Pathophysiology Katia Ferdowsi UCF Exam 1, PATHo!
1/295
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
296 Terms
Patho
suffering
Physio
Nature
ology
the study of
Pathophysiology
study of abnormalities in physiologic function of living things
What is the purpose of studying Pathophysiology?
Reveals physiologic responses of the body to
disruptions
four interrelated topics of Pathophysiology
Etiology
Pathogenesis
Clinical manifestations
Treatment implications
Etiology
study of causes & reason. identify causal factors that cause the disease
Risk factor
When factor is present it increases likelihood of disease. Knowing this prevents disease
Idiopathic etiology
unknown cause
Iatrogenic
causes from unintended/unwanted medical treatment
some etiologic classifications of disease
Congenital (inborn) diseases or birth defects
Degenerative diseases
Immunologic diseases
Infectious diseases
Pathogenesis
Developtment of disease. Starting from 1st stimulus to expression.
Pathogenesis describes
Describes how etiologic factors can alter physiologic function and lead to develop disease.
Symptoms
subjective abnormal feeling. ex: headache, nausea, pain
Signs
objective, observed manifestation of disease
Syndrome
set of symptoms & signs typically associated with a particular disease or condition
Latent Period
Time between exposure of infectious agent to first appearance of sign and symptoms
Prodromal period
first appearance of signs and symptoms indicating disease
Acute phase
disease in full intensity
Acute clinical course
less than a month, short lived sever manifestation. Short incubation period
Chronic clinical course
More than 1-3 months. can last month to years
Exacerbation
increased severity of signs and symptoms
Remission
decrease in severity; sign of cure >5yrs
Convalescence
stage of recovery after disease or surgery.
Sequela
Subsequent (coming after) condition result from acute illness. Ex: Paralysis is sequela of stroke
Complication
Secondary pathologic condition produced by the original problem
Treatment
Understanding the etiology, pathogenesis, and clinical
consequences of a particular disorder/disease/illness to help
general ______
three main Individual Factors affecting health and disease?
Culture,Age,Gender
Withstand the assault (Reversible cell injury)
if change is short lived the cell can withstand and then go back to normal
Cellular adaptation (reversible)
cell adapts by changing structure or function that can stand injury
Cellular death (irreversible)
cell death occurs if problem is prolonged
Ischemia
Most common cause of cell injury. This is inadequate blood supply to an organ. It injures cell faster than hypoxia. Ischemia deals with hypoxia
Hypoxia
lack of oxygen
Nutritional injury
inadequate of sufficient amount of fats,carbs,protein,vitamin, & minerals. this can injure the cell. Some cells are more susceptible than others.
infectious & immuno injury
Bacteria & viruses
chemical injury
Toxic chemicals or poisons can cause cellular injury
Physical mechanical injury
Temp, pain, electrical etc. Ex: Hypothermia from cold temperature
Reversible cell injury
Cellular swelling (hydropic) & Accumulation of excess substance in cell
Cause of swelling
- 1st manifestation could be malfunction in sodium- potassium pump. Accumulate sodium ions in cell. -
- Also injury with loss of ATP cause swelling.
Hydropic swelling Characterized by
large, pale cytoplasm; dilated endoplasmic reticulum; and swollen mitochondria
megaly
increase in size and weight
Intracellular accumulation
Space is taken up within cell so it can't grow. Accumulation of substance in cell = injury. Toxicity immune response, taking up space
Common site of intracellular accumulation
liver
Complex substrate + enzyme= soluble product
Without this enzyme the cell is filled with substrates that aren't soluble.
Chaperone protein
if there is protein damage then the number of ________________ increase to refold the protein. This accumulates within the cell.
Ubiquitin proteasome enzyme
degrades unfolded protein. This activates caspases which then leads to apoptosis
Atrophy
Respond to injury by reducing cell size.
Caused by:
-Disuse
-Ischmeia
-aging
- Nutrient starvation
Hypertrophy
Cell size increases with function. Ex: increase sex hormone= increase breast size or increase muscle= harder for ventricles to pump blood
Hyperplasia
increase cell #. This can be physio or abnormal due to mitotic division. Ex: callus on foot, rubbing/ irritation = accumulated cell death .
Metaplasia
replacement of differentiated cell type due to adaptation of persistent injury. Reversible
Ex: Barret syndrome: change of esophageal cells due to acid reflux burns. Goes back to normal once done.
Dysplasia
disorganized look on cells due to abnormal cell variation. adaptive effort gone bad. This can cause cancer. Preneoplastic lesion
Indication of cell death
pain, elevated enzyme levels, inflammation, loss of function.
