AP biology Unit 3
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
enzymes work by
lowering the activation energy of a reaction
catabolism is to
break down molecules
anabolism
built up molecules
exergonic
release of energy
endergonic
energy is absorbed
pH will __________________ as H+ increases
decrease
competitive inhibition
binds to the enzyme's active site
noncompetitive inhibition
binds to allosteric site (not the active site) of an enzyme causing shape to change
Oxidation
is the lost of an electron
Reduction
is the gaining of electrons
what are the end products of glycolysis
2 pyruvates, net of 2 ATP, 2 NADH
substrate level phosphorylation
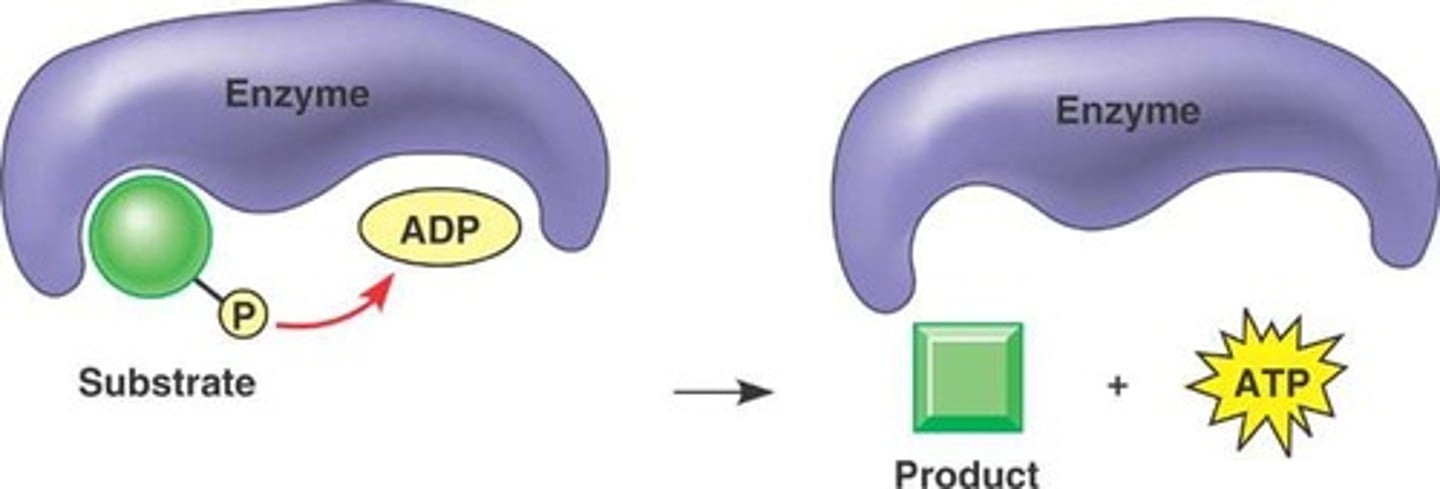
which of the steps of cellular respiration does not require oxygen
glycolysis
the prep step converts pyruvate into
acetyl-CoA
the final electron acceptor in the ETC of cellular respiration is
oxygen
NADH and FADH2 job is to
carry electrons to the ETC
after glycolosis if there is no oxygen available the pyruvate molecules can be converted into
ethanol or lactic acid
the two functions of fermentation
produce a little ATP and oxidize NADH to NAD+
What occurs as the electrons move from protein to protein in the ETC of cellular respiration?
H+ protons are pumped out into the intermembrane space
ATP synthase
produces ATP
Chemiosmosis
the diffusion of ions (H+) from area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
as the electron passes through the ETC the proteins embedded in the inter mitochondria membrane
alternate between being reduced and being oxidized
oxygen produced in the light reactions of photosynthesis comes from
the water
what are the products of the light reaction of photosynthesis
Oxygen, ATP, NADPH
where do the light reaction take place?
thylokoid membrane
what replaces the electron lost by P680
the electrons from the splitting of water
what replaces the electrons lost by P700
the electrons from P680 that has traveled down the ETC
RuBP is a 5 carbon molecule that
combines with CO2 in the Calvin Cycle
what enzyme combines RuBP with CO2
RuBisCo
the primary function of the Calvin Cycle is to produce
G3P/PGAL that will be used to make glucose
CAM plants keep stomata close in the daytime and are able to fix CO2 into ______________________
organic acids during the night and covert it back to CO2 in the morning to undergo the Calvin Cycle
photorespiration
uses oxygen instead of CO2 in the Calvin cycle