Stages of viral replication and their main characteristics.
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Virion
extracellular particle
Vegetative virus
replicative form (autonomous extrachromosomal element)
Permissive cell
a host cell that supports the complete viral replication cycle
Types of infection based on outcome
• Productive infection
• Proliferative infection
• Persistent infection
Stages of Infection
1. Adsorption (attachment)
2. Penetration (entry)
3. Decapsidation (uncoating)
4. Eclipse phase (synthesis)
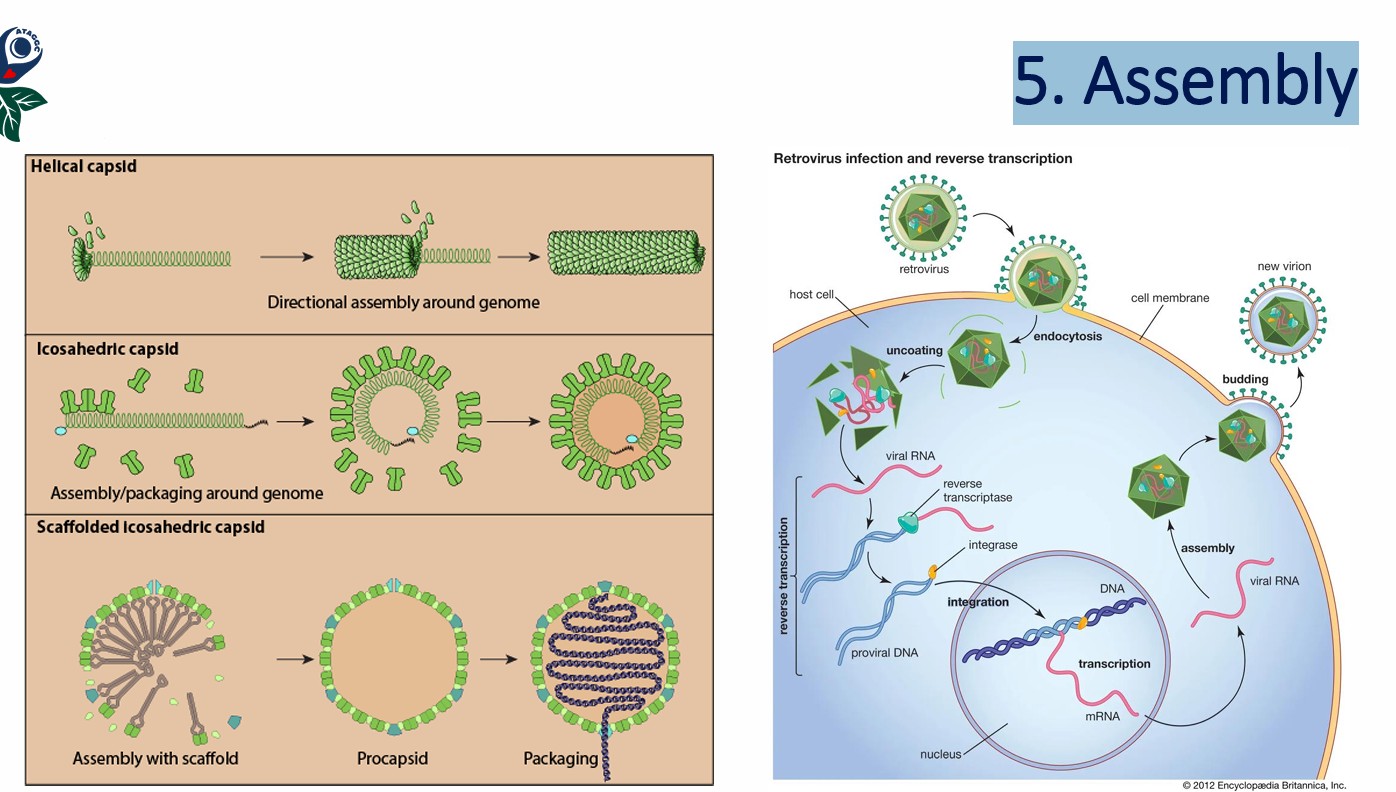
5. Assembly of new virion
6. Maturation
7. Egress and Envelope Formation
8. Viral Specificity– Receptors
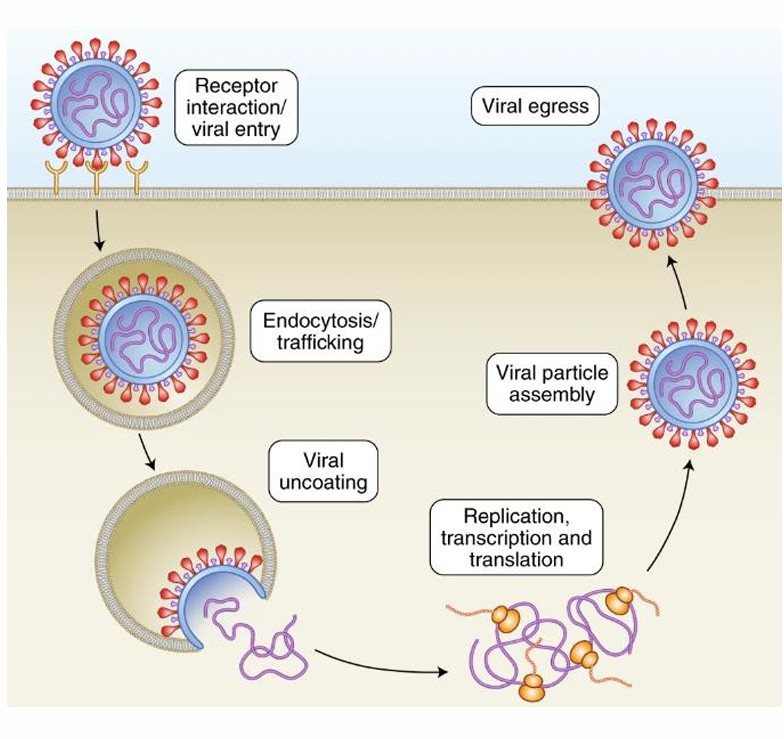
1. Adsorption
Binding to the adhesion receptor
Binding to the specific receptor
