Biology 20-1 Unit D-2 (Human Cardiovascular System)
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Functions of the Circulatory Syste
Transport of Oxygen and Nutrients
Delivers O2 from lungs to blood
Nutrients from digestive system to cells throughout body
Removal of Waste Products and CO2 via lungs and kidneys
Regulation of Body Temperature and pH
Blood regulates body temperature by redistributing heat
maintains pH balance to ensure cellular function
Blood pH (CO2 transported in blood as a buffer system)
Defensive Mechanisms (Immune Response)
White blood cells fights infections and removing damaged cells (produce antibodies)
Immune system relies on the circulatory system to distribute antibodies
Clotting and Healing (Preventing / Stopping blood loss)
Platelets help in blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding when injured
Heart (Components of the Circulatory System)
Pumps blood throughout the body, ensuring circulation of oxygen and nutrients.
Enclosed in a fluid-filled membrane thats called the pericardium (Prevents friction (protection) between heart and surrounding tissues)
Muscle tissue that make up the heart wall is called myocardium
Myocardium is made of functional unit cells that are contractile called cardiomyocytes
Cardiac Muscles
Branched appearance
Striated
Have lots of mitochondria
Needs lots of ATP
Blood Vessels (Components of the Circulatory System)
Includes:
Arteries and Veins
Largest
Arterioles and Venules
Smaller
Capillaries
Smallest
Blood (Components of the Circulatory System)
Function:
Carries O2, nutrients, hormones, wastes, clotting factors (platelets), antibodies, and immune components
Types:
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): Carry O2 to all cells in body
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): Important to immune system
Platelets (Thrombocytes): Make Blood clot to stop bleeding
“cyte“ suffix = cell
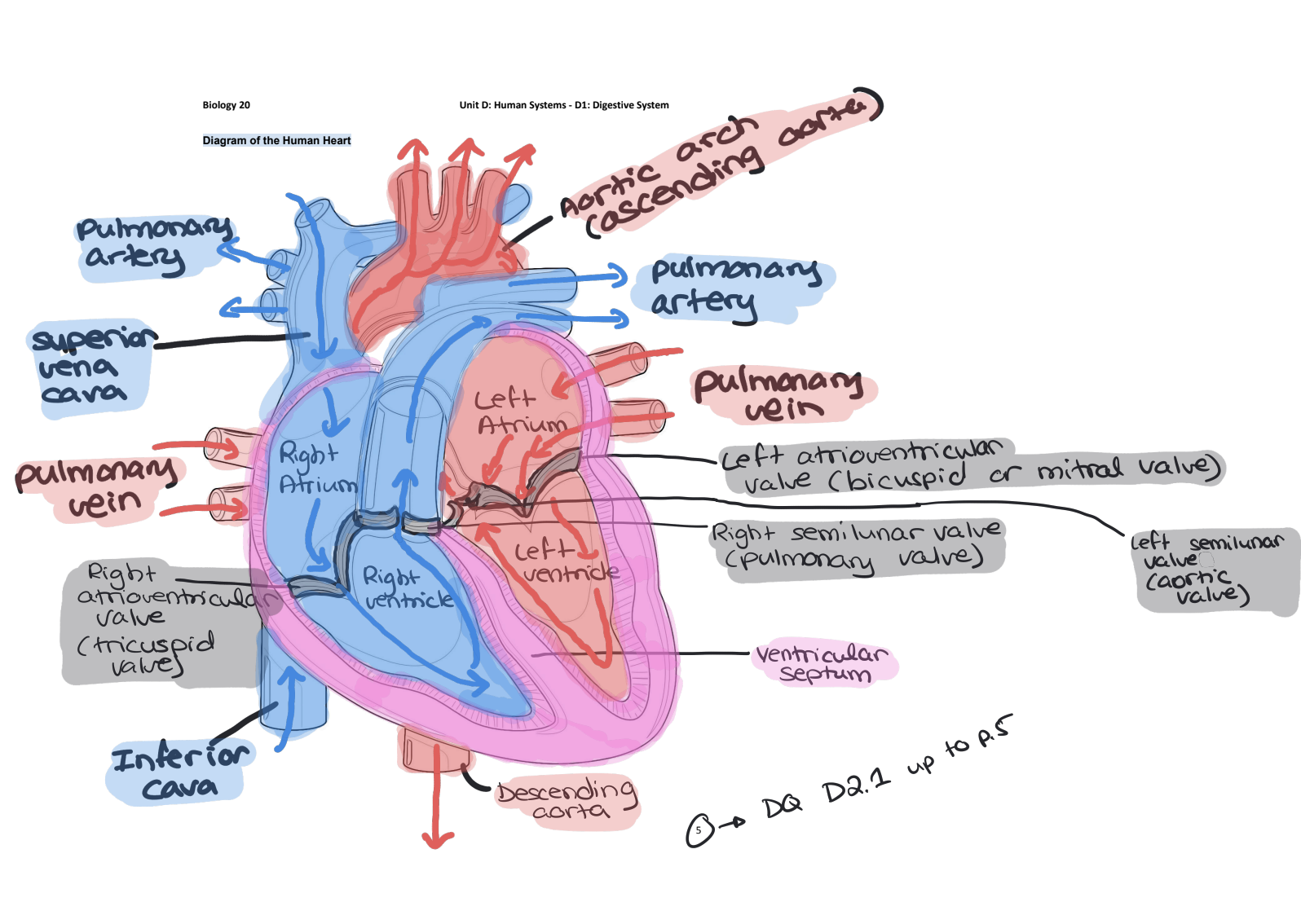
Structure of the Heart
4 Chambers:
Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from body
Right Ventricle: Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from lungs
Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to body
Heart is divided into 2 parallel systems separated by the septum to ensure no mixing of O2 rich and O2 poor blood
