Unit 3: Cell Function
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What four things need to be included in a diagram of the cell membrane?
phospholipid bilayer (philic heads/phobic tails)
cholesterol
integral proteins
peripheral proteins
Describe the traits of the hydrophilic head in a phospholipid bilayer
made up of phosphate which makes it polar, allowing it to interact with water molecules
Describe the traits of the hydrophobic tail in a phospholipid bilayer
made up of hydrocarbon chains, non polar (does not like water molecules)
Why must something be polar to interact with water?
because water itself is polar (has unequally distributed charges - two hydrogen and one oxygen)
What is simple diffusion?
the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration, does not require energy or a channel protein (ex. osmosis)
What is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is similar to diffusion in the way that it does not require energy (passive), however larger molecules such as potassium and sodium require help from a channel integral protein because the cell membrane’s selectivity.
Integral proteins
proteins within the cell membrane that span from either end (ex. channel proteins)
Peripheral proteins
proteins that are attached (but not embedded) to the plasma membrane, they provide support, enzymes and signaling.
Active transport
the movement of molecules across a concentration gradient with the help of energy in the form of ATP (low to high concentration). protein pump is required, molecules can only enter from one side and they exit from the other.
Glycoproteins
polypeptides with carbohydrate attached, thus part protein part carbohydrate
Glycolipid
lipids with carbohydrates attached, lipid part usually consists of one or two hydrocarbon chains
Why are glycolipids and glycoproteins important aspects of the plasma membrane?
they aid in cell recognition and the formation of tissues
Why is cholesterol important?
helps the plasma membrane maintain fluidity in both hot/cold environments
Cholesterol in HOT environments
maintain orderly arrangement of phospholipids, prevents over fluidness
Cholesterol in COLD environments
prevents the restriction of cell movement, restriction can lead to lysis
Endocytosis
enter of large molecules into the cell with the help of vesicles
Exocytosis
when a vesicle fuses to the membrane and releases a larger molecule into the bloodstream (or outside environment)
What is the symbol used for water potential and what are the units it is measured in?
water potential is represented by the Greek symbol psi and is measured in kilopascals (kPa)
Solvent
substance
solute
the sample being dissolved by the solvent
solvation
the act of a solute being dissolved in a solvent
Explain why water is able to dissolve charged molecules.
because of its polar structure water can dissolve many distinct molecules. one part is positive the other negative which allows it to bond to a variety of substances, effectively pulling them apart in the process.
Outline the net movement of water in hypertonic, isotonic and hypotonic solutions.
hypertonic solutions - cell will shrink because there is a higher solute concentration and water will exit the cell to balance out the two “solutions”
isotonic solutions - there is very little (or no) movement of water because the two environments are in equilibrium, cell remains stable
Hypotonic solutions - in a hypotonic solution the cell will gain mass as water enters the cell until it has reached equilibrium with the solution.
State the effects of hypertonic and hypotonic solutions on a cell without a cell wall.
cells in a hypertonic solution risk dying because of the drastic decrease in volume
cells in a hypotonic solution risk lysis (bursting) because they are intaking so much water
Why must fluid in multicellular organisms be isotonic to the tissue cells?
so that no cell shrinks or expands due to osmosis and they can remain stable, performing their functions with no difference or stress
Turgor pressure
plant cells in a hypotonic environment in take water and as their membrane expands it puts pressure against their cell wall
Plasmolysis
when plant cells are in a hypertonic solution they shrink and detach from their cell wall, this process is called plasmolysis
What are two properties a stem cell has?
can endlessly divide - plentiful
can differentiate into many different cell types
What are two different types of stem cells found in the human body and state their niche/function.
bone marrow stem cells - produce all types of blood cells (red for oxygen and white for fighting against infection) as well as platelets (clotting agents)
neural stem cells - in the brain, produce new neurons
Totipotent
term that refers to stem cells that can become ANY cell type
Pluripotent
term that refers to stem cells that can develop into most (but not all) cell types
Multipotent
stem cells that can differentiate into a few different cell types
What six cells serve as evidence that cell size is an aspect of differentiation?
sperm cells
egg cells
red blood cell
white blood cell
neuron cells
striated muscle fiber cells
Pneumocytes in alveoli
specialized cells that line the alveoli (air sacs in the lungs)
Outline the adaptations of type l pneumocytes and their function in the alveolus.
they are flat and have few mitochondria. they aid in gas exchange which is important for getting oxygen into the bloodstream.
