Bio 260 midterm 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
importance of cholorphyll a
used to measure primary productivity (measured by satellites)
normally higher concentrations near the coast (specifically west coast), mid-latitudes
primary productivity
the rate at which biomass is produced by photosynthesis
bioassay experiment
study done to test the effects of a substrate on a living organism
bioassay for nitrates and phosphates
found that adding nitrates increased productivity, adding phosphates alone did not increase productivity, but adding both created more productivity than the sum of both nitrate and phosphate
nitrogen
usable form for phytoplankton is NO3- (nitrate). nitrogen is essential for making amino acids and proteins. a large part of it comes from runoff
phosphorus
phosphates come from eroding land and poo (guano — good fertilizer because it’s full of phosphorus)
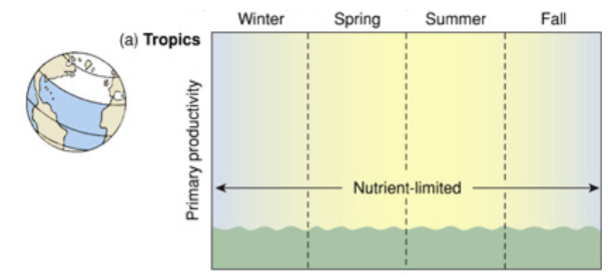
chlorophyll a concentration in tropics
sunlight year-round, so the nutrients are used as fast as they are deposited, and then the water is nutrient-limited
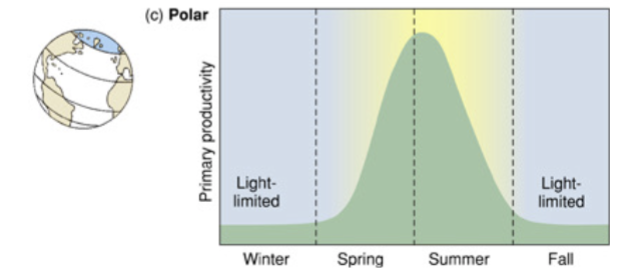
chlorophyll a concentration in polar regions
no light in winter → no photosynthesis. nutrients build up and then during the summer all the nutrients get used up
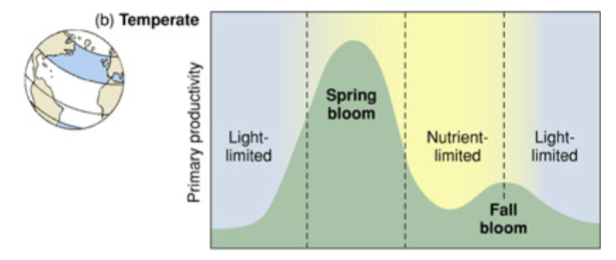
chlorophyll a concentration in temperate regions
light limited in winter → less photosynthesis, low production. then there is a huge bloom in spring but then nutrients are depleted by the summer. in the fall there is a secondary bloom because the dead plankton from the spring bloom begin to be recycled and the nutrient concentration increases
upwelling: northern hemisphere
wind from the north pushes the water to the west (coriolis) so then cold water upwells near the coast

Ekman transport
bulk of the water goes right while the surface current follows the wind south
downwelling: northern hemisphere
wind comes from the south and the bulk of the water is pushed east by ekman transport. thermocline drops, warm water near coast
why is there high primary productivity on the west coast?
because of the circulation of the currents, in the mid latitudes, the winds tend to go towards the equator on the west coast, which creates strong upwelling in those areas due to ekman transport
somalia is the one exception that occurs because the strong winds from the indian summer monsoon create seasonal upwelling
why is there high productivity in the south pole but low productivity in the north pole?
both have cold water, but there is no landmass in the north pole. in the south pole, antarctica creates a landmass to upwell against, and a source of nutrients from runoff
how is primary productivity related to fish?
