Human and Social Biology - Circulatory System
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
What is the circulatory system?
the network of blood vessels and the heart that moves blood throughout the body
What is the purpose of the circulatory system?
supply oxygen and nutrients to the body cells and remove waste through your blood
What is another name for red blood cells?
erythrocytes
What are the most numerous cells in the blood?
Red blood cells
Where are red blood cells made?
red bone marrow (tissue inside bones)
What vitamin is needed to make red blood cells?
B12
How long do red blood cells live?
120 days
Where are red blood cells destroyed?
liver and spleen
What is the function of the red blood cells?
transport oxygen around the body
When oxygen diffuses into the blood stream and combines with haemoglobin, what is formed?
oxyhaemoglobin
Can haemoglobin combine with carbon dioxide?
yes, to a lesser extent for transport
Red blood cells squeeze through the what of capillaries?
lumen (bore)
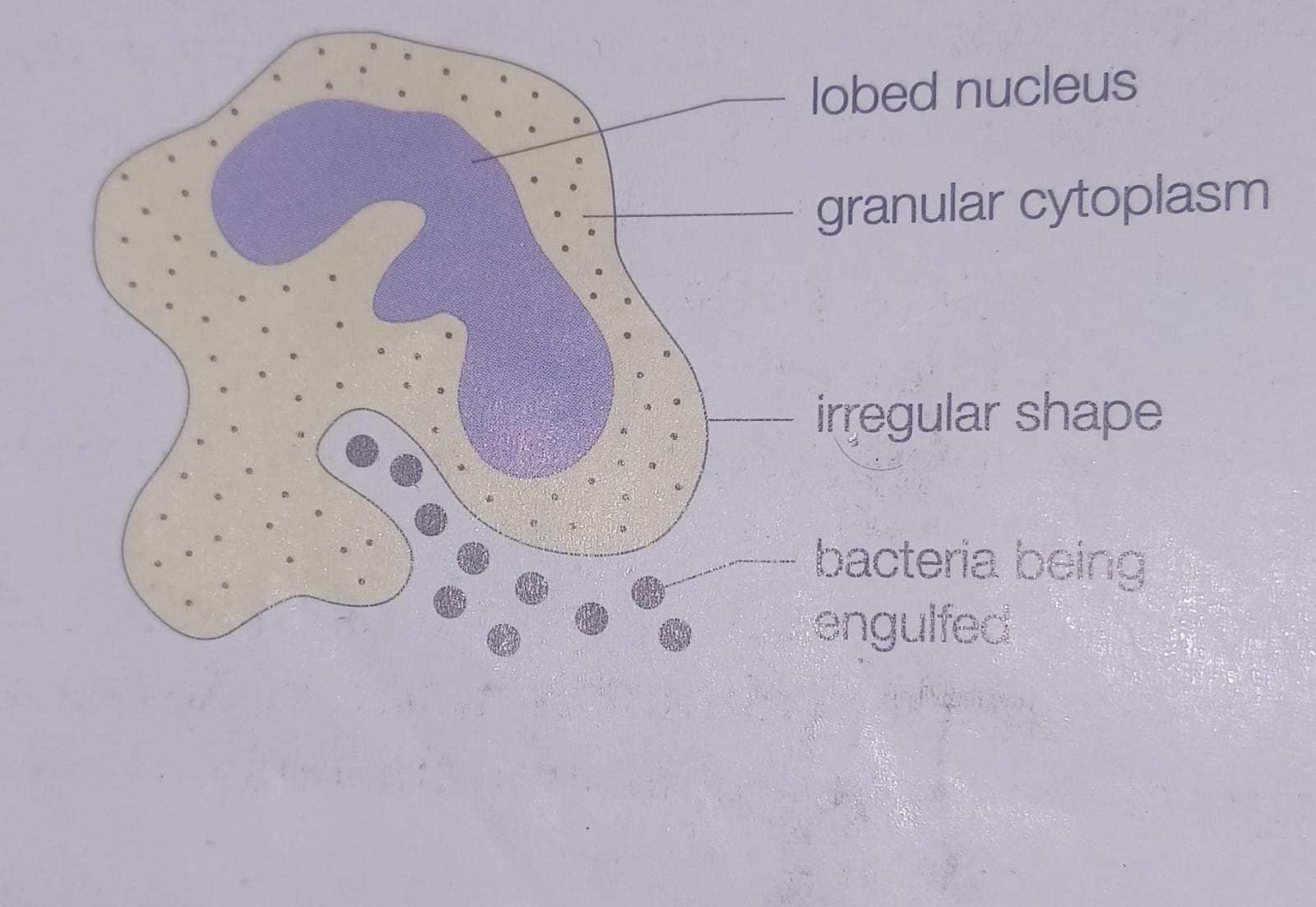
What type of white blood cells is depicted?
