micro test
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
differences in rRNA
The phylogenetic classification of bacteria is based on
biochemical testing
based on the presence of bacterial enzymes
Serology
based on specific reactions between antibodies and the antigen
Nucleic Acid Hybridization
based on pairing between complimentary bases
DNA Base Comparison
based on the %G+C content
1.Differential Staining
2. Morphological Characteristics
3. Biochemical tests
4.Serology
Name 4 Identification methods used in a standard bacteriology lab
1.Nucleotide base composition (Guanine and Cytosine)
2.rRNA Sequences
Name 2 Methods that are NOT used to identify bacteria, but can be used in classification
Prions
an infectious protein
Latent viral infection
Virus remains asymptomatically in host cells for long period (ex. herpes simplex virus)
Persistent viral infection
Disease processes occur over a long period, generally fatal (ex. measles virus)
Stucture of Capsid
the viruses are divided into 4 morphological types based on
Helical Virus
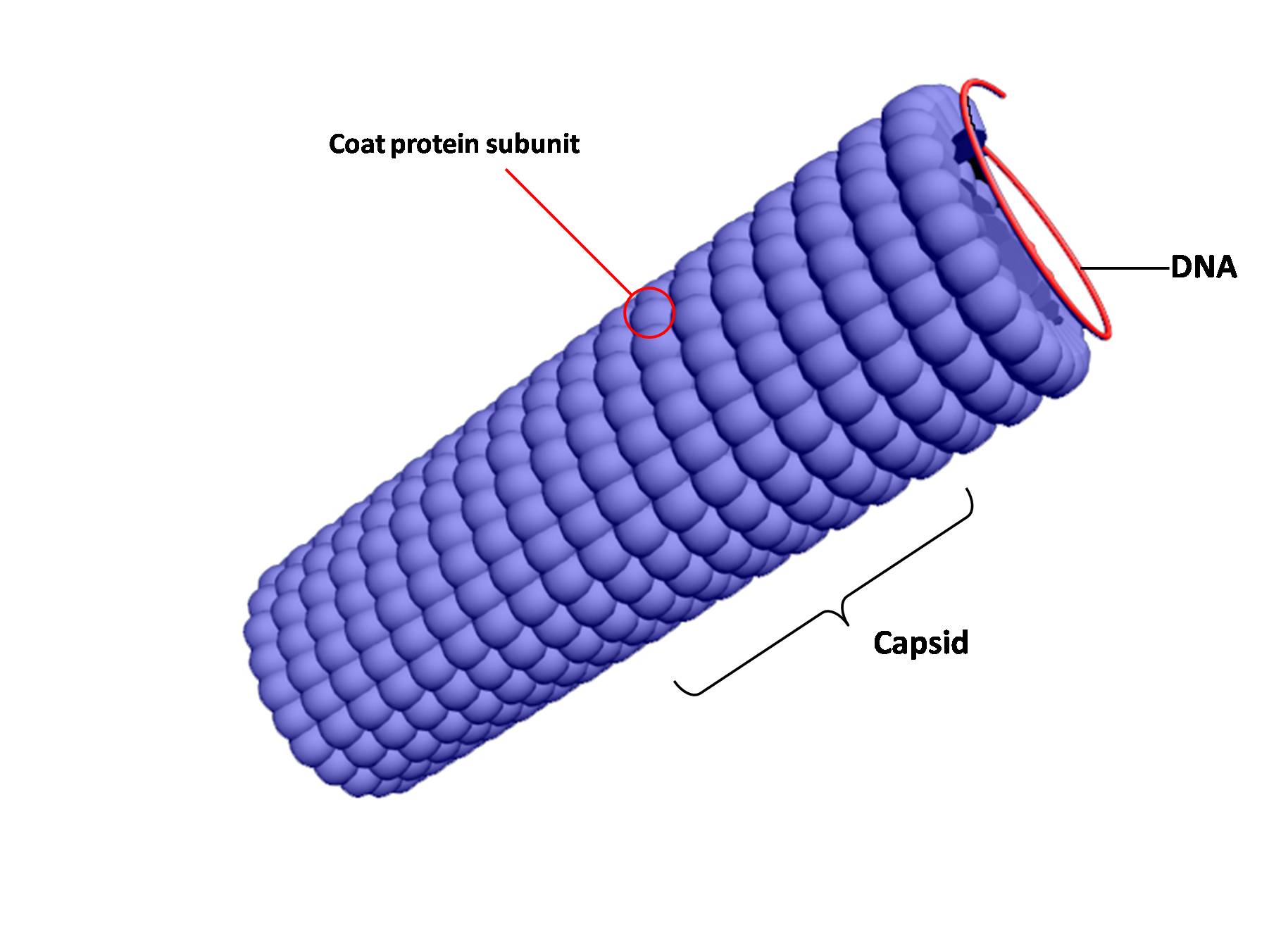
Polyhedral Virus
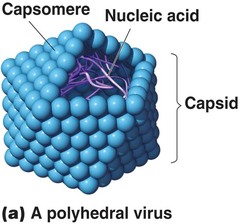
Envelope Virus
