamental law is the basis of the Euler Equations?
Newton’s Second Law (ΣF = ma)
What equation is obtained by integrating a Euler equation along a streamlines?
The Bernoulli Equation
Does Bernoulli equation assume inviscid form?
Yes, meaning there are no viscous forces like friction
Write down the part of the momentum equation representing “local change” for a fluid with a density ρ and a velocity v in a control volume CV with a control surface CS and a unit normal vector n. (Use arrows over variables names to denote vectors.)

Write down the part of the momentum equation representing “convective change” for a fluid with a density ρ and a velocity v in a control volume CV with a control surface CS and a unit normal vector n. (Use arrows over variables names to denote vectors.)
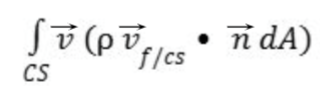
Write down a simplified form of the momentum equation (without any integrals) that applies to a steady, incompressible flow through a fixed (not moving) control volume with a single inflow section with an average velocity vin, a single outflow section with an average velocity v_out, a discharge Q, and a density ρ. (Use arrows over variables names to denote vectors.)
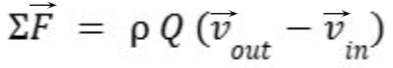
Write down a mass conservation equation for a fluid with density and velocity v in control volume CV with a control surface CS and unit outward normal vector n, (Use arrows over variable names to denote vectors)
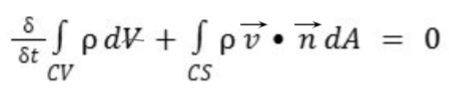
Write down a simplified (no integrals) volume conservation equation for a cylindrical tank of diameter D filled to a depth y that is being filled by a constant discharge Q. The tank has no outflow.
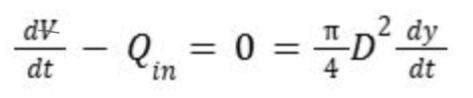
When cross-sectional Area (A) decreases
speed (V) increases
Bernoulli’s Principle
Pressure is high when speed is low and vice versa
When height (h) increases
Pressure (P) decreases
Pressure is lower at higher elevation
When velocity (V) increases
Pressure (P) decreases
EGL (Energy Grade Line)
represents the total head height
HGL (Hydraulic Grade Line)
represents the sum of elevation and static pressure heads
HGL declines more rapidly than EGL
True! because some of the potential energy of the liquid is converted into kinetic energy
Pumps boost mechanical energy (through increase in pressure) so EGL and HGL rise
True
Which dimensionless number should be used for physical modeling of water waves?
(a) Reynolds, (b) Froude, (c) Weber, (d) Euler, (e) Mach
(b) Froude
Which dimensionless number should be used for physical modeling of low velocity air flows?
(a) Reynolds, (b) Froude, (c) Weber, (d) Euler, (e) Mach
(a) Reynolds
Which dimensionless number should be used for physical modeling of capillary rise in porous media?
(a) Reynolds, (b) Froude, (c) Weber, (d) Euler, (e) Mach
(c) Weber
Which dimensionless number should be used for physical modeling of high velocity air flows?
(a) Reynolds, (b) Froude, (c) Weber, (d) Euler, (e) Mach
(e) Mach (At high speed → compressibility effects dominate)

Which of the following conditions must apply when using this form of the Bernoulli Equation?
(a) steady flow, (b) incompressible fluid, (c) inviscid flow, (d) 1&2 along streamline, (e) none of these
(a) steady flow,
(b) incompressible fluid,
(c) inviscid flow,
(d) 1&2 along streamline
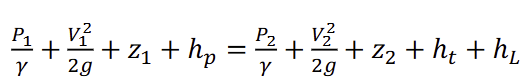
Which of the following conditions must apply when using this form of the Energy Equation?
a) steady flow, (b) incompressible fluid, (c) inviscid flow, (d) 1&2 along streamline, (e) none of these
(a) steady flow,
(b) incompressible fluid
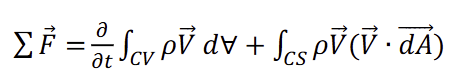
Which of the following conditions apply must when using this form of the Momentum Equation?
(a) steady flow, (b) incompressible fluid, (c) inviscid flow, (d) 1&2 along streamline, (e) none of these
e) none of these
Which of the following discoveries is not attributed to Archimedes?
(a) Buoyant force = weight of displaced fluid,
(b) Floating object displaces fluid equal to its own weight,
(c) shear stress equals velocity times strain rate,
(d) Volume of object can be measured by displacement of fluid,
(e) pressure acts equally in all directions
(c) shear stress equals velocity times strain rate,
(e) pressure acts equally in all directions
From what basic law is the Energy Equation (shown above) derived?
(a) First Law of Thermodynamics, (b) Newton’s Law of Viscosity, (c) Newton’s Second Law
(a) First Law of Thermodynamics,
From what basic law is the Bernoulli Equation (shown above) derived?
(a) First Law of Thermodynamics, (b) Newton’s Law of Viscosity, (c) Newton’s Second Law
(c) Newton’s Second Law