phagocyte
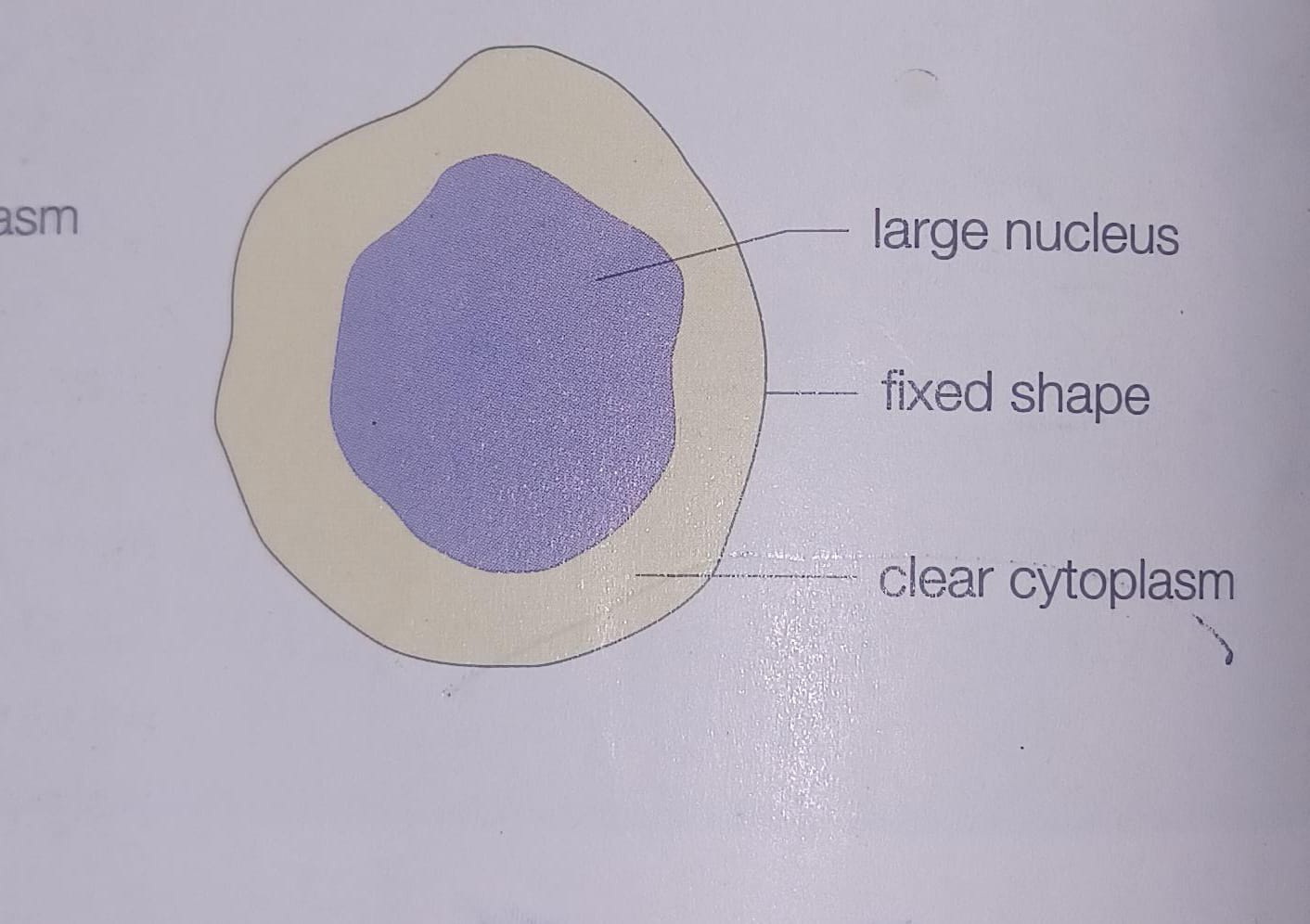
What type of white blood cells is depicted?
lymphocte
What are granulocytes?
a type of phagocyte that contains granules
How can the movement of white blood cells be defined?
amoeboid movement to move and squeeze through capillary walls
What is the shape of red blood cells?
bi-concave
Another name for white blood cells?
leucocyte
What is the process by which phagocytes engulf bacteria
phagocytosis
Which white blood cells produce large protein molecules called antibodies to destroy disease organism
lymphocyte
What are the two main ways white blood cells protect the body
engulfing bacteria (phagocytes) and directly destroying them (lymphocytes)
Where are white blood cells made?
bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes
What percent of plasma is water and solutes?
90% water, 10% solutes
digested nutrients in the capillaries of the villi pass into tiny veins that join together to form what?
hepatic portal vein
What does the hepatic portal vein do?
carry digested foods to the liver and then to the body cells
Where is nitrogenous wastes from proteins transported from and to?
from the cells to the kidneys via the blood plasma
Hormones are carried in plasma from where to where?
endocrine glands to the organs where the hormones function
What supplies water to the tissues and helps blood carry heat around the body
plasma
What are platelets (thrombocytes)?
small, nuclei lacking, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding
What does μm
micrometre
What is the size of red blood cells (across)
8 μm
What is the size of white blood cells (across)
20-60 μm
What is the size of platelets (across)
approx 2 μm
How many red blood cells are found in 1mm3 of blood?
4 - 5 million
How many white blood cells (leucocytes) are found in 1mm3 of blood?
8 - 10 000
How many platelets are found in 1mm3 of blood?
250 000
What is blood clotting and what does it consist of?
the process of forming a clot to stop bleeding when a blood vessel is damaged. It consists of mesh fibres , which trap the blood cells and platelets at the surface of the wound.
Describe the mechanism of clotting?
damaged blood vessels release the protein thromboplastin
the thromboplastin acts on the blood protein prothrombin and turns it into thrombin with the aid of calcium salts
Thrombin acts on fibrinogen (soluble protein) and turns it into insoluble fibrin
This fibrin forms the fibres in the clot
Red blood cells and platelets become trapped in the forming the clot
Where is prothrombin made? What must be present to make it?
the liver, vitamin K
At high carbon dioxide concentration what does oxyhaemoglobin break down into?
oxygen and haemoglobin that is purple-red
What does plasma transport carbon dioxide as?
bicarbonate
Which part of the blood transports waste such as urea from tissues to excretory organs such as kidneys
plasma
Which part of the blood transports nutrients from intestine to liver and then to tissues?
plasma
Do arteries carry blood to or away from the heart
away
Do veins carry blood to or away from the heart
to
What type of blood vessel is this?