Ex: Troponin enzyme level increases during a heart attack. This means cell death
Necrosis
Stage of dying, turns dark.
Consequences of ischemia/ injury.
Cell ruptures and spill components.
has inflammation
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death.
This can come with necrosis.
This is good in cancer so it can kill malignant cells
No inflammation
Coagulative Necrosis
Most common. Process begins with ischemia and then ends plasma membrane degradation. It is a solid substance. Gangrene is a form.
Liquefactive
occurs with dissolution of dead cells, liquification of lysosomal enzymes, and formation of abscess or cyst from dissolved dead tissue. Cell ruptures and the material flows out
Fat necrosis
Degeneration of fat cells. This comes from cell trauma or pancreatitis. Appears white and chalky.
Caseous necrosis
degeneration and death of tissue with a cheese-like appearance. Happens in lungs from tuberculosis
Gangren
cell death in large area due to interrupted blood flow.
Dry gangrene
form of coagulation necrosis. Blackened dry tissue. Separated from a line of demarcation of healthy tissue. caused by microorganism.
Wet gangrene
fatal. A form of liquefactive necrosis in internal organs
gas gangrene
fatal. Formation of gas due to microorganism. formation of damage muscle tissue in gas bubble form.
- result in infection of necrotic tissue by anaerobic bacteria (Clostridum).
Apoptosis
respond to injury that does not directly kil the cell.
- triggers intracellular cascades
- activate cell suicide response
- Not always pathologic
-No inflammation
Apoptosis is triggered by
Extrinsic (death receptor) & Intrinsic (mitochondrial response)
Extrinsic "death receptor"
Withdraws survival signal that stops apoptotic pathway.
- extracellular signal FAS ligand binds to cell and then triggers death cascade through "death receptors"
intrinsic mitochondrial pathway
response to cell damage.Protein P53 is normally in a low count but is increase one cell DNA has been damaged. This causes its own cell death.
Main component: Caspases.
Cellular aging
cell ages and functions/ size decreases
cumulative result factors of aging
1. progressive decline in repair of cells
2. exposure environmental factors.
Somatic death
Death of entire organism. No inflammation before death occurs.
To declare Death
- no cessation of respiration & heartbeat.
- Presence of stiff muscles (rigor mortis) due to release of lytic enzyme in body tissue (post mortem autolysis)
- brain dead= proof of somatic death
Congenital disorder
At birth, genetic or environment or both
Congenital malformation
structural defects caused by error in fetal development. Mainly due to genetics. If caused by environmental it is mostly unknown.
Inherited genetic disorder
found later in life. Not congenital
Gregor Mendel
discovered traits are passed down from parents to offspring
Chromosome characteristics
The total size
length arm of X
banding pattern once exposed to stain
Chromatids
2 identical linear chromosomes, separated in meiosis
Centromere
where the chromatids join
Diploid
- one member of pair from each parent
- pairs are homologous with different DNA sequence
- 23 pair total, 22 auto some (homologous), 1 sex chromosome.
- Female 2x Male 1X 1Y
Phenotype
physical appearance & biochemical attributes
Meiosis
2 germ cells (1 egg sperm) combine to make 46 chromosomes.
- Produce 4 haploid.
- Each germ cell has 23 chromosomes
- 2 divisions
Genetic Traits
Genes code for specific trait.