Pulmonary Circulation
Carries deoxygenated blood to lungs and returns oxygenated blood to heart
Systemic Circulation
Distributes oxygenated blood to body and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart
Full Heart
Parts:
Involve Deoxygenated Blood IN ORDER:
Superior Vena Cava
Inferior Vena Cava
Right Atrium
Right Ventricle
Pulmonary Artery
Involve Oxygenated Blood IN ORDER:
Pulmonary Vein
Left Atrium
Left Ventricle
Aortic Arch (Ascending Aorta)
Descending Aorta
All Valves:
Right Atrioventricular Valve (Tricuspid Valve)
Left Atrioventricular Valve (Bicuspid Valve or Mitral Valve)
Right Semilunar Valve (Pulmonary Valve)
Left Semilunar Valve (Aortic Valve)
4 Main Blood Vessels (Aorta)
Aorta (CARRIES Oxygenated blood): Largest blood vessel in the body, exits the left ventricle and goes to the rest of the body as well as the heart
Ascending Aorta
Supplies O2 rich blood to head + upper body
Aortic Arch
Loops up and down behind the heart
Descending Aorta
Supplies O2 rich blood to lower body
Aorta branches off into various arteries including coronary arteries
4 Main Blood Vessels (Vena Cava)
Vena Cava (CARRIES Deoxygenated blood): Largest vein in the body, enters in the right atrium from the rest of the body
Superior Vena Cava:
Blood returned thru veins to heart (venous) from top half of the body (all above diaphragm)
Inferior Vena Cava:
Blood returned thru veins to heart (venous) from bottom half of the body (all below diaphragm)
4 Main Blood Vessels (Pulmonary Arteries)
Pulmonary Arteries (CARRIES Deoxygenated blood): 4 pulmonary arteries, 2 to each lung, exits the right ventricle and goes to the lungs
ONLY ARTERY that carries DEOXYGENATED blood
4 Main Blood Vessels (Pulmonary Veins)
Pulmonary Veins (CARRIES Oxygenated blood): 4 pulmonary veins, 2 to each lung, enters the left ventricle and comes from the lungs
ONLY VEIN that carries OXYGENATED blood
2 of 4 Valves of the Heart (Atrioventricular (AV) Valves)
Atrioventricular (AV) Valves: Prevents back flow of blood into right/left atrium from ventricle
Right AV Valve: Tricuspid = Tri means 3 flaps opening/closing in the valve
Left AV Valve: Bicuspid (AKA Mitral) = Bi means 2 flaps opening/closing in the valve
2 of 4 Valves of the Heart (Semilunar Valves)