higher productivity generally is associated with higher fisheries yield. the exception is coral reefs because coral reef fishes are not usually fished commercially. → fisheries data isn’t always all-encompassing
trophic relationships: socal bays and estuaries
multiple types of primary producers (eelgrass, benthic microalgae (diatoms), macroalgae, phytoplankton)
rich food web
ex: diatoms → copepods → topsmelt
transfer efficiency
percent of biomass consumed that results in newly created biomass in then next trophic level
typically 10 percent
fisheries efficiency
depends on how much energy the predator spends to eat the prey
anchovies spend little energy catching their prey so their transfer efficiency is about 20 percent
tuna are high in the trophic level so they have a low efficiency
productivity in estuaries
shallow, lots of sunlight, lots of runoff → multiple kinds of primary producers and high primary productivity
fish biomass over the year
after the spring bloom there is a slight delay before the uptick in fish biomass. so there is more fish production in the summer (and dont really see fall bloom reflected in fish biomass)
Bolsa Chica Ecological Reserve
became paved over by oil fields and roads but was then restored successfully in 2006
shovelnose guitarfish
uses bays and estuaries for mating, pupping, and feeding in summer
high level predator - eats benthic inverts and fishes
use the full tidal basin of bolsa chica
acousitc fish tracking
transmitters last months to years, picked up by recievers that are put in the estuary called synch transmitters
used to track shovelnose guitarfish
proportional habitat use
a value above 1 means significant correlation - in this case it means selection for that habitat as opposed to random use
findings on the guitarfish using acoustic tracking
they stayed in the basin for about 2.5 months
they use subtidal mud
were more active during incoming and high tide (because more habitat is available during high tide)
more active at night
most recorded in bolsa chica were juveniles (born offshore and migrate in)
fisheries independent data
no effort made to catch one specific thing or to catch more or less. more random
CPUE
catch per unit effort (can be fisheries dependent)
fisheries dependent data
can be biased because fisheries target one thing or will try to catch more so they go to certain areas or at certain times
Anaheim Bay Estuary
restored in late 1980s
restored tidal basins tend to be warmer in the summer because of their location farther up the estuary (farther from tidal fluctuations)
round stingray
internal fertilization
matrotrophic (mother provides additional nutrition via uterine secretions)
viviparous
findings on round stingrays in anaheim bay estuary using beach seines
in restored areas: majority caught were females, and a majority of those were pregnant
over time: the temp decreased (august -october) and the pregnant females were moving out of the estuary
caught no newborns/juveniles
what were the round stingrays using the warm areas of anaheim bay estuary for?
elasmobranch maternity ward!
warm water shortens gestation period and the young turn out larger
they dont absorb food as well in this warm water but they tolerate it so they can be pregnant for a shorter amount of time
takeaway from round stingrays in anaheim bay estuary
if you know when/where individuals of a species are captured in an estuary, you can classify them
for example: round stingrays are marine migrants
community definition
a group of populations that coexist/interact in space and time
species richness
number of species
species evenness
proportion of individuals of each species
species diversity
richness and evenness (ex: shannon index)
Shannon Diversity Index
H’ = - sum(piln(pi))
pi is the proportional representation of each species
higher number means higher diversity
generally get a more accurate value with a larger sample size
diversity value only matters in comparison to other examples of the same habitat
predation
animals eating animals, animals eating plants (herbivory)
ecology of fear
prey animals who are more fearful survive better, so the behavior is selected for by natural selection
sub-lethal effect of predation
presence of predators causes prey to grow more slowly because they hide more and therefore eat less and reproduce less
competition
two or more individuals attempt to use an essential limited resource
intraspecific competition
generally thought to be more intense than interspecific because the animals are competing for the exact same thing
interspecific competition
animals on the same trophic level and same habitat are more likely to compete with each other
resource partitioning
when animals avoid competing with each other by living in different areas (even though they technically dont have to live only in those specific areas)
eelgrass traits
vascular
have rhizome
blades are basically just solar panels
sequesters carbon (b/c they have belowground biomass because of rhizome)
angiosperm
more like an orchid or lily
not directly fed on by other animals
function of the rhizome for eelgrass
gets nutrients from sediment
allows the plant to be more resilient
belowground so it sequesters carbon when it dies
distribution of eelgrass
soft bottom substrate (sand, silt)
light is the major limiting resource (depth)
pretty wide distribution across globe
2 species in CA
2 species of eelgrass in ca
zostera marina: narrow bladed, bays and harbors, low energy environment
zostera pacifica: wider blade, open ocean habitat, harbors different species than z. marina
surf grass
not eelgrass
grows on rocks
fine blades
is still a type of sea grass
ecosystem services of eelgrass
dampens energy of storms and waves — reduces erosion
sequesters carbon
structural habitat for fishes
cycles nutrients
valuable for recreation (human)
algae grows on it (epiphyte) that the fish feed on
ontogenetic shift paradigm
change in an organism's ecological niche, behavior, or habitat use over its lifetime
many larvae settle in seagrass to grow
not well understood outside the tropics