DNA & RNA
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
1
New cards
Why do we add detergent or soap to the squished strawberries in the DNA extraction lab?
To dissolve the nuclear membrane
2
New cards
In prokaryotic cells, where is the DNA found in the cell?
Cytoplasm
3
New cards
What was the source of your DNA in the DNA extraction lab?
DNA contained in your cheek cells
4
New cards
Which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines?
* Cytosine
* thymine
* uracil
* thymine
* uracil
5
New cards
Which nitrogenous bases are purines?
* Guanine
* Adenine
* Adenine
6
New cards
What are the nucleotides made of?
* Sugar
* phosphate
* nitrogen base
* phosphate
* nitrogen base
7
New cards
Guanine bonds with ________.
Cytosine
8
New cards
The shape of an entire DNA molecule is?
Double helix
9
New cards
Which parts of the nucleotide are connected by a covalent bond?
* Sugar group
* phosphate group
* phosphate group
10
New cards
What type of bond connects nitrogenous bases?
Hydrogen bonds
11
New cards
What is similar between a strawberries, DNA and human DNA?
* The “backbone” is made of sugars and phosphates
* The number of strands in the DNA molecule
* The number of strands in the DNA molecule
12
New cards
Adenine bonds with _______
Thymine
13
New cards
Cytosine bonds with ________
Guanine
14
New cards
Thymine bonds with ______
Adenine
15
New cards
\
Why do we had alcohol to the solution of detergent and strawberries in the DNA extraction lab?
Why do we had alcohol to the solution of detergent and strawberries in the DNA extraction lab?
To isolate the DNA, which is repelled by alcohol
16
New cards
Why do we smash the strawberry very well for a few minutes in the DNA extraction lab?
To the break the cell walls
17
New cards
What is the sugar in DNA?
deoxyribose
18
New cards
What is the sequence of DNA bases that would pair with this partial strand— ATG TGA CAG?
TAC ACT GTC
19
New cards
In eukaryotic cells, where is DNA found in the cell?
Nucleus
20
New cards
What about a strawberries DNA is different from your human DNA?
* The arrangement of the bases
21
New cards
What part of the DNA molecule makes up the rungs of the ladder?
Nitrogenous bases
22
New cards
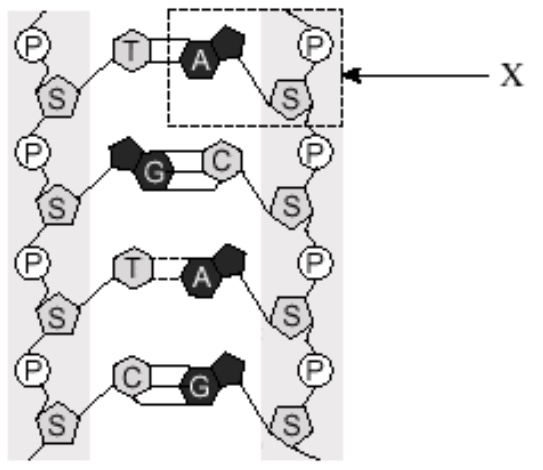
X outlines a(n)
Nucleotide
23
New cards
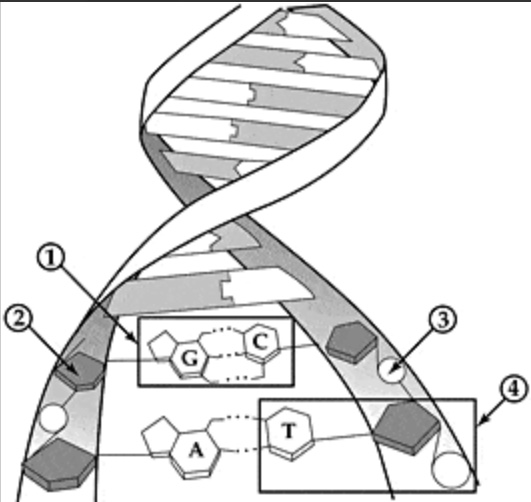
Identify #2
Deoxyribose sugar
24
New cards
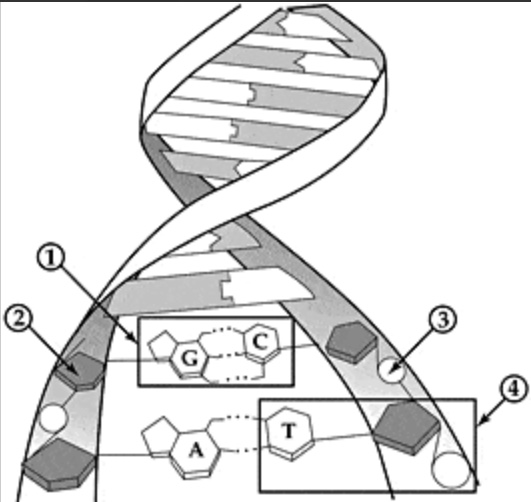
Identify #1
Base pairs
25
New cards
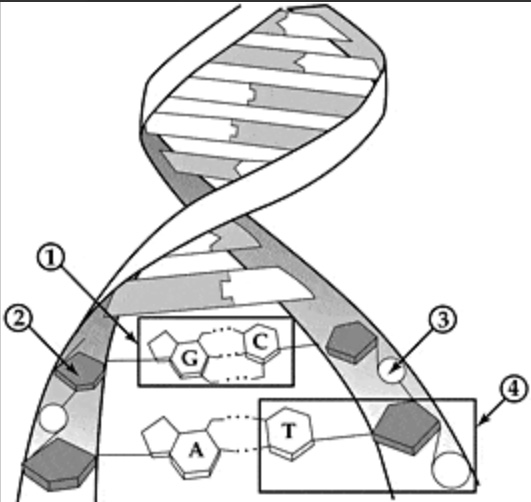
Identify #3
Phosphate
26
New cards
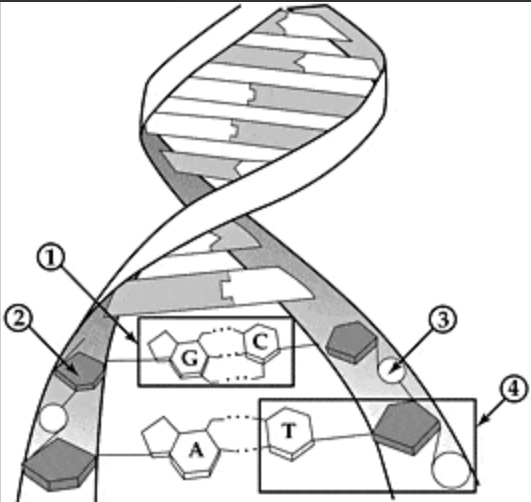
Identify #4
Nucleotide
27
New cards
A single subunit of DNA is called a:
Nucleotide
28
New cards
What is an organism’s genome?
all the genes in an organism
29
New cards
What are genes?
Information about how cells function and information about characteristics
30
New cards
What is the genome made up of?
chromosomes and chromatin
31
New cards
What are chromosomes made of?
Nuclear DNA
32
New cards
What is in the prokaryotic genome?
singular circular DNA molecule
33
New cards
What is the eukaryotic genome made of?
multiple chromosomes and histones
34
New cards
What are histones?
The silver thing wrapping around
They help “pack in” the genetic material
Wrap or spool the DNA into nucleosomes
They help “pack in” the genetic material
Wrap or spool the DNA into nucleosomes
35
New cards
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
36
New cards
What is the structure of DNA?
Double helix and nucleotides
37
New cards
What nucleotides made of?
Sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogenous Base
38
New cards
Which bases are purines?
Adenine and Guanine
39
New cards
What bases are the pyrimidines?
thymine, cytosine, and uracil
40
New cards
Where is uracil located?
in RNA
41
New cards
What is the formation of the double helix?
sides and rungs
42
New cards
What are the sides of the double helix made out of?
sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate group
43
New cards
What are the rungs of the double helix made of?
nitrogenous bases
44
New cards
What are the two sides of the DNA ladder held together with?
hydrogen bonds?
45
New cards
How many hydrogen bonds hold Adenine and Thymine together?
2 hydrogen bonds
46
New cards
How many hydrogen bonds hold Cytosine and Guanine together?
3 hydrogen bonds
47
New cards
What forms 2 complimentary sides to the DNA ladders?
the base pairings
48
New cards
How many base pairs are in each full turn of the helix?
10
49
New cards
Describe the chains that run in opposite directions
One strand has an exposed phosphate and one strand has an exposed hydroxyl group (-OH)
50
New cards
What is mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)?
genetic material unique to the mitochondria
51
New cards
What does mitochondrial DNA contain?
Contains information for 37 genes. The instructions for making enzymes in ATP production and for making transfer and ribosomal RNA.
52
New cards
Who is mitochondrial DNA inherited from?
the mother, it is a key indicator for tracing human heritage and migrations
53
New cards
What are the key components in the construction of a DNA molecule?
Deoxyribose, Phosphate, Hydrogen Bonds, Nitrogen Bases (Purines and Pyrimidines), the Nucleotide made of the sugar, phosphate, and the base.