Semilunar Valves: Prevents back flow of blood into right/left ventricles from pulmonary artery/aorta
Pulmonary Valve: (Right Ventricle to Pulmonary Artery)
Aortic Valve: (Left Ventricle to Aorta)
Path of Blood Through the Heart
O2 poor blood enters the right atrium from superior/inferior vena cava
Passes tricuspid valve into right ventricle
Right ventricle pumps O2 poor blood thru pulmonary valve into pulmonary arteries and to the lungs
O2 rich blood enters left atrium from lungs thru pulmonary veins
Passes bicuspid valve into left ventricle
Left ventricle pumps O2 rich blood thru aortic valve to the the aorta which supplies the rest of the body
Heart Sounds
“LUB-DUB” sounds created by the heart because of the closing of the valves in the heart
“LUB”: Closing of AV valves during ventricular contractions (Systole)
“DUB”: Closing of Semilunar valves during ventricular relaxation (Diastole)
Myogenic
Means the heart can contract without external nerve stimulation
Generate their own electrochemical impulses
Trigger muscle contractions
different regions have different contraction rates with the atria contracting quicker then ventricles
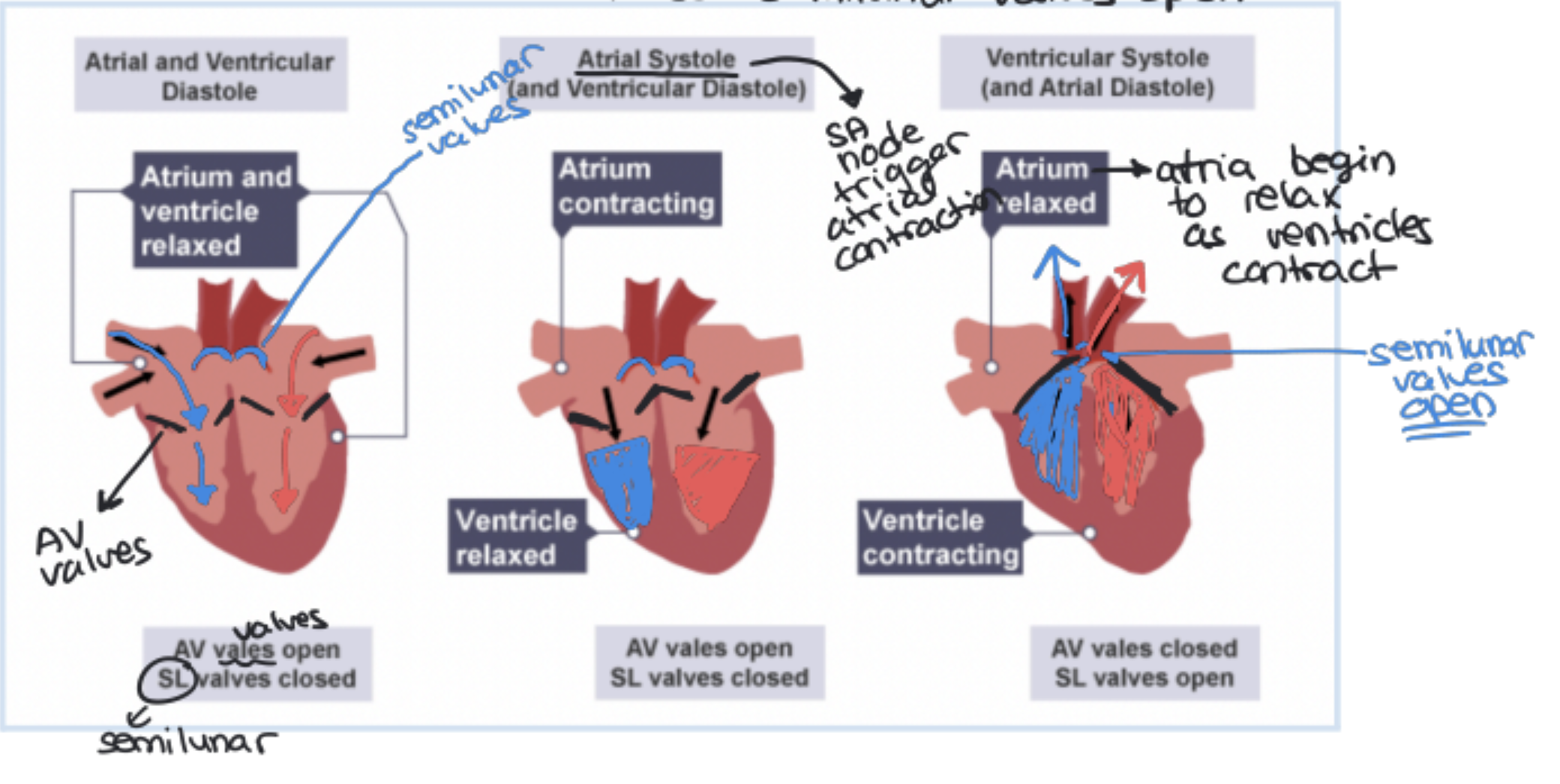
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
"Pacemaker" of the heart
○ Located in the upper right atrium.
○ Sets the heart rate at about 70 beats per minute.
○ Initiates electrical impulses that spread through the atria, causing them to contract.
2. Atrioventricular (AV) Node
Conductor of impulses
○ Located in the right atrioventricular region.
○ Receives impulses from the SA node and relays them down the Purkinje fibers.
3. Purkinje Fibers
Distribute impulses to ventricles
○ Run along the septum and spread electrical impulses to the ventricular walls.
○ Ensure the ventricles contract from the bottom up, efficiently pumping blood.
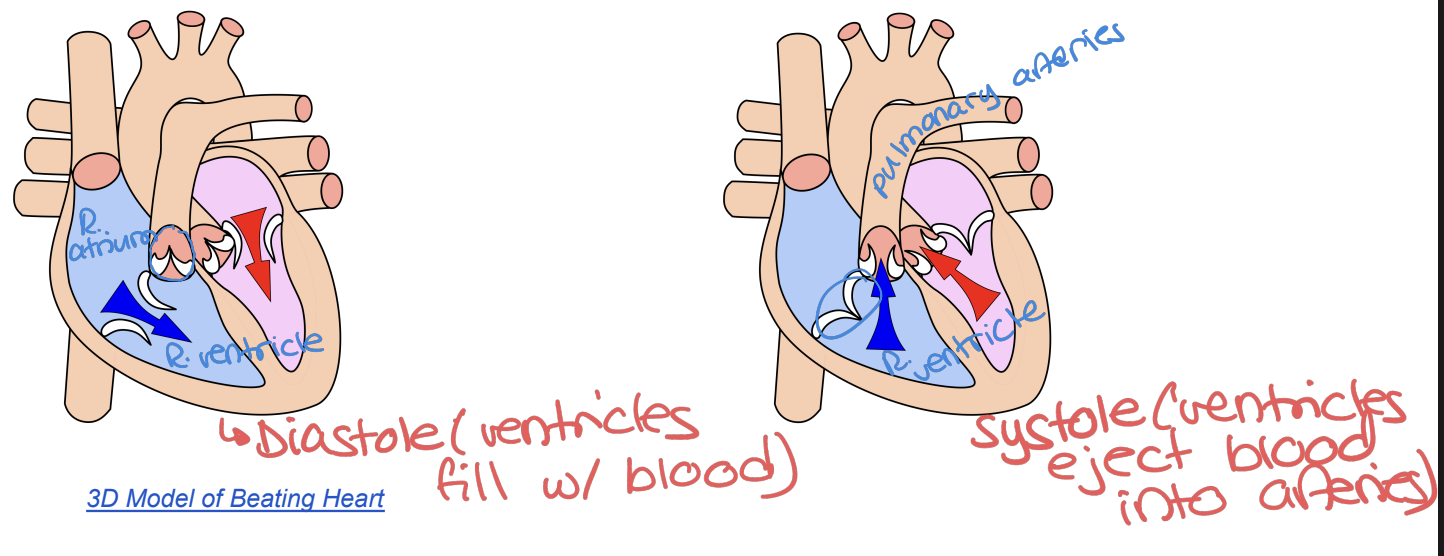
The Cardiac Cycle
3 Step Process:
Atrial and Ventricular Diastole (chambers are relaxed and filling with blood)
Atrial Systole (atria contract and remaining blood is pushed into ventricles)
Ventricular Systole (ventricles contract and push blood out through aorta and pulmonary artery)
Autonomic Nervous System Control
Sympathetic Nervous System: Increases heart rate (e.g. during stress).