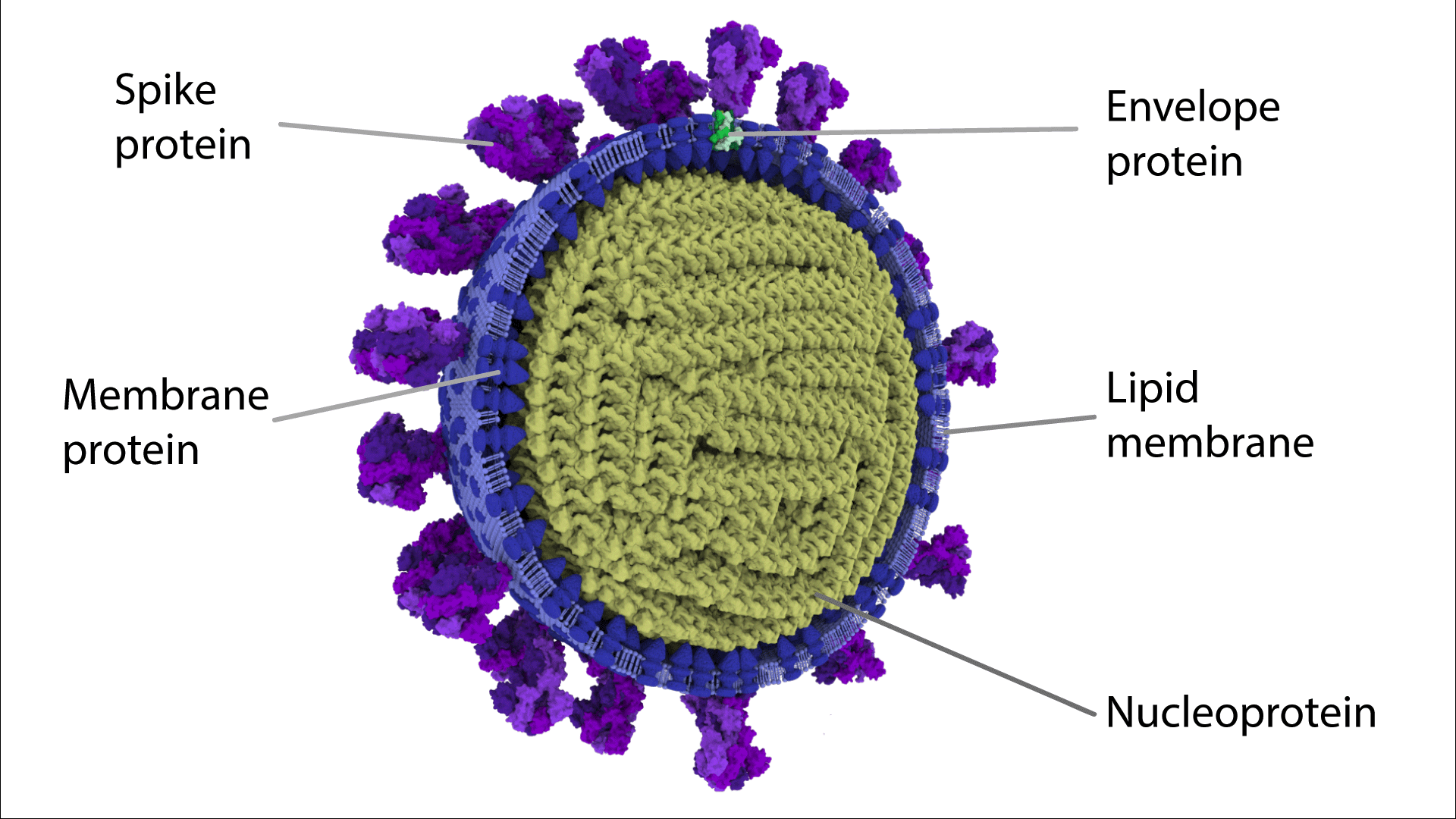
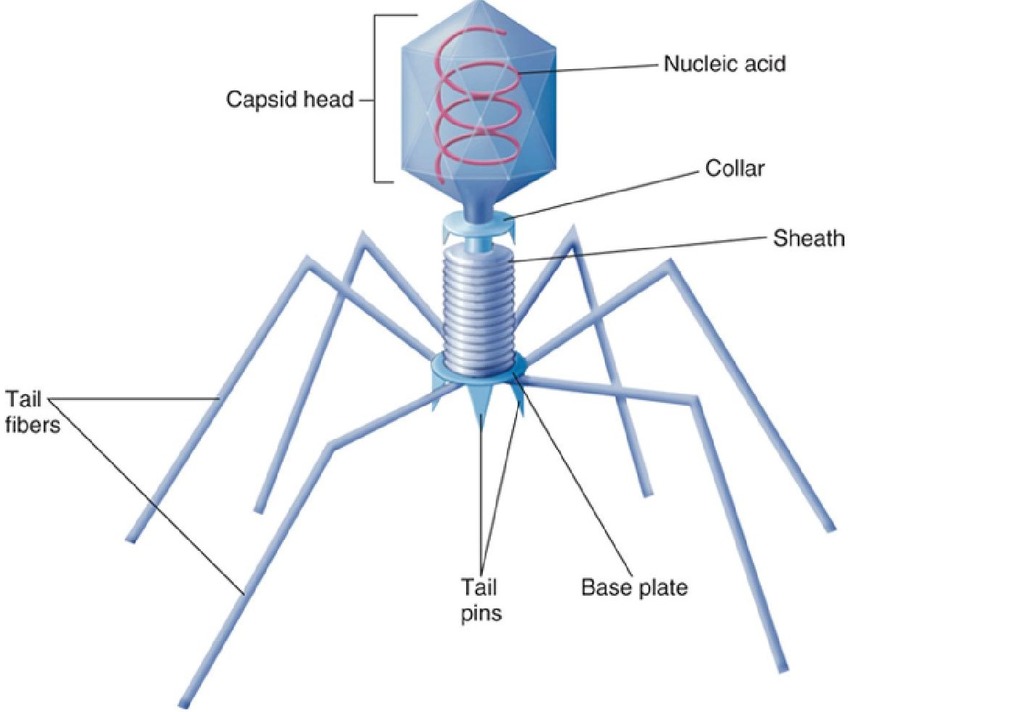
Complex Virus
Rotavirus
In “Human Rotavirus 2” what is the genus name?
Human Rotavirus
In “Human Rotavirus 2” what is the species name?
Human Rotavirus 2
In “Human Rotavirus 2” what is the sub species name?
Viral Species
a group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and ecological niche/host. Common names are used for species.
Lysogeny
phage DNA is incorporated into host cell DNA to form a prophage
Bacteriophage or phage
Viruses that infect bacteria
Cell Culture
eukaryotic cells (animal or plant) grow in culture media
Oncogenic Viruses
viruses that activate oncogenes, transform normal cells into cancerous cells
Mycobacterium
Acid-Fast stain is used to identify
Treponema
Spirochaete that cause Syphilis
haemophilus
Require hemoglobin or X and V factors for growth
Bordetella
Cause of pertussis (whooping cough)
Salmonella
Enteric Bacteria; cause of typhoid fever
Borrelia
Spirochaete that cause lyme disease
Yersinia
Transmitted by Fleas; cause of plague
Bartonella
Cause of cat-scratch disease
Streptococcus
Cause of great variety of diseases
Vibrio
Slightly curved rods; cause of cholera
Escherichia
most common inhabitant of the human intestinal tract
Mycoplasma
does not have a cell wall
clostridium
Cause of tetanus
Pseudomonas
Can grow at 4 C responsible for food spoilage
Neisseria
Gram negative diplococcus; cause of gonorrhea
Staphylococcus
grow in high salt concentrations
Rickettsia/ Enrlichia
require an arthropod for transmission
Corynebacterium
Cause of diphtheria
bacterial enzymes
biochemical testing is based on the presence of
genus
In the scientific name Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter is the:
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The following figure demonstrates how _________ works
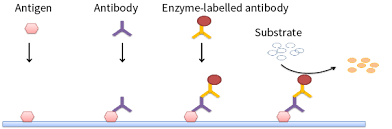
slide agglutination
western blot
ELISA
The following is an example for serological tests
Archaea
Are prokaryotic, unicellular, non-pathogenic, and lack peptidoglycan in their cell wall
aceae
in bacteria, the family name ends with
ales
order ends up with
Kingdom
for bacteria _____ is not assigned
Archae, bacteria, Eukarya
The three-domain system are
Bacteria
Are prokaryotic, pathogenic, has peptidoglycan in cell wall, and is sensitive to antibiotics.