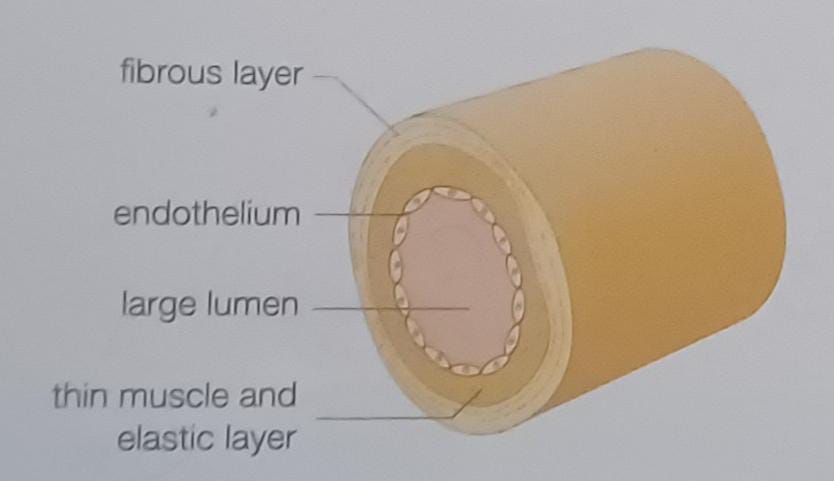
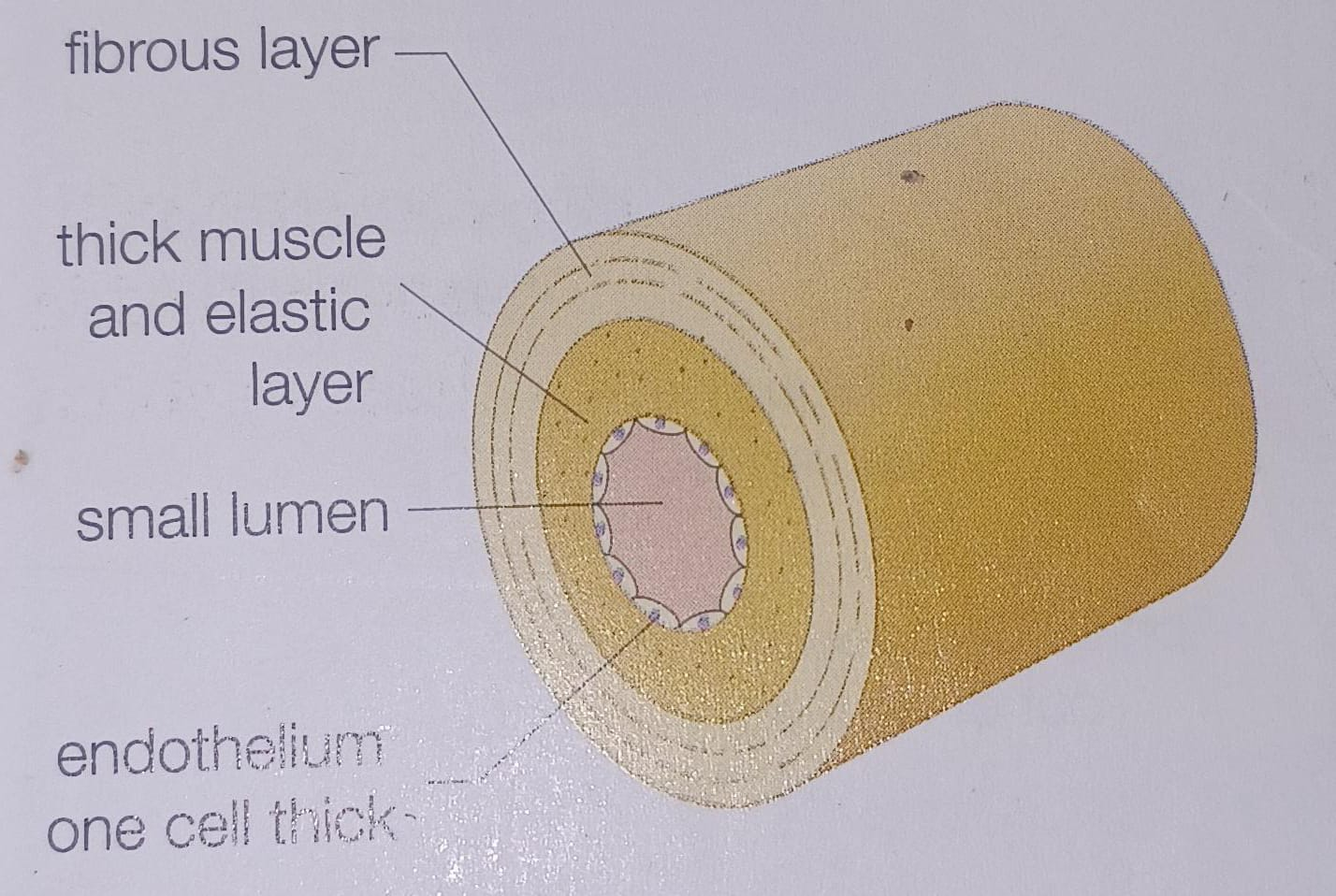
Vein
What type of blood vessel is this?
