Quantitative Chemistry
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Law of conservation of mass
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction.
→ So the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants.
Relative atomic mass (RAM)
Average mass of atoms in an element taking into account masses and abundance of its isotopes, relative to 12C.
Relative formula mass (Mr)
Sum of relative atomic masses of all atoms in the formula.
Avogadro's constant
The number of atoms, molecules or ions in a mole of a given substance. The value of the constant is 6.02 x 10^23.
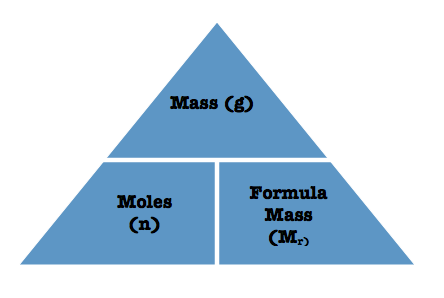
Formula linking mass, molecular mass and moles
(Massive Mr Mol)
Mass = Mr x Moles
Limiting reactant definition
The reactant that is completely used up in a chemical reaction.
→ limits the amount of products.
Percentage by mass equation
% by mass = (Mr of element / Mr of total compound) x 100
Equation linking concentration, mass and volume
(MCV)
Mass (g) = concentration (g/dm3) * volume (dm3)
Equation linking concentration, moles and volume
(MCV)
Moles (mol) = concentration (mol/dm3) * volume (dm3)
Equation linking volume, amount of gas, and 24
(VA24)
Volume (dm3) = amount of gas (mols) * 24dm3
Molar volume of a gas at room temperature and pressure
1 mole of a gas occupies 24 dm3.
Titration
A technique for finding the concentration of a solution by reacting a known volume of a solution with a solution of known concentration.
Theoretical amount of product in a chemical reaction
The expected yield based on stoichiometric calculations.
Reasons for not obtaining theoretical yield
Reversible reactions
product loss during separation
side reactions
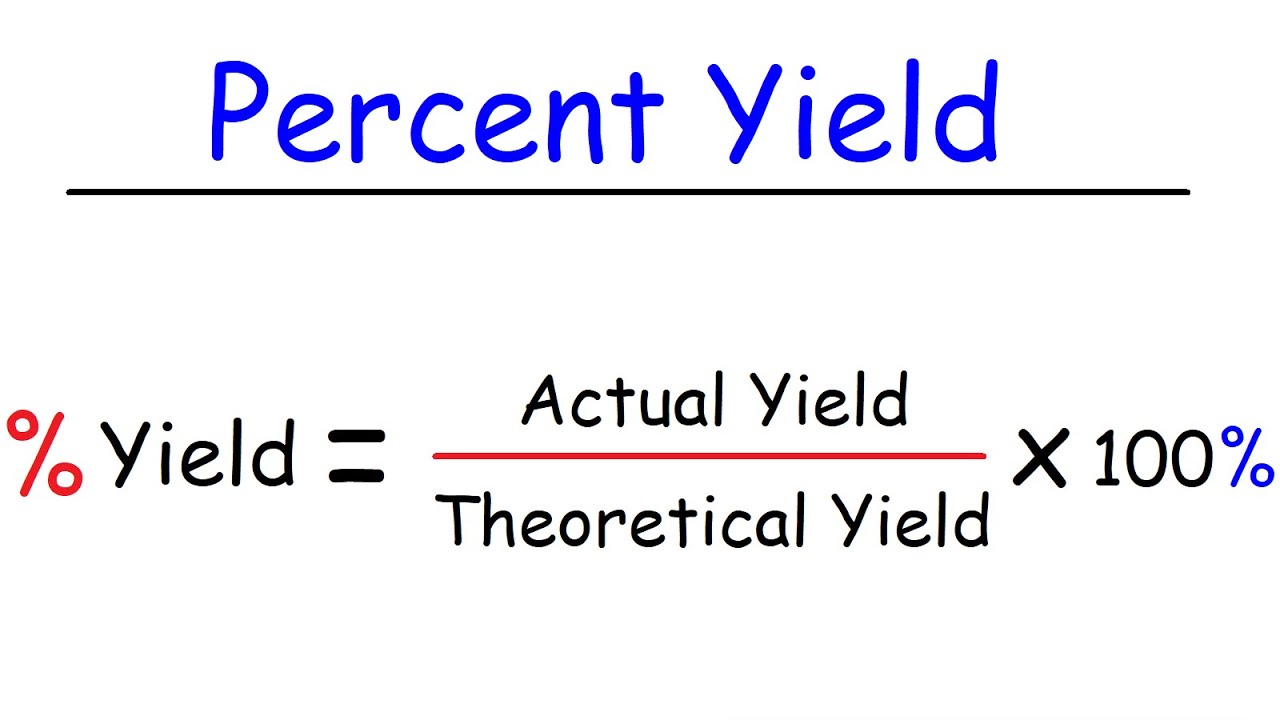
Percentage yield of a product equation
% Yield = (Actual mass of a product / theoretical mass of product) x 100
Atom economy
A measure of the amount of starting materials that end up as useful products.
Atom economy equation
% Atom economy = (Mr of desired product / Mr of total reactants) x 100
Why is high atom economy important?
Reduces amount of waste produced
Conserves resources
Minimizes environmental impact
Cost-effective
What is % atom economy for a reaction with one product?
100%
Uncertainty
The degree of uncertainty of measurements regardless of precision or accuracy.
→ Can be due to the limitations of measuring equipment or skill of experimenter carrying out the measurements.