17.1 aldehydes and ketones
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
State the way by which aldehydes can be produced
oxidation of primary alcohols with acidified KMnO4 and distillation to produce aldehydes
Must be distilled and collected or else carboxylic acids can form
State the way by which ketones can be produced
Oxidation of secondary alcohols using acidified KMnO4 and distillation to produce ketones
Colour change when KMnO4 is oxidised
Purple to colourless
Describe the reduction of aldehydes and ketones.
NaBH4/ LiAlH4 2[H]
Aldehydes reduced to primary alcohols
Ketones reduced to secondary alcohols
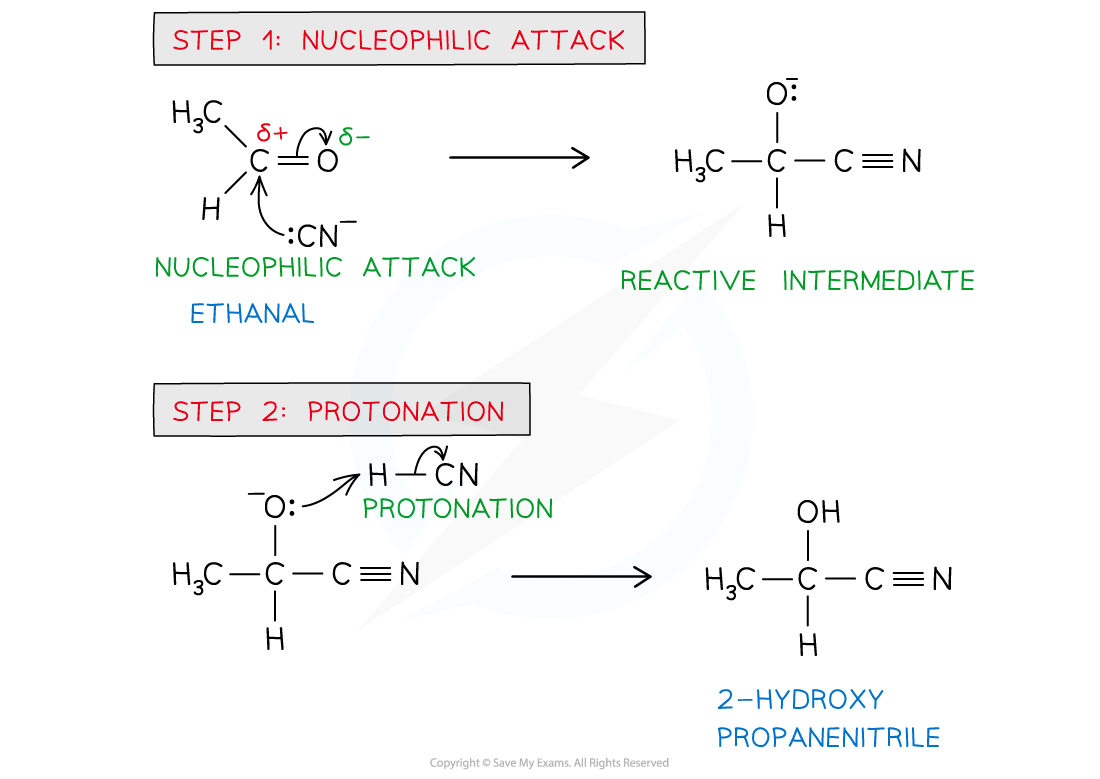
Explain how aldehydes and ketones can react with HCN
Reacts via nucleophilic addition
HCN behaves as nucleophile and adds across C-O bond
Aldehydes and ketones react with HCN
KCN catalyst and heat to produce hydroxynitrilees
Draw out the mechanism for nucleophilic addition
2,4-DNPH
Tests for presence of carbonyl compounds
Forms orange precipitate
Fehling’s solution
Oxidising agent that detects presence of an aldehyde group (-CHO)
Clear blue to opaque red precipitate
Tollen’s reagent
Detects presence of aldehyde by oxidising it
Forms silver mirror
Iodoform
Detects present of methyl ketones and ethanal (CH3CO)
Reagent heated with NaOH + Iodine
Forms yellow ppt of CHI3 and salt RCO2-
Ethanal is…
The only aldehyde to react with iodo form