Parasympathetic Nervous System: Slows heart rate (e.g., during relaxation).
Electrocardiogram (ECG) or (EKG)
Is a diagnostic tool that records the electrical activity of the heart over time
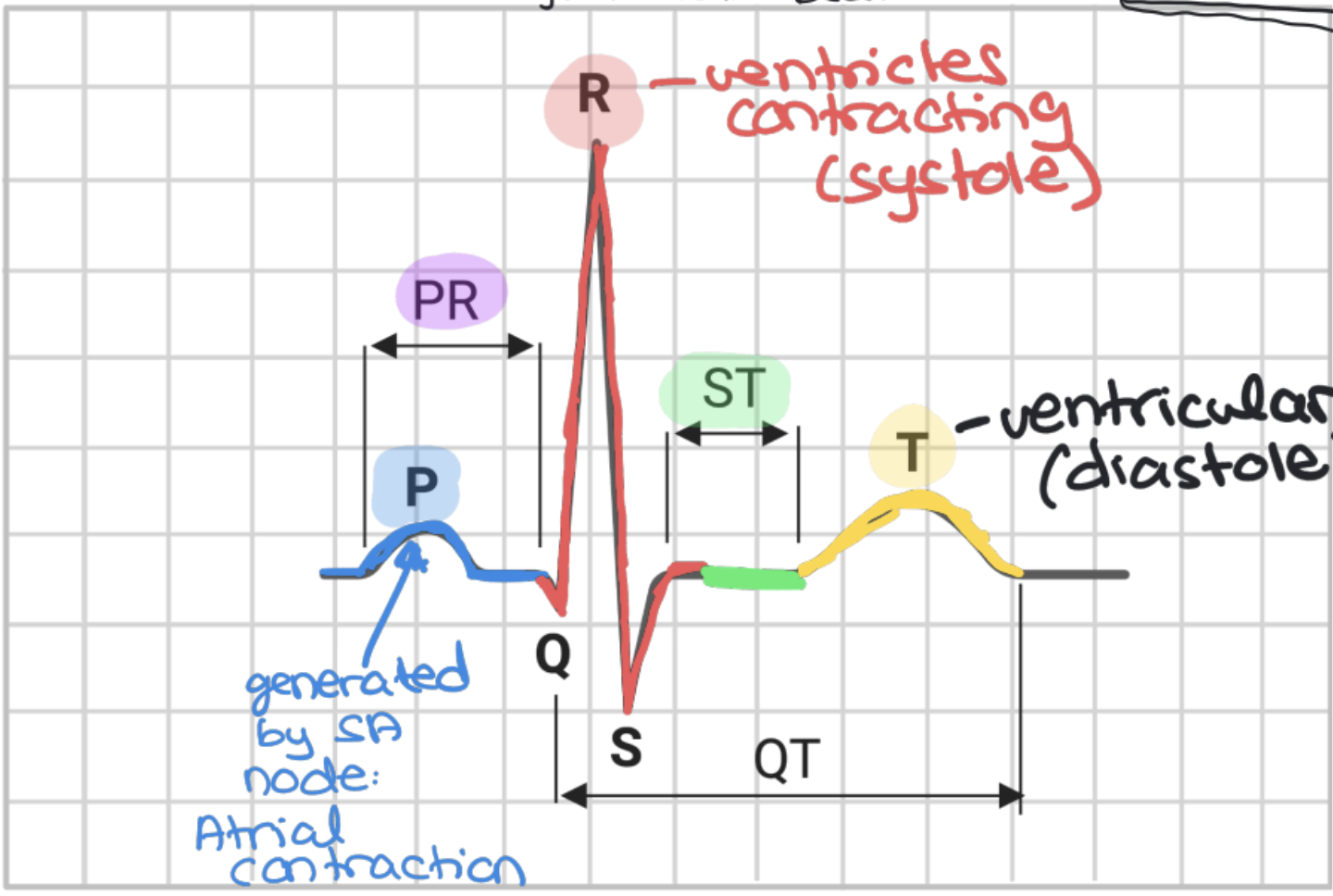
P Wave (on ECG)
represents the atrial depolarization (charge reversal, triggers muscle contraction)
QRS Complex (on ECG)
represents the ventricle depolarization (signals sent from the SA node to AV node —> leads to purkinje, triggers muscle contraction)
T Wave (on ECG)
represents the ventricle repolarization (charge reversal, triggers muscle relaxation)
PR Interval (on ECG)
Time implulse takes to travel from the SA node to the ventricles
ST Segment (on ECG)
Represents time between ventricular contraction and relaxation
Uses of ECG’s
Measure arrhythmias (irregular heart beats)
Identify heart attacks
Assesses electrical conduction problems
Watch vitals after receiving medication or pacemakers
Pacemaker
Electrical device implanted into the chest to regulate heartbeats, prevents arrhythmias.
Blood vessels
are responsible for transporting blood throughout the body.