54
New cards
What is the purpose of replication?
A way to copy the DNA during cell division. The cell can’t reproduce or grow without replication.
55
New cards
What kind of process is the replication process?
Semiconservative Process
56
New cards
What is a semiconservative process?
Each side pairs with a new “side”
It keeps 1/2 the DNA to make new DNA
It keeps 1/2 the DNA to make new DNA
57
New cards
What is the replication process (generally)?
Each side of the helix serves as a template for copying
58
New cards
What results from the replication process?
2 new strands that are identical to the original strand
59
New cards
Where does replication begin?
specific sites on the DNA molecule
60
New cards
What are the spots replication begins at called?
Origins of Replication
61
New cards
What is the first step of replication?
The enzyme DNA **helicase** breaks the bonds between the nitrogenous bases?
62
New cards
What does the enzyme DNA helicase do?
destabilizes hydrogen bonds
63
New cards
What is the second step of replication?
the DNA strand unzips and forms a replication fork
64
New cards
What is the third step of replication?
The SSB protein joins in
65
New cards
What does SSB stand for?
Single Strand Binding protein
66
New cards
What is the role of SSB?
prevent the double helix from reforming
67
New cards
What is step four of replication?
Free nucleotides bond to the single strands using DNA polymerases
68
New cards
How do free nucleotides bond to the single strands in the 5’ to 3’ direction?
It starts at the 5’ end and adds nucleotides only to the 3’ end
69
New cards
Which strand goes in the 5’ to 3’ direction?
leading strand
70
New cards
Which strand is more efficient and how fast is it?
the leading strand (5’ to 3’) with about 1200 nucleotides per minute
71
New cards
What is the fifth step of replication?
On the lagging strand, RNA primer is used to start replication at the 3’ end. RNA primer is formed by DNA primerase and is quickly replaced by DNA polymerases.
72
New cards
Describe the leading strand in replication.
(5’-3’) Adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the NEW strand, toward the replication fork, DNA polymerase, SMOOTH
73
New cards
Describe the lagging strand in replication.
(3’-5’) Adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of the NEW strand, going AWAY from the replication fork, short segments at a time, DNA polymerase, DISCONTINUOUS
74
New cards
What are the short segments formed on the lagging strand called?
Okazaki fragments
75
New cards
What is the sixth step of replication?
DNA polymerases also “proofread” filling in gaps or fixing mismatched sections
76
New cards
What is the seventh step of replication?
DNA ligase zips up the new helixes (re-establishes hydrogen bonds)
77
New cards
What is the role of DNA polymerases?
helps free nucleotides bond to the single strands and “proofread” the replicated DNA
78
New cards
What is the role of DNA primerase?
create the RNA primer to start replication on the lagging strand
79
New cards
What is the role of DNA ligase?
re-establish the hydrogen bonds in DNA
80
New cards
How many points of origins of replication are there?
There are multiple on one strand of DNA
81
New cards
Describe what happens because of multiple points of origin of replication
more than one replication fork per strand of DNA, the replication continues until meets another origin, speeds up the process
82
New cards
What is the end result of replication?
2 new identical DNA strands are formed
83
New cards
What are Telomeres? (physical)
protective end caps
84
New cards
T/F Telomeres contain protein coding genes
False
85
New cards
What are telomeres? (in terms of dna)
short simple noncoding DNA sequences that repeat many times
86
New cards
What is the role of telomeres?
protective advantage due to the lagging strand not being completely replicated
87
New cards
What does the length of a telomere sequence depend on?
cell type and age of the cell
88
New cards
What makes each organism or individual unique?
nucleotide sequences in DNA
89
New cards
What do similarities in DNA code show?
evolutionary relationships
90
New cards
What are proteins made from?
long chains of amino acids
91
New cards
What makes up the sequence for protein synthesis?
nitrogenous bases in DNA (&RNA)
92
New cards
How many Amino Acids are there?
20
93
New cards
What are the functions of proteins?
growth, repair, and control reactions
94
New cards
How do we get 20 amino acids from just 4 bases?
Bases are put together in different combinations of three.
95
New cards
What is a codon?
combination of three bases is used to code for all the amino acids
96
New cards
What is codon specific too?
mRNA
97
New cards
What are the two special codons?
Stop and Start Codons
98
New cards
What is the role of a start codon?
Signals the beginning of Transcription/Translation
99
New cards
What is the role of a Stop Codon?
Signals the end of the process of Transcription/Translation
100
New cards
What do codons tell us about all organisms?
They demonstrate that ALL organisms are linked to a common ancestor