Chemistry- aldehydes and ketones 🟣
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Describe the bonding in carbonyl compounds
(Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides)
Carbonyl functional group
Planar carbon-oxygen double bond with bond angles of 120º
Why is the carbon-oxygen bond polar
due to the difference in electronegativities between carbon and oxygen
The more electronegative oxygen atom draws electrons in the double bond towards itself resulting in a delta positive charge on the carbon atom and delta negative on the oxygen
This leaves the delta positive carbon atom susceptible to attack by nucleophiles
Why are all carbonyl compounds unsaturated?
What reactions can they undergo?
Due to the C=O bond
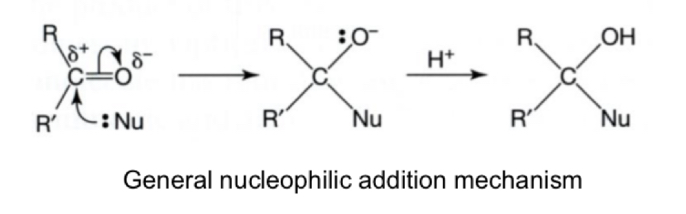
Nucleophilic addition reactions
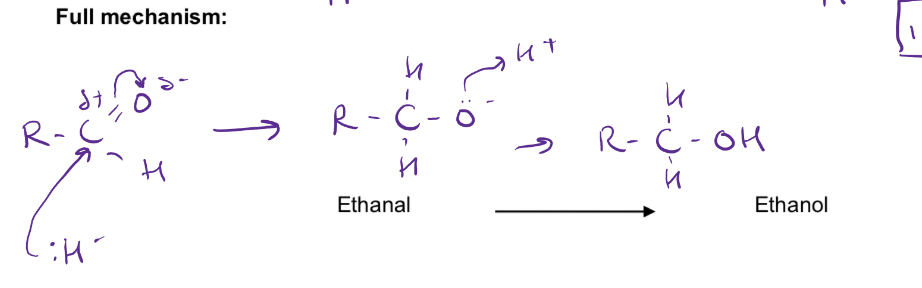
The nucleophile attacks the delta positive carbon and an addition reactions occurs
The carbon-oxygen bond becomes single (and H+ adds from acidified solution/water? to form neutral compound)
Steps of reduction of aldehydes and ketones
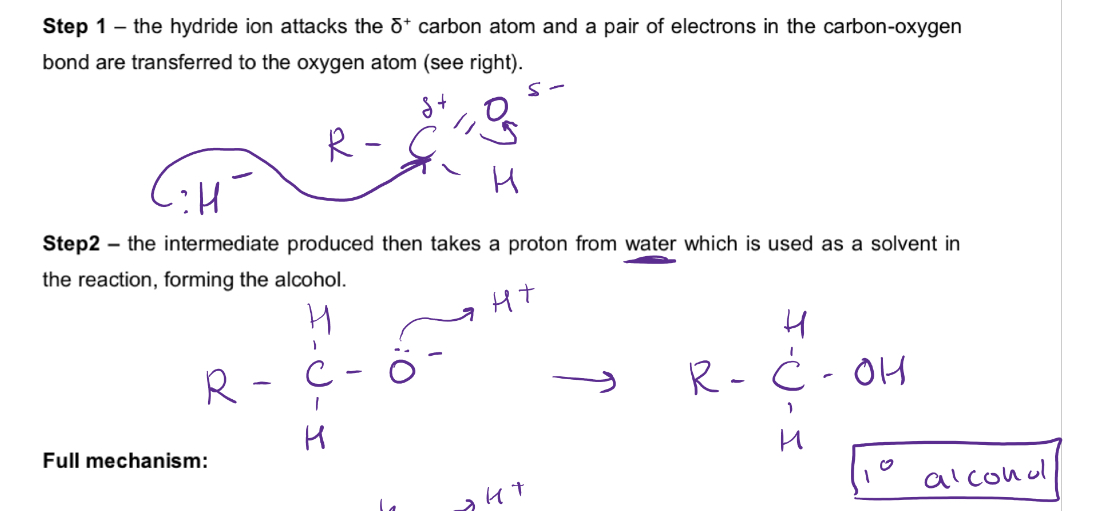
Reduction of carbonyls reagents and conditions
Reagent- NaBH4 in aqueous ethanol
Conditions- room temp and pressure
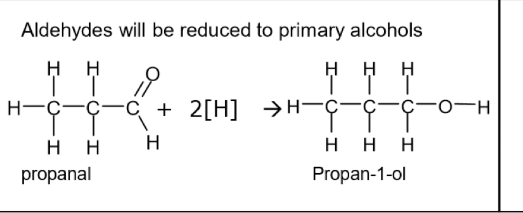
Reduction of aldehydes eg propanal reaction- reagents, conditions, equation
Aldehydes will be reduced to primary alcohols
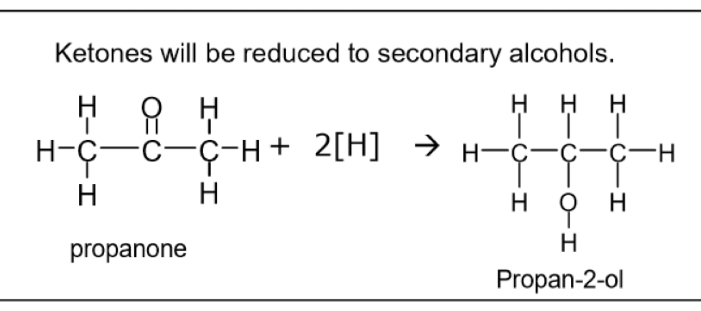
Reduction of ketones eg propanone reaction- reagents, conditions, equation
