SL Chem - Unit #1: Covalent Bonding
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Molecular Compounds
They’re made up of non-metals that are bonded together with a covalent bond where the electrons are shared between both atoms
Have an electronegativity difference of <1.7
Molecules
The name for atoms in a covalent bond
Molecular Compounds form by the…
Electrostatic attraction between the nuclei and the shared electron pairs
Drawing Covalent Compounds
Draw the element with the lowest # of valence electrons (or lowest electronegativity) in the middle and the other atoms go around it
Make sure all atoms have a stable octet if not you can make double/triple bonds to make them stable
Relationship between # of bonds, their strength and their length
The more bonds between molecules the stronger the bond
Stronger bonds are shorter and vice versa
Some examples…
Nitrogen2: Triple bond - strongest- shortest
Oxygen2: Double bond
Hydrogen2: Single bond- weakest - shortest
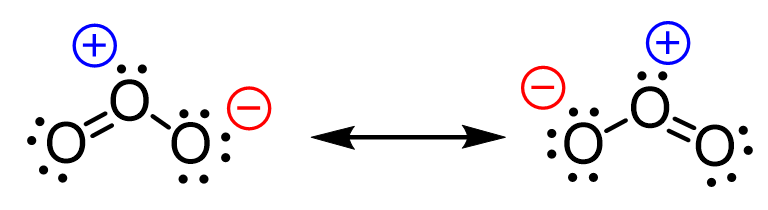
Resonance
The actual structure of a molecule is a composite/ average (like a possibility) of the number (different variations) of lewis structures that can be drawn
Resonance Structures
Every single Lewis structure that can be drawn
If you’re in a scenario where you can choose between multiple possibilities to make the stable octet it’s a resonance structure
Octet Rule
In some covalent bonds we can reach a stable octet with less/more than 8 electrons in the valence shell
Expanded Octet
If there are more than 8 electrons in the third valence shell for elements in the 3rd or beyond periods
Common elements that follow the octet rule (4)
Boron, Phosphor, Sulfur and Beryllium
Coordinate (Dative) Covalent Bonds
A covalent bond where one molecule will share two of its own electrons to make a shared bond with the other molecule
Shows using arrows rather than a line