Unit 5: Thermo (Packets 1 & 2)
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1YPrRJbkzGHFWGFqQR6sAI0sheC9pwzZv/view?usp=sharing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Exo or Endo: Bond formation
Exothermic
Exo or Endo: Bond breakage
Endothermic
Bond Energy
Amount of energy required to break a covalent bond


To solve this equation:
1: Balance stoichiometric equation.
2: Draw Lewis Dot Structure for all reactants and products.
3: Substitute correct bonds into equation and apply mole ratio, e.g.
ΔH = 4(C-H) + 2(O=O) - 2(C=O) - 4(O-H)
4: Substitute correct numerical values into equation.
ΔH = 4(393) + 2(433) - 2(433) - 4(464)
Bond energies found in DP data booklet
5: Solve the equation.
ΔH = -890 kJ
Hess’ Law
The enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states.
Standard Enthalpy Change of Combustion
Amount of heat released from 1 mol of a substance in the presence of oxygen.
C3H8 + 5O2 —> 3CO2 + 4H2O
ΔH: Need to use ΔHformation to find ΔHcombustion

Standard Enthalpy Change of Formation
Amount of heat needed to make (released) from the formation of 1 mol of a compound from its elements in standard state.
Does not apply to diatomic and metals (they aren’t compounds)
0 for elements at standard state
Standard state = state the element exists as at 25 ºC (298.15 K) and 1 atm (101 kPa)
CANNOT USE COMBUSTION VALUES FOR FINDING ΔH OF A COMBUSTION REACTION

ΔHformation vs ΔHBE
ΔHformation: Uses standard states and not gas volumes —> accurate
ΔHBE: Averages of bond energies in gaseous phase and are used as a guide —> approximate
ALWAYS A QUESTION ON IB EXAM
Born-Haber Cycle
BHC is an application of Hess’ Law used to show energy changes in the formation of an ionic compound.
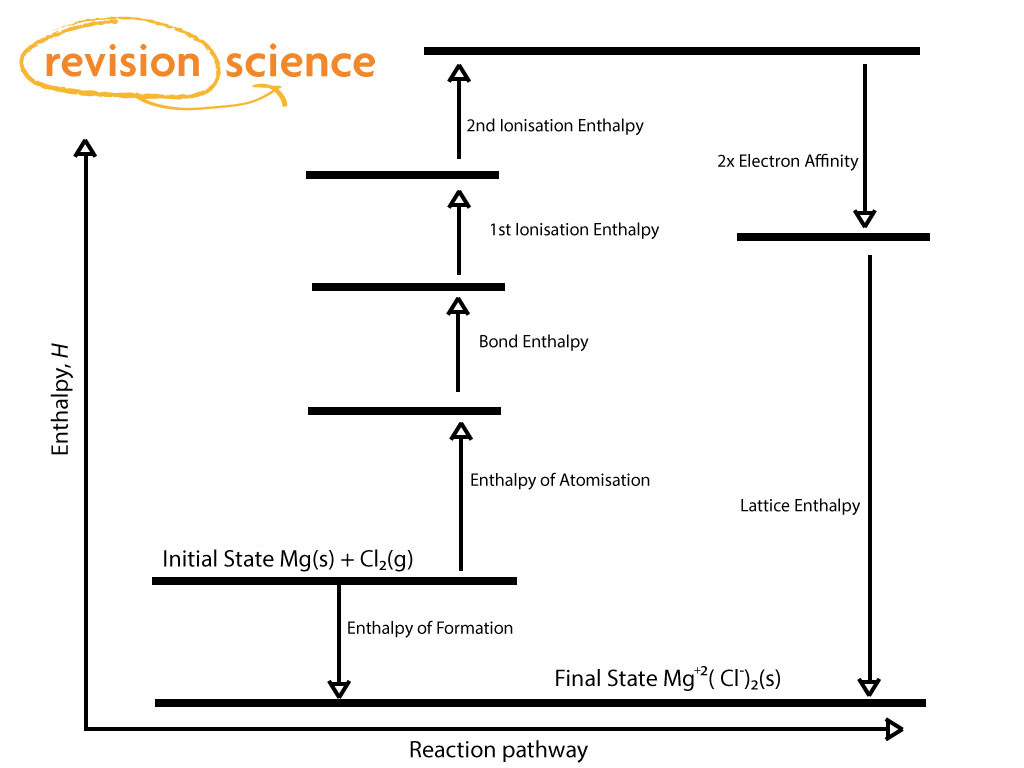
Lattice Enthalpy
Energy required to make gaseous ions from 1 mol of solid ionic compound.
Endothermic
Experimental values at 298K are found in section 18 of data booklet
ΔHºlat > 0
Enthalpy of atomization / sublimation
Standard enthalpy change that occurs on the formation of 1 mol of separate gaseous atoms of an element in its standard state.
M(s) —> M(g) ΔHºatom > 0 Sublimation
½ X2 (g) —> X(g) ΔHºatom > 0 BE
Ionization Energy (ΔHºIE)
Standard enthalpy change that occurs on the removal of 1 mol of e- from 1 mol of atoms or positively charged ions in the gaseous phase.
For metal ions with multiple ve- the 1st, 2nd and 3rd IEs are defined.
M(g) —> M+(g) + e- ΔHºIE > 0
M+(g) —> M2+(g) + e- ΔHºIE > 0
Electron Affinity (ΔHºEA)
The standard enthalpy change on the addition of 1 mol of e- to 1 mol of atoms in the gaseous phase.
X(g) + e- —> X-(g) ΔHºEA < 0
Lattice Enthalpy Steps
1: ΔHformation (↓ -ΔH (heat released))
2: ΔHatomisation / sublimation (↑ +ΔH)
3: IE1 (↑ +ΔH)
4: ½ ΔHBE (↑ +ΔH)
5: EA (↓ -ΔH)
ΔHlattice = ΔHatom + IEcation + ½ ΔHBE + EAanion - ΔHf
