Hematology Hemoglobin Lecture
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Hemoglobin
Primary Oxygen-Carrying proteins of RBCs
HBA, HBA2, and HBF
The hemoglobin electrophoreisis
Heme
Iron-containing prosthetic group
Globin
The protein chains (A, B, etc)
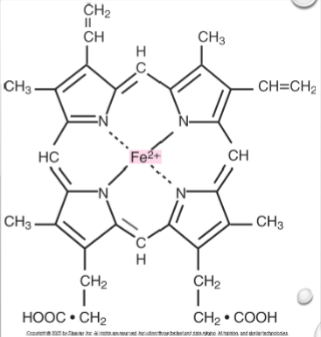
Heme structure
A ring of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms with 1 atom of ferrous iron in the center
A
Alpha Chain
B
Beta chains
Γ
Gamma chains
Δ
Delta chains
141 amino acids
A on chromosome 16 with…
146 amino acids
B on chromosome 11 with…
Primary protein structure
Amino acid sequence of polypeptide chains
Secondary structure
Chain arrangements in Helices and Nonhelices
Tertiary Strucutre
Arrangement of helices into a pretzel like configuration (3D structure)
Quaternary structure (Tetramer)
Complete hemoglobin molecules
Glycinated hemoglobin
Post translation modification formed by nonenzymatic binding of various sugars to globin chain amino groups of the life span of the RBC
HBA1c
nORMALLY ABOUT 4-6% BUT HIGHER IN UNCONTROLLED Diabetes mellitius
Pronormoblast
Where hemoglobin synthesis begins
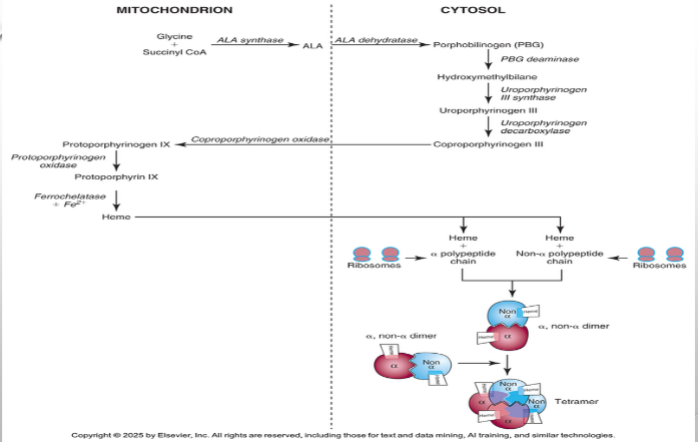
Ribosomes in cytoplasm
Where globin biosynthesis begins
Embryonic > Fetal > Adult
Developmental regulation
Hemoglobin Assembly
Heme + Globin assembled into tetramers, where each globin chain bind to heme molecule forming a heterodimer
HBA
2 alpha, 2 beta chains
HBA2
2 alpha,, 2 delta chains
HBF
2 alpha, 2 gamma chains
Hemoglobin ontogeny
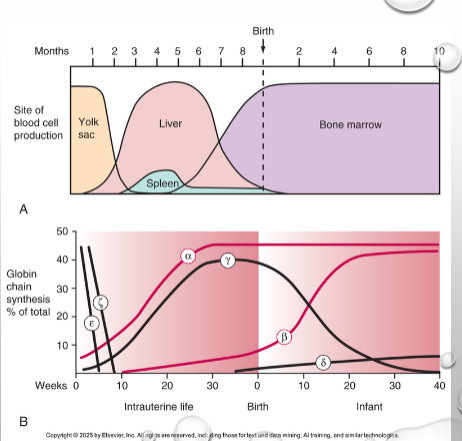
Fetal hemoglobin
HBF
Adult hemoglobin
HBA, HBA2
Alas
Rate limiting that regulates heme
Causes of Cell Damage
Excess globin chauin, protoporphyrinx IX, or iron accumaltes
Globin Regulation
Highly regulated to ensure balance; controlled at translation when MRNA codes for globin chain
13.5-18 g/dL
Hemoglobin reference range for men
12-16 g/dL
Hemoglobin reference range for women
16.5-21.5 g/dL
Hemoglobin reference range for newborns
1.34ml
The amount of oxygen carried by each gram of hemoglobin
1/3rbc
The space hemoglobin takes up in a rbc
Rule of 3
HGB * 3 = HCT ± 3; HCT/3 = HGB ± 3
Hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve
Affinity for oxygen is related to the partial pressure of oxygen
Low affinity
Oxygen at low oxygen tension
High affinity
Oxygen at high oxygen tension
Carbonic acid
Made form carbon dioxide diffusing into RBCs and water; then dissociates to release hydrogen and bicarbonate
Nitric Oxide Transport
Hemoglob binds, inactivates and transports nitric oxide that is secreted by vascular endothelial cells which causes relaxatio of vascular wall smooth muscle and vasodilation
Oxygen curve normal
PO2 ~ 27mmHG; 50% oxygen saturation; P50
Oxygen curve shift left
P50 <27 MMHG; higher oxygen affinity
Oxygen curve shift right
P50 >27mmHG; lower oxygen affinity
Myoglobin
Oxygen binding heme protein with greater affinity for oxygen than hemoglobin. Oxygen released only at very low partial pressure
Hemoglobin F
Higher affinity for oxygen resulting in a left shift of oxygen dissociation curve due to weakened ability to bind 2,3-DPG
Dyshemoglobins
Nonfunctional HB derivatives
Methehmoglobin
Hemoglobin with ferric iron; cannot bind to oxygen
Acquired Methemoglobin
Causes cyanosis; removal from toxic agent may suffice in treatment
Hereditary methemoglobin
HGM compromised 30-50% with no effective treatment; elevations occur in those who are homozygous or compound heterozygous
Sulfhemoglobin
Sulfur incorporated into HB; irreversible; ineffective in oxygen transport; presents with cyanosis
Carboxyhemoglobin
HB binds to carbon monoxide; 240*affinity vs oxygen (shift left); CO poisoning; 40% of this results in coma, seizure, hypotension, cardiac arrythmias, pulmonary edema, and death; cherry red blood and skin
Cyanmethemoglobin
Reference method for hemoglobin measurement; lysing agent frees hemoglobin from RBC; measured at 540NM spectrophotometrically