- Has particular position on chromosomes
- has several alleles
- 2 alleles for each gene (1 from each parent)
Codominant
allele not clearly dominant or recessive
Monogenic
results from interaction of 1 gene loci
Polygenic
interaction from several gene loci
- inheritable
-difficult to predict
-affected by environment factor (multifactoral)
Permanent change in DNA
is rare. Can be environmental due to potential mutagens : Radiation, chemicals, viruses
Point mutation
single base pair substitution
May cause affected codon (3 base pair) to signify abnormal amino acid
- Affects one amino acid
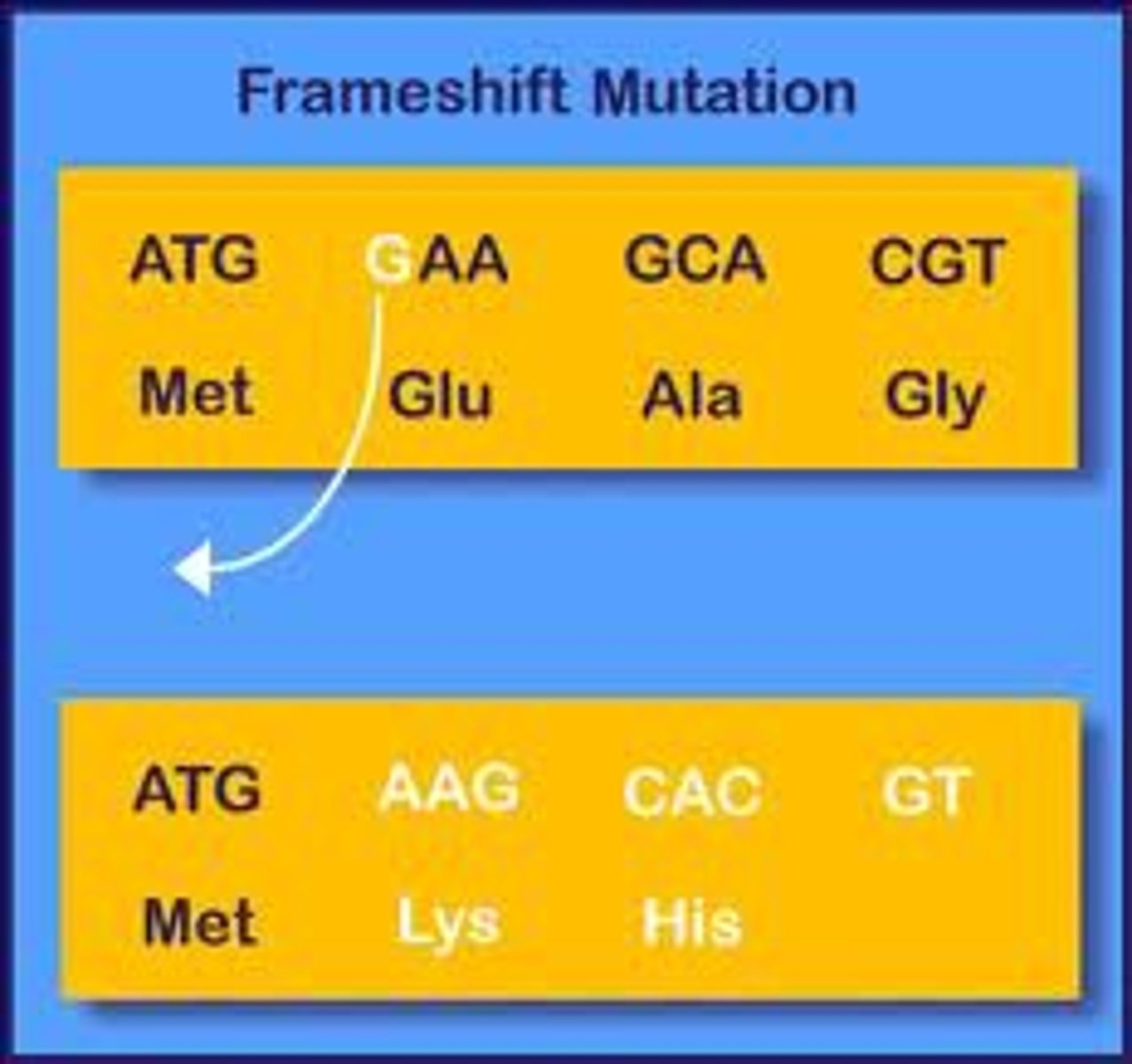
frameshift mutation
- Causes dramatic change in genetic code
- Addition/ subtraction of 1 or more base reading frame
- remaining codon triplets have altered the rest of the amino acid sequence.
Single strand vs double strand
single strand is easier to break.
Double strands are harder to break and can cause a permanent loss of genetic info at break point
Medelian gene disorders
loci & allele on chromosome is changed. A trait that can be predicted
Multifactorial
Caused by contributing factors other than genes. Ex: diabetes is caused by genes and other factors
Abnormal (aberrant) chromosome structure
caused by separation during meiosis
Anueploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes, more or less than 23
Nondisjunction
failure of pairs to separate.
1st meiotic division failure to separate = 22 chromosomes
2nd meiotic division = 24 chromosomes
Combine abnormal with normal
produces fertilized cell with 45 or 47 chromosomes
Monosomy
Daughter cell with a deficiency of 1 chromosome
Usually not compatible with life
ex: Turner Syndrome
Similar to Anaphase lag (One chromosome left out of newly formed cell nucleus)
Polysomy
Daughter cell with to many chromosomes
- viable life with disability
- extra or missing chromosome
Abnormal chromsome structure
breakage/ loss/ rearranged pieces of chromosome during meiosis & mitosis
Meiosis errors
during crossing over
- chromosome portion is lost
- attach upside down
- attach wrong chromosomes
Mitosis errors
opportunity for it to break or rearrange
Translocation
exchange DNA pieces between non homologous chromosome