Nucleophilic addition mechanism for reduction of aldehydes eg ethanal
Nucleophilic addition mechanism for reduction of propanone
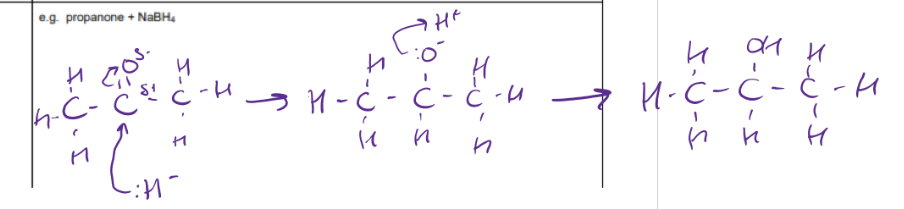
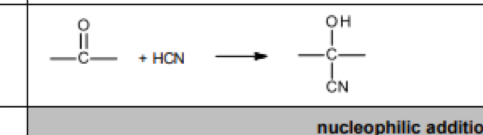
Reagent, conditions and equation nucleophilic addition reaction addition of HCN
KCN followed by dilute acid
Aqueous
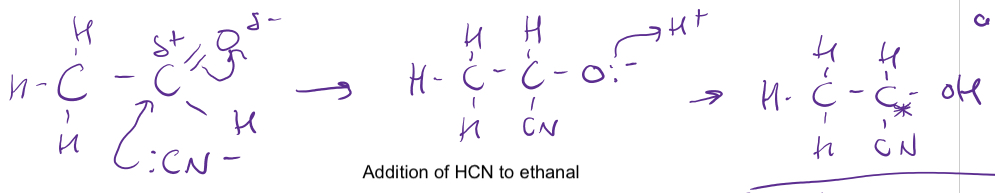
Steps of reaction of aldehydes and ketones with HCN
The lone pair of electrons in the carbon atom in the cyanide ion attacks the delta positive carbon atom of the aldehyde/ketone
The intermediate then takes a proton from the reaction solvent to form the hydroxynitrile
Extends the carbon chain by 1 carbon atom
As C=O group is planar, the CN- ion has an equal chance of attacking the delta positive carbon from above or below so a racemic mixture would be formed
Why dont we use HCN in the lab
What do we use instead and why
Highly toxic
HCN is a weak acid so only partially ionises into its ions so gives a low yield of :CN-
HCN rev → :CN- + H+
Instead use KCN as fully ionises into :CN- giving high yield of nucleophile (add H+ via sulfuric acid solvent)
KCN → K+ and :CN-
Mechanism for the nucleophilic addition of cyanide to aldehydes and ketones
Optical activity of symmetrical vs asymmetrical ketones
Symertrical ketone will not be optically active as there is no chiral centre in the product
Asymmetrical ketones will contain a chiral centre and show optical isomerism Eg butanone