2. Penetration
Non-enveloped viruses: entry via direct penetration or endocytosis
Enveloped viruses: envelope derived from internal membranes; entry via receptor-mediated endocytosis
Bacteriophages: transfection; only the nucleic acid enters the host cell
3. Decapsidation
yer
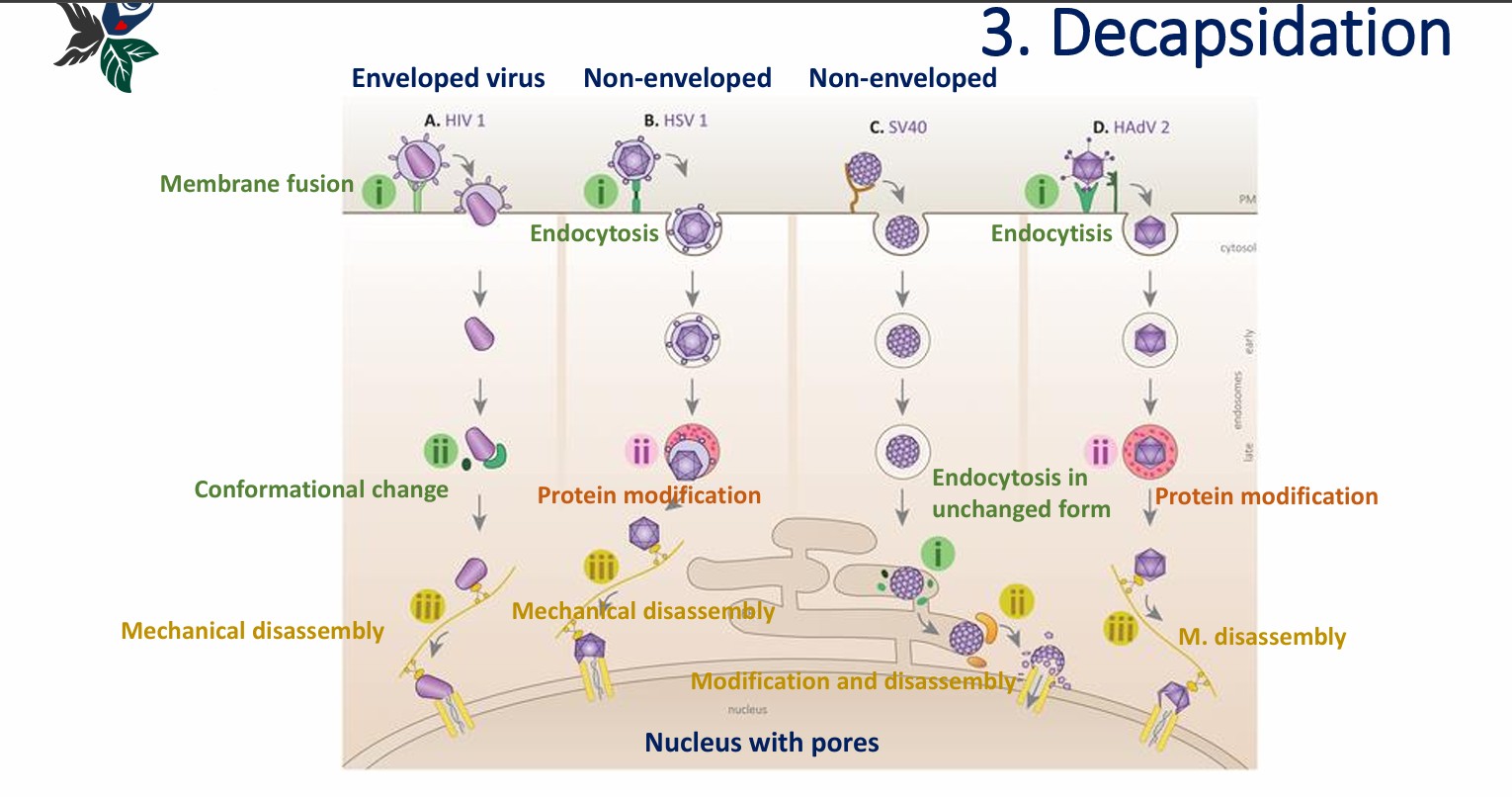
4. Eclipse phase - Synthesis
1. transcription - synthesis of mRNA from the viral genome to serve as a template for subsequent protein synthesis
2. Protein synthesis (Translation) using the viral mRNA
3. Nucleic acid synthesis (Replication) – replication of the viral genome and synthesis of capsid components
5. Assembly
mhm
6. Maturation and 7. Release
• Maturation
• Cell lysis
• Budding – paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses, togaviruses, and retroviruses
• Exocytosis