Outline the adaptations of type ll pneumocytes and their functions in alveolus.
they are cube shaped and have lots of organelles, act as a surfactant (prevent cells from sticking together)
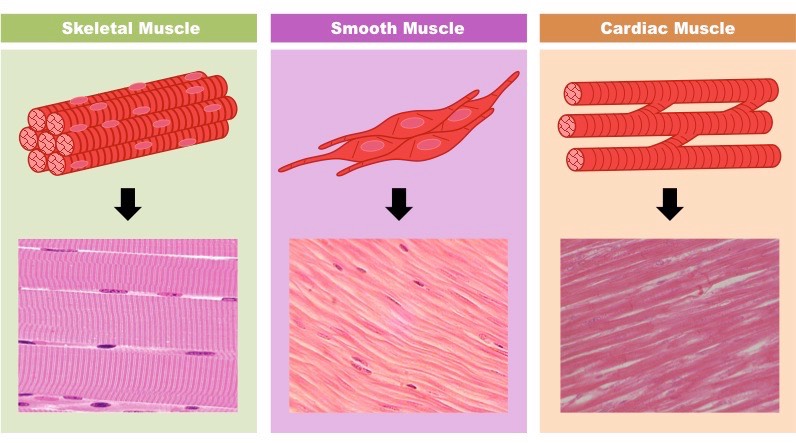
Compare and contrast cardiac muscle tissue and skeletal muscle tissue.
cardiac - short, branched with intercalated disc, ONE NUCLEUS
skeletal muscle tissue - long, can contract to create pulling force, multinucleated (efficient tRNA), striated
What are three important things cells are needed for? Why must cells divide?
growth, reproduction and repair
Cytokinesis in plant and animal cells
splitting of the cytoplasm in a parent cell
animal - cleavage furrow
plant cell - vesicles form in the center and a new cell wall is formed
Difference between mitosis and meiosis?
mitosis produces two identical daughter cells while meiosis produces cells with only half of the identical DNA (ex. 23 chromosomes from each parent to create genetically different BUT SIMILAR child)
Why must DNA condense into chromosomes for mitosis and meiosis?
to allow for organized and efficient splitting of genetic material to daughter cells.
What is the role of cyclins and cdk complexes in the cell cycle?
What is the difference between a primary tumor, secondary tumor, malignant tumor and cancer?
a primary tumor is the first tumor that forms in the body, a lot of the time its not dangerous but cancerous cells with mutations can grow and spread
a secondary tumor (also known as a metastatic tumor) is when cells from the primary tumor break apart and spread to a different part in the body
a malignant tumor is a cancerous tumor that grows uncontrollably
cancer is a disease in which cells divide uncontrollably and harm nearby tissues and organs
What solutions have a low water potential?
solutions with more solute have a lower water potential because there are fewer “free water” molecules to move around.
What has the highest water potential?
pure water because it has no solute concentration and can move freely
Define water potential.
water potential is a measure of potential energy which can tell us how likely water is to move from one area to another
What are three adaptations of cells that maximize the SA:V ratio?
flattening, branched structures (microvilli) and invagination or small cell size
What happens during prophase?
the nuclear envelope begins to break down and the nucleolus is no longer visible. Additionally chromosomes are condensed and spindle fibers from microtubules are created.
What happens during metaphase?
during metaphase, the chromosomes are aligned along the cell’s equator and the spindle fibers formed in prophase attach to the centromere of each chromosome to allow for proper orientation before the chromatids are separated.
What happens in telophase?
new nuclear membrane forms and chromosomes “de-condense” back into chromatin, occurs simultaneously with cytokinesis
Mutagen
factors that cause changes to an organism or cell’s genetic material
List three different types of mutagens with examples.
physical (x-ray/radiation)
Chemical
Biological (retrovirus that integrates their own DNA into host DNA)