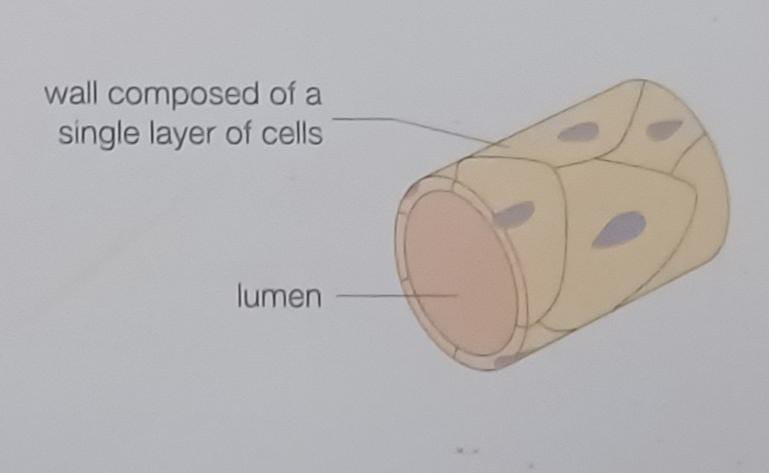
Capillary
What type of blood vessel is this?
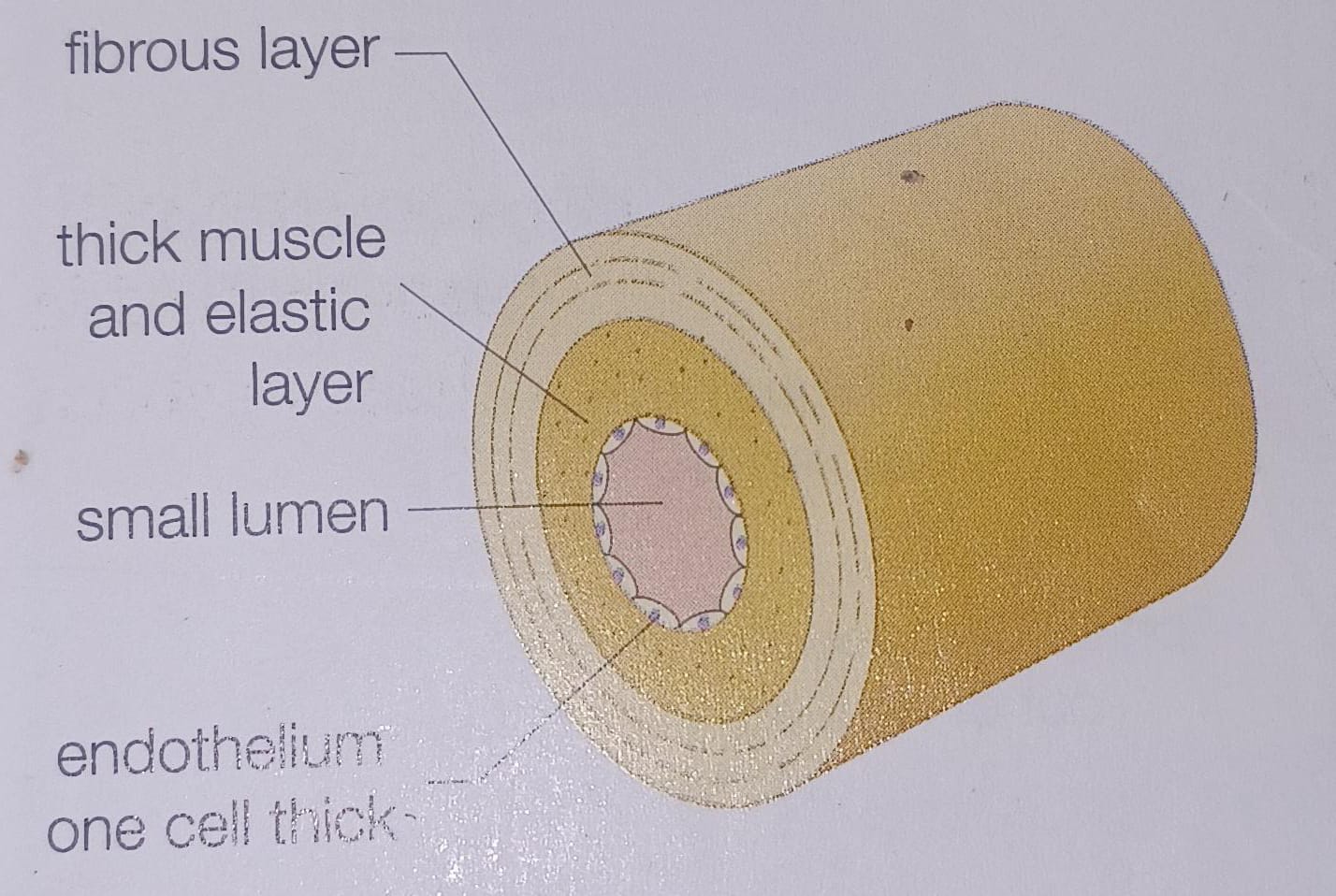
Artery
What do arteries branch into? and what does that branch into?
smaller vessels callled arterioles which branch into capillaries
What do the muscles of arterioles contract during?
vasoconstriction
Why do arteries have thick, elastic walls?
so they stand the high pressure caused by the pumping heart as they carry the blood away
Why do veins have thinner walls and larger lumen than arteries
they carry blood that isn’t under as high a pressure
what is the lumen?
the hollow opening or the space inside the blood vessel
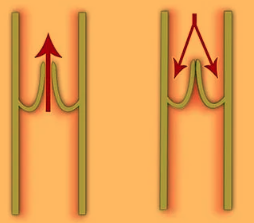
which blood vessels contain valves to prevent the back-flow of blood?