Three main types: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
● (Leaving the heart) Arteries branch into arterioles which branch off into capillaries
● Capillaries then branch off into venules which branch into larger veins (Returning to the heart)
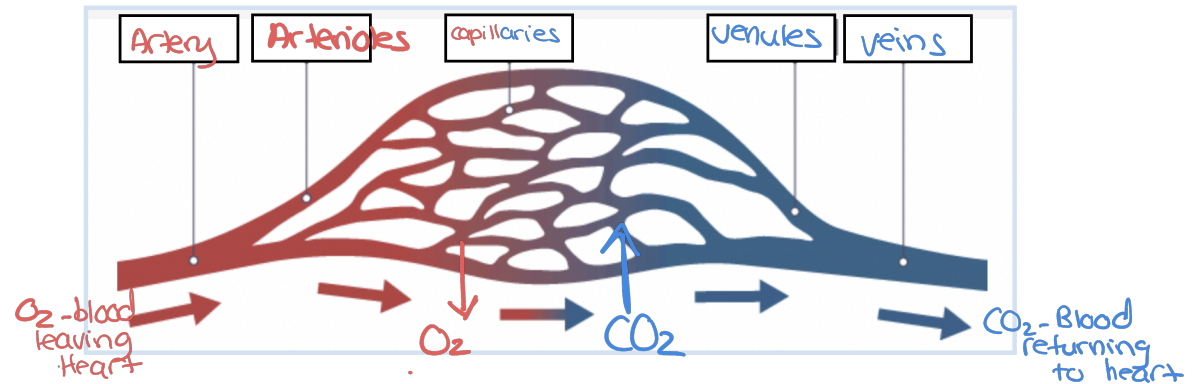
Arteries and arterioles
Function: Carries O2 rich blood away from the heart
Structure: has a very thick-walled structure (3 layers)
● Pulse: Arteries expand and contract with each heartbeat, creating a detectable pulse.
● Arterioles: Smaller branches of arteries, regulate blood flow into capillaries through (constricting or dilating)
High pressure
Capillaries
Function: Site of fluid, gas, and nutrient exchange between blood and tissues (selectively permeable which is why proteins stay in blood)
Structure: Extremely thin walls with a small diameter (one-cell layer thick thats only one red blood cell thick) to allow diffusion (gas exchange - CO2, O2).
Capillary Beds
Beds: Networks of capillaries supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues (capillary beds/networks surround tissues)
Veins and Venules
Function: Carry O2 poor blood toward the heart
Structure: Thinner walls compared to arteries, as pressure is lower. Contain valves to prevent backflow of blood. Skeletal muscle contractions help push blood through veins toward the heart.
● Venules: Small veins that collect blood from capillaries and
transport it to larger veins.
● Blood Reservoir: Veins store about 65% of total blood
volume and can redirect blood to other parts of the body
when needed (e.g. blood loss).
Blood Flow Regulation
● The autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions, regulates the diameter of the arterioles
○ Vasoconstriction: Arterioles constrict to reduce blood flow (e.g., during cold exposure).
○ Vasodilation: Arterioles relax to increase blood flow (e.g., when blushing or during exercise).
● Effects on Circulation:
○ Increased metabolic activity → more vasodilation → increased oxygen supply.
○ Fight-or-flight response → blood redirected to muscles and vital organs.
Common Disorders
● Atherosclerosis: Plaque buildup in arteries, narrowing the passage and reducing blood flow.
● Aneurysm: A weakened artery wall bulges and may rupture, leading to serious complications like a stroke.
● Varicose Veins: Weak or damaged vein valves cause blood pooling, leading to swollen twisted veins.
Cardiac output
Is the amount of blood the heart is able to pump per minute
Stroke volume × Heart rate
Average resting person pumps about 4900 mL/min.
Stroke volume
amount of blood pumped per heartbeat
Blood pressure
The force exerted on the arteriole walls by the blood.
Baroreceptors
Pressure-sensitive receptors located in the aorta and carotid arteries that detect changes in blood pressure and signal the brain.
Hypertension
A condition of chronically high blood pressure, increasing the risk of stroke, heart attack, and kidney disease
Sphygmomanometer
A device used to measure blood pressure, typically reported as systolic/diastolic pressure (e.g., 120/80 mmHg).
Systolic Pressure
The pressure in arteries when the heart contracts (ventricular systole).
Diastolic Pressure
The pressure in arteries when the heart relaxes (ventricular diastole).
Metabolic Control of Blood Flow
Blood flow regulation based on tissue activity—active tissues trigger vasodilation for more oxygen, while inactive tissues receive less blood.