Eukarya
is eukaryotic, cell wall varies; carbs
1.pathogens
2.mutations in cancer cells
3.genes responsible for genetic disorders
DNA chips and microarrays can be used to detect
Domain-phylum-class-order-family-genus-species
Correct order
rRNA sequence
bacteria are classified based on their
Western Blot
The following figure demonstrates how the ______________ works
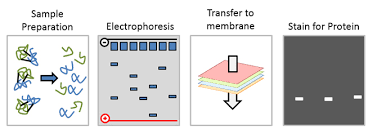
Polymerase Chain Reaction
PCR stands for
3&6
Gel electrophoresis with DNA fragments of 7 bacterial species are shown in the following figure, which of them are closely related?
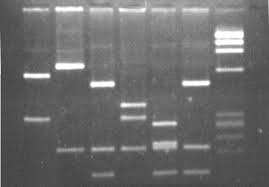
Taxonomy
Classifying organisms
Patient is A is positive for Salmonella because of clumps
Slide agglutination test was performed using the serum of two patients, patient A and patient B, to detect antigen for Salmonella,
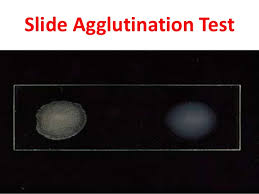
Serological testing is based on the fact that
Antibodies react specifically with an antigen
Their DNA can hybridize
What indicates that the two organisms are closely related
Phenotypic Classification
Based on the differences in bacterial morphology
Gram reaction
You have isolated a prokaryotic cell. The first step in identification is:
Mycoplasma
Small, pleomorphic, doesn’t have a cell wall
Leptospirosis, Lyme disease, syphilis
The bacteria in the following figure can cause:
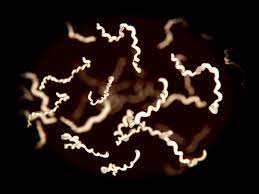
Clostridium Tetanii
causes tetanus, gram negative rods, produce terminal endospores
Shigella
infect only humans
Lyme
Rash at the bite site
Brucella
World’s most common zoonosis is caused by
Enterics are
gram negative rods, found in the human intestine.
Salmonella
Cause typhoid fever, enteric, all species of salmonella are pathogenic
Pseudomonas
grow at refrigerator temperatures
Proteobacteria
E.coli is a gram negative bacteria, hence it belongs to phylum
gram negative diplococcus
Neisseria gonorrhoeae can be identified by performing a simple gram stain because it is a:
1.chains
2.single or pairs
3.clusters
Arrangement of cocci can be
firmicute 33-44%
The (G+C) content of Bacillus anthracis is 35%, hence it belongs to phylum:
The two organisms are unrelated and belongs to two different phyla
The (G+C) content of organism X is 65% and (G+C) content of organism Y is 42%. Which of the following can be concluded from these data?
Actinobacteria
The (G+C) content of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is 66%, hence it belongs to phylum:
proteobacteria
gram negative bacteria
firmicutes and actinobacteria
gram positive bacteria
Chlamydia and spirochetes
Assorted Phyla
lysozymes
Bacteriophages derive all of the following from the host cell except:
Viroids
does not have a protein coat, consists mainly of ss RNA, are plant pathogens
Prions
infections proteins
latent Viruses
Some viruses, such as Human Herpes virus 1, infect cells without causing symptoms, these are called:
Coronaviridae
family
Human Coronavirus
species
coronavirus
genus
coronavirus 1 or 2
subspecies
Viridae
Virus family name ends with
they cannot reproduce themselves outside of a host cell
support the idea that viruses are non-living chemicals?
viruses
Cytopathic effects can be seen when cells are infected with:
cancer
Continuous cell lines originate from ______________________ cells.
electron
Viruses can be observed using a/an __________________ microscope.
Lytic Cycle
phage causes lysis and death of host cell
viridae
family names ends in
virus
genus names ends in
cytopathic effects
cells pile up and round up
Multiplication of bacteriophages(Lytic Cycle)
1.Attachment-phage attaches by tail fibers to host cell
2.Penetration-Phage lysozyme opens cell wall, tail sheath contracts to force tail core and DNA into cell
3. Biosynthesis-production of phage DNA and proteins
4.Maturation-Assembly of phage particles
5.Release-Phage lysozyme breaks cell wall