veins
Why do arteries not have valves?
the high pressure of blood pumped directly from the heart ensures that blood flows in only one direction
What do veins branch into?
smaller vessels called venules
What assists veins in the flow of blood back into the heart
muscular movements in the body
Which blood vessel has 1-cell thick walls that are permeable to oxygen, C02, water and nutrients?
capillaries
Capillaries branch many times before connecting the what to the what?
arteries to the veins
What do capillaries supply from the plasma to the cells?
oxygen, nutrients, and substances
How do substances pass from the capillaries into the tissue fluid surrounding the body cells before entering the cells themselves?
diffusion
Waste material diffuse out of cells and pass into the ______ _____ and then the _________. Some materials are drained away by the _____ in the _____ ______.
tissue fluid, capillary
What is Lymph formed from?
tissue fluid drained away from the cells in lymphatics
What key characteristics differentiate the arteries from veins and capillaries?
thick, muscular, elastic walls, absent valves, blood flows under high pressure and flows in spurts, oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery), carries blood away from the heart
What key characteristics differentiates the veins from arteries and capillaries?

Thinner walls, valves are present, blood flows under low pressure and flows smoothly, deoxygenated blood except pulmonary veins, carry blood towards the heart
What key characteristics differentiate the capillaries from veins and arteries?

1 cell thick walls, valves are absent, low pressure and slow flow, oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, substances pass through the walls, carries blood from arteried to venules

What is blood pressure and what is it measured in?
the force of blood pushing against blood vessels as the heart pumps blood. millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
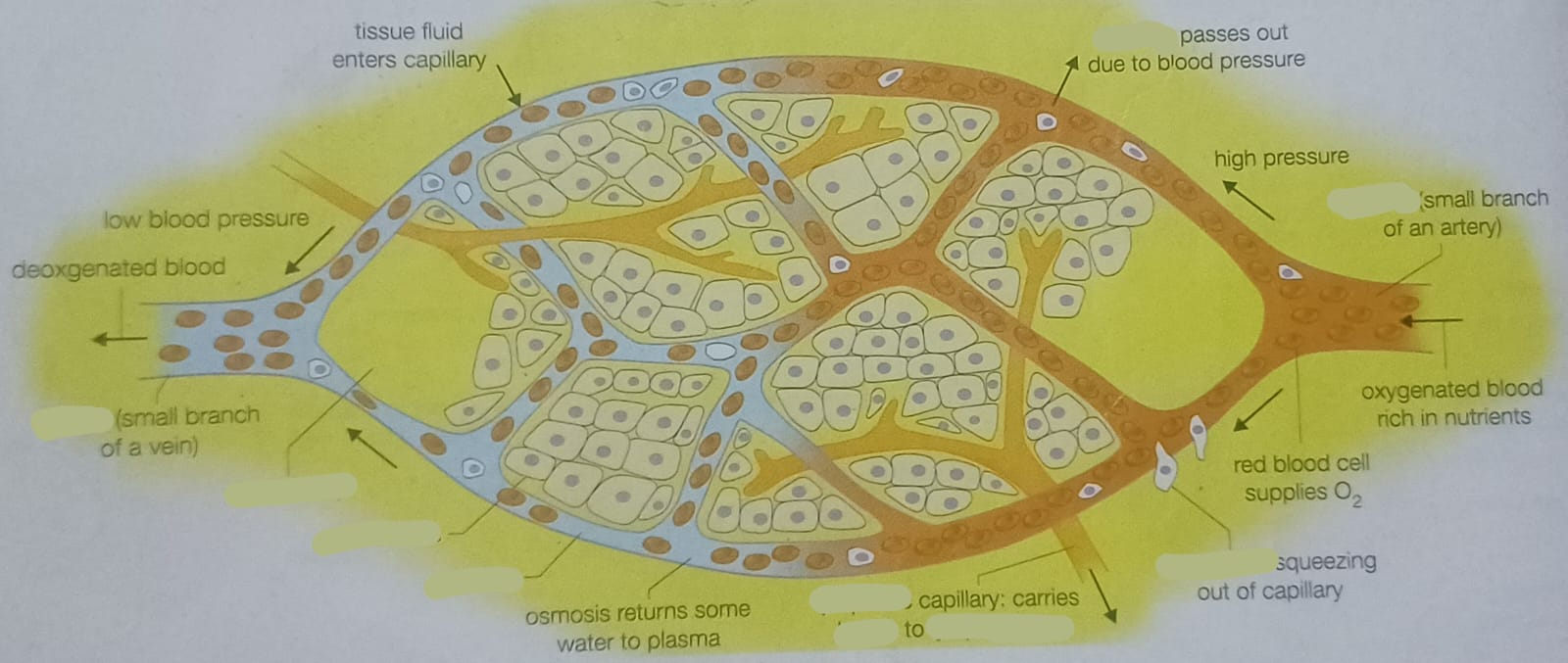
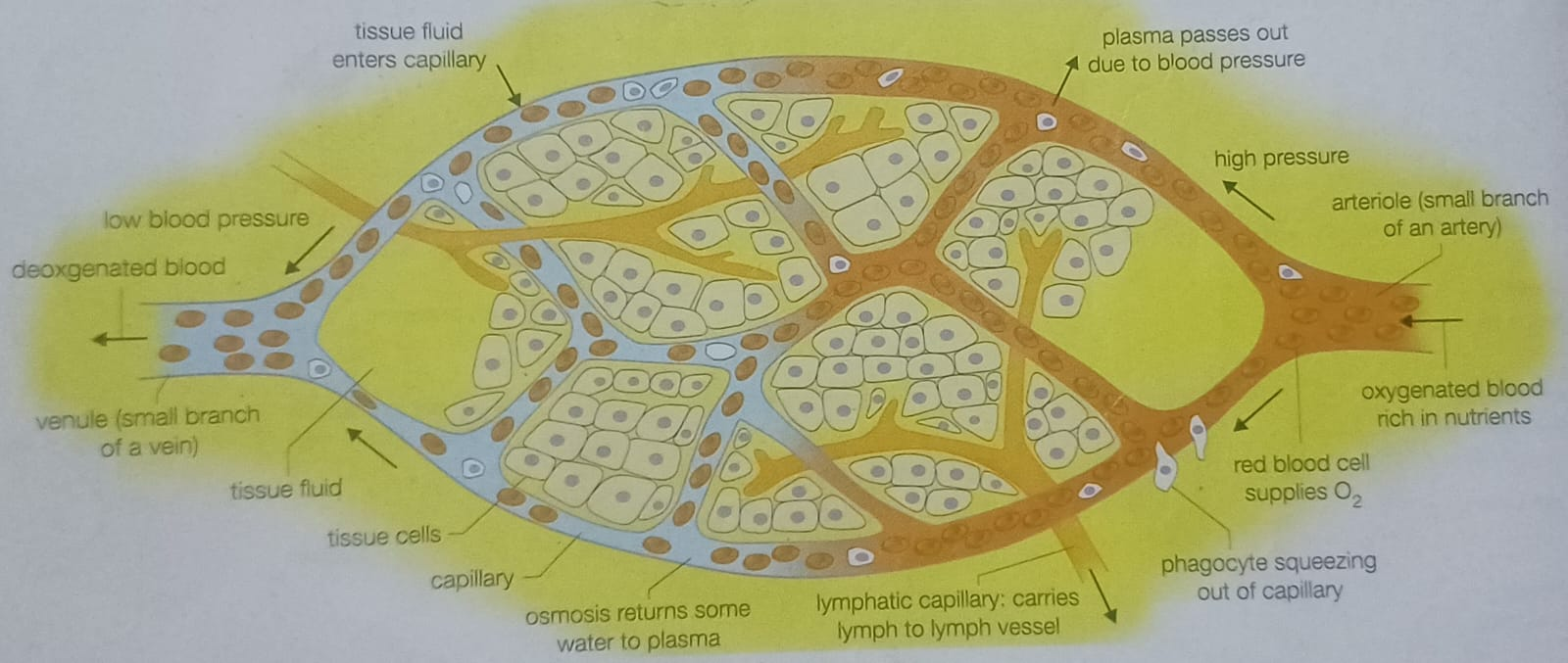
The liquid that leaks through the thin capillary walls becomes a part of the what?
tissue fluid
Which component of the blood is forced into the tissue fluid?
plasma
Which components of the blood are NOT forced into the tissue fluid?
proteins, red blood cells, platelets
What is the role of the lymph vessel?
drain away excess tissue fluid

State the name, function and special feature(s) of the image.
red blood cell, carries oxygen, biconcave shape

State the name, function and special feature(s) of the image.
lymphocytes, form antibodies, large single nucleus

State the name, function and special feature(s) of the image.
phagocyte, engulf bacteria, lobed nucleus

State the name, function and special feature(s) of the image.
platelets, clotting, cell fragments
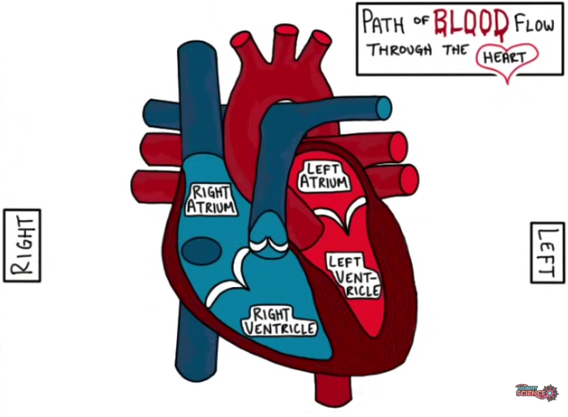
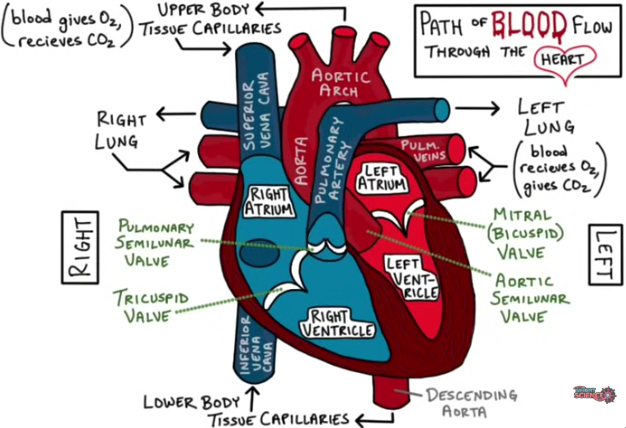
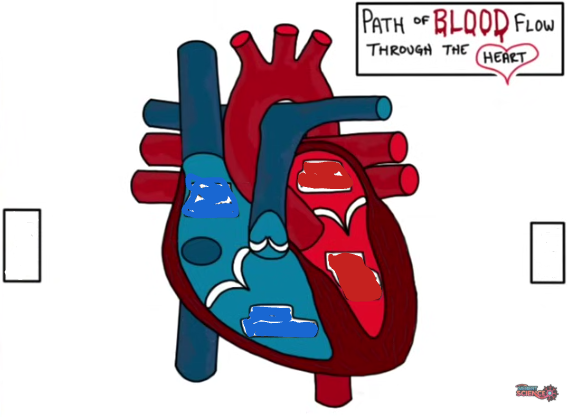
If you start from the right atrium, how would blood flow? use a pencil and trace as you go along.