Homeostasis
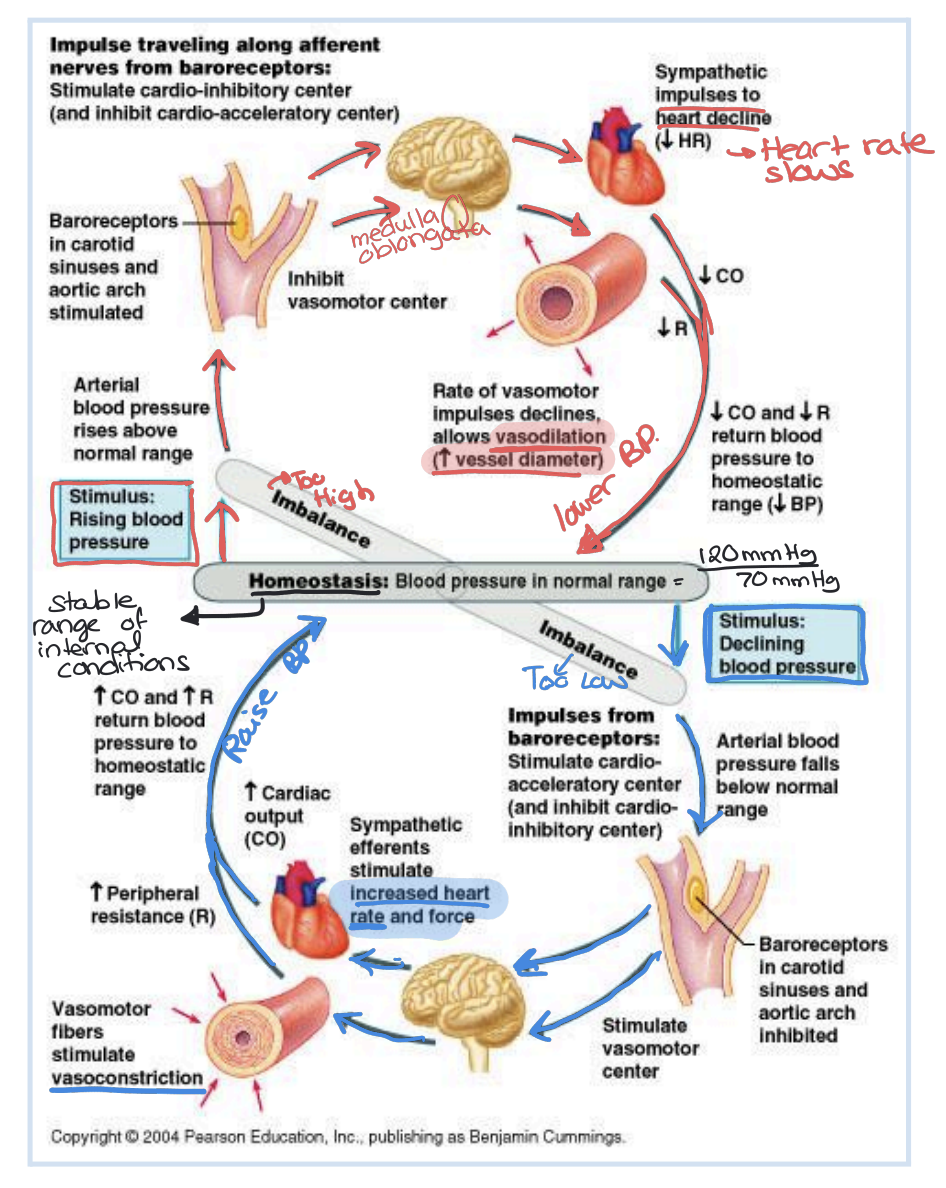
Thermoregulation
The body's ability to regulate temperature by vasodilation (heat release) or vasoconstriction (heat retention).
Filtration
The selective movement of materials through the capillary walls by a pressure gradient into the Extracellular fluid
At the arterioles pressure is higher than in the Extracellular fluid causing the materials to move out
Reabsorption
Osmotic pressure drives movement of materials from the Extracellular fluid into the venules by a pressure gradient
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Occupies the gap between cells and tissue made of plasma (not the same one as in blood) and interstitial fluid
Between capillaries/arterioles/venules and the muscular tissue
Osmotic pressure
The minimum pressure needed to prevent the net movement of solvent (usually water) from a solution with a lower solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration across a semi-permeable membrane
Fluid pressure
the force exerted by a fluid, like blood or interstitial fluid, against the walls of a vessel or tissue
Maintaining Equilibrium in Capillary Fluid Exchange
Balance of osmotic and fluid pressure which is important in maintaining equilibrium in the body
If disrupted:
Hemorrhage (Excessive internal / external bleeding): Decreased blood volume causes fluid pressure to decrease, but osmotic pressure stays the same THEREFORE blood is drawn back into the capillaries (lower filtration)
Starvation: Causes swelling, plasma proteins in blood are used as a last resort leading to osmotic pressure to decrease, but fluid pressure stays the same THEREFORE less reabsorption
Inflammation (Allergic response): A chemical Histamine is released by cells who believe they are being attacked, this causes capillary permeability to increase (proteins enter ECF) and lowers osmotic pressure THEREFORE less fluid reabsorption
Lymphatic System
Network of vessels and nodes that helps maintain fluid balance and supports the immune system
Drains excess proteins and fluids from tissues and returns them to the circulatory system/heart
Lymph
Clear fluid similar to blood plasma with white blood cells, proteins, and cellular debris in it
Lymph Vessels
A whole other set of vessels under the capillaries that to the following:
Transport lymph one-way direction (like veins)
Contain valves to prevent back-flow (low pressure)
Depends on muscle contractions and low pressure
Lymph nodes
Found in the intervals along the lymph vessels
Function:
Filter bacteria, damaged cells, and debris from lymph
contain white blood cells (lymphocytes) that use phagocytosis (form of endocytosis where white blood cells eat pathogens) to fend off invaders
swell during infections because of increased immune activity
Lymphoid organs
Places where lymph is stored/produced include:
Red bone marrow: produces all blood cell types including white blood cells
Found in most bones in kids and in the skull, sternum, ribs, spine and long bones
Thymus Gland: located above the heart and is where T lymphocytes mature
Spleen: Stores and purifies blood (filters damaged cells)
Releases red blood cells in response to low O2 levels or low blood pressure
Main Components of Blood
55% Plasma: Fluid portion containing water, electrolytes, proteins, glucose, hormones, and waste.
45% Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): Transport oxygen via hemoglobin (iron-containing protein)
<1% White Blood Cells ((Leukocytes): <1%): Defend against infections and foreign substances (pathogens)
Platelets: Small cell fragments involved in blood clotting
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
Biconcave disc shape (concave on both sides) → Increases surface area by 20-30% for better gas exchange.
● Primary function: Transport oxygen via hemoglobin (O2 binding protein in red blood cells)
● Lifespan: ~120 days, after which they become brittle and rupture in narrow capillaries (get broken down)
● No nucleus in mature RBCs, allowing more space for hemoglobin but preventing self-replication (continuously broken up, continuously built up)
● RBC count per milliliter of blood:
● Males: ~5.5 billion.
● Females: ~4.5 billion.
● High-altitude individuals (Including Calgary): Up to 8 billion for better oxygen transport
Hemoglobin and Oxygen Transport
Each RBC contains 280 million hemoglobin
molecules.
Hemoglobin structure:
Heme group (contains iron) binds to oxygen.
Globin protein structure supports the molecule.
Oxyhemoglobin: Hemoglobin bound to oxygen → Bright red color (Arterial Blood).
Deoxygenated Hemoglobin: When oxygen is released, it changes shape, resulting in a darker red colour (Venous Blood)
Carbon dioxide transport
27% binds to hemoglobin → Carbaminohemoglobin.
64% forms bicarbonate ions to maintain pH balance
Most CO2 is transported as HCO3- in plasma
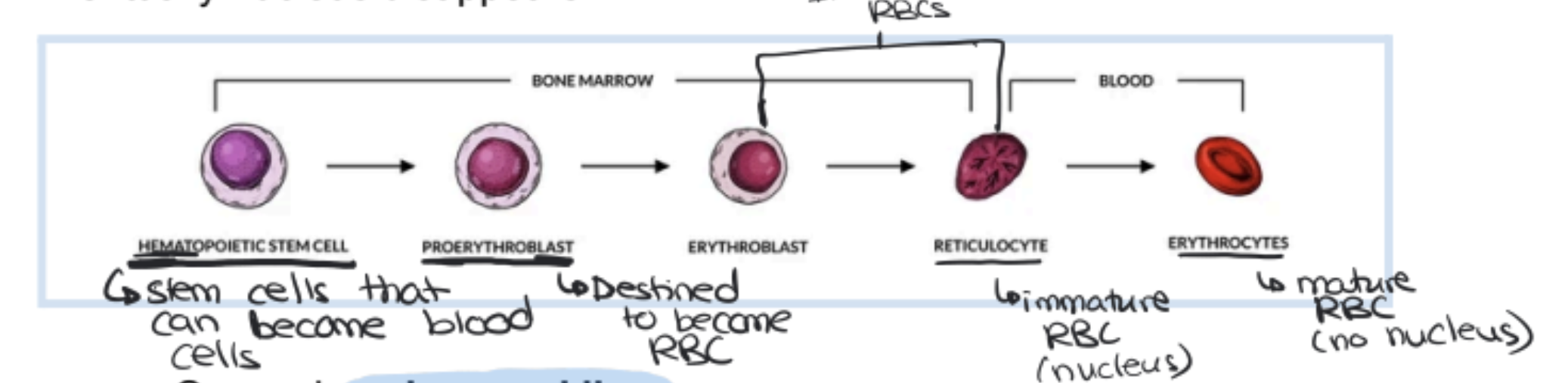
Erythropoiesis and Cellular Breakdown
Erythropoiesis (How RBC’s are born) is the process by which red blood cells are made
Produced in bone marrow from nucleated stem cells (undifferentiated potential to become different types of cells)
Cells divide and shrink as they take up hemoglobin
Eventually nucleus disappears
Breakdown process: Occurs in spleen and liver.
Hemoglobin breakdown → Iron is stored in liver and bone marrow for new RBC production.
Heme group → Converted into bile pigments (in liver)
RBC Disorders and Adaptations
Anemia: Low RBC or hemoglobin levels → Reduced oxygen delivery, fatigue, weakness.
Causes: Blood loss, iron deficiency, bone marrow
disorders, genetics (sickle cell anemia)
Erythropoietin (EPO): Hormone that stimulates RBC production in response to low oxygen levels.
High-altitude adaptation: People who live at high altitudes have more hemoglobin for efficient oxygen transport
Blood Types
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner in the early 20th century.
Differences in blood types are due to glycoprotein markers (antigens) on red blood cells
Antigens are a surface marker of cells (exist to signal to the immune cells that they are a part of the body)
ABO Blood Group System
Blood types are classified based on A and B antigens present on red blood cells.
Individuals also have antibodies in their plasma that react against foreign blood antigens.
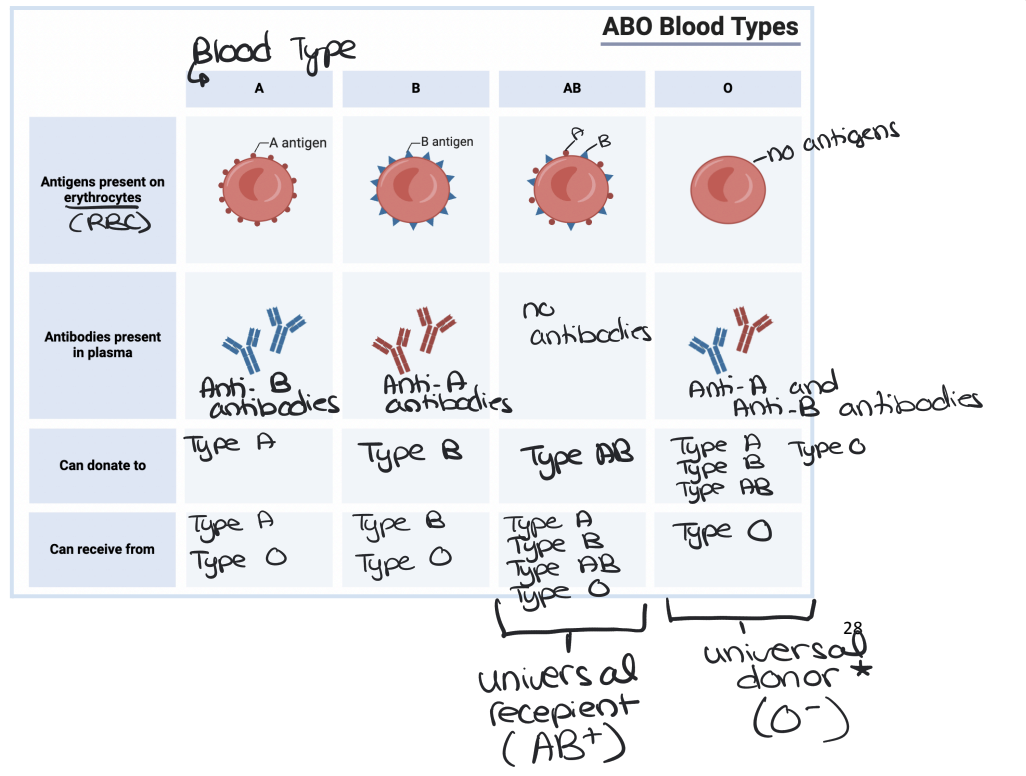
Agglutination (clumping)
occurs if incompatible blood types mix.
● Example: Type O cannot receive A or B blood because it produces antibodies against both antigens
Rhesus (Rh) Factor
A separate blood antigen discovered in the 1940s.
● Rh+ individuals have the Rh antigen; Rh- individuals lack it.
● Rh- individuals should not receive Rh+ blood as their immune system may develop antibodies against it (anti-Rh antibodies)
Universal Donor
Blood Type O- because there are no antigens so it doesn’t trigger the immune system
Universal Recipient
Blood Type AB+ because it has all of the antigens so it doesn’t produce antigens against any blood types
Mismatched Transfusions
Can cause fatal immune reactions due to agglutination and blockage of the capillaries
Rh Incompatibility in Pregnancy (Erthroblastosis Fetalis)
Only occurs in Rh- mothers carrying a Rh+ baby
Rh- mother, Rh+ father
The first pregnancy usually has little danger but during childbirth fetal and maternal blood can mix in the mothers bloodstream triggering the production of antibodies in the blood
In the second and all other pregnancies the maternal antibodies that formed in the first birth attack the Rh+ fetus and causes anemia, jaundice and organ enlargement
ALL of this can be prevented by the RhoGAM injection which prevents antibody formation
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
They have no nucleus, are irregular shapes, and are produced in bone marrow.
Initiates the Blood Clotting Process in 3 steps
Platelet Activation:
When a blood vessel is injured platelets adhere to the damaged area
platelets change shape and release clotting factors such as Thromboplastin
Formation of a Clotting Cascade
Thromboplastin (from platelets) + Calcium Ions —> Activates Prothrombin
Prothrombin (A plasma protein from the liver) is converted to Thrombin
Formation of Fibrin Mesh
Thrombin acts like an enzyme, cutting amino acids from fibrinogen (another plasma protein)
The fibrinogen then converts to fibrin and fibrin forms a mesh that traps the red blood cells and more platelets to seal the wound
This is what a scab is on external wounds
Blood Clot Disorders
Cerebral Thrombosis: Clot in the Brain (causes a stroke)
Coronary Thrombosis: Clot in the coronary artery (causes a heart attack)
Embolism: A clot (embolus) dislodges and moves through the bloodstream potentially blocking vital organs
The Immune System
Protects the body from harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
Antigens
Are foreign substances (proteins on pathogens) that trigger an immune response
The immune system recognizes its own antigens and attacks foreign antigens
Defense System of the Immune System
The first line of defence is physical and chemical barriers with physical barriers like skin which encapsulates the whole body for protection, mucous membranes that can trap pathogens inside of its sticky mucus. The chemical barriers which would burn or disintegrate the pathogens include acidic skin secretions, stomach acid, and lysozymes in saliva and tears.
The second line of defence is non-specific immunity where phagocytosis occurs which is when macrophages or neutrophils swallow the pathogens. It also has the inflammatory response in which is when the body increases blood flow to the affected area to bring immune cells (like phagocytes) to fight pathogens.
The third line of defence is specific immunity which involves lymphocytes (B cells and T cells), which recognize and attack specific pathogens. There are 3 types of B and T cells including: helper T cells which activate B cells, killer T cells which Destroy infected cells by puncturing the membranes, suppressor T cells which Inhibit the immune response, plasma B cells which Produce lots of antibodies, and memory B cells which store antigen information for faster responses in the future
Antibody-Antigen Interaction
Antibodies bind to Antigens —> Form antigen-antibody complexs which:
Mark pathogens for destruction by macrophages
Neutralize toxins by blocking their binding sites
Prevent viruses from attaching to host cells
covering acceptors
Immune Memory and Vaccination
Memory B cells ensure a faster and stronger response upon reinfection
Vaccines introduce weakened pathogens to stimulate memory cell production