Bioenergetics Unit Vocab
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Chlorophyll
Green Pigment
Main photosynthetic pigmnet
Absorbs primarily violet-blue and red wavelengths
Metabolism
the totality of an organisms chemical reactions that result from interactions between molecules within the cell
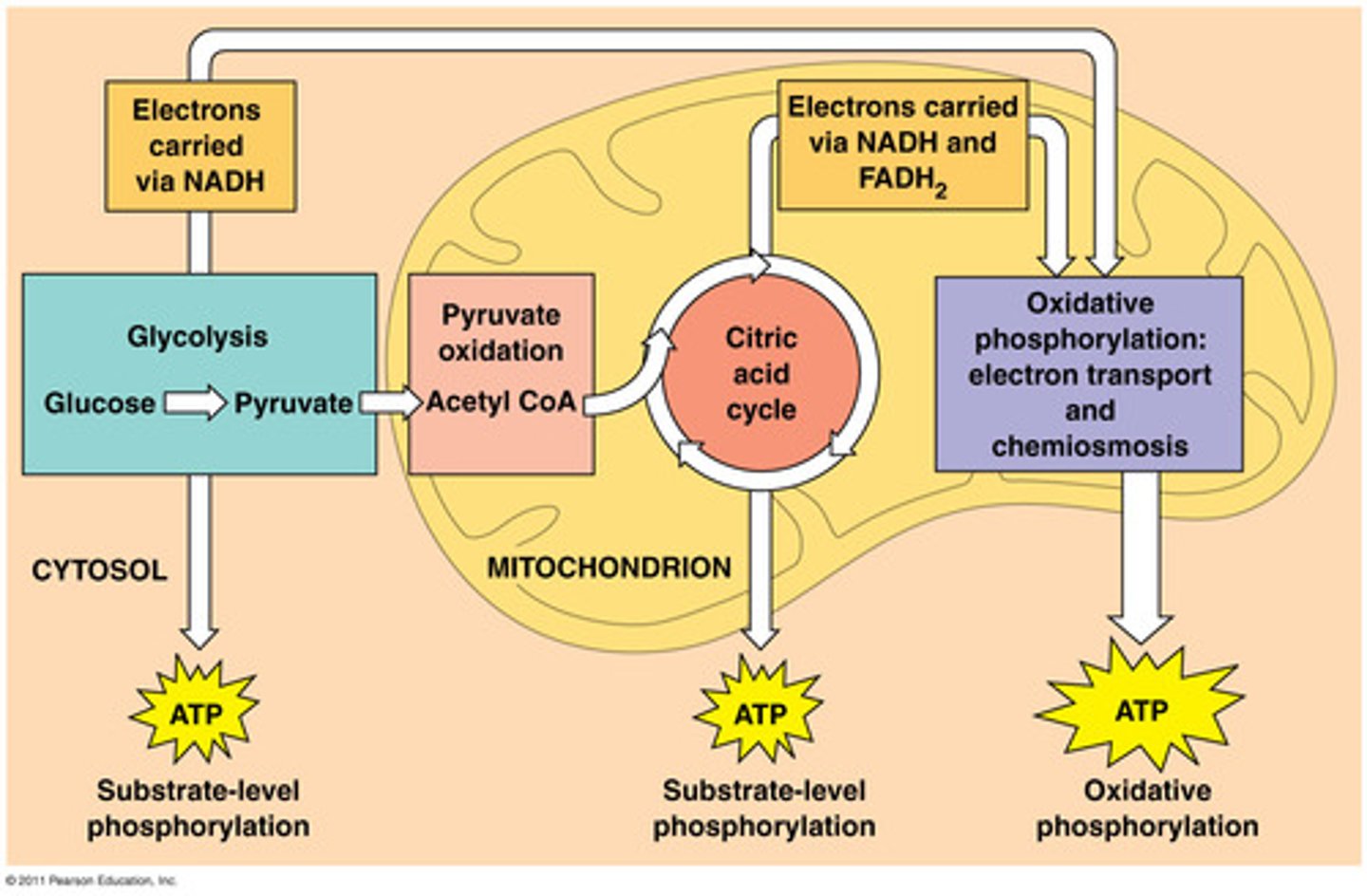
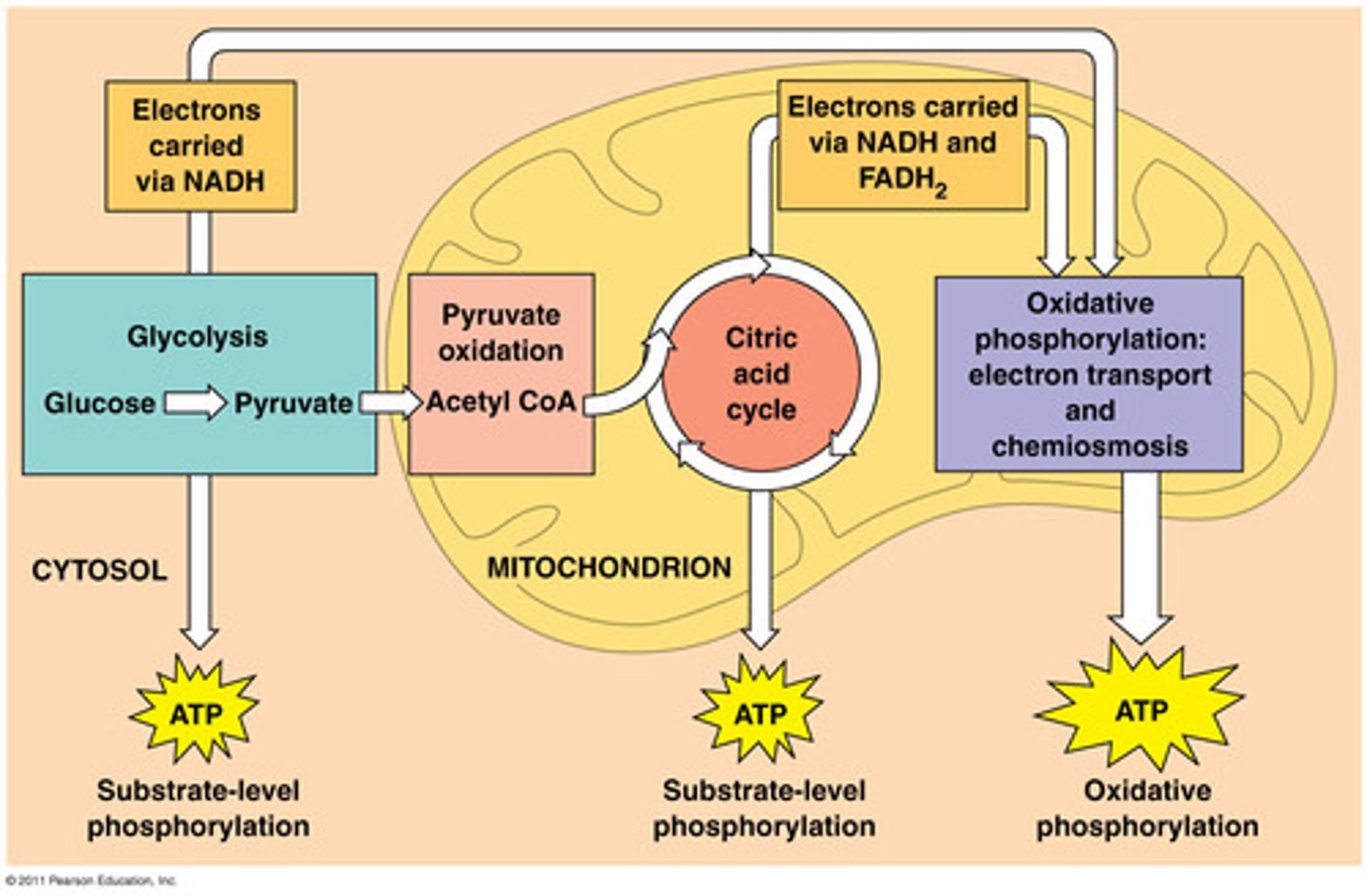
Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells produce energy (ATP)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6H2O + energy
(oxidative process)
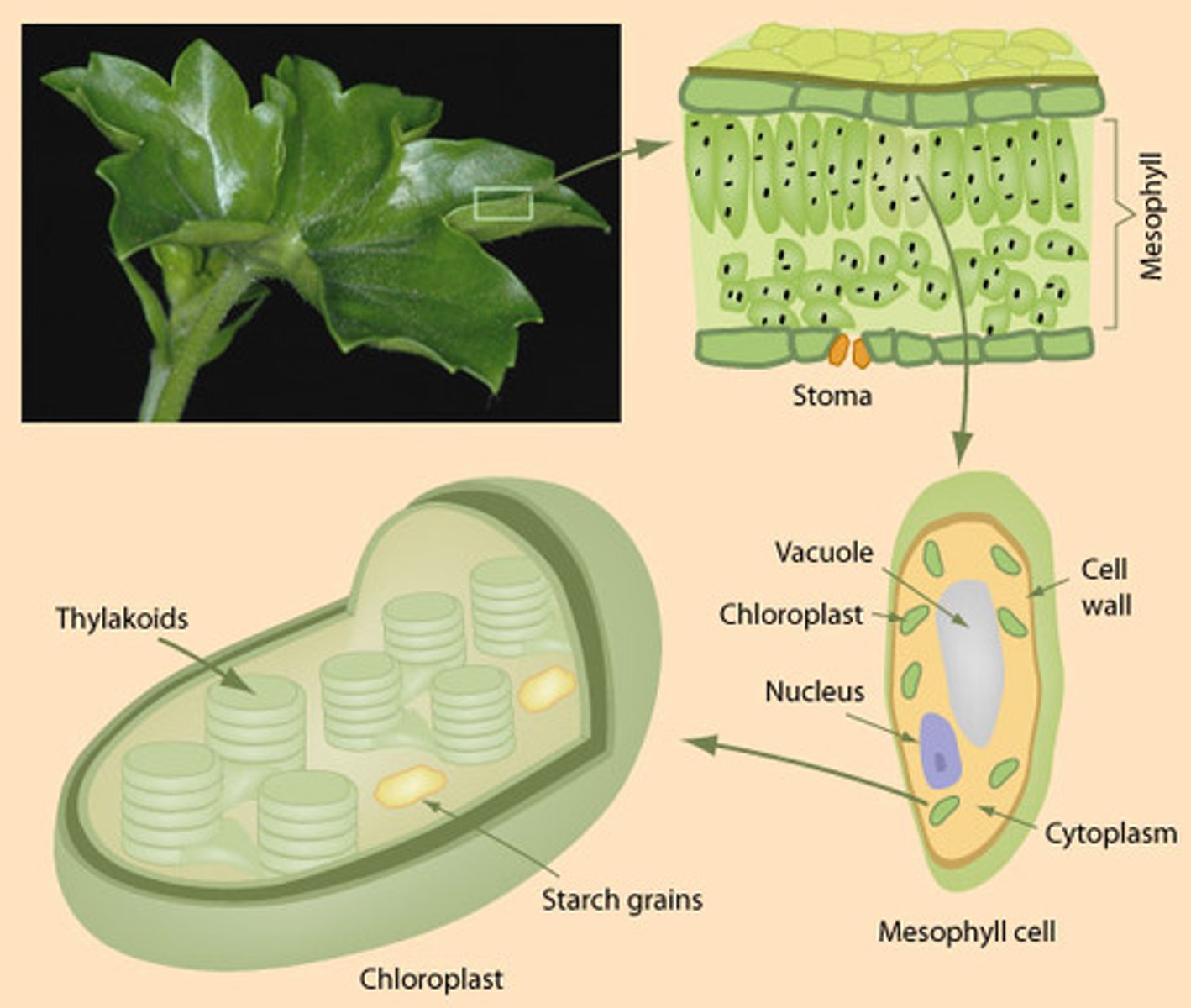
Thylakoids
dense interconnected membranous sacs where the light reactions occur
metabolic pathway
a sequence of chemical reactions undergone by a compound in a living organism, start with substrate end with product
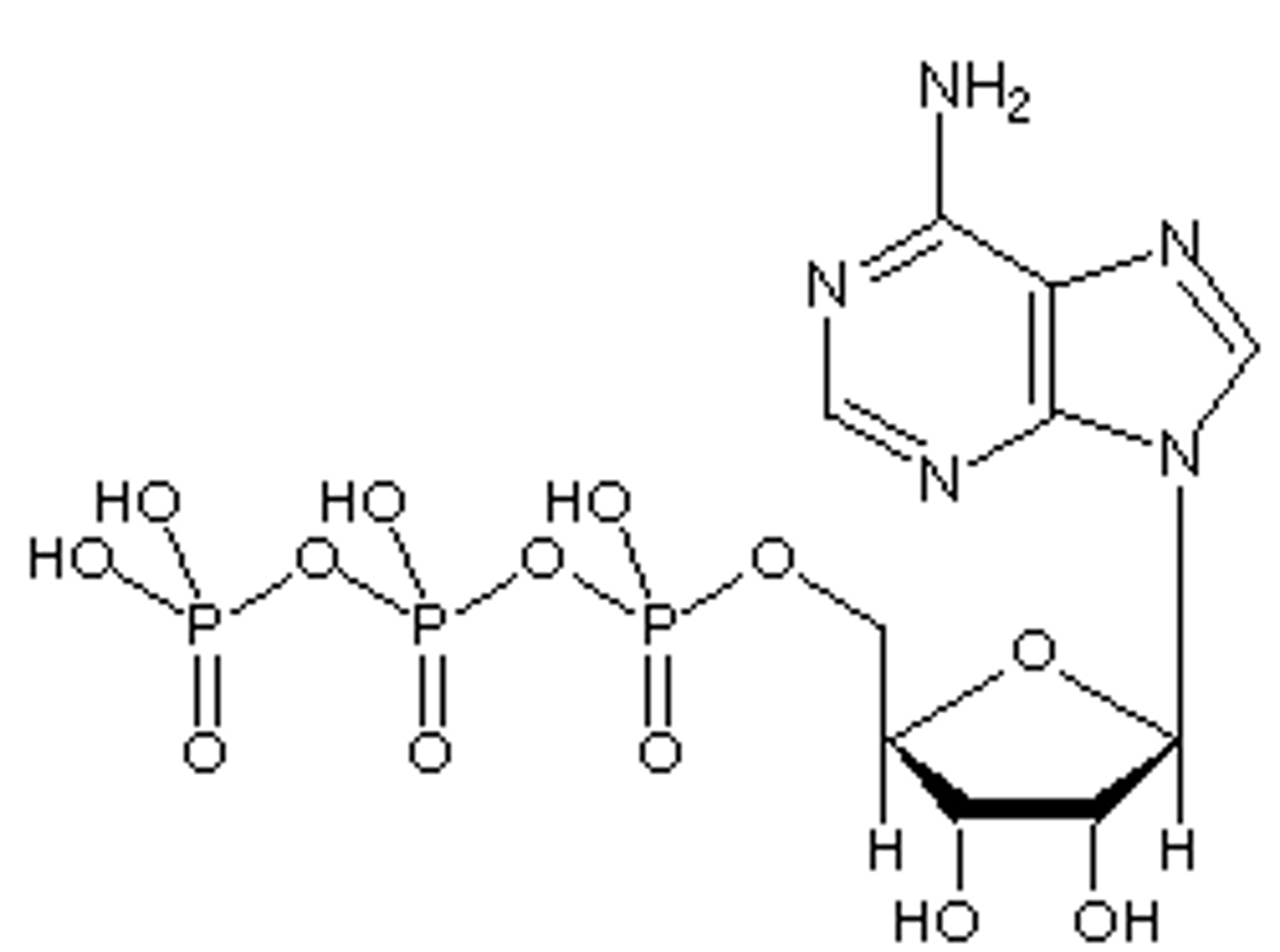
ATP
Consists of adenosine plus 3 phosphates; source of immediate energy
(know this structure)
Grana
stacks of thylakoid
catabolic
breaking a complex molecule down into its simpler parts, releasing energy. ie. cellular respiration
Glycolysis
Anaerobic phase of cellular respiration that breaks down glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvate
- Occurs in cytoplasm
- Makes 2 Net ATP molecules and 2 molecules of NADH
Fermentation
A process that produces a small amount of energy in the absence of oxygen
- Begins with glycolysis and produces 2 molecules of pyruvate and then alcohol or lactic acid
- Converts NADH to NAD+ by transferring electrons to pyruvate
anabolic
using energy to build complex molecules from simpler molecules. ie. protein synthesis
Granum
singular of grana
Chloroplast
sites of photosynthesis
Bioenergetics
the study of how organisms manage their energy resources
Aerobic Respiration
Consists of Krebs cycle and electron transport chain (ETC) and oxidative phosphorylation
- Requires oxygen
- Occurs after the anaerobic respiration
- Produces 34 ATP
- Occurs in the mitochondria
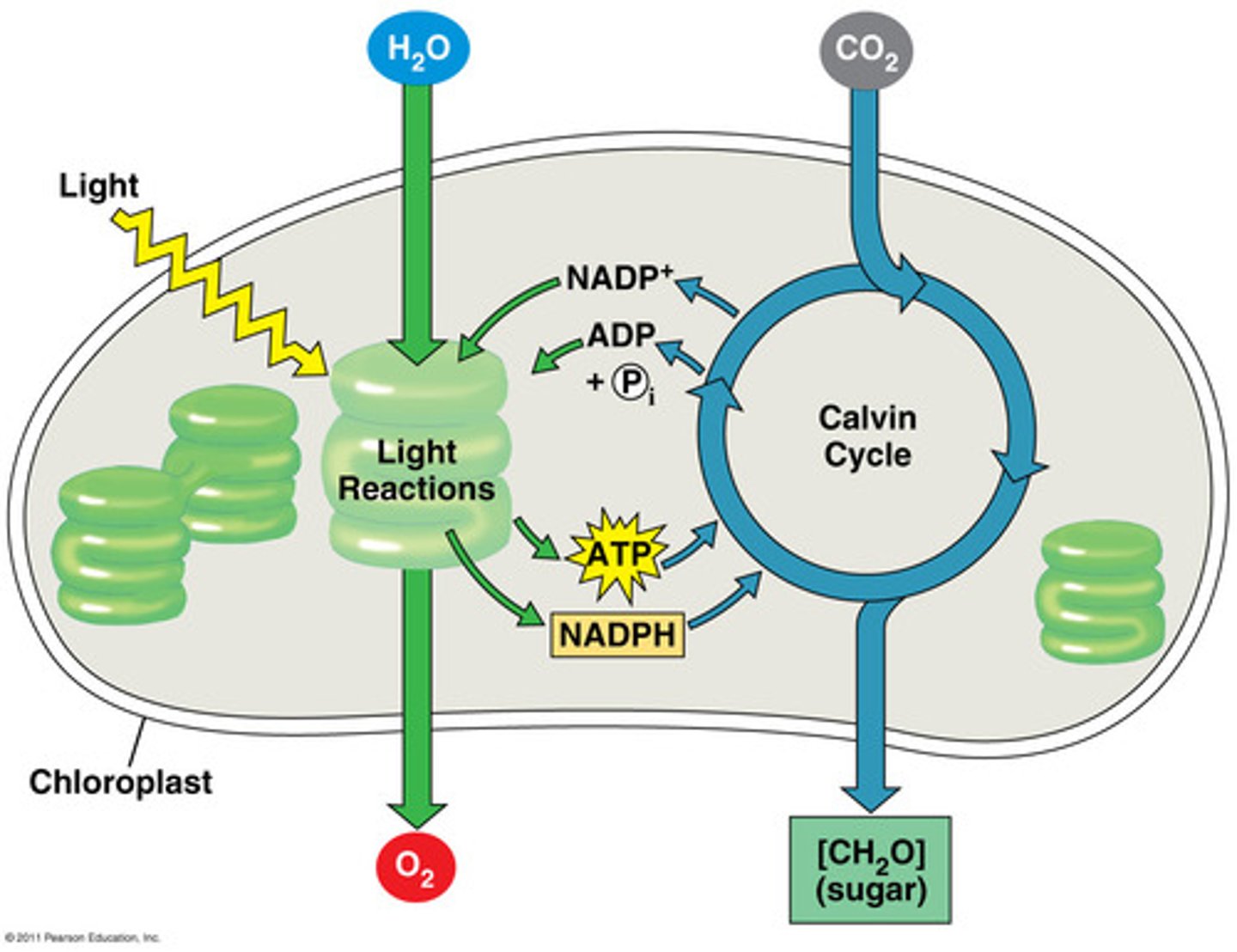
Photosynthesis
conversion of light energy into chemical energy stored in sugar and other organic molecules
energy
capacity to cause change, do work
Citric Acid Cycle
Synonym for Krebs Cycle
Photosynthesis Equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light --> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
heat(thermal energy)
kinetic energy associated with random movement of molecules
Anaerobic Respiration
respiration without oxygen present, common synonym for fermentation
Aerobic
With oxygen
chemical energy
potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction, energy within bonds
Carbon Dioxide
source of inorganic carbon used in photosynthesis
Anaerobic
Without oxygen

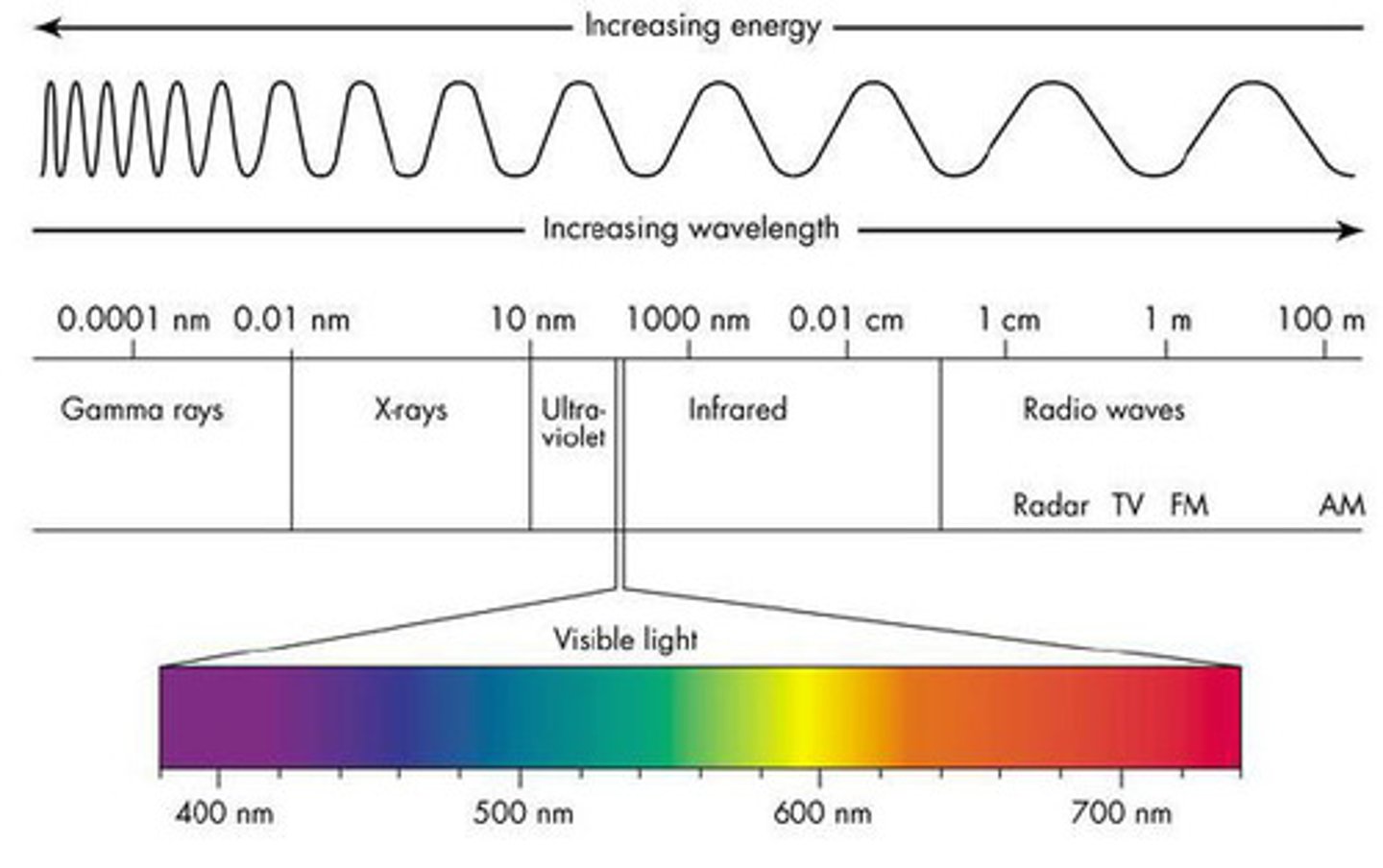
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electromagnetic energy which travels in waves
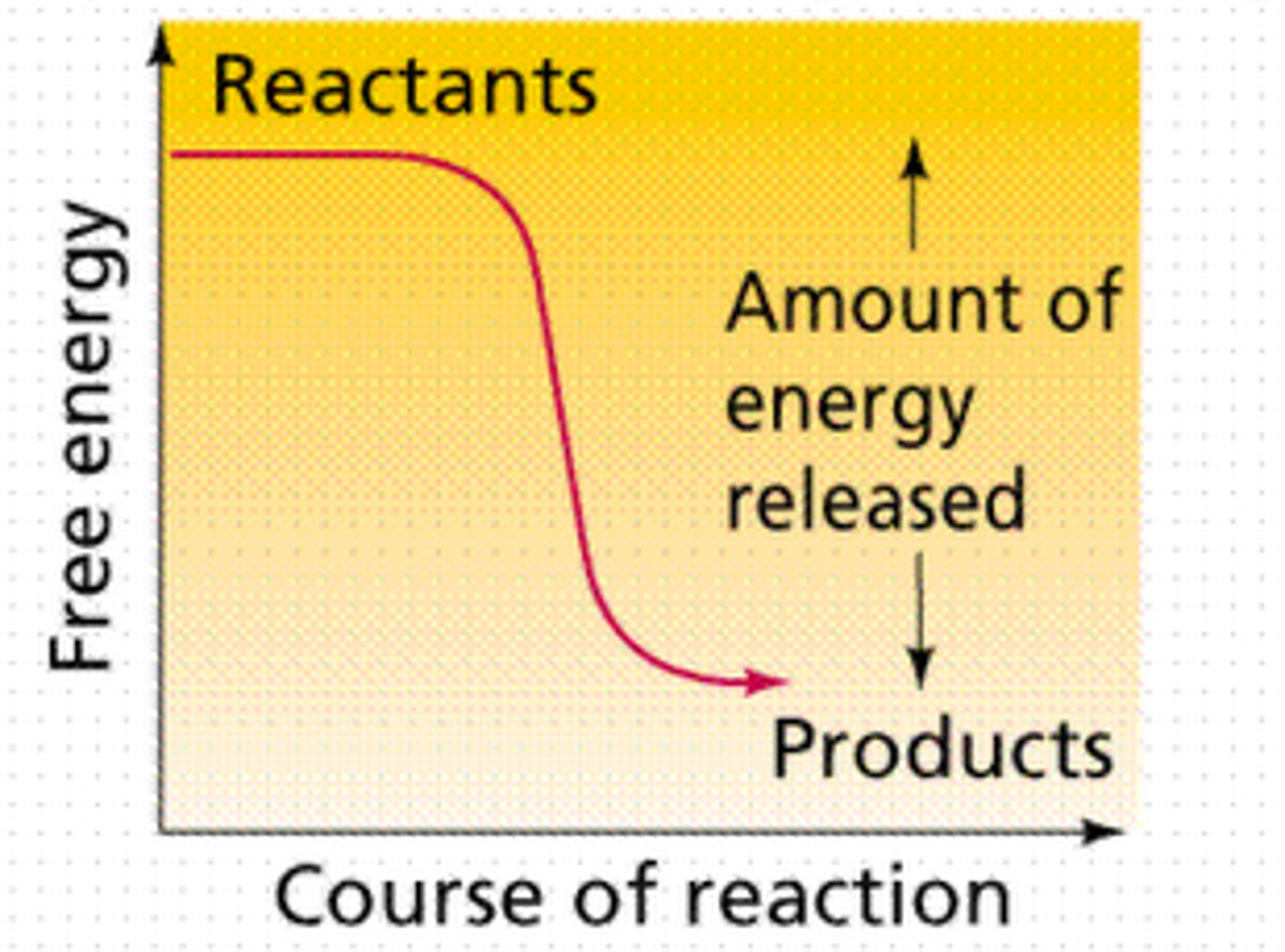
exergonic reaction
a reaction with a net release of free energy, negative free energy, spontaneous
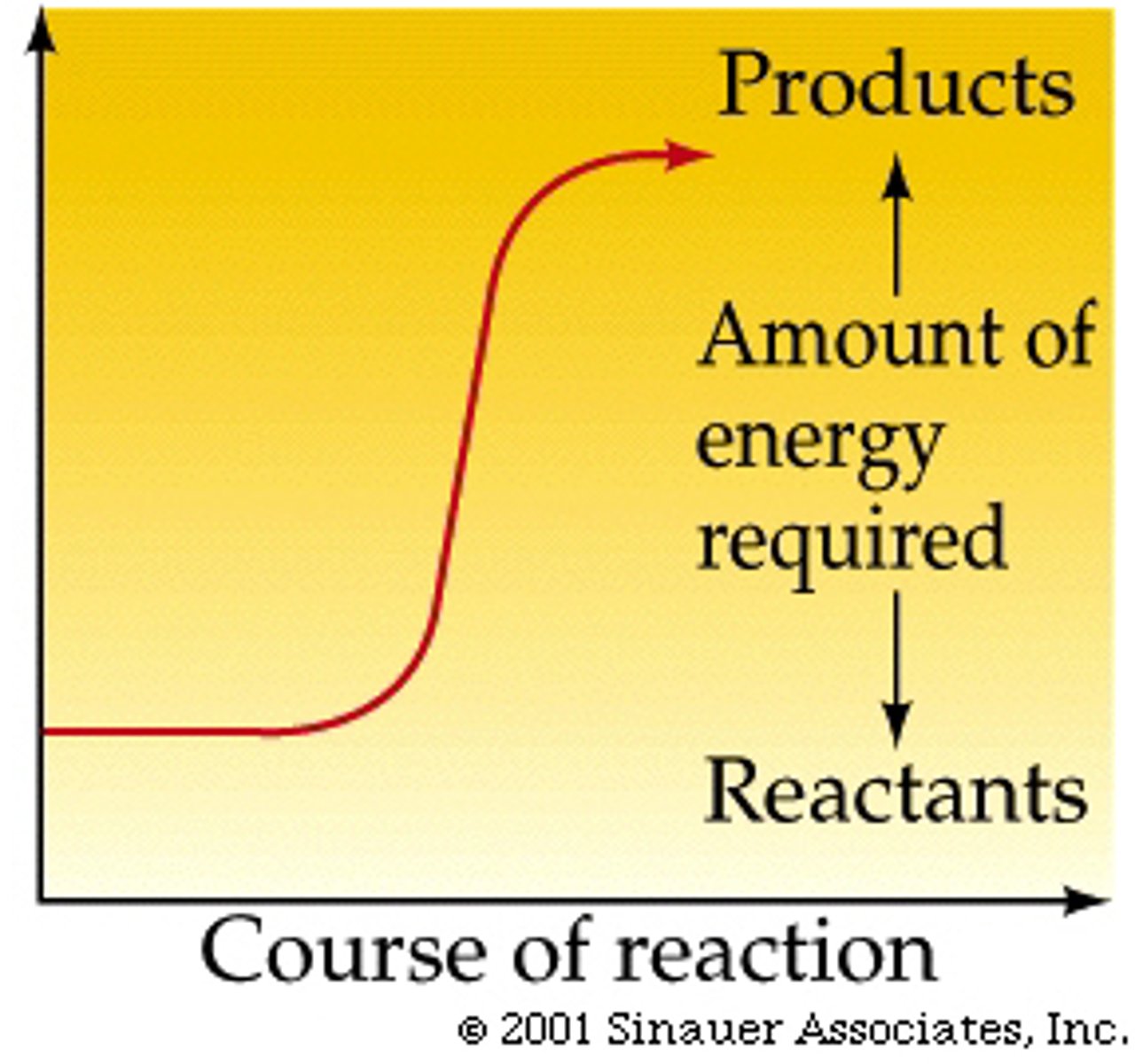
endergonic reaction
a reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings, non-spontaneous, positive free energy
Krebs cycle
Uses 2 acetyl co-A to produces 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, and 2 ATP and CO2 as waste
- Occurs in the mitochondrial inner matrix
- Part of aerobic respiration
- Turns twice for each molecule of glucose
(also known as Citric Acid Cycle)
Colors
Light we see is reflected off objects and light we don't see is absorbed by objects
White
All colors reflected
catalyst
a chemical agent that speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction
Acetyl co-A
coenzyme combined with pyruvate created in middle step; raw material of Krebs cycle
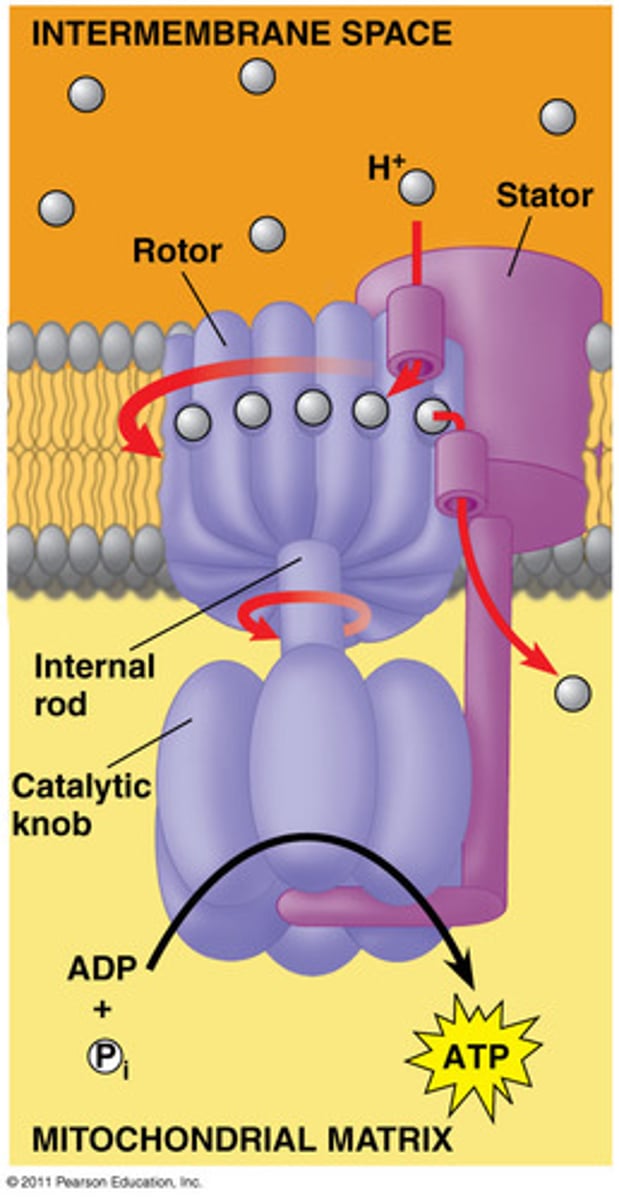
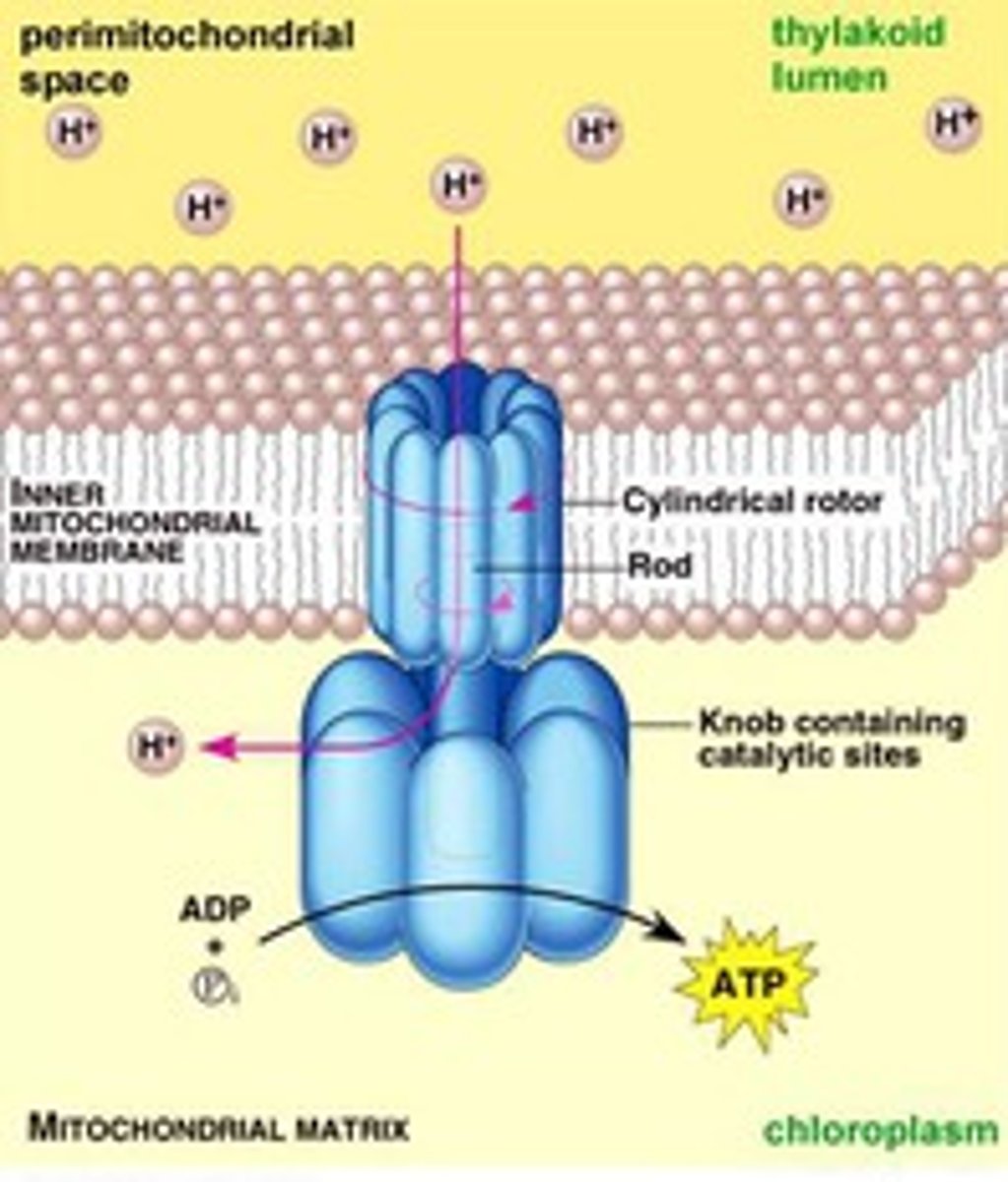
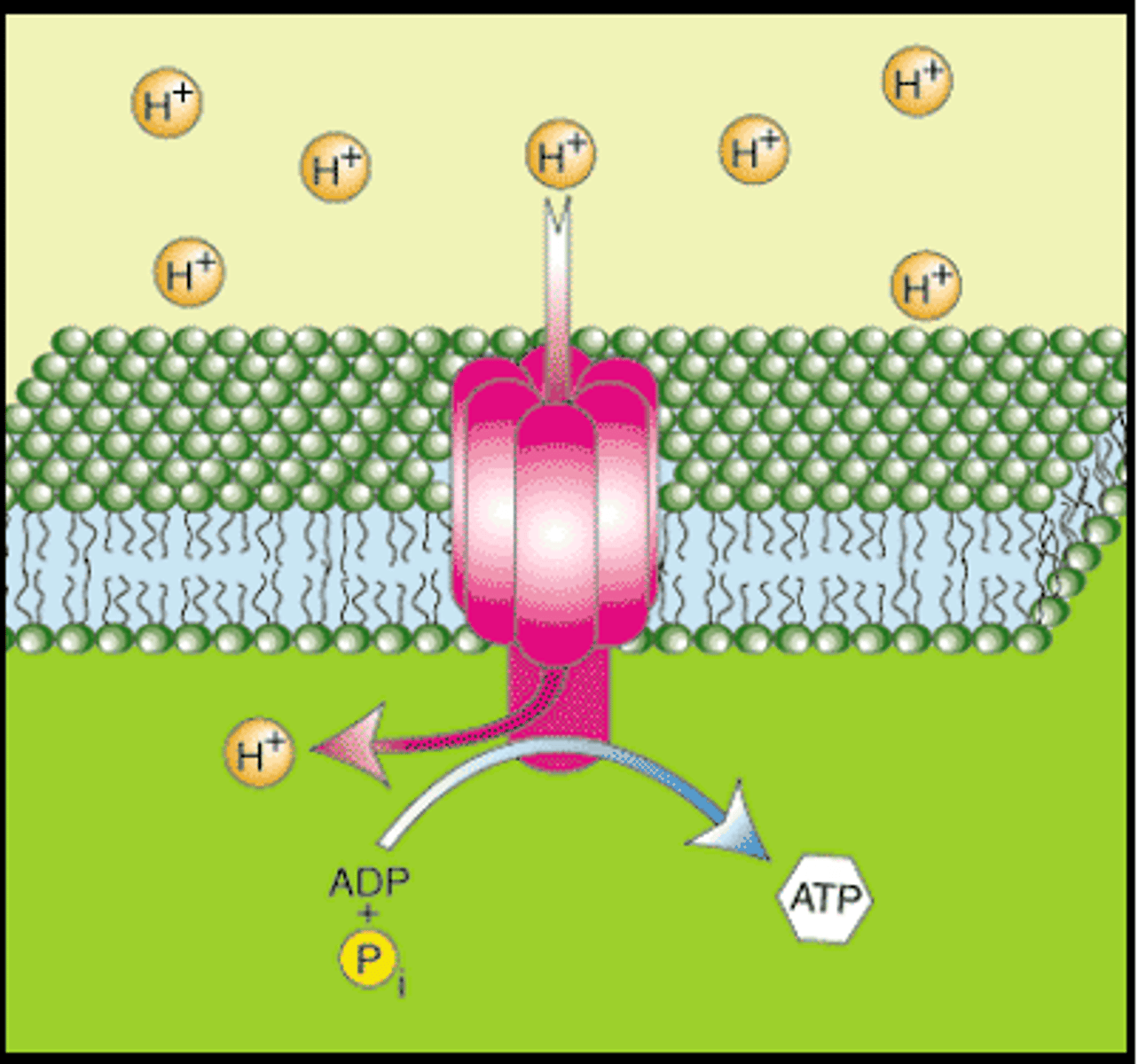
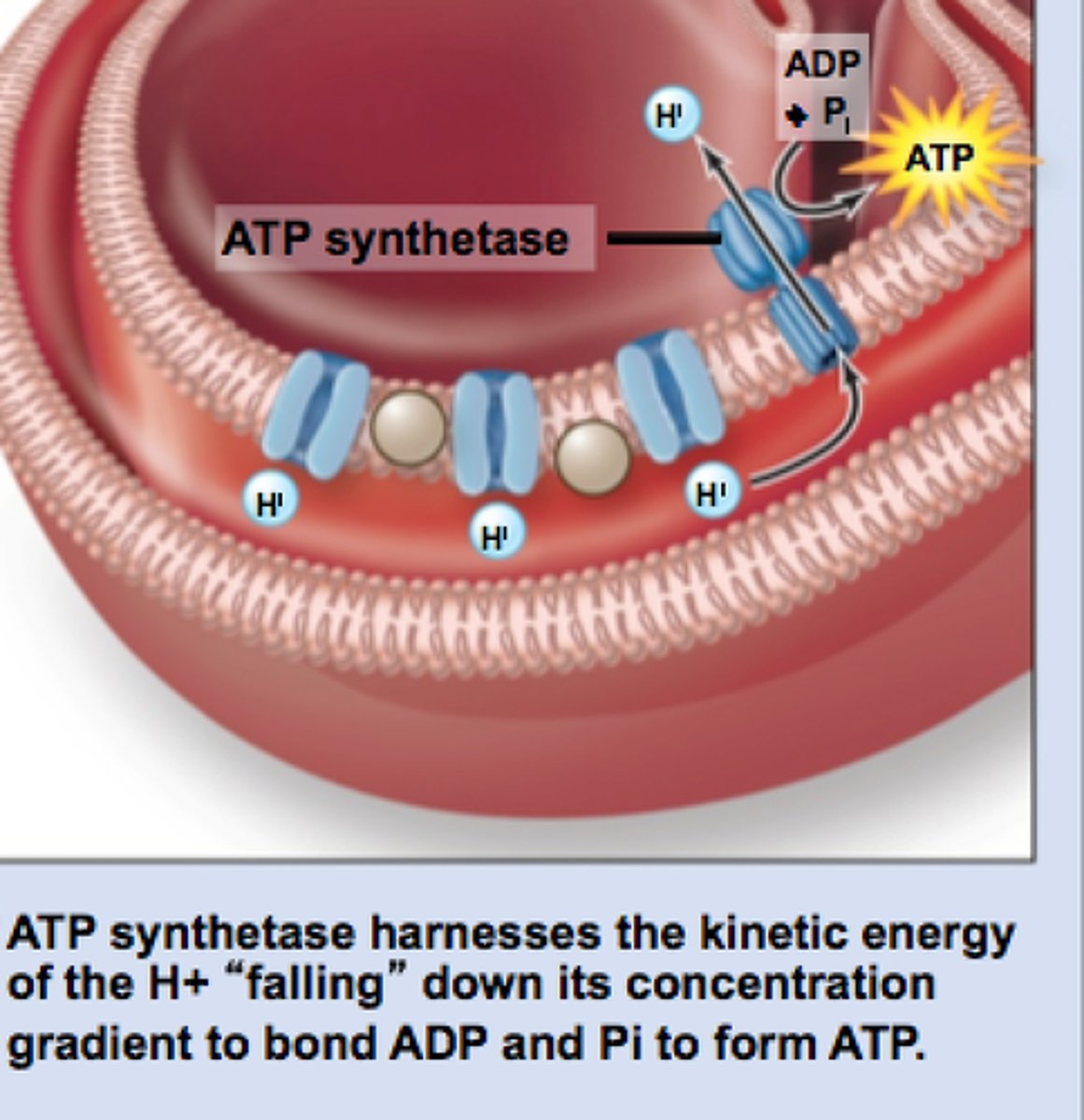
ATP synthase
An enzyme that produces ATP as protons (H+) flow down a gradient through chemiosmosis or oxidative phosphorylation
enzymes
a catalytic protein, speeds up metabolic reactions by lowering activation energy, very specific, reusable, unchanged by reaction
Black
All colors absorbed
activation energy
initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction, free energy for activating reaction, given off by heat
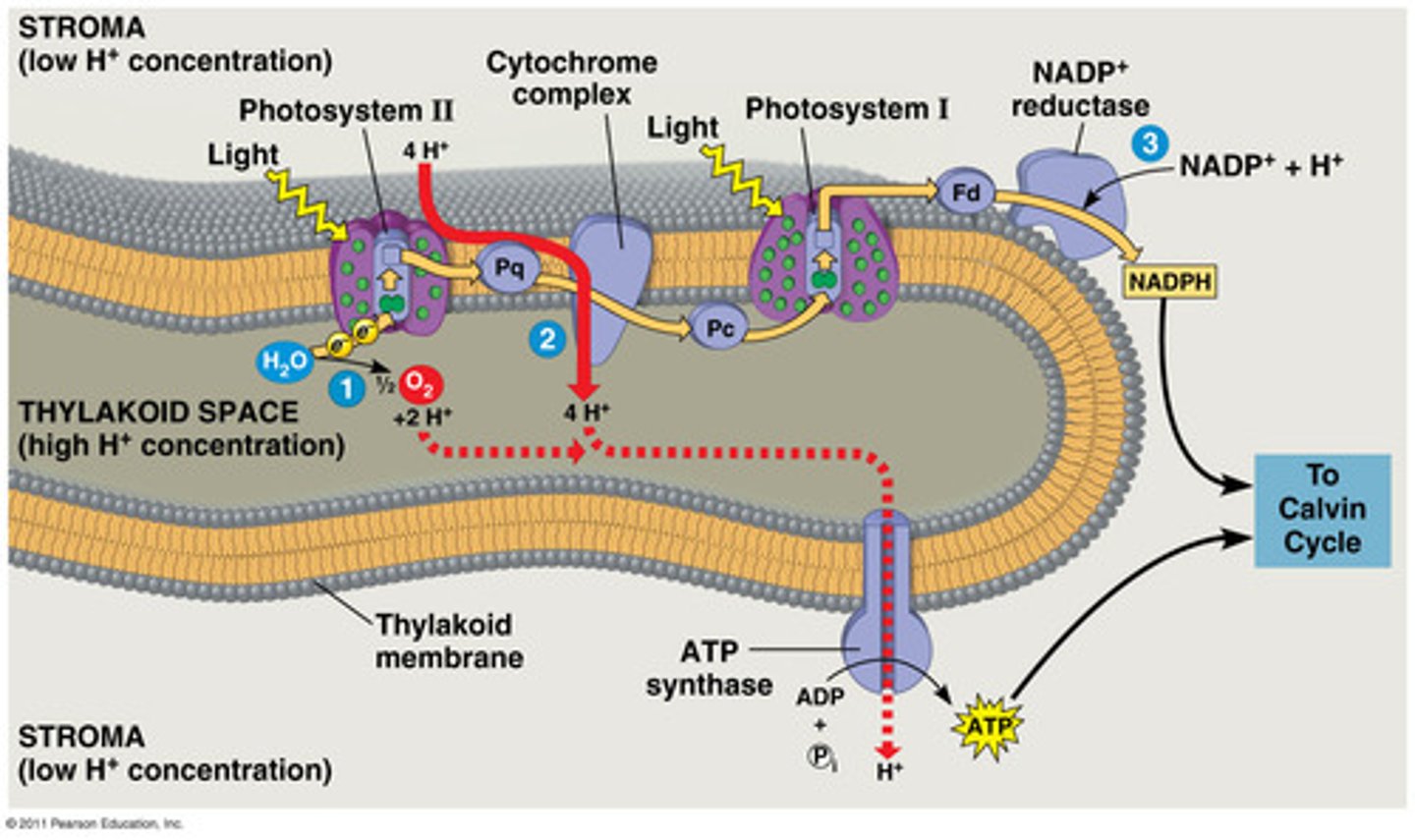
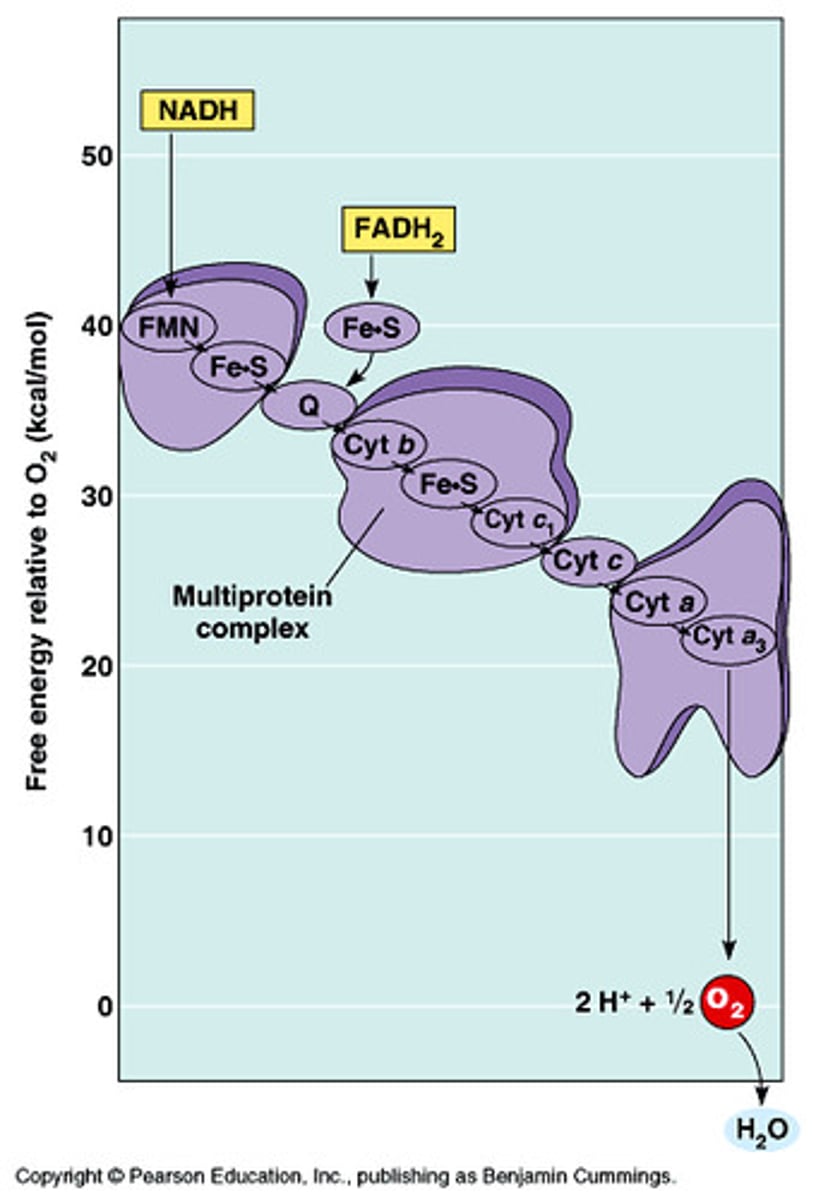
Electron Transport Chain
Energy-coupling reaction that creates H+ gradient in the membrane necessary for the production of ATP through chemiosmosis or oxidative phosphorylation
- Energy released from the exergonic flow of electrons is used to pump protons across the membrane to create a proton gradient
- Electrons flow down the chain from one carrier molecule to the next in a series of redox reactions
- The final hydrogen (H+) acceptor in the chain is oxygen (H2+1/2O2 --> H2O) / Water is the waste product and is exhaled
Pigment
a molecule that absorbs wavelengths in the visible light spectrum
induced fit
brings the chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to catalyze the reaction, makes the enzyme more effective
Oxygen
Final electron acceptor in the ETC
Carotenoid
Group of pigments that absorb blue and blue-green wavelengths, appear orange, yellow, and red
Water
Waste product created by at the end of the ETC
Chemiosmosis
A process by which ATP is formed as protons flow down a proton gradient through the ATP synthase complex
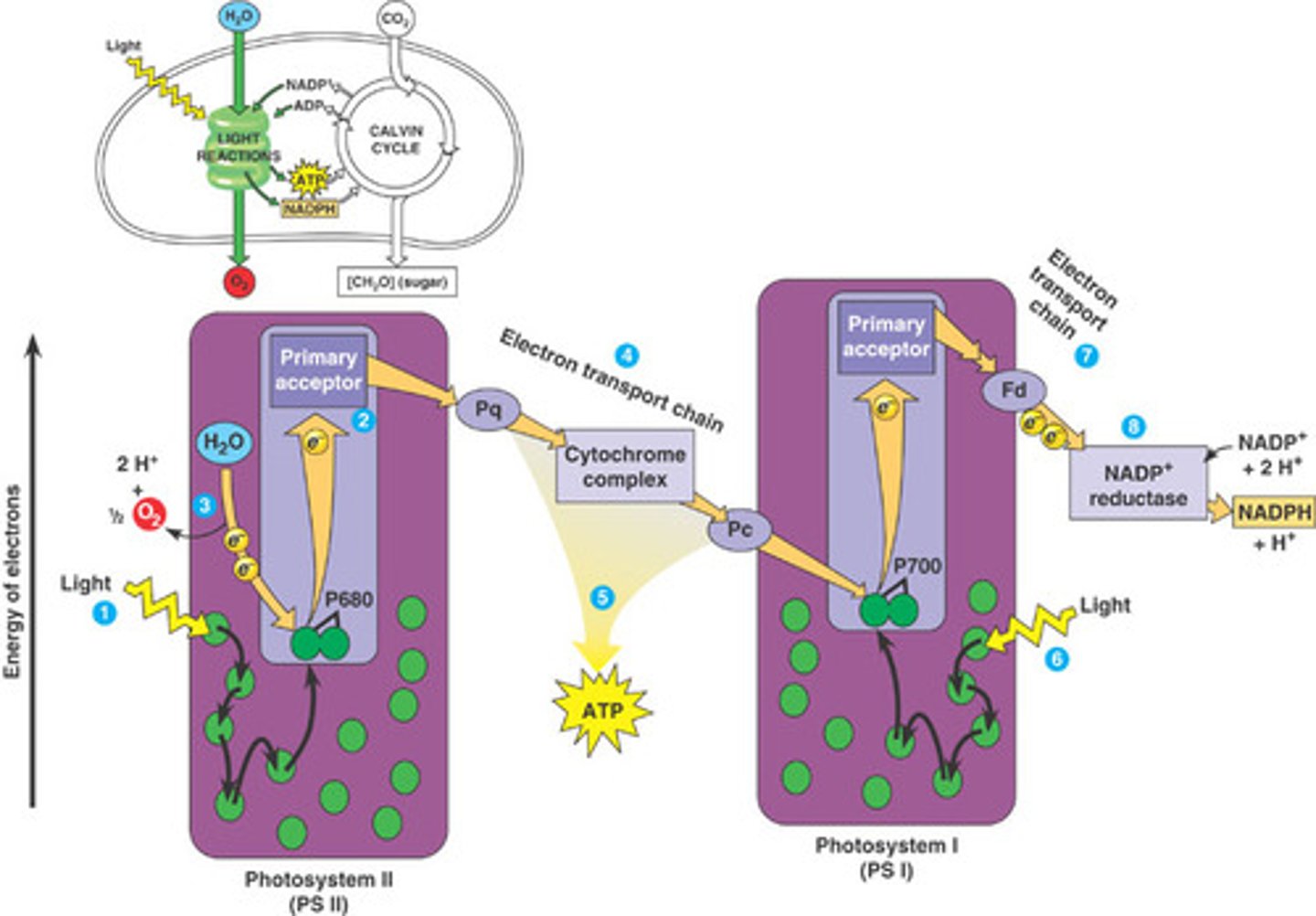
Light Reactions
Occur in thylakoid membrane and are also called light dependent reactions
Substrate
the REACTANT that an enzyme acts on
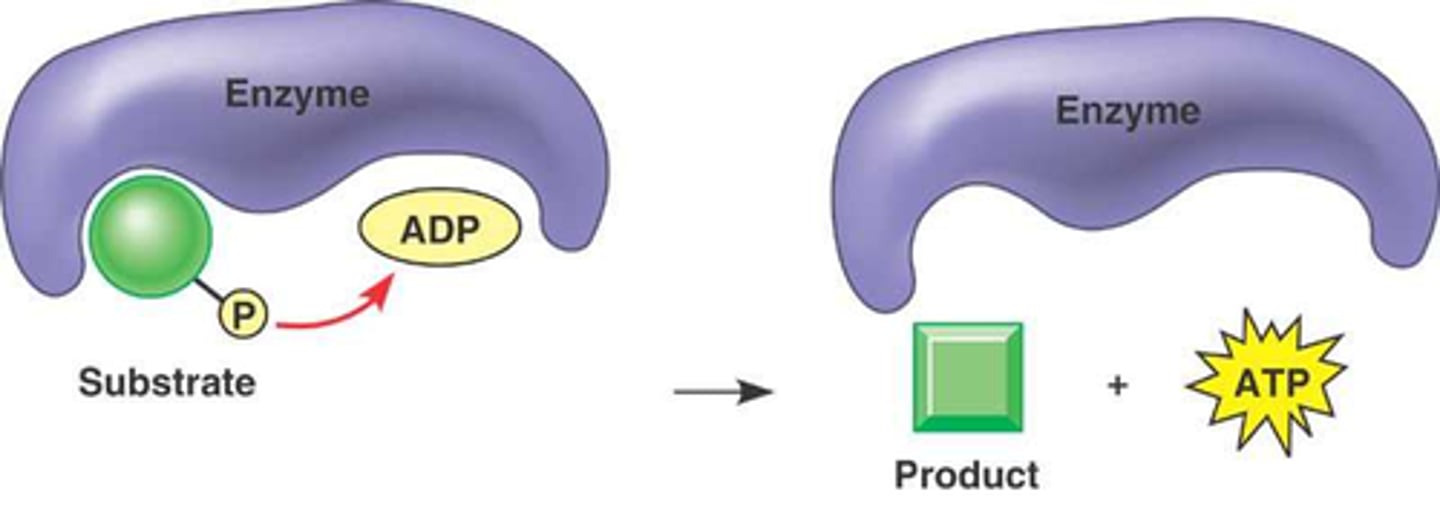
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Process that produces a small amount of ATP during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle
During this process, the enzyme kinase transfers a phosphate from a susbtrate directly to ADP, forming ATP
Photosystem
Consists of a reaction-center complex surrounded by light-harvesting complexes which split water to create electrons that get transferred to NADP+ to create NADPH and H+ which are used to create ATP
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
The enzyme and substrate bound together
Active Site
region on the enzyme where substrate binds
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy from the electron transport chain. Ends with the production of water.
Light-Harvesting Complex
Contains chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids (within the photosystem) that will trap light energy for use in the light reactions
Photosystem 1
Has P700 chlorophyll a in reaction-center complex, thought to have evolved first because it can work alone to create primary acceptors, 2nd of the photosystems
Hydrogen and Ionic Bonds
substrate held in active site by WEAK interactions
NADH
Primary electron transporter to the ETC from glycolysis and Krebs cycle
FADH2
Secondary electron transporter to the ETC from Krebs cycle, entering at lower energy levels than NADH
Lock and Key
active site on enzyme fits substrate exactly
Photosystem 2
Has P680 chlorophyll a in reaction-center complex, first of the photosystems. splits water into electrons, oxygen, and hydrogen ions
Ways enzymes lower activation energy
can do this by having a favorable environment, straining substrate molecules, orienting substrates correctly
NAD+
Oxidized form of NADH
Cytochrome
Protein in the electron transport chain of the photosystems that transfers the electrons to create NADPH
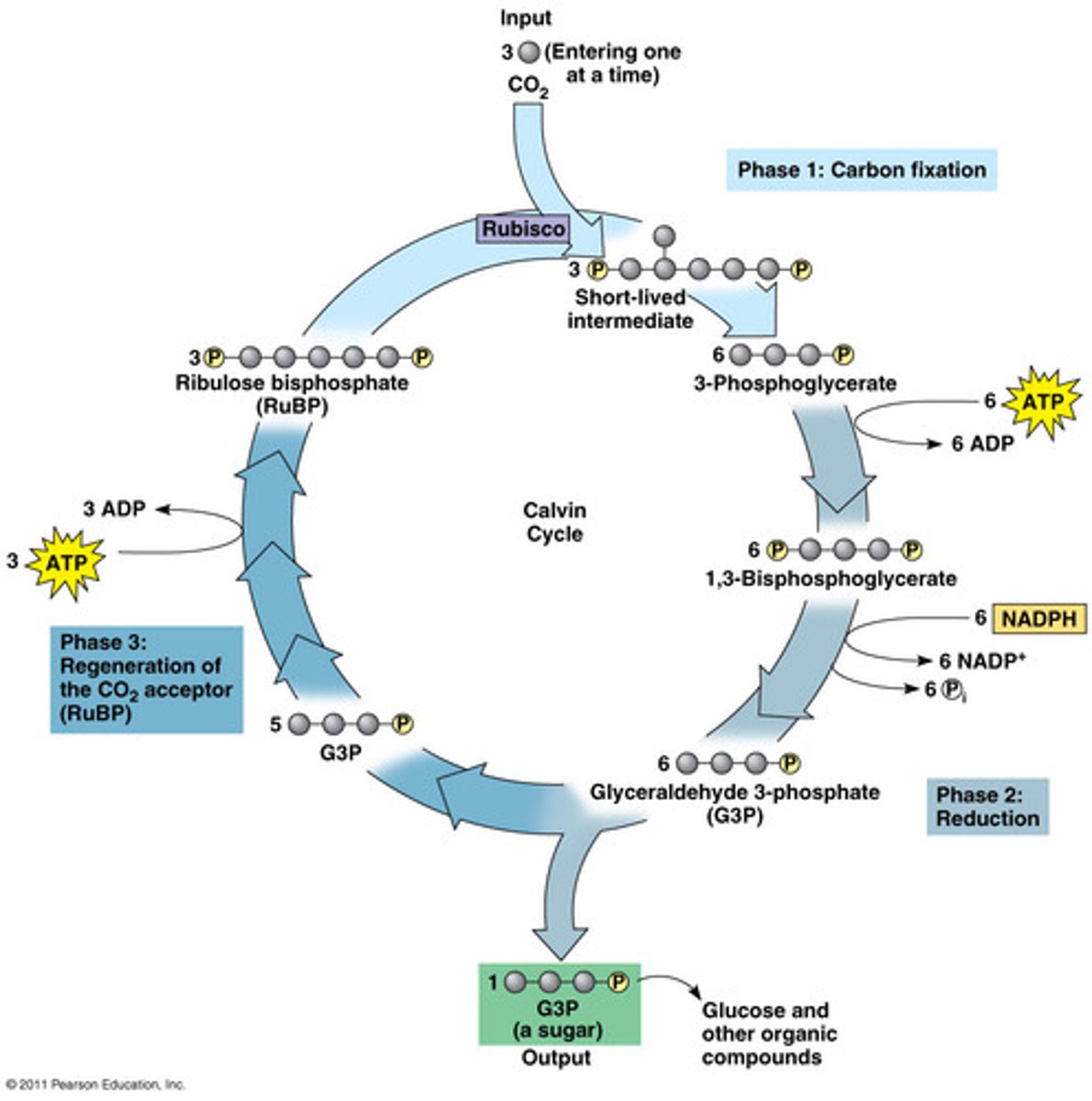
Calvin Cycle
Light-Independent reactions
Occurs in stoma, does not use light directly. Uses the enzyme Rubisco to create 2 molecules of G3P which is then either used to create glucose or recycled back into RuBP to restart the cycle
hydrolysis
The addition of water to a polymer to split it into monomers.
FAD
Oxidized form of FADH2
Rubisco
The most abundant protein on Earth
Carbon Fixation is catalyzed by Rubisco
cofactors
non-protein enzyme helpers ex. zinc, iron, copper
Redox Reactions
Reduction and oxidation
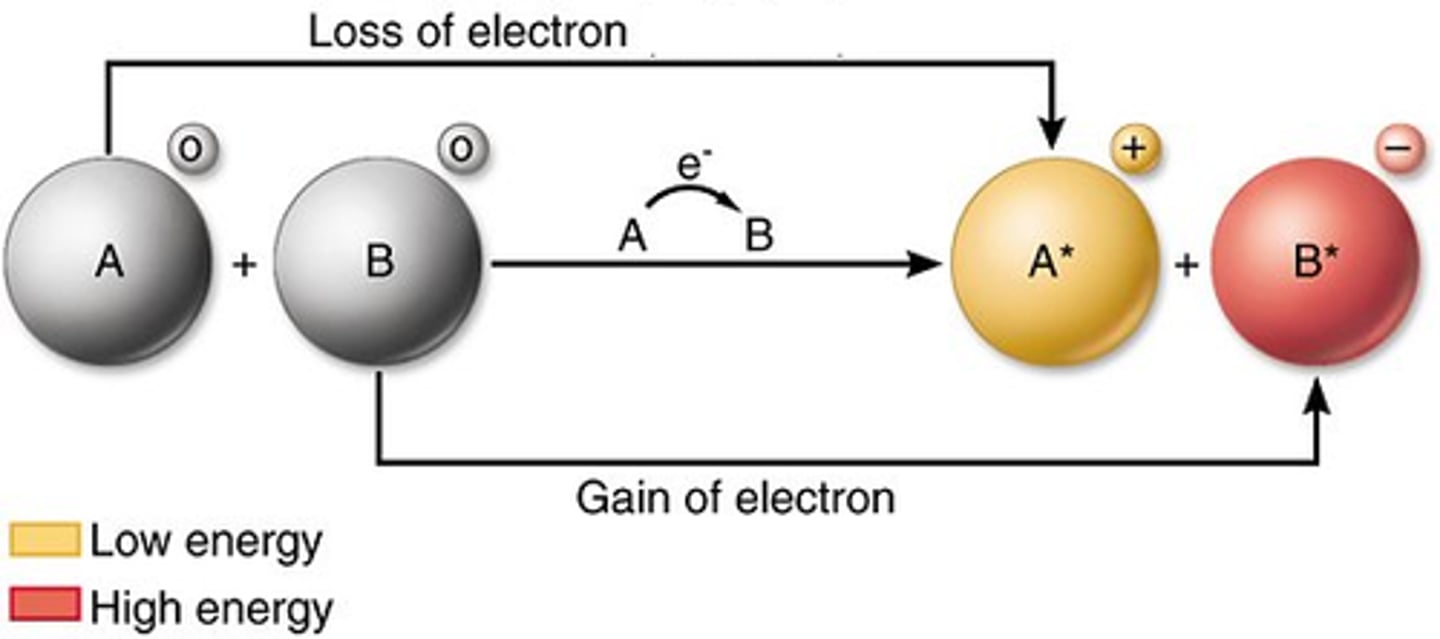
Reduction
gain of electrons; gain of hydrogen -> for storing energy
coenzymes
organic enzyme helpers
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things).
Oxidation
loss of electrons; loss of hydrogen -> for releasing energy
1 Cycle of Calvin Cycle
1 CO2 is fixed
3 ATP are used
2 NADPH are used
1 RuBP is regenerated
6 cycles needed to make 1 glucose molecule
C4 Photosynthesis
A method that bypasses photorespiration
Happens in corn, sugarcane, and other plants in hot, dry environments
Converts carbon dioxide to a 4-carbon intermediary which is then stored in bundle-sheath cells
Renature
removing reagent that denatures protein brings to this state
Cytochromes
Proteins that help make up the ETC; transport electrons
C3 Plant
Plants that use the Calvin Cycle without creating carbon intermediaries, take in carbon dioxide through stomata. An enzyme called RuBisCO helps the carbon dioxide combine to make sugar.

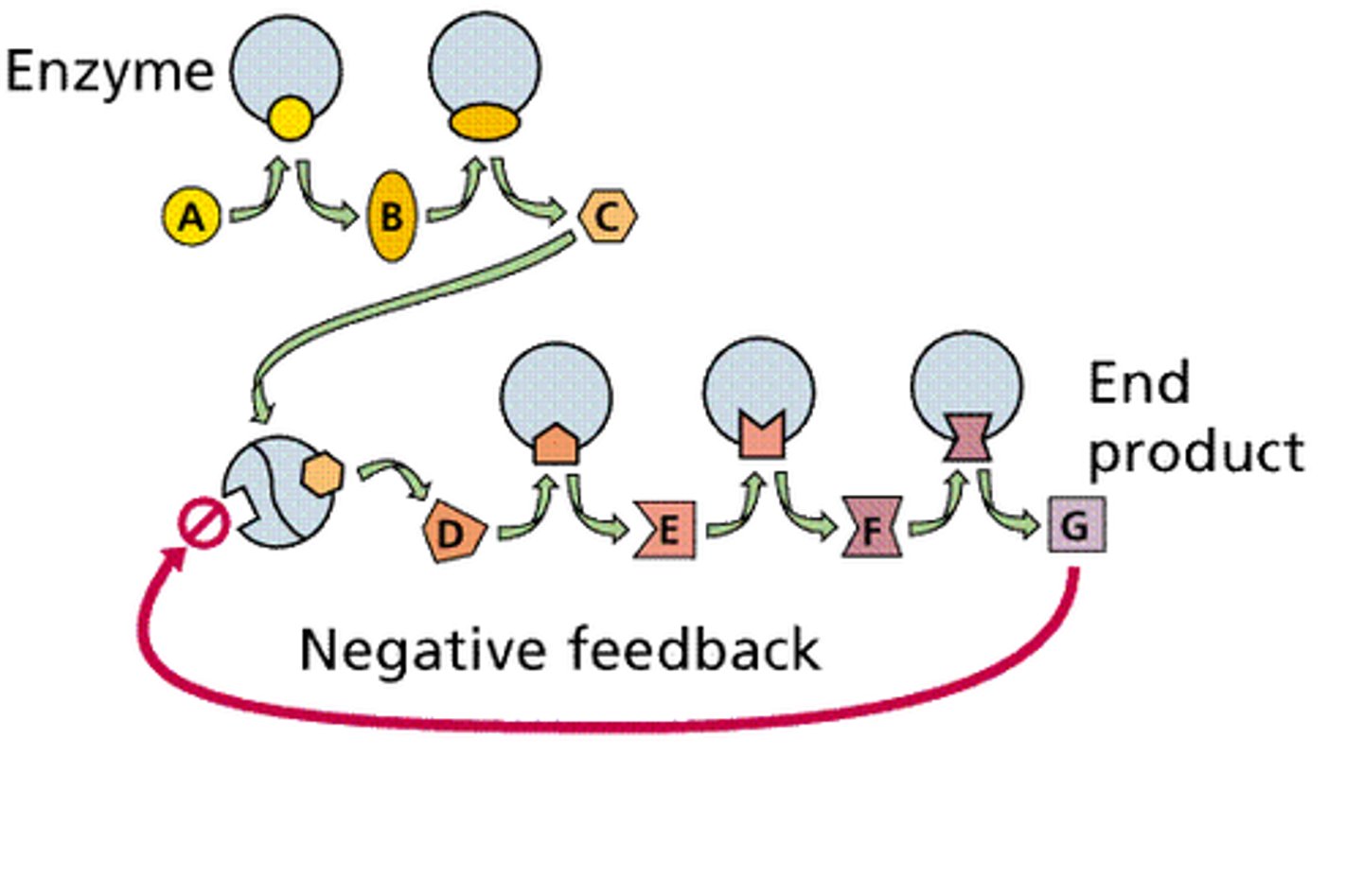
Feedback inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
Inner-membrane space
Mitochondrial part where the ETC pumps protons
Matrix
Site of Krebs cycle in mitochondria
Allosteric Regulation
can accelerate or inhibit production and enzyme activity by attaching to another part of the protein. this changes the shape of the active site which inhibits substrates from bonding and producing more products
CAM Plants
Plants that only open stomata at night. They convert carbon dioxide to malic acid which is then converted back into carbon dioxide during the day for the Calvin cycle
Activator
one of the allosteric regulators, stabilizes and keeps active site open for production, wedges open
Inner mitochondrial membrane
site of oxidative phosphorylation and the electron transport chain

Inhibitor
a substance that interferes with the action of a catalyst
Competitive Inhibitor
inhibitor that mimics original substrate by blocking the original substrate
noncompetitive inhibitor
bind to another part of enzyme to change shape and block substrate from producing
Conditions that affect enzymes
environment, pH, temp, salinity, chemicals that infuse enzyme, increase activity by increasing substrate concentration
reducing agent
The electron donor in a redox reaction. The reducing agent gets oxidized.
oxidizing agent
Accepts electrons and becomes reduced.
pyruvate oxidation
Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and CO2 that occurs in the mitochondrial matrix in the presence of O2.
Link reaction
Stage of aerobic respiration that links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle. In eukaryote cells it occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. (sometimes called the prep reaction or the oxidation of pyruvate)
prep reaction (link reaction)
Reaction that oxidizes pyruvate with the release of carbon dioxide; results in acetyl CoA and connects glycolysis to the citric acid cycle. (sometimes called the oxidation of pyruvate)
cyclic electron flow
A route of electron flow during the light reactions of photosynthesis that involves only photosystem I and that produces ATP but not NADPH or oxygen.
linear electron flow
the primary pathway, involves both photosystems and produces ATP and NADPH using light energy (non-cyclic electron flow)
glucose
C6H12O6
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy.
Contains potential energy in the form of chemical bonds
Engelmann's experiment
He took a plant and put it under different colored lights to see how that affected rates of photosynthesis (like a boss)