Right atrium —> tricuspid valve —> right ventricle —> pulmonary semilunar valve —> pulmonary artery —> pulmonary veins —> left atrium —> Mitral (bicuspid) valve —> left ventricle —> aortic semilunar valve —> aorta —> aortic arch —> descending aorta —> superior vena cava/ inferior vena cava
Why is the cardiac muscle on the left side of the heart thicker?
the left side has to pump blood throughout the entire body whereas the right only needs to pump blood to the lungs
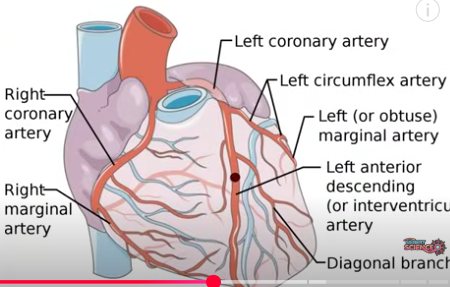
How does the cardiac muscle receive oxygenated blood?
coronary arteries which branch off from the aorta
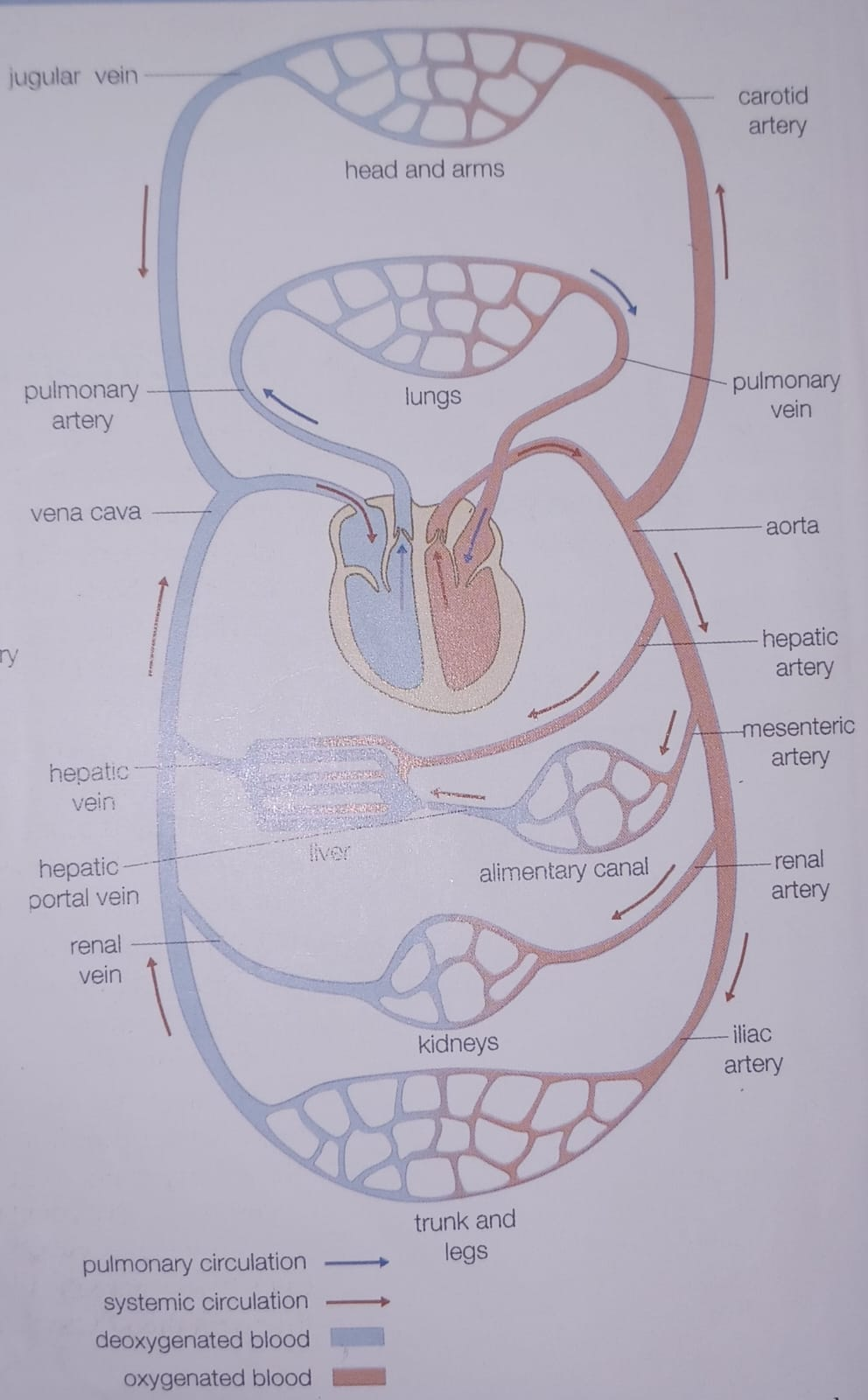
What is pulmonary circulation?
the passage of blood from the heart to the lungs and back
What is systemic circulation?
the passage of blood from the heart to the body’s tissues and cells then back to the heart.
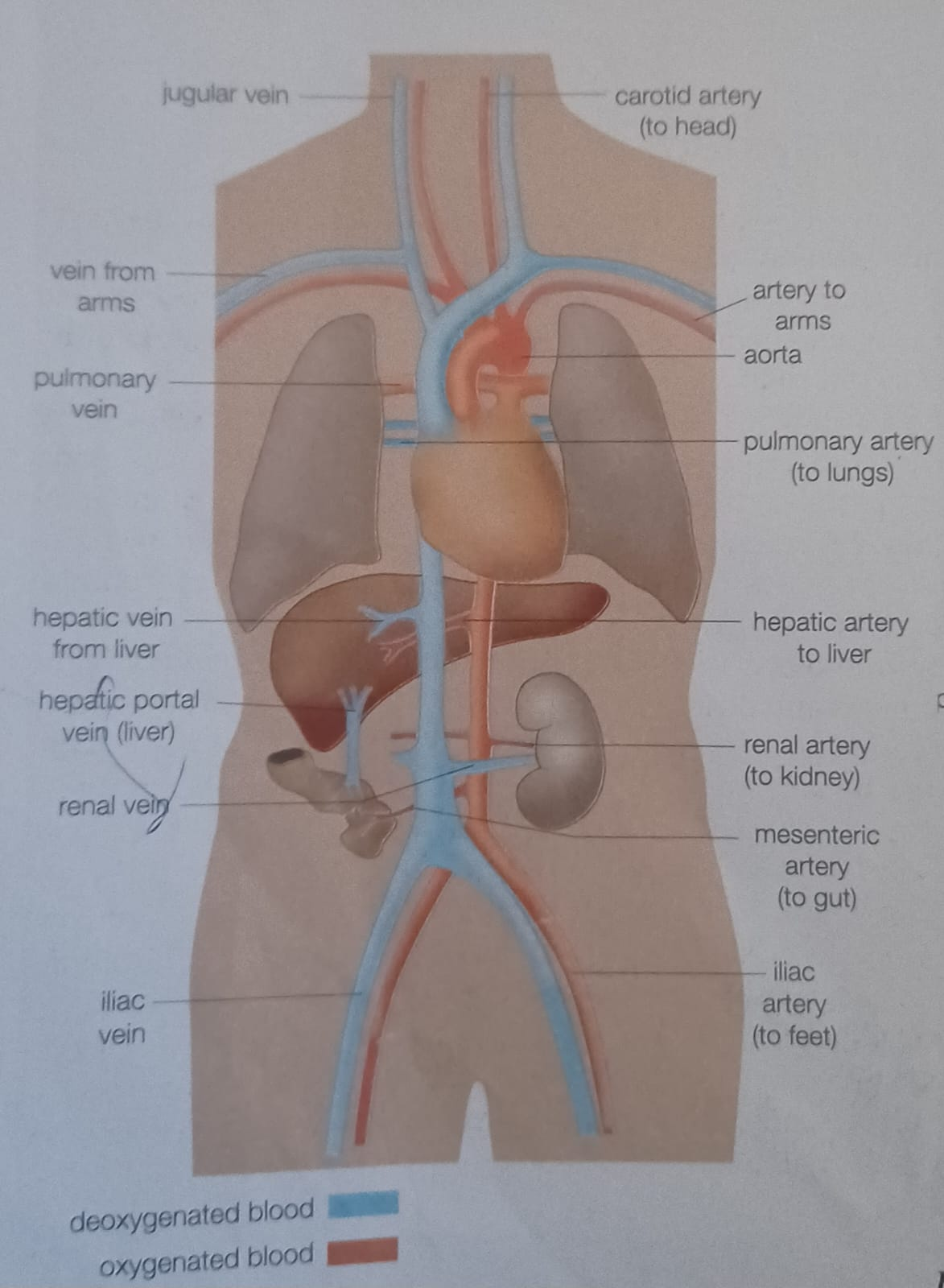
Most veins carry oxygenated blood and most arteries carry deoxygenated blood, what are the exceptions?
pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein
The aorta supplies the hepatic artery to the what?
liver
The aorta supplies the gastric artery to the what?
stomach
The aorta supplies the mesenteric arteries to the what?
intestine
The aorta supplies the renal arteries to the what?
kidneys
Which vein does not return blood directly to the heart and pass from one organ to the other?
portal veins
The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the __________ _____ to the _____, bringing undigested food. From the liver the blood enters the _______ ____.
alimentary canal, liver, hepatic vein
Where do all veins eventually lead to?
The inferior vena cava or to the (anterior) superior vena cava
Where can the heart be found?
in the thorax, behind the sternum (breastbone) between the lungs and slightly to the left of centre.
What are the two upper chambers of the heart called?
atria
What Is the cardiac cycle?
the complete sequence of events during one beat of the heart
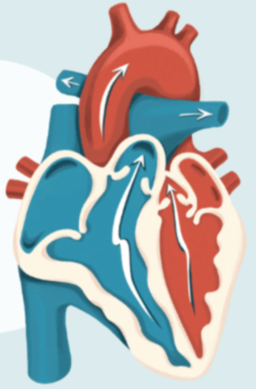
What are contractions of the upper heart chambers called?
systole
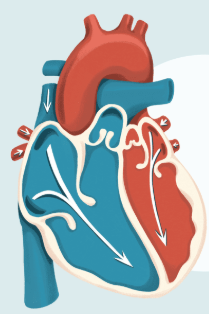
What is it called when the lower chambers ( relax?
diastole
Fright, stress and anger increase the heart rate why?
adrenaline is released into the blood which stimulates the pacemaker
How does the artificial pacemaker work?
small battery that makes regular shocks to stimulate and control the normal heartbeat. replace batteries abt every 7 years
What should systolic pressure be between?
100 and 139